Abstract
Background
The C. bescii genome does not encode an acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase or an acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and no ethanol production is detected in this strain. The recent introduction of an NADH-dependent AdhE from C. thermocellum (Fig. 1a) in an ldh mutant of this strain resulted in production of ethanol from un-pretreated switchgrass, but the thermolability of the C. thermocellum AdhE at the optimum growth temperature of C. bescii (78 °C) meant that ethanol was not produced above 65 °C.

Proposed scheme for the pyruvate to ethanol pathway in C. thermocellum and T. pseudethanolicus 39E. a The C. thermocellum ethanol pathway. The red colored AdhE (Cthe_0423) is already expressed and tested in C. bescii [26]. b The T. pseudethanolicus 39E ethanol pathway. The green colored AdhE (Teth39_0206) and blue colored AdhB (Teth39_0218) are expressed and tested in C. bescii in this study
Results
The adhB and adhE genes from Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus 39E, an anaerobic thermophile that produces ethanol as a major fermentation product at 70 °C, were cloned and expressed in an ldh deletion mutant of C. bescii. