Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), one of the common complications of diabetes, is the leading cause of visual loss in working-age individuals in many industrialized countries. It has been traditionally regarded as a purely microvascular disease in the retina. However, an increasing number of studies have shown that DR is a complex neurovascular disorder that affects not only vascular structure but also neural tissue of the retina. Deterioration of neural retina could precede microvascular abnormalities in the DR, leading to microvascular changes. Furthermore, disruption of interactions among neurons, vascular cells, glia and local immune cells, which collectively form the neurovascular unit, is considered to be associated with the progression of DR early on in the disease. Therefore, it makes sense to develop new therapeutic strategies to prevent or reverse retinal neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation and impaired cell-cell interactions of the neurovascular unit in early stage DR. Here, we present current perspectives on the pathophysiology of DR as a neurovascular disease, especially at the early stage. Potential novel treatments for preventing or reversing neurovascular injuries in DR are discussed as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), one of the common microvascular complications of diabetes, remains the leading cause of visual loss in working-age population (20-74 years) in most industrialized countries [1]. Although some studies indicate that the prevalence of DR in the US has decreased after the improvement in controlling risk factors in diabetes care, the proportion of people with DR is expected to increase globally due to population aging, increasing prevalence of diabetes and longer lifespan of these diabetes patients [1, 2].
Clinically, the diagnosis and classification of DR depend mainly on the retinal microvascular lesions observed by ophthalmic fundus examination [3]. However, numerous investigations suggest that DR is a more sophisticated neurovascular complication, wherein multiple types of cells (neurons, glia, immune and vascular cells) in the retina are disrupted [4]. DR can be generally divided into two stages: the early stage of non-proliferative DR and the advanced stage of proliferative DR. In non-proliferative DR, the classic microvascular features include microaneurysms, hemorrhages, venous beading, hard lipid exudates, cotton-wool spots and intraretinal microvascular abnormalities [1, 3]. In proliferative DR, retinal neovascularization develops owing to ischemia and hypoxia. The new aberrant blood vessels are fragile, leading to vitreous hemorrhage and/or tractional retinal detachment from progressive fibrosis, which may result in severe visual impairment and even blindness [1]. Another important manifestation of DR is diabetic macular edema (DME) present at all stages of DR, although it is more common in severe phases. DME is characterized by the pathological macula thickening due to fluid accumulation in the neural retina resulting from breakdown of blood-retinal barrier (BRB) [5]. DME and retinal neovascularization are the two central reasons for vision loss in patients with DR. Main treatments for DR currently include intravitreal injection of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and steroid drugs, laser photocoagulation and vitreous surgical interventions, which target only microvascular damages at the later stage when patients have already suffered severe vision impairment [3, 5]. Moreover, many patients fail to respond to intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy, which has been adopted as the current first-line treatment for DR, especially for DME. In these poor responders, the effects of anti-VEGF drugs seem to be transient [6, 7]. Therefore, new therapeutic approaches are highly needed to focus on not only vascular but also nonvascular cells and begin treatment at the early stage. In this review, current views on the pathophysiology of DR as a neurovascular disease at the early stage are discussed. In addition, potential therapeutic strategies arising from laboratory studies and clinical trials are also summarized.
Main text
A systematic literature search up to September 2020 was performed using the PubMed database for original articles written in English using the following key words: “diabetic retinopathy”, “neurovascular unit”, “neurodegeneration”, “retinal gliosis”, “inflammation”, “neuroprotection” and “treatment”. A further search of references from the retrieved articles was conducted. The relevant articles were selected, studied and summarized.
The neurovascular unit in retina
The concept of ‘neurovascular unit’, which was first introduced to the central nervous system and then to the retina, refers to the complex functional coupling and interdependency among neuronal, glial, immune and vascular cells that is important to maintain hemostasis and modulate neuronal activities [8,9,10]. In the retina, all the component cells of the neurovascular unit are integrated to maintain the integrity of the inner BRB and dynamically coordinate local blood flow in response to metabolic demands of the retinal neuropil [11]. Any disruption in the retinal neurovascular unit may have pathophysiological influences on each type of component cells, leading to impairment in the structure and function of microvasculature and neurons. As a complex network, retinal neurons and vasculature are organized in a stratified manner, with superficial vascular plexus lies in the nerve fiber layer (NFL), intermediate vascular plexus reside in the boundary between the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and inner nuclear layer (INL), while deep vascular plexus line the outer surface of the INL [12, 13].
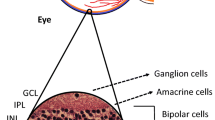
The retinal neurovascular unit is composed of several types of neurons (ganglion cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells and amacrine cells), glia (astrocytes and Müller cells), immune cells (microglial cells) and vascular cells (endothelial cells and pericytes) (Fig. 1) [8, 14, 15]. Generally speaking, neurons in the retinal neurovascular unit transmit the electrical impulses converted by photoreceptors from light signals to the brain to form vision. The functions of neurons mainly rely on the blood vessels to supply nutrients and oxygen while eliminating metabolic wastes and carbon dioxide [13]. Furthermore, neurons can regulate local blood flow through glial cells and pericytes to maintain their functions [16].
The schematic illustrations of the retinal neurovascular unit and cross-section. (a) The schematic illustration of the neurovascular unit in the retina. It is composed of neurons, vascular cells (endothelial cells and pericytes), glia (Müller cells and astrocytes) and related immune cells (microglial cells), forming functional coupling and interactions. Neurons are closely associated with neighboring pericytes, glial cells and microglial cells. Pericytes directly communicate with endothelial cells through peg-socket contacts. Glia and microglial cells are connected with neurons and retinal pericytes. (b) The schematic illustration of a retinal cross-section. The cell bodies of retinal neurons are located in the ganglion cell layer (ganglion cells), inner nuclear layer (amacrine cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells) and outer nuclear cell (rods and cones). Retinal neurons, glial cells, microglial cells and blood vessels are interactively connected. ILM: internal limiting membrane; GCL: ganglion cell layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer
Müller cells are the major support glial cells in the retina [17]. Their processes wrap around the blood vessels and coordinate vascular responses to provide nutrients to the outer retina, maintain extracellular pH value, recycle transmitter and transport metabolites [17]. Astrocytes encircle the neuronal axons and vessels to form an irregular network to support the integrity of the inner BRB [18]. They may function partially the same as Müller cells and play a role in the maintenance of vascular tone by autoregulation [19].
Microglial cells are in direct contact with neurons and retinal pericytes [15]. As highly specialized phagocytic cells, microglia continuously monitor local synaptic activity and sweep away dying cells as well as metabolic debris [20, 21]. In physiological conditions and acute inflammation, microglial cells produce anti-inflammatory cytokines and neurotrophic factors that support neural retina health [22]. However, in a chronic retinal disease such as DR, they will secrete a large number of pro-inflammatory cytokines, affecting the hemostasis of neurovascular unit [23, 24].
Vascular endothelial cells form a monolayer that covers the inner surface of the vascular lumen. The endothelium is a semi-selective barrier, known as the inner BRB, regulating the flux of fluid and macromolecules between the blood and neural retina by the intercellular tight junctions [25]. Pericytes, which envelope retinal capillaries, are intimately associated with neighboring endothelial cells, neurons, glial cells and microglial cells [14]. Thus, pericytes are crucial in maintaining the neurovascular unit and inner BRB [26]. Despite being separated from endothelial cells by the basement membrane, pericytes are directly connected with endothelial cells via peg-socket contacts at discrete points in the basement membrane [26,27,28]. In addition to structural support for blood vessels, these contractile pericytes also control blood flow in response to intricate systemic and local messenger molecules [29]. Extracellular matrix (ECM) plays a role in the neurovascular unit too, of which various isoforms such as fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin and collagen IV constitute the basement membrane [30]. ECM is critical to maintain proper neurovascular unit functions since it provides a beneficial environment for the interaction of endothelial cells and pericytes, diffusion of ions, neurotransmitters and ATP [31]. The integrated activity of neurons, glia, microglial, vascular cells and ECM is crucial for the normal function of the retina; however, much work needs to be done to further elucidate the relationships between these components in the neurovascular unit, for instance, the mechanisms of astrocytes interfere with neurons and other astrocytes, the activity of the ECM within the context of the neurovascular unit.
Pathology related to neurovascular unit in DR
With the improvements of retinal imaging techniques and deep investigations into the early cellular changes, it has been demonstrated that the dysfunction of retinal neurovascular unit plays an important role in the development and progression of DR [13,14,15,16, 32, 33]. Additionally, other cell types that are not components of the neurovascular unit such as immune cells and RPE cells are also involved in DR [15, 34, 35] (Table 1).
Neurodegeneration in DR
Since Wolter reported the death of retinal ganglion cells and degeneration of the INL in postmortem eyes of people with diabetes in 1961, there is accumulating evidence that neurodegeneration also occurs in diabetic retina, probably even prior to visible microvascular pathologies in DR [36,37,38]. Increased number of apoptotic neurons has been widely accepted as the most important feature of neurodegenerative disease. In diabetic murine models, apoptosis of retinal neurons, mainly the retinal ganglion and amacrine cells, have been detected before overt microvascular lesions [39]. Another study conducted by Bogdanov et al. also demonstrated apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in db/db mice, an animal model of spontaneous type 2 diabetes [40]. Similar results were observed as well in several studies examining the retinas of individuals with diabetes [37, 80]; altered expression of some proteins was reported to be linked with retinal neurodegeneration in diabetics, such as somatostatin (SST), apolipoprotein A1, fibrinogen A, pigment epithelial derived factor (PEDF), interphotoreceptor retinol binding protein (IRBP) [81, 82]. The progressive loss of retinal ganglion cells lead to a significant reduction of neuroretinal thickness in both diabetic patients and experimental animal models of diabetes [40, 41, 83]. Furthermore, although patients with advanced DR exhibited increased thickness of whole retina due to inner retinal hemorrhage or retinal edema, decrease in combined thickness of NFL and IPL as well as INL thickness was revealed in type I diabetic patients without or with minimal DR using optical coherence tomography imaging [42].
The structural alterations mentioned above cause retinal dysfunctions, which have been well documented in patients with no or minimal microvascular retinopathy, in some cases even existing before the onset of diabetes [84, 85]. Impairment of retinal functions corresponds to a broad range of manifestations, including reduction of mean amplitudes in pattern electroretinogram (ERG), delayed scotopic implicit time in multifocal ERG, decreased oscillatory potential and b-wave amplitudes, abnormal dark adaption and color vision, loss of contrast sensitivity [84, 86,87,88,89,90,91]. Diabetes-induced retinal neurodegeneration may be further associated with the development of microvascular abnormalities in DR. This notion is supported by clinical studies showing that the retinal region where neurodegeneration was detected by multifocal ERG would develop microvascular lesions after 12 months [88, 92]. Retinal neurons, such as photoreceptors, may act as the crucial source of oxidative stress and local inflammation [93]. In addition, semaphorin 3A secreted by neural retina may contribute to the breakdown of the BRB via conjugation with its receptor neuropilin-1 [94]. The pathogenic contributions of neurons in DR and the underlying mechanisms of neurodegeneration, including oxidative stress, glutamate excitotoxicity and decrease of trophic factors, have broadened potential therapeutic approaches for DR focusing on neuroprotection [15].
Reactive gliosis in DR
The astrocytes and Müller cells of the neurovascular unit become activated by neuronal stress and cell death in early DR, which is defined as reactive gliosis [15, 43]. These activated glial cells fail to perform their physiological functions to maintain tissue homeostasis, especially regulation of retinal blood flow, water balance in the neural parenchyma, and maintenance of barrier integrity [44]. In normal conditions, only retinal astrocytes express glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP); however, in DR, there is upregulation of this intermediate filament protein in Müller cells, which can be used as a marker of reactive gliosis in the retina [95]. Moreover, activated Müller cells secrete various inflammatory cytokines resulting from the overexpression of innate immune-related pathways [96, 97]. Müller cell studies using diabetic animal models have proposed a potential important role of these cells in retinal water imbalance and vascular abnormalities [58, 98]. In diabetic rats, hyperglycemia induced disruption of Kir4.1 channels in Müller cell end-feet at the interface of retinal capillaries, contributing to the water dysregulation and BRB dysfunction [98]. Another study using a conditional knockout mouse model with disrupted VEGF in Müller cells demonstrated vascular leakage and a significant reduction in the expression of inflammatory biomarkers (tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB)) as well as depletion of tight junction proteins [58]. This finding has indicated that activated Müller cells may be closely related to retinal inflammation and disruption of the BRB. Likewise, DR also causes Müller cell death, primarily in the form of pyroptosis, which subsequently impairs structural and functional integrity of the neurovascular unit [45].
Microvascular pathology in DR
Early in diabetes, patients have demonstrated diminished vasodilation in the retina after flicker light excitation, suggesting the disrupted interactions between local blood flow and neural retina due to hyperglycemia [46, 47]. Although the reduced response indicates the subsequent retinal damage, the patients at this stage are not diagnosed as having DR until the clinical presence of microvascular lesions such as microaneurysms are detected by ophthalmic microscopy [46]. In terms of histopathological alterations at the early stage of DR, vascular basement membrane thickening as well as the demise of pericytes and endothelial cells have been observed [48, 99].
The vascular basement membrane is one of the major components in the neurovascular unit and is crucial to maintain integrity of inner BRB and normal cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions [30]. The thickening of retinal vascular basement membrane, an early microvascular change in diabetes, has been demonstrated to be involved in the development of hyperpermeability and angiogenesis in DR [49, 50]. Furthermore, intravitreal injection of antisense oligos in diabetic rats resulted in the prevention of basement membrane thickening, significant reduction of pericytes loss, acellular capillaries and vascular leakage [100, 101]. It is the imbalance between synthesis and degradation of ECM that contributes to vascular basement membrane thickening. The expression of ECM proteins in the basement membrane are significantly increased, while the degradation of these components by the enzymes are decreased [50]. Due to the alterations of protein components in the thickened basement membrane, cell-cell communication (mainly the communication between vascular endothelial cells and other cells in the neurovascular unit) is impaired, which will subsequently affect the physiological structure and functions of the neurovascular unit [5]. Moreover, the thickened basement membrane damages the inner BRB as a selective barrier, thus leading to vascular leakage [100].
Loss of pericytes and endothelial cells is also a hallmark of early DR [16]. However, it has been revealed that pericyte loss occurs prior to endothelial cell death in animal models of DR [51]. Pericyte apoptosis and migration away from the original blood vessels may contribute to the diabetes-induced pericyte dropout [13, 51, 52]. A recent research has revealed that in hyperglycemic conditions, pericytes detached from the underlying endothelial cells, migrated off the vessels and formed bridges across two or more capillaries [102]. Increased pericyte bridges were observed in diabetic animal models several months before loss of any pericytes or endothelial cells, suggesting that this is associated with the subsequent pericyte loss and can be used as an indicator of vascular damage [102]. Without the structural support from pericytes, retinal capillaries become weakened, resulting in the formation of microaneurysms and vascular leakage due to the increase of inner BRB permeability [53, 55]. These changes are recognized as the clinical signs in non-proliferative DR patients, of which microaneurysms are one of the first lesions seen in ophthalmoscopic examination and fluorescein angiography [53]. Microaneurysms, outpouchings of the capillary wall, are predominately located on the arteriolar side of the circulation upstream of acellular capillaries [25]. There are several distinct structures of microaneurysms, including intact endothelium without pericytes, loss of both pericytes and endothelial cells, and sclerosed walls of thickened basement membrane (Fig. 2) [54]. The exact mechanism of microaneurysms formation still remains unclear. It is now regarded that the loss of pericytes together with high hydrostatic pressure in capillaries contributes to the formation of microaneurysms [25, 103,104,105]. The high capillary pressure is caused by the compromised autoregulation in retinal vessels resulting from the death of vascular smooth cells in the arteries and pre-capillary arterioles [25, 54]. Regarding the loss of pericytes, Cai and coworkers demonstrated that angiopoietins (Ang) 2 increased apoptosis of bovine retinal pericytes treated with high glucose via functional Tie-2 receptors, indicating that the Ang-2/Tie-2 system plays an important role in regulating pericytes dropout [106]. Consistent results have been obtained in the animal study, where Ang-2 deficient mice showed reduced pericytes loss by inhibiting hyperglycemia-induced migration of pericytes [51]. Injection of Ang-2 in STZ-induced diabetic mice resulted in the transient elevation of pericyte bridge density, which could be adopted as a predictor of pericyte loss [102]. In mice with selective inactivation of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-B gene in endothelial cells, reduced number of pericytes was observed and proliferative retinopathy developed when more than half of normal pericytes were lost [107]. Moreover, other signaling pathways, such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) signaling, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, polyol pathway etc., may also contribute to diabetes-induced pericytes loss [105]. Although a series of pathways have been revealed to be associated with diabetic pericyte loss, the underlying mechanisms still need to be fully elucidated.
The structure of microaneurysms in DR. Ultrastructurally, there are 4 types of microaneurysms: (a) Type I microaneurysms exhibit intact endothelium and basement membrane without the encirclement of pericytes, and circulating leukocytes is extensively accumulated in the lumen; (b) Type II microaneurysms are characterized by the absence of both endothelial cells and pericytes, thickened basement membrane, as well as a multitude of red blood cells inside the lumen; (c) Type III microaneurysms share similar appearances with Type II microaneurysms, but debris of red blood cells are contained; (d) Type IV microaneurysms are in sclerosed forms with heavily thickened basement membrane and fibrous infiltration into the lumen. Moreover, early in DR, retinal neurons undergo apoptotic cell death, accompanied by a decreased number of astrocytes and activation of microglial cells with amoeboid morphology
Endothelial cell damage secondary to pericyte dropout is the key pathological feature in DR. Under hyperglycemic conditions, tight junctions between endothelial cells are compromised, which causes the breakdown of the inner BRB, increase of vascular leakage and eventually DME [56, 57]. Reduced expression of tight junction proteins, such as Occludin, claudin-5, ZO-1 and cadherin, has been observed in both human retinal endothelial cells treated with high glucose concentration as well as in diabetic rats [55]. Oxidative stress, cytokines and vascular growth factors alter the expression and organization of tight junction proteins [56]. When the endothelial cells die, capillaries appear as the nude basement membrane tube. Degeneration of these blood vessels is known as retinal vasodegeneration or vasoregression, which leads to the non-perfusion of retinal capillaries and triggers progressive retinal ischemia and hypoxia in DR [13]. By exposure to persistent high levels of blood glucose, endothelial cells undergo apoptosis due to oxidative stress and ischemia [52]. Furthermore, inflammatory mediators released by neighboring neurons, neuroglial and microglial cells may also contribute to endothelial cell death [20]. In response to non-perfusion in the retina, a broad range of angiogenic factors and cytokines, most notably VEGF, are secreted by ischemic retinal neurons to facilitate the formation of abnormal new blood vessels [8]. This so-called neovascularization is the central microvascular characteristic of proliferative DR and causes irreversible blindness resulting from extensive bleeding in the vitreous of these fragile neovessels. Vasoregression and neovascularization are regulated by a highly complicated system in which several crosslinked signaling pathway (such as Wnt, Notch and NF-κB) and imbalance between angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors are involved [108, 109].
Immuno-inflammation in DR
Local inflammation acts as a pivotal risk factor in the development and progression of DR, and thus DR has also been regarded as chronic inflammatory disorder [15, 59, 62, 65, 66]. With progression of the disease, inflammatory reactions including activation of immune cells and production of diverse inflammatory cytokines are present within the retina [15]. At the early stage of DR, the adherence of circulating leukocytes such as neutrophils and monocytes to vascular walls is enhanced by the increased expression of ICAM-1 and P-selectin in endothelial cells [60]. This enhanced leukocyte-endothelial interactions, which is known as leukostasis, can induce injury to retinal vascular endothelium and neighboring tissue through capillary occlusion and non-perfusion as well as secretion of inflammatory molecules [61]. The genetically modified mice that lack expression of ICAM-1 and CD18 have exhibited fewer adherent leukocytes after streptozotocin treatment, leading to protection against damage of endothelial cells and hyperpermeability of blood vessels [59].
Apart from intravascular immune cells, microglial cells, the resident immune cells in the retina, are activated by advanced glycation end products and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in DR [62,63,64]. The activation can be observed by the morphological changes, from ramified to amoeboid morphology. At the early stage of DR, the major effects of activated microglia are phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, clearance of debris and secretion of neurotrophic molecules [65]. Nevertheless, as DR progresses, persistently activated microglial cells become detrimental to retinal neurons and vasculature via release of inflammatory cytokines [66]. TNFα and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) could cause retinal neuron death and vascular endothelial impairment with subsequent breakdown of the inner BRB through caspase-3 activation [65, 67]. Vincent and Mohr also demonstrated that IL-1β could lead to the apoptosis of retinal capillary cells via activation of caspase-1. Furthermore, mice deficient in IL-1β receptor suppressed the caspase activation and capillary degeneration in the diabetic retina of mice [110]. IL-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) are chemotactic factors that recruit neutrophil and monocytes to the inflammatory sites in the retina, respectively, increasing their infiltration within the retina [68, 69]. Moreover, IL-6 induces production of VEGF by activating the STAT3 pathway in vascular endothelium, promoting vascular leakage and DME [69]. These events act in concert to create an inflammatory environment that poses pathological changes in DR.
Dysfunction of RPE and choroid in DR
Although more attention has been paid to the diabetes-induced deterioration of retinal vasculature and neurons, DR also impacts RPE and its underlying choroid. RPE cells form a continuous and polarized cell monolayer with a variety of physiological functions, including transportation of nutrients, ions and water between the photoreceptors and choriocapillaris, phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments, conversion of all-trans-retinal into 11-cis-retinal in the visual cycle, absorption of light and protection against photooxidation, and secretion of a series of essential factors to maintain retinal integrity [111]. In diabetic rats, activity of the Na+-K+-ATPase, the major energy source for active transportation of ions and water in RPE cells, was significantly decreased [70]. Therefore, the transport of water driven by a transport of K+ and Cl- from the subretinal space to the blood was damaged, favoring the macular edema in DR [34, 71]. The key proteins involved in the visual cycle, such as IRBP and RPE65, have been reported to be significantly reduced in both diabetic animal models and patients, indicating the decrease of 11-cis-retinal supplied to the photoreceptors [71, 72]. Additionally, various factors secreted by RPE cells, such as VEGF, PDGF, TNFα, IL-6, IL-8 etc., are upregulated, contributing to the development and progression of DR [73]. Most importantly, under hyperglycemic conditions, the integrity of outer BRB formed by RPE cells and their intercellular tight junctions is disrupted with reduced expression of tight junction proteins (claudin-1 and occludin), leading to fluid leakage from the choriocapillaris [34, 74, 75]. In hyperglycemic rats, the breakdown of the outer BRB has also been confirmed with wider tight junctions and large holes observed between cells when examining another tight junction protein-zona occludens (ZO-1) [34, 76]. Severe macular detachment resulting from RPE barrier dysfunction has been observed in a third of DME cases, suggesting the co-occurrence of inner and outer BRB breakdown in the progression of DME [55, 112]. It has been reported that the outer BRB accounts for more than one third of total vascular leakage in diabetic retinas [71]. Meanwhile, impaired fluid clearance from the neural retina due to RPE dysfunction occurs, which, along with outer BRB destruction, plays an important part in DME [113]. Diabetic rats have also presented increased accumulation of immune cells in the outer retina and apoptosis of photoreceptors caused by damaged RPE [114]. Diabetic choroidal degeneration has been reported in both patients and animal models, and exhibits decreased choroidal thickness, increased Bruch’s membrane thickness, aneurysms and choroidal neovascularization [77,78,79]. The further understanding of RPE and choroidal pathology in DR still needs clinical and experimental investigation.
Potential therapeutic strategies for DR
Although therapies for DR have been greatly improved for the past decades, there is still a large demand in additional therapeutic options. Current treatments focus exclusively on the advanced stage of DR, in which irreversible injuries in the retina have occurred [3, 5]. Therefore, therapies that target early pathology or have preventive actions are highly required. Here, some of the novel therapeutic approaches based on pathology of the neurovascular unit in DR will be briefly discussed.
Neurotrophic factors
Neurotrophic factors are beneficial for neuronal growth, differentiation and neurovascular interactions [115, 116]. Reduction of these molecules has been considered to play a crucial role in retinal neurodegeneration [115,116,117]. A series of neurotrophic factors, such as PEDF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), SST as well as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), is of great importance to provide neuroprotection in DR [118,119,120,121,122,123,124].
PEDF secreted by RPE cells, vascular endothelial cells, glial cells, Müller cells, and neurons shows both neuroprotective and anti-angiogenic effects under hyperglycemic conditions through inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation as well as glutamate excitotoxicity [120, 125, 126]. In both patients with proliferative DR and diabetic rats, PEDF levels were decreased in the retina [120, 125]. Furthermore, early in the course of experimental DR, intravenous administration of PEDF could ameliorate retinal neuron damage and reduce increased expression of VEGF via antioxidant effects [120]. In addition, topical administration of PEDF has demonstrated reduced retinal ganglion cell death, Müller cell activation and microvascular leakage in a mouse model of DR [127]. It has been further confirmed in vitro that PEDF secreted by Müller cells promoted survival of retinal ganglion cells via activation of the STAT 3 pathway [128, 129].
BDNF is crucial as it supports tje survival of amacrine cells and retinal ganglion cells. Similar to PEDF, reduction of BDNF levels in the retina, which was associated with the degeneration of dopaminergic amacrine cells, was observed in diabetic rats induced by streptozotocin [130]. Intravitreal injection of BDNF have promoted density of dopaminergic amacrine cells, indicating its protective role in retinal neurodegeneration [130, 131]. Delivery of BDNF with recombinant adeno-associated virus has been beneficial in that it improved retinal ganglion cell survival and function in an experimental animal model of DR [121, 131]. However, the effects of BDNF in the retina have been reported to be dependent on various concentrations. At optimal concentrations, BDNF may exhibit a neuroprotective role in DR, while higher concentrations might elicit inflammatory responses [131, 132].
Insulin and its receptor signaling pathway provide support to maintain the normal state of retinal neurons. Impairment of insulin and its receptor signaling pathway contributes to the neuroretinal deterioration at the early stage of DR [122, 133]. Systemic and local (intravitreal and subconjunctival) administration of insulin has been proven to regain the insulin receptor activity, which in turn prevent the loss of retinal neurons [122, 134]. Therefore, biodegradable hydrogels or chitosan nanoparticles that can be implanted subconjunctivally has been developed to supply a sustained release of insulin to the rat retina with no negative effects [135, 136]. IGFs are the hormones involved in the progression of diabetes-induced retinal disease. In particular, decreased IGF-1 mRNA has been observed in the initial stage of both clinical and experimental diabetic eyes [137]. Diabetic rats treated with an IGF-1 analog have shown prevention of early retinal biochemical abnormalities related to DR pathogenesis [138].
SST is produced in the retina and exhibits neuroprotective and anti-angiogenetic properties in conjugation with its receptors, especially with the SST receptor 2 [123]. Low SST level, an early event of DR, has been reported to stimulate apoptosis of neurons and glial activation in the retina through extracellular accumulation of glutamate and downregulation of glutamate transporter [82, 123]. Therefore, SST has been applied to diabetic murine models via topical administration and found to ameliorate retinal neurodegeneration and gliosis by reducing glutamate excitotoxicity and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) level [123, 139]. Furthermore, a multi-center, randomized controlled clinical trial (EUROCONDOR) has shown that topical administration of SST could stop worsening of pre-existing neuroretinal dysfunction, although no retinal neuroprotection was observed in subjects included in this clinical trial [140].
GLP-1 is secreted by L cells (specific endocrine cells) in the small intestine in response to food intake. Apart from its anti-hyperglycemic effects, GLP-1 also exhibits neuroprotective functions in the central and peripheral nervous system [141]. Moreover, both GLP-1 and its receptor GLP-1R have been detected in human and murine retinas, indicating its potential neuroprotective role in the retina [142]. Expression of GLP-1 was reduced in the retina of diabetic patients when compared with controls, and similar findings were observed in diabetic animal models as well [142,143,144,145]. In animal models of DR, administration of GLP-1, GLP-1R agonists, or dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DDP-IV) prevented apoptosis of retinal neurons, loss of pericytes, and decrease of retinal thickness, resulting in the improvement of retinal functions as evaluated by ERG [124, 143, 146,147,148]. The underlying mechanisms might be inhibition of oxidative stress and decrease of glutamate excitotoxicity [143, 147, 148]. However, in clinical trials, GLP-1R agonists did not show protective effects on DR. On the contrary, a nonsignificant increase in the progression of DR was reported in the LEADER trial (liraglutide), and significant increase of DR incidence was shown in the SUSTAIN-6 trial (semaglutide) [149, 150]. Simo and Hernandez explained the possible reasons of the discrepancies, including short follow-up duration, lack of grading of DR, and rapid lowering of HbA1c [141].
Antioxidants
Oxidative stress has been shown to play a central role in the development of DR in many studies [15, 52, 56, 63, 120, 151, 152]. Thus, usage of antioxidants may be adopted as potential treatment options for DR. Flavonoids and carotenoids are examples of phytochemicals that are able to counteract diabetes-induced oxidative stress in the retina.
Flavonoids have antioxidant, anti-inflammation and anti-angiogenic functions, and effects of selected flavonoids have been examined for the prevention and/or treatment of DR [153,154,155,156,157,158]. For instance, quercetin could prevent oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis in the retina of diabetic rats [153, 154]. After administration of quercetin, the rats have exhibited restored antioxidant activities, decreased expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive gliosis as well as reduction of retinal ganglion cell apoptosis [153, 154]. In addition, treatment of quercetin has inhibited overexpression of aquaporin-4 (protein forming water-specific channel in the membrane), which has been thought to contribute to neuroglial edema [153]. A number of studies have been carried out to investigate the antioxidant and anti-angiogenic role of curcumin in the treatment of diabetic complications, including DR. Administration of curcumin in diabetic rats led to the reduction of VEGF expression; inhibition of oxidative stress; protection of inner nuclear layer cells, retinal ganglion cells and Müller cells; as well as prevention of glutamine synthetase downregulation [155,156,157]. In addition, treatment with curcumin has also diminished the levels of inflammatory mediators, such as TNFα and VEGF, as well as limiting structural degeneration and increased thickness of capillary basement membrane in experimental diabetic retina [158].
Lutein and zeaxanthin, the carotenoids highly concentrated in the retina, play a major role in filtering blue light, preventing oxidative damage and protecting neural retina [159,160,161,162,163,164]. In non-proliferative DR patients, the serum concentration of lutein and zeaxanthin was significantly lower than individuals without diabetes [160]. A three-month supplementation of lutein (6mg/day) and zeaxanthin (0.5mg/day) resulted in a significant increase of blood lutein and zeaxanthin level, as well as the improvement in visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and DME in non-proliferative DR [160]. These data were consistent with the conclusions drawn from the administration of 10mg/day lutein for 36 weeks in patients with non-proliferative DR [161]. In type 2 diabetics, an increased thickness in the central fovea and improved retinal response density were observed after a two-year supplementation of combined lutein (10mg/day), zeaxanthin (2mg/day) and meso-zeaxanthin (10mg/day) [162]. The studies using diabetic animal models to investigate lutein and zeaxanthin effects have also demonstrated protection from diabetes-induced retinal apoptosis, abnormal capillaries formation, and visual dysfunction through decreased ROS, and inflammatory factors such as VEGF, IL-1β, and NF-ΚB in the retina [159, 163, 164].
Anti-inflammation agents
As mentioned above, elevation of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and VEGF, are associated with DR pathogenesis [58, 65, 67,68,69, 110]. Moreover, upregulation of ICAM-1 leads to leukostasis in retinal vessels, which may subsequently contribute to neuroretinal ischemia, favoring neurodegeneration in the retina [58,59,60]. Agents that counteract the impact of inflammatory molecules, therefore, may be considered an option for DR therapy.
TNFα antagonist, etanercept, has shown beneficial effects in suppressing retinal cell apoptosis, increase of ICAM-1 expression and loss of vascular endothelial cells and pericytes in experimental diabetic animal models [165,166,167]. Nevertheless, after three months of intravitreal injection of etanercept, no significant improvement was observed in patients with refractory DME [168]. Likewise, a pilot clinical study using intravitreal administration of adalimumab and infliximab (the other two TNFα inhibitors) has not revealed any benefits for the eyes with refractory DME. Furthermore, 2mg infliximab administration could stimulate serious intraocular inflammation [169]. Hence, clinical trials failed to show beneficial effects of TNFα inhibitors, albeit TNF’s role in disrupting the neurovascular unit.
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 belongs to the family of SOCS proteins that regulate cytokine responses through a negative feedback loop [170]. SOCS 1 plays a crucial role in negatively regulating TNFα and IL-6, which are closely related with DR. Two weeks after topical administration of SOCS 1-derived peptide in db/db mice, reactive gliosis and presence of activated microglial cells were significantly decreased, indicating reduced glial activation [171]. In terms of proinflammatory cytokines, retinal levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and perivascular TNFα deposition were dramatically reduced in the SOCS 1-derived peptide treated group in comparison with the vehicle group. In addition, SOCS 1-derived peptide ameliorated abnormal retinal functions induced by diabetes due to preservation of the neural retina [171].
Minocycline, one of tetracycline derivatives, has also been studied for the treatment of DR due to its inhibition of microglial activation and PARP-1 expression properties [67, 172,173,174]. Minocycline could reduce inflammatory molecules including TNFα and IL-1β released by activated microglial cells, suggesting its potential role in preventing neuroretinal and microvascular atrophy in DR [172]. Data from the in vitro study was further confirmed by the findings in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model with prevention of retinal neuron death triggered by activated microglia through decreased caspase-3 activation and abnormal histone methylation levels [67, 173]. Diabetic rats fed with minocycline daily for 8 weeks exhibited decreased apoptosis of retinal cells through inhibition of PARP-1, which was abnormally activated by diabetes-induced DNA damages [174]. Furthermore, a single-centered, phase I/II clinical trial has been conducted to evaluate the effects of oral administration of minocycline on DME. Catherine and colleagues treated the patients with 100mg minocycline twice a day for up to six months. After the treatment, improvement of central macular edema, vascular leakage and visual function was observed in all five participants [175]. Doxycycline, another tetracycline derivative, has been tested on 33 patients with mild to moderate non-proliferative DR for two years. However, no significant protective effects were detected in diabetes-induced visual function and retinal injury [176].
Cell-based therapeutic strategies
Since the loss of several different cells in the retina is involved in the pathology of DR, cell replacement using stem cells has drawn attention from researchers in the past years. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC), hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), endothelial progenitor cells (EPC), and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) have been evaluated in either preclinical or clinical studies for the treatment of DR [177].
MSC are multipotent stem cells and can be easily harvested from the bone marrow, adipose tissue, dental pulp, umbilical cord blood and Wharton’s jelly, making them a promising cell source for cell therapy of DR [99]. In a rat model with pathological features of early DR, intravitreal injection of MSC significantly restored the retinal function by improving b-wave amplitudes in ERG and protected retinal structure by decreasing vascular leakage and apoptosis of cells around the vessels [178]. Treatment of diabetic mice with MSC completely attenuated the death of retinal ganglion cells which is an early event in the onset of DR, indicating the therapeutic potential of MSC at the initial stage of DR [179, 180]. Furthermore, MSC administration suppressed diabetes-induced damage to the neurovascular unit of the retina by reducing ROS levels and increasing neurotrophic factors including nerve growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor [179]. Another study performed by Yang and colleagues has shown differentiation of MSC into photoreceptors and glial-like cells in the retina, resulting in improved integrity of the BRB in diabetic rats [181]. In one ongoing clinical trial (NCT01736059), the safety and feasibility of intravitreal injection of bone marrow MSC is being investigated in individuals suffering from irreversible visual loss caused by retinal degenerative diseases or retinal vascular diseases, including DR. The safety and efficacy of intravenous administration of autologous bone marrow MSC has been evaluated by Gu et al., demonstrating decrease of macular thickness and significant improvement of best corrected visual acuity in non-proliferative DR patients, but not in proliferative DR patients [182].
EPC are regarded as a heterogeneous group of cells which can differentiate into endothelial cells directly or induce angiogenesis via paracrine action to restore impaired vasculature [183]. The functions of human EPC in ischemic retinal diseases have been evaluated in animal models of DR, ischemia/reperfusion and oxygen-induced retinopathy [184,185,186]. Transplantation of IL-10-transfected EPC from the rat bone marrow led to significant improvement of retinal structure and reduced retinal vascular permeability through inhibiting inflammation in diabetic rats [184]. Intravitreal and intravenous administration of healthy human EPC from bone marrow or peripheral circulation could rapidly settle down and integrate into damaged retinal vasculature, suggesting the use of these cells as a potential therapy for DR [185, 186]. However, EPC from diabetic patients failed to repair vascular impairment in the retina of murine models as mentioned above [185]. Therefore, a variety of approaches have been adopted to restore functions of EPC in patients with diabetes, including inhibition of TGFβ1, treatment with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and δ, improvement of EPC mobilization with stromal cell-derived factor-1 [183].
Dysfunction of HSC resulting from the disturbance of the vasoprotective axis of the renin angiotensin system is a feature of DR, thus, making the activation of protective renin angiotensin system within HSC a treatment option for DR [187]. Human iPSC derived from cord blood could generate vascular progenitor cells, which exhibited homing and integration into injured retinal vessels for up to 45 days [188]. Human iPSC-derived endothelial cells formed more complex vascular networks in vitro and integrated into host regenerating retinal vessels in a mouse model of ischemic retinopathies when compared to human mature endothelial cells, suggesting its superior angiogenic potential in ischemic retinopathies (such as proliferative DR) [189]. One clinical trial (NCT03403699) is evaluating the ability of human iPSC to generate endothelial cells and pericytes for revascularization of vasodegenerative capillaries occurring in DR.
Other treatment approaches for improving retinal neurovascular coupling
Activity of neurons in the inner retina is closely coupled with the retinal blood flow in physiological conditions [8, 9, 11, 190]. Indeed, it is the interaction between neural retina and microvascular networks that supply more oxygen and nutrients to match the increased neuronal activity in the retina [9, 11]. For instance, visual stimulation such as flicker light stimulation could induce increased metabolism of retinal neurons, which in turn dilates retinal blood vessels, especially the smaller vessels via neurovascular coupling, thus eventually leading to the increase of retinal blood flow [191, 192]. However, this response, known as functional hyperemia, is diminished in early DR due to the impairment of retinal neurovascular coupling [16, 193].
Early in DR, the vascular response in neurovascular coupling is compromised, depriving the retinal neurons of adequate oxygen and nutrients, and thus contribute to the death of neuronal cells. Increased iNOS produces high nitric oxide (NO) levels in the diabetic retina, which would cause defective interconnections between neuronal activity and arteriole dilation via inhibition of glia-derived dilatory molecules [16]. Moreover, up-regulation of NO concentrations has shown an association with increased number of acellular capillaries and pericytes loss in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice; while all the abnormalities have been prevented in diabetic iNOS knockout mice [194,195,196]. In patients with DR, high levels of NO generated by iNOS led to neurotoxicity and angiogenesis in the retina [194, 197]. Hence, suppression of iNOS and reduction of NO levels may be useful in promoting neurovascular coupling and ameliorate damages to neurons, pericytes as well as endothelial cells. Administration of the iNOS inhibitor, aminoguanidine, recovered vessel dilations in experimental DR [198]. Sesamin, a natural compound, could restrain the progression of diabetic retinal damage through the reduction of hyperglycemia and inflammation in the retina of diabetic mice including inhibition of iNOS [199].
Dopamine is a pivotal neurotransmitter in the retina and brain. Reduced synthesis of dopamine has been proved to be closely associated with diabetes-induced malfunctions of retinal neurons in both diabetic animal models and patients [200,201,202]. Treatment with L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA), a precursor of dopamine, has partially restored visual functions, showing preservation of delayed b-wave latencies and oscillatory potential as well as reduced contrast sensitivity thresholds and spatial frequency in STZ diabetic mice [200, 201]. In diabetics without clinically visible retinal vascular defects, oscillatory potential implicit time was delayed, which was preserved after a two-week treatment of Sinemet (L-DOPA plus carbidopa), suggesting that L-DOPA may be one potential candidate for treating early DR [202].
Endothelin-1(ET-1), mainly synthesized in the vascular endothelium, is one of the most potent vasoconstrictor peptides. It has been reported that elevated serum concentration of ET-1 is intimately correlated with microangiopathy in Type 2 diabetic patients [203]. Moreover, through ETA receptors, ET-1 makes contribution to retinal hemodynamic disruption and pathogenesis of DR in experimental animal models, indicating its evident role in the interaction between vascular abnormalities and neural retina damage [203]. In this regard, blocking ET-1 actions through ETA receptors may be considered a potential treatment for DR. Indeed, atrasentan (the ETA receptor antagonist) attenuated the reduction of red blood cell velocity, flow rate and wall shear rate, loss of pericytes, percentage of acellular capillaries as well as protected the inner retina in several animal models of diabetes [204, 205]. Recent studies have also shown retinal neurodegeneration via the activation of ETB receptors, the other type of ET-1 receptor, in several animal models [206]. Therefore, inhibition of ETB receptor activation could prevent degeneration of the neural retina. A study conducted by Patricia and colleagues has reported that bosentan (a dual ET-1 receptor antagonist) significantly decreased glial activation and apoptotic cells in all retinal layers of db/db mice, making it an ideal candidate for treating DR at an early stage [206].
In addition to the aforementioned therapeutic approaches (Table 2), other treatments including implantation of whole retinal cell sheets, use of bioelectronic prostheses transplanted in the subretina, modification of other types of retinal cells to generate retinal neurons, use of agents to block glutamate signaling pathway and so on are also under investigation [207,208,209,210].
There is still one issue that needs to be considered: the appropriate administration route for treating early DR. It would be too much aggressive to choose intravitreal administration at the early stage of DR, although this route provides direct, local and relatively prolonged pharmacological effects on the retina [211]. In addition, certain complications have been observed, including cataract, endophthalmitis, retinal detachment, vitreous hemorrhage, etc [212]. The therapeutic effects of systemically administered drugs targeting the posterior eye are limited by the BRB as evidenced by the limited penetration of drugs (only 1-2%) across the BRB and into the intraocular tissue [212]. It seems that drug delivery through the topical route might be the suitable administration route in the initial stage of DR because of its convenience, non-invasiveness and high patient compliance. However, the concentration of drugs that reaches the retina is very low (less than 5% of the administered dosage), owing to the blood-ocular barriers, nasolacrimal drainage and tear dilution [211,212,213,214]. Recently, Simό and coworkers have demonstrated that a number of drugs administered topically could reach the retina at effective concentrations in animal models of DR [123, 124, 143, 206, 215]. But, to best of our knowledge, there is no supporting data from clinical trials. Now, scientists from multidisciplinary teams are trying to develop drug delivery systems that target the posterior segment of the eye via the topical route. One of them is polymeric nanoparticles, namely Mucus Penetrating Particles, which are capable of bypassing all ocular barriers and delivering drugs to the retina due to the enhanced migration through mucus [216, 217]. Another technology owned by Macregen Inc. is to add cell-penetrating peptides in the eye drop, which can penetrate across the corneal barriers and reach the posterior of the eye, achieving the equivalent therapeutic efficacy as intravitreal injection [218, 219]. Additionally, a hydrogel ring made of hydroxyethyl methacrylate has been designed to deliver topically administered drugs to the retina/choroid via the sclera and conjunctiva [219, 220]. With the development in drug delivery systems, topical administration would be the preferred choice to deliver drugs to the posterior eye in the early course of DR.
Conclusions
DR is one of the most common causes of irreversible vision loss around the world. For a long time, DR has been considered as a microvascular disease featured with vascular leakage and capillary occlusion at the early non-proliferative stage and neovascularization at the late proliferative stage. To date, current treatments for DR mainly focus on retinal microvascular lesions, including intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF as the first-line therapy and laser photocoagulation, intravitreal corticosteroids, and vitreous surgery as adjuvants. However, these interventions are invasive, expensive and visits to the ophthalmologist’s clinic are needed at certain intervals. Therefore, new therapeutic strategies drawing from a deeper understanding of DR pathogenesis are required. A growing body of evidence based on clinical and experimental studies suggests that rather than DR being solely a microvascular disorder, DR can be an intricate disorder with the disruption of vascular cells, neurons, glia, local immune cells, RPE cells as well as interconnections among these cells. This concept has broadened our understanding of the cells involved in the pathophysiology of DR and provided additional clues for developing novel therapies to prevent or halt the disease at the initial stage in comparison with current treatment modalities targeting on DME and proliferative DR at the advanced stage. A variety of novel treatment options focusing on the components of the neurovascular unit and their interactions, such as neurotrophic factors, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, cell replacement and so on, have demonstrated protective effects on retinal functions and structure in both animal models and clinical trials. Although numerous potential interventions have shown exciting results, further studies to evaluate not only the long-term effects and safety of these interventions, but also the appropriate drug delivery routes are still needed before implementation in clinical practice.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BRB:
-
blood-retinal barrier
- DDP-IV:
-
dipeptidyl peptidase IV
- DME:
-
diabetic macular edema
- DR:
-
diabetic retinopathy
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- EPC:
-
endothelial progenitor cells
- ERG:
-
electroretinogram
- ET-1:
-
endothelin-1
- GFAP:
-
glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GLP-1:
-
glucagon-like peptide-1
- HSC:
-
hematopoietic stem cells
- ICAM-1:
-
intercellular adhesion molecule 1
- IGF-1:
-
insulin-like growth factor-1
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1beta
- INL:
-
inner nuclear layer
- iNOS:
-
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- IPL:
-
inner plexiform layer
- iPSC:
-
induced pluripotent stem cells
- IRBP:
-
interphotoreceptor retinol binding protein
- L-DOPA:
-
L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine
- MCP-1:
-
monocyte chemoattractant protein 1
- MSC:
-
mesenchymal stem cells
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa-B
- NFL:
-
nerve fiber layer
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PDGF:
-
platelet-derived growth factor
- PEDF:
-
pigment epithelium-derived factor
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RPE:
-
retinal pigment epithelium
- SOCS:
-
suppressor of cytokine signaling
- SST:
-
somatostatin
- TGFβ:
-
transforming growth factor-beta
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
- ZO-1:
-
zona occludens 1
References
Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY. Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet. 2010;376(9735):124–36.
Sloan FA, Belsky D, Ruiz D Jr, Lee P. Changes in incidence of diabetes mellitus-related eye disease among US elderly persons, 1994-2005. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126(11):1548–53.
Wang W, Lo ACY. Diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiology and treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1816.
Solomon SD, Chew E, Duh EJ, Sobrin L, Sun JK, VanderBeek BL, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: a position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(3):412–8.
Stitt AW, Curtis TM, Chen M, Medina RJ, McKay GJ, Jenkins A, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;51:156–86.
Gonzalez VH, Campbell J, Holekamp NM, Kiss S, Loewenstein A, Augustin AJ, et al. Early and long-term responses to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in diabetic macular edema: analysis of Protocol I data. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016;172:72–9.
Maggio E, Sartore M, Attanasio M, Maraone G, Guerriero M, Polito A, et al. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment for diabetic macular edema in a real-world clinical setting. Am J Ophthalmol. 2018;195:209–22.
Antonetti DA, Klein R, Gardner TW. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(13):1227–39.
Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173–85.
Liu J, Wang YH, Li W, Liu L, Yang H, Meng P, et al. Structural and functional damage to the hippocampal neurovascular unit in diabetes-related depression. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):289–97.
Simό R, Hernández C. Neurodegeneration in the diabetic eye: new insights and therapeutic perspectives. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014;25(1):23–33.
Chan G, Balaratnasingam C, Yu PK, Morgan WH, McAllister IL, Cringle SJ, et al. Quantitative morphometry of perifoveal capillary networks in the human retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(9):5502–14.
Moran EP, Wang ZX, Chen J, Sapieha P, Smith LE, Ma JX. Neurovascular cross talk in diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiological roles and therapeutic implications. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;311(3):H738–49.
Gardner TW, Davila JR. The neurovascular unit and the pathophysiologic basis of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arc Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2017;255(1):1–6.
Duh EJ, Sun JK, Stitt AW. Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight. 2017;2(14):e93751.
Nakahara T, Mori A, Kurauchi Y, Sakamoto K, Ishii K. Neurovascular interactions in the retina: physiological and pathological roles. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;123(2):79–84.
Newman E, Reichenbach A. The Müller cell: a functional element of the retina. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19(8):307–12.
Vecino E, Rodriguez FD, Ruzafa N, Pereiro X, Sharma SC. Glia-neuron interactions in the mammalian retina. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;51:1–40.
Filosa JA, Morrison HW, Iddings JA, Du W, Kim KJ. Beyond neurovascular coupling, role of astrocytes in the regulation of vascular tone. Neuroscience. 2016;323:96–109.
Cuenca N, Fernández-Sánchez L, Campello L, Maneu V, De la Villa P, Lax P, et al. Cellular responses following retinal injuries and therapeutic approaches for neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014;43:17–75.
Schafer DP, Lehrman EK, Kautzman AG, Koyama R, Mardinly AR, Yamasaki R, et al. Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron. 2012;74(4):691–705.
Osman AM, Rodhe J, Shen X, Dominguez CA, Joseph B, Blomgren K. The secretome of microglia regulate neural stem cell function. Neuroscience. 2019;405:92–102.
Langmann T. Microglia activation in retinal degeneration. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81(6):1345–51.
Mugisho OO, Rupenthal ID, Squirrell DM, Bould SJ, Danesh-Meyer HV, Zhang J, et al. Intravitreal pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-obese diabetic mice: Modelling signs of diabetic retinopathy. PLoS one. 2018;13(8):e0202156.
Gardiner TA, Archer DB, Curtis TM, Stitt AW. Arteriolar involvement in the microvascular lesions of diabetic retinopathy: implications for pathogenesis. Microcirculation. 2007;14(1):25–38.
Klaassen I, Van Noorden CJ, Schlingemann RO. Molecular basis of the inner blood-retinal barrier and its breakdown in diabetic macular edema and other pathological conditions. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013;34:19–48.
Berthiaume AA, Grant RI, McDowell KP, Underly RG, Hartmann DA, Levy M, et al. Dynamic remodeling of pericytes in vivo maintains capillary coverage in the adult mouse brain. Cell Rep. 2018;22(1):8–16.
Jindatip D, Fujiwara K, Kouki T, Yashiro T. Transmission and scanning electron microscopy study of the characteristics and morphology of pericytes and novel desmin-immunopositive perivascular cells before and after castration in rat anterior pituitary gland. Anat Sci Int. 2012;87(3):165–73.
Kur J, Newman EA, Chan-Ling T. Cellular and physiological mechanisms underlying blood flow regulation in the retina and choroid in health and disease. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012;31(5):377–406.
McConnell HL, Kersch CN, Woltjer RL, Neuwelt EA. The translational significance of the neurovascular unit. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(3):762–70.
Muoio V, Persson PB, Sendeski MM. The neurovascular unit - concept review. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2014;210(4):790–8.
Amato R, Rossino MG, Cammalleri M, Locri F, Pucci L, Dal Monte M, et al. Lisosan G protects the retina from neurovascular damage in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1932.
Fehér J, Taurone S, Spoletini M, Birό Z, Varsányi B, Scuderi G, et al. Ultrastructure of neurovascular changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018;31:394632017748841. https://doi.org/10.1177/0394632017748841.
Zhang C, Xie H, Yang Q, Yang Y, Li W, Tian H, et al. Erythropoietin protects outer blood-retinal barrier in experimental diabetic retinopathy by up-regulating ZO-1 and occludin. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019;47(9):1182–97.
Jo DH, Yun JH, Cho CS, Kim JH, Kim JH, Cho CH. Interaction between microglia and retinal pigment epithelial cells determines the integrity of outer blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy. Glia. 2019;67(2):321–31.
Simό R, Stitt AW, Gardner TW. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: does it really matter? Diabetologia. 2018;61(9):1902–12.
Garcia-Martin E, Cipres M, Melchor I, Gil-Arribas L, Vilades E, Polo V, et al. Neurodegeneration in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus without diabetic retinopathy. J Ophthalmol. 2019;2019:1825819. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1825819.
Frydkjaer-Olsen U, Hansen RS, Peto T, Grauslund J. Structural neurodegeneration correlates with early diabetic retinopathy. Int Ophthalmol. 2018;38(4):1621–6.
Gastinger MJ, Singh RS, Barber AJ. Loss of cholinergic and dopaminergic amacrine cells in streptozotocin-diabetic rat and Ins2Akita-diabetic mouse retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(7):3143–50.
Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, Villena JA, Carvalho AR, Garcia-Arumí J, Ramos D, et al. The db/db mouse: a useful model for the study of diabetic retinal neurodegeneration. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97302.
Barber AJ, Baccouche B. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: potential for novel therapies. Vision Res. 2017;139:82–92.
van Dijk HW, Kok PH, Garvin M, Sonka M, Devries JH, Michels RP, et al. Selective loss of inner retinal layer thickness in type 1 diabetic patients with minimal diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50(7):3404–9.
Liu C, Li CP, Wang JJ, Shan K, Liu X, Yan B. RNCR3 knockdown inhibits diabetes mellitus-induced retinal reactive gliosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479(2):198–203.
Subirada PV, Paz MC, Ridano ME, Lorenc VE, Vaglienti MV, Barcelona PF, et al. A journey into the retina: Müller glia commanding survival and death. Eur J Neurosci. 2018;47(12):1429–43.
Feenstra DJ, Yego EC, Mohr S. Modes of retinal cell death in diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;4(5):298.
Garhöfer G, Zawinka C, Resch H, Kothy P, Schmetterer L, Dorner GT. Reduced response of retinal vessel diameters to flicker stimulation in patients with diabetes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004;88(7):887–91.
Nguyen TT, Kawasaki R, Wang JJ, Kreis AJ, Shaw J, Vilser W, et al. Flicker light-induced retinal vasodilation in diabetes and diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(11):2075–80.
Durham JT, Herman IM. Microvascular modifications in diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2011;11(4):253–64.
Chronopoulos A, Trudeau K, Roy S, Huang H, Vinores SA, Roy S. High glucose-induced altered basement membrane composition and structure increases trans-endothelial permeability: implications for diabetic retinopathy. Curr Eye Res. 2011;36(8):747–53.
Roy S, Bae E, Amin S, Kim D. Extracellular matrix, gap junctions, and retinal vascular homeostasis in diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res. 2015;133:58–68.
Pfister F, Feng Y. vom Hagen F, Hoffmann S, Molema G, Hillebrands JL, et al. Pericyte migration: a novel mechanism of pericyte loss in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 2008;57(9):2495–502.
Hammes HP, Feng Y, Pfister F, Brownlee M. Diabetic retinopathy: targeting vasoregression. Diabetes. 2011;60(1):9–16.
Curtis TM, Gardiner TA, Stitt AW. Microvascular lesions of diabetic retinopathy: clues towards understanding pathogenesis? Eye (Lond). 2009;23(7):1496–508.
Stitt AW, Gardiner TA, Archer DB. Histological and ultrastructural investigation of retinal microaneurysm development in diabetic patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 1995;79(4):362–7.
Daruich A, Matet A, Moulin A, Kowalczuk L, Nicolas M, Sellam A, et al. Mechanisms of macular edema: beyond the surface. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018;63:20–68.
Frey T, Antonetti DA. Alterations to the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes: cytokines and reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(5):1271–84.
Kady NM, Liu X, Lydic TA, Syed MH, Navitskaya S, Wang Q, et al. ELOVL4-mediated production of very long-chain ceramides stabilizes tight junctions and prevents diabetes-induced retinal vascular permeability. Diabetes. 2018;67(4):769–81.
Wang J, Xu X, Elliott MH, Zhu M, Le YZ. Müller cell-derived VEGF is essential for diabetes-induced retinal inflammation and vascular leakage. Diabetes. 2010;59(9):2297–305.
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Le ML, Koizumi K, Esser C, Janicki H, et al. A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 2004;18(12):1450–2.
McLeod DS, Lefer DJ, Merges C, Lutty GA. Enhanced expression of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 and P-selectin in the diabetic human retina and choroid. Am J Pathol. 1995;147(3):642–53.
Valle A, Giamporcaro GM, Scavini M, Stabilini A, Grogan P, Bianconi E, et al. Reduction of circulating neutrophils precedes and accompanies type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(6):2072–7.
Wang J, Lin J, Schlotterer A, Wu L, Fleming T, Busch S, et al. CD74 indicates microglial activation in experimental diabetic retinopathy and exogenous methylglyoxal mimics the response in normoglycemic retina. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(5):813–21.
Milne R, Brownstein S. Advanced glycation end products and diabetic retinopathy. Amino Acids. 2013;44(6):1397–407.
Wang AL, Li Z, Yuan M, Yu AC, Zhu X, Tso MO. Sinomenine inhibits activation of rat retinal microglia induced by advanced glycation end products. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7(12):1552–8.
Santiago AR, Boia R, Aires ID, Ambrόsio AF, Fernandes R. Sweet stress: coping with vascular dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy. Front Physiol. 2018;9:820.
Ibrahim AS, El-Remessy AB, Matragoon S, Zhang W, Patel Y, Khan S, et al. Retinal microglial activation and inflammation induced by amadori-glycated albumin in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetes. 2011;60(4):1122–33.
Krady JK, Basu A, Allen CM, Xu Y, LaNoue KF, Gardner TW, et al. Minocycline reduces proinflammatory cytokine expression, microglial activation, and caspase-3 activation in a rodent model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 2005;54(5):1559–65.
Henkels KM, Frondorf K, Gonzalez-Mejia ME, Doseff AL, Gomez-Cambronero J. IL-8-induced neutrophil chemotaxis is mediated by Janus kinase 3 (JAK3). FEBS Lett. 2011;585(1):159–66.
Mendonca HR, Carpi-Santos R, da Costa CK, Blanco Martinez AM. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress act in concert to promote neurodegeneration in the diabetic retina and optic nerve: galectin-3 participation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(4):625–35.
Bensaoula T, Ottlecz A. Biochemical and ultrastructural studies in the neural retina and retinal pigment epithelium of STZ-diabetic rats: effect of captopril. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2001;17(6):573–86.
Xia T, Rizzolo LJ. Effects of diabetic retinopathy on the barrier functions of the retinal pigment epithelium. Vision Res. 2017;139:72–81.
Garcia-Ramírez M, Hernández C, Villarroel M, Canals F, Alonso MA, Fortuny R, et al. Interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) is downregulated at early stages of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 2009;52(12):2633–41.
Ponnalagu M, Subramani M, Jayadev C, Shetty R, Das D. Retinal pigment epithelium-secretome: a diabetic retinopathy perspective. Cytokine. 2017;95:126–35.
Rosales MA, Silva KC, Duarte DA, Rossato FA. Lopes de Faria JB, Lopes de Faria JM. Endocytosis of tight junctions caveolin nitrosylation dependent is improved by cocoa via opioid receptor on RPE cells in diabetic conditions. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(9):6090–100.
Beasley S, El-Sherbiny M, Megyerdi S, El-Shafey S, Choksi K, Kaddour-Djebbar I, et al. Caspase-14 expression impairs retinal pigment epithelium barrier function: potential role in diabetic macular edema. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:417986. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/417986.
Desjardins DM, Yates PW, Dahrouj M, Liu Y, Crosson CE, Ablonczy Z. Progressive early breakdown of retinal pigment epithelium function in hyperglycemic rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(6):2706–13.
Muir ER, Rentería RC, Duong TQ. Reduced ocular blood flow as an early indicator of diabetic retinopathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(10):6488–94.
Hua R, Liu L, Wang X, Chen L. Imaging evidence of diabetic choroidopathy in vivo: angiographic pathoanatomy and choroidal-enhanced depth imaging. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e83494.
Laíns I, Talcott KE, Santos AR, Marques JH, Gil P, Gil J, et al. Choroidal thickness in diabetic retinopathy assessed with swept-source optical coherence tomography. Retina. 2018;38(1):173–82.
Abu-El-Asrar AM, Dralands L, Missotten L, Al-Jadaan IA, Geboes K. Expression of apoptosis markers in the retinas of human subjects with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45(8):2760–6.
García-Ramírez M, Canals F, Hernández C, Colomé N, Ferrer C, Carrasco E, et al. Proteomic analysis of human vitreous fluid by fluorescence-based difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE): a new strategy for identifying potential candidates in the pathogenesis of proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 2007;50(6):1294–303.
Carrasco E, Hernández C, Miralles A, Huguet P, Farrés J, Simό R. Lower somatostatin expression is an early event in diabetic retinopathy and is associated with retinal neurodegeneration. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(11):2902–8.
Tavares Ferreira J, Alves M, Dias-Santos A, Costa L, Santos BO, Cunha JP, et al. Retinal neurodegeneration in diabetic patients without diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(14):6455–60.
Hernández C, Simό-Servat A, Bogdanov P, Simό R. Diabetic retinopathy: new therapeutic perspectives based on pathogenic mechanisms. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017;40(9):925–35.
McAnany JJ, Park JC. Cone photoreceptor dysfunction in early-stage diabetic retinopathy: association between the activation phase of cone phototransduction and the flicker electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60(1):64–72.
Pardue MT, Barnes CS, Kim MK, Aung MH, Amarnath R, Olson DE, et al. Rodent hyperglycemia-induced inner retinal deficits are mirrored in human diabetes. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2014;3(3):6.
Drasdo N, Chiti Z, Owens DR, North RV. Effect of darkness on inner retinal hypoxia in diabetes. Lancet. 2002;359(9325):2251–3.
Han Y, Adams AJ, Bearse MA Jr, Schneck ME. Multifocal electroretinogram and short-wavelength automated perimetry measures in diabetic eyes with little or no retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122(12):1809–15.
Kizawa J, Machida S, Kobayashi T, Gotoh Y, Kurosaka D. Changes of oscillatory potentials and photopic negative response in patients with early diabetic retinopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2006;50(4):367–73.
McAnany JJ, Park JC. Temporal frequency abnormalities in early-stage diabetic retinopathy assessed by electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59(12):4871–9.
McAnany JJ, Park JC. Reduced contrast sensitivity is associated with elevated equivalent intrinsic noise in type 2 diabetics who have mild or no retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59(6):2652–8.
Harrison WW, Bearse MA Jr, Ng JS, Jewell NP, Barez S, Burger D, et al. Multifocal electroretinograms predict onset of diabetic retinopathy in adult patients with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(2):772–7.
Du Y, Veenstra A, Palczewski K, Kern TS. Photoreceptor cells are major contributors to diabetes-induced oxidative stress and local inflammation in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(41):16586–91.
Cerani A, Tetreault N, Menard C, Lapalme E, Patel C, Sitaras N, et al. Neuron-derived semaphorin 3A is an early inducer of vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy via neuropilin-1. Cell Metab. 2013;18(4):505–18.
Araszkiewicz A, Zozulinska-Ziolkiewicz D. Retinal neurodegeneration in the course of diabetes-pathogenesis and clinical perspective. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(8):805–9.
Zong H, Ward M, Madden A, Yong PH, Limb GA, Curtis TM, et al. Hyperglycaemia-induced pro-inflammatory responses by retinal Müller glia are regulated by the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE). Diabetologia. 2010;53(12):2656–66.
Tu Y, Zhu M, Wang Z, Wang K, Chen L, Liu W, et al. Melatonin inhibits Müller cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine production via upregulating the MEG3/miR-204/Sirt1 axis in experimental diabetic retinopathy. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(11):8724–35.
Pannicke T, Iandiev I, Wurm A, Uckermann O. vom Hagen F, Reichenbach A, et al. Diabetes alters osmotic swelling characteristics and membrane conductance of glial cells in rat retina. Diabetes. 2006;55(3):633–9.
Fiori A, Terlizzi V, Kremer H, Gebauer J, Hammes HP, Harmsen MC, et al. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells as potential therapy in diabetic retinopathy. Immunobiology. 2018;223(12):729–43.
Oshitari T, Polewski P, Chadda M, Li AF, Sato T, Roy S. Effect of combined antisense oligonucleotides against high-glucose- and diabetes-induced overexpression of extracellular matrix components and increased vascular permeability. Diabetes. 2006;55(1):86–92.
Roy S, Sato T, Paryani G, Kao R. Downregulation of fibronectin overexpression reduces basement membrane thickening and vascular lesions in retinas of galactose-fed rats. Diabetes. 2003;52(5):1229–34.
Corliss BA, Ray HC, Doty RW, Mathews C, Sheybani N, Fitzgerald K, et al. Pericyte bridges in homeostasis and hyperglycemia. Diabetes. 2020;69(7):1503–17.
Lόpez-Luppo M, Nacher V, Ramos D, Catita J, Navarro M, Carretero A, et al. Blood vessel basement membrane alterations in human retinal microaneurysms during aging. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(2):1116–31.
Price TO, Sheibani N, Shah GN. Regulation of high glucose-induced apoptosis of brain pericytes by mitochondrial CA VA: a specific target for prevention of diabetic cerebrovascular pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(4):929–35.
Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Valdez CN, Marko CK, D'Amore PA. From pathobiology to the targeting of pericytes for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2015;15(2):573.
Cai J, Kehoe O, Smith GM, Hykin P, Boulton ME. The angiopoietin/Tie-2 system regulates pericyte survival and recruitment in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008;49(5):2163–71.
Enge M, Bjarnegård M, Gerhardt H, Gustafsson E, Kalén M, Asker N, et al. Endothelium-specific platelet-derived growth factor-B ablation mimics diabetic retinopathy. EMBO J. 2002;21(16):4307–16.
Korn C, Augustin HG. Mechanisms of vessel pruning and regression. Dev Cell. 2015;34(1):5–17.
Simό R, Carrasco E, García-Ramírez M, Hernández C. Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006;2(1):71–98.
Vincent JA, Mohr S. Inhibition of caspase-1/interleukin-1beta signaling prevents degeneration of retinal capillaries in diabetes and galactosemia. Diabetes. 2007;56(1):224–30.
Strauss O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol Rev. 2005;85(3):845–81.
Shereef H, Comyn O, Sivaprasad S, Hykin P, Cheung G, Narendran N, et al. Differences in the topographic profiles of retinal thickening in eyes with and without serous macular detachment associated with diabetic macular oedema. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014;98(2):182–7.
Simό R, Villarroel M, Corraliza L, Hernández C, Garcia-Ramírez M. The retinal pigment epithelium: something more than a constituent of the blood-retinal barrier–implications for the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:190724.
Omri S, Behar-Cohen F, de Kozak Y, Sennlaub F, Verissimo LM, Jonet L, et al. Microglia/macrophages migrate through retinal epithelium barrier by a transcellular route in diabetic retinopathy: role of PKCzeta in the Goto Kakizaki rat model. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(2):942–53.
Unsicker K. Neurotrophic molecules in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease with focus on the retina: status and perspectives. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;353(2):205–18.
Blesch A. Neurotrophic factors in neurodegeneration. Brain Pathol. 2006;16(4):295–303.
Hernández-Pinto A, Polato F, Subramanian P, Rocha-Munoz A, Vitale S, de la Rosa EJ, et al. PEDF peptides promote photoreceptor survival in rd10 retina models. Exp Eye Res. 2019;184:24–9.
Hernández C, Dal Monte M, Simό R, Casini G. Neuroprotection as a therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:9508541.
Stem MS, Gardner TW. Neurodegeneration in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(26):3241–50.
Yoshida Y, Yamagishi S, Matsui T, Jinnouchi Y, Fukami K, Imaizumi T, et al. Protective role of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) in early phase of experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25(7):678–86.
Gong Y, Chang ZP, Ren RT, Wei SH, Zhou HF, Chen XF, et al. Protective effects of adeno-associated virus mediated brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression on retinal ganglion cells in diabetic rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(3):467–75.
Reiter CE, Wu X, Sandirasegarane L, Nakamura M, Gilbert KA, Singh RS, et al. Diabetes reduces basal retinal insulin receptor signaling: reversal with systemic and local insulin. Diabetes. 2006;55(4):1148–56.
Hernández C, García-Ramírez M, Corraliza L, Fernández-Carneado J, Farrera-Sinfreu J, Ponsati B, et al. Topical administration of somatostatin prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(7):2569–78.
Hernández C, Bogdanov P, Solá-Adell C, Sampedro J, Valeri M, Genís X, et al. Topical administration of DPP-IV inhibitors prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Diabetologia. 2017;60(11):2285–98.
Barnstable CJ, Tombran-Tink J. Neuroprotective and antiangiogenic actions of PEDF in the eye: molecular targets and therapeutic potential. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004;23(5):561–77.
Shen X, Zhong Y, Xie B, Cheng Y, Jiao Q. Pigment epithelium derived factor as an anti-inflammatory factor against decrease of glutamine synthetase expression in retinal Müller cells under high glucose conditions. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248(8):1127–36.
Liu Y, Leo LF, McGregor C, Grivitishvili A, Barnstable CJ, Tombran-Tink J. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) peptide eye drops reduce inflammation, cell death and vascular leakage in diabetic retinopathy in Ins2(Akita) mice. Mol Med. 2012;18(1):1387–401.
Eichler W, Savković-Cvijić H, Bürger S, Beck M, Schmidt M, Wiedemann P, et al. Müller cell-derived PEDF mediates neuroprotection via STAT3 activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(4):1411–24.
Unterlauft JD, Claudepierre T, Schmidt M, Müller K, Yafai Y, Wiedemann P, et al. Enhanced survival of retinal ganglion cells is mediated by Müller glial cell-derived PEDF. Exp Eye Res. 2014;127:206–14.
Seki M, Tanaka T, Nawa H, Usui T, Fukuchi T, Ikeda K, et al. Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in early retinal neuropathy of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic amacrine cells. Diabetes. 2004;53(9):2412–9.
Afarid M, Namvar E, Sanie-Jahromi F. Diabetic retinopathy and BDNF: a review on its molecular basis and clinical applications. J Ophthalmol. 2020;2020:1602739.
Liu Y, Tao L, Fu X, Zhao Y, Xu X. BDNF protects retinal neurons from hyperglycemia through the TrkB/ERK/MAPK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(6):1773–8.
Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA, et al. Insulin rescues retinal neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(35):32814–21.
Fort PE, Losiewicz MK, Reiter CE, Singh RS, Nakamura M, Abcouwer SF, et al. Differential roles of hyperglycemia and hypoinsulinemia in diabetes induced retinal cell death: evidence for retinal insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26498.
Misra GP, Singh RS, Aleman TS, Jacobson SG, Gardner TW, Lowe TL. Subconjunctivally implantable hydrogels with degradable and thermoresponsive properties for sustained release of insulin to the retina. Biomaterials. 2009;30(33):6541–7.
Rong X, Ji Y, Zhu X, Yang J, Qian D, Mo X, et al. Neuroprotective effect of insulin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles/PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel on diabetic retinopathy in rats. Int J Nanomed. 2018;14:45–55.
Gerhardinger C, McClure KD, Romeo G, Podestá F, Lorenzi M. IGF-I mRNA and signaling in the diabetic retina. Diabetes. 2001;50(1):175–83.
Kummer A, Pulford BE, Ishii DN, Seigel GM. Des (1-3) IGF-1 treatment normalizes type 1 IGF receptor and phospho-Akt (Thr 308) immunoreactivity in predegenerative retina of diabetic rats. Int J Exp Diabesity Res. 2003;4(1):45–57.
Hernández C, Arroba AI, Bogdanov P, Ramos H, Simό-Servat O, Simό R, et al. Effect of topical administration of somatostatin on retinal inflammation and neurodegeneration in an experimental model of diabetes. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):2579.
Simό R, Hernández C, Porta M, Bandello F, Grauslund J, Harding SP, et al. Effects of topically administered neuroprotective drugs in early stages of diabetic retinopathy: results of the EUROCONDOR clinical trial. Diabetes. 2019;68(2):457–63.
Simό R, Hernández C. GLP-1R as a target for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: friend or foe? Diabetes. 2017;66(6):1453–60.
Cervia D, Catalani E, Casini G. Neuroprotective peptides in retinal disease. J Clin Med. 2019;8(8):1146.
Hernández C, Bogdanov P, Corraliza L, García-Ramírez M, Solà-Adell C, Arranz JA, et al. Topical administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 2016;65(1):172–87.
Hebsgaard JB, Pyke C, Yildirim E, Knudsen LB, Heegaard S, Kvist PH. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expression in the human eye. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(9):2304–8.
Cai X, Li J, Wang M, She M, Tang Y, Li H, et al. GLP-1 treatment improves diabetic retinopathy by alleviating autophagy through GLP-1R-ERK1/2-HDAC6 signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(12):1203–12.
Dietrich N, Kolibabka M, Busch S, Bugert P, Kaiser U, Lin J, et al. The DPP4 inhibitor linagliptin protects from experimental diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0167853.
Zeng Y, Yang K, Wang F, Zhou L, Hu Y, Tang M, et al. The glucagon like peptide 1 analogue, exendin-4, attenuates oxidative stress-induced retinal cell death in early diabetic rats through promoting Sirt1 and Sirt3 expression. Exp Eye Res. 2016;151:203–11.
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang Q, Lei X, Chu Q, Xu GT, et al. Intravitreal injection of exendin-4 analogue protects retinal cells in early diabetic rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(1):278–85.
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):311–22.
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jόdar E, Leiter LA, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1834–44.
Lei XW, Li Q, Zhang JZ, Zhang YM, Liu Y, Yang KH. The protective roles of folic acid in preventing diabetic retinopathy are potentially associated with suppressions on angiogenesis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Ophthalmic Res. 2019;62(2):80–92.
Duraisamy AJ, Mishra M, Kowluru A, Kowluru RA. Epigenetics and regulation of oxidative stress in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59(12):4831–40.
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Nag TC, Srivastava S, Saxena R, Jha KA, et al. Retinal neuroprotective effects of quercetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Eye Res. 2014;125:193–202.
Ola MS, Ahmed MM, Shams S, Al-Rejaie SS. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin in diabetic rat retina. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017;24(6):1186–94.
Mrudula T, Suryanarayana P, Srinivas PN, Reddy GB. Effect of curcumin on hyperglycemia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(2):528–32.
Zuo ZF, Zhang Q, Liu XZ. Protective effects of curcumin on retinal Müller cell in early diabetic rats. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013;6(4):422–4.
Yang F, Yu J, Ke F, Lan M, Li D, Tan K, et al. Curcumin alleviates diabetic retinopathy in experimental diabetic rats. Ophthalmic Res. 2018;60(1):43–54.
Gupta SK, Kumar B, Nag TC, Agrawal SS, Agrawal R, Agrawal P, et al. Curcumin prevents experimental diabetic retinopathy in rats through its hypoglycemic, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2011;27(2):123–30.
Shen Nian, Amy C.Y. Lo. “Lutein and the aging eye”. In: Leila Queiroz Zepka editor. Progress in carotenoid research. IntechOpen;2018. p. 171-195.
Hu BJ, Hu YN, Lin S, Ma WJ, Li XR. Application of lutein and zeaxanthin in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2011;4(3):303–6.
Zhang PC, Wu CR, Wang ZL, Wang LY, Han Y, Sun SL, et al. Effect of lutein supplementation on visual function in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Asia Pac J clin Nutr. 2017;26(3):406–11.
Moschos MM, Dettoraki M, Tsatsos M, Kitsos G, Kalogeropoulos C. Effect of carotenoids dietary supplementation on macular function in diabetic patients. Eye Vis (Lond). 2017;4:23.
Wang W, Tam KC, Ng TC, Goit RK, Chan KLS, Lo ACY. Long-term lutein administration attenuates retinal inflammation and functional deficits in early diabetic retinopathy using the Ins2(Akita/+) mice. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):e001519.
Kowluru RA, Zhong Q, Santos JM, Thandampallayam M, Putt D, Gierhart DL. Beneficial effects of the nutritional supplements on the development of diabetic retinopathy. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2014;11(1):8.
Joussen AM, Doehmen S, Le ML, Koizumi K, Radetzky S, Krohne TU, et al. TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis plays an important role in the development of early diabetic retinopathy and long-term histopathological alterations. Mol Vis. 2009;15:1418–28.
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Mitsiades N, Kirchhof B, Koizumi K, Döhmen S, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prevent early diabetic retinopathy via TNF-alpha suppression. FASEB J. 2002;16(3):438–40.
Ye Q, Lin YN, Xie MS, Yao YH, Tang SM, Huang Y, et al. Effects of etanercept on the apoptosis of ganglion cells and expression of Fas, TNF-alpha, caspase-8 in the retina of diabetic rats. Int J Ophthalmol. 2019;12(7):1083–8.
Tsilimbaris MK, Panagiotoglou TD, Charisis SK, Anastasakis A, Krikonis TS, Christodoulakis E. The use of intravitreal etanercept in diabetic macular oedema. Semin Ophthalmol. 2007;22(2):75–9.
Wu L, Hernandez-Bogantes E, Roca JA, Arevalo JF, Barraza K, Lasave AF. Intravitreal tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in the treatment of refractory diabetic macular edema: a pilot study from the Pan-American Collaborative Retina Study Group. Retina. 2011;31(2):298–303.
Linossi EM, Babon JJ, Hilton DJ, Nicholson SE. Suppression of cytokine signaling: the SOCS perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24(3):241–8.
Hernández C, Bogdanov P, Gόmez-Guerrero C, Sampedro J, Solà-Adell C, Espejo C, et al. SOCS1-derived peptide administered by eye drops prevents retinal neuroinflammation and vascular leakage in experimental diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3615.
Wang AL, Yu AC, Lau LT, Lee C, Wu Le M, Zhu X, et al. Minocycline inhibits LPS-induced retinal microglia activation. Neurochem Int. 2005;47(1-2):152–8.
Wang W, Sidoli S, Zhang W, Wang Q, Wang L, Jensen ON, et al. Abnormal levels of histone methylation in the retinas of diabetic rats are reversed by minocycline treatment. Sci Rep. 2017;7:45103.
Wu Y, Chen Y, Wu Q, Jia L, Du X. Minocycline inhibits PARP1 expression and decreases apoptosis in diabetic retinopathy. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4):4887–94.
Cukras CA, Petrou P, Chew EY, Meyerle CB, Wong WT. Oral minocycline for the treatment of diabetic macular edema (DME): results of a phase I/II clinical study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(7):3865–74.
Scott IU, Jackson GR, Quillen DA, Klein R, Liao J, Gardner TW. Effect of doxycycline vs placebo on retinal function and diabetic retinopathy progression in mild to moderate nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: a randomized proof-of-concept clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014;132(9):1137–42.
Park SS. Cell therapy applications for retinal vascular diseases: diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(5):ORSFj1–ORSFj10.
Rajashekhar G, Ramadan A, Abburi C, Callaghan B, Traktuev DO, Evans-Molina C, et al. Regenerative therapeutic potential of adipose stromal cells in early stage diabetic retinopathy. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e84671.
Ezquer M, Urzua CA, Montecino S, Leal K, Conget P, Ezquer F. Intravitreal administration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells triggers a cytoprotective microenvironment in the retina of diabetic mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:42.
Zhang W, Wang Y, Kong J, Dong M, Duan H, Chen S. Therapeutic efficacy of neural stem cells originating from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic retinopathy. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):408.
Yang Z, Li K, Yan X, Dong F, Zhao C. Amelioration of diabetic retinopathy by engrafted human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248(10):1415–22.
Gu X, Yu X, Zhao C, Duan P, Zhao T, Liu Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(1):40–52.
Kramerov AA, Ljubimov AV. Stem cell therapies in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy and keratopathy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(6):559–68.
Wang Y, Fan L, Meng X, Jiang F, Chen Q, Zhang Z, et al. Transplantation of IL-10-transfected endothelial progenitor cells improves retinal vascular repair via suppressing inflammation in diabetic rats. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016;254(10):1957–65.
Caballero S, Sengupta N, Afzal A, Chang KH, Li Calzi S, Guberski DL, et al. Ischemic vascular damage can be repaired by healthy, but not diabetic, endothelial progenitor cells. Diabetes. 2007;56(4):960–7.
Yazdanyar A, Zhang P, Dolf C, Smit-McBride Z, Cary W, Nolta JA, et al. Effects of intravitreal injection of human CD34(+) bone marrow stem cells in a murine model of diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res. 2020;190:107865.
Duan Y, Beli E, Li Calzi S, Quigley JL, Miller RC, Moldovan L, et al. Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 exacerbates diabetic retinopathy by promoting bone marrow dysfunction. Stem Cells. 2018;36(9):1430–40.
Park TS, Bhutto I, Zimmerlin L, Huo JS, Nagaria P, Miller D, et al. Vascular progenitors from cord blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cells possess augmented capacity for regenerating ischemic retinal vasculature. Circulation. 2014;129(3):359–72.
Cho H, Macklin BL, Lin YY, Zhou L, Lai MJ, Lee G, et al. iPSC-derived endothelial cell response to hypoxia via SDF1a/CXCR4 axis facilitates incorporation to revascularize ischemic retina. JCI Insight. 2020;5(6):e131828.
Chow BW, Nuñez V, Kaplan L, Granger AJ, Bistrong K, Zucker HL, et al. Caveolae in CNS arterioles mediate neurovascular coupling. Nature. 2020;579(7797):106–10.
Aschinger GC, Schmetterer L, Fondi K. Aranha Dos Santos V, Seidel G, Garhöfer G, et al. Effect of diffuse luminance flicker light stimulation on total retinal blood flow assessed with dual-beam bidirectional doppler OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(2):1167–78.
Fondi K, Bata AM, Luft N, Witkowska KJ, Werkmeister RM, Schmidl D, et al. Evaluation of flicker induced hyperemia in the retina and optic nerve head measured by Laser Speckle Flowgraphy. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207525.
Lim LS, Ling LH, Ong PG, Foulds W, Tai ES, Wong TY. Dynamic responses in retinal vessel caliber with flicker light stimulation and risk of diabetic retinopathy and its progression. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(5):2449–55.
Opatrilova R, Kubatka P, Caprnda M, Büsselberg D, Krasnik V, Vesely P, et al. Nitric oxide in the pathophysiology of retinopathy: evidences from preclinical and clinical researches. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018;96(3):222–31.
Leal EC, Manivannan A, Hosoya KI, Terasaki T, Cunha-Vaz J, Ambrόsio AF, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase isoform is a key mediator of leukostasis and blood-retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(11):5257–65.
Zheng L, Du Y, Miller C, Gubitosi-Klug RA, Kern TS, Ball S, et al. Critical role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in degeneration of retinal capillaries in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007;50(9):1987–96.
Sharma S, Saxena S, Srivastav K, Shukla RK, Mishra N, Meyer CH, et al. Nitric oxide and oxidative stress is associated with severity of diabetic retinopathy and retinal structural alterations. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015;43(5):429–36.
Mishra A, Newman EA. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase reverses the loss of functional hyperemia in diabetic retinopathy. Glia. 2010;58(16):1996–2004.
Ahmad S, ElSherbiny NM, Jamal MS, Alzahrani FA, Haque R, Khan R, et al. Anti-inflammatory role of sesamin in STZ induced mice model of diabetic retinopathy. J Neuroimmunol. 2016;295-296:47–53.
Aung MH, Park HN, Han MK, Obertone TS, Abey J, Aseem F, et al. Dopamine deficiency contributes to early visual dysfunction in a rodent model of type 1 diabetes. J Neurosci. 2014;34(3):726–36.
Kim MK, Aung MH, Mees L, Olson DE, Pozdeyev N, Iuvone PM, et al. Dopamine deficiency mediates early rod-driven inner retinal dysfunction in diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018;59(1):572–81.
Motz CT, Chesler KC, Allen RS, Bales KL, Mees LM, Feola AJ, et al. Novel detection and restorative levodopa treatment for preclinical diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 2020;69(7):1518–27.
Kalani M. The importance of endothelin-1 for microvascular dysfunction in diabetes. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(5):1061–8.
Chou JC, Rollins SD, Ye M, Batlle D, Fawzi AA. Endothelin receptor-A antagonist attenuates retinal vascular and neuroretinal pathology in diabetic mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(4):2516–25.
Wang Z, Yadav AS, Leskova W, Harris NR. Attenuation of streptozotocin-induced microvascular changes in the mouse retina with the endothelin receptor A antagonist atrasentan. Exp Eye Res. 2010;91(5):670–5.
Bogdanov P, Simό-Servat O, Sampedro J, Solà-Adell C, Garcia-Ramírez M, Ramos H, et al. Topical administration of bosentan prevents retinal neurodegeneration in experimental diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3578.
Radtke ND, Aramant RB, Petry HM, Green PT, Pidwell DJ, Seiler MJ. Vision improvement in retinal degeneration patients by implantation of retina together with retinal pigment epithelium. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146(2):172–82.
Yue L, Castillo J, Gonzalez AC, Neitz J, Humayun MS. Restoring color perception to the blind - an electrical stimulation strategy of retina in patients with end-stage retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology. 2020;S0161-6420(20):30837-X.
Hu Q, Chen R, Teesalu T, Ruoslahti E, Clegg DO. Reprogramming human retinal pigmented epithelial cells to neurons using recombinant proteins. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(12):1526–34.
Izumi Y, Hammerman SB, Kirby CO, Benz AM, Olney JW, Zorumski CF. Involvement of glutamate in ischemic neurodegeneration in isolated retina. Vis Neurosci. 2003;20(2):97–107.
Nayak K, Misra M. A review on recent drug delivery systems for posterior segment of eye. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1564–82.
Peptu CA, Popa M, Savin C, Popa RF, Ochiuz L. Modern drug delivery systems for targeting the posterior segment of the eye. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(42):6055–69.
Djebli N, Khier S, Griguer F, Coutant AL, Tavernier A, Fabre G, et al. Ocular drug distribution after topical administration: population pharmacokinetic model in rabbits. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017;42(1):59–68.
Eljarrat-Binstock E, Pe'er J, Domb AJ. New techniques for drug delivery to the posterior eye segment. Pharm Res. 2010;27(4):530–43.
Sampedro J, Bogdanov P, Ramos H, Solà-Adell C, Turch M, Valeri M, et al. New insights into the mechanisms of action of topical administration of GLP-1 in an experimental model of diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Med. 2019;8(3):339.
Schopf LR, Popov AM, Enlow EM, Bourassa JL, Ong WZ, Nowak P, et al. Topical ocular drug delivery to the back of the eye by mucus-penetrating particles. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2015;4(3):11.
Popov A, Enlow E, Bourassa J, Chen H. Mucus-penetrating nanoparticles made with "mucoadhesive" poly (vinyl alcohol). Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):1863–71.
de Cogan F, Hill LJ, Lynch A, Morgan-Warren PJ, Lechner J, Berwick MR, et al. Topical delivery of anti-VEGF drugs to the ocular posterior segment using cell-penetrating peptides. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(5):2578–90.
Cabrera FJ, Wang DC, Reddy K, Acharya G, Shin CS. Challenges and opportunities for drug delivery to the posterior of the eye. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(8):1679–84.
Shikamura Y, Yamazaki Y, Matsunaga T, Sato T, Ohtori A, Tojo K. Hydrogel ring for topical drug delivery to the ocular posterior segment. Curr Eye Res. 2016;41(5):653–61.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Long Wei for his contribution in the illustrations of this article.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81873740, 81860174), Natural Science Basic Research Plan of Shaanxi Province (2020JM-612), Applied Basic Research Program of Yunnan Province (2017FE468(-143)) and National Fund Cultivation Project in Xi’an Medical University (2017GJFY29).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SN, YM and KR performed literature search. SN and KR drafted the manuscript. AL and DY revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Nian, S., Lo, A.C.Y., Mi, Y. et al. Neurovascular unit in diabetic retinopathy: pathophysiological roles and potential therapeutical targets. Eye and Vis 8, 15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40662-021-00239-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40662-021-00239-1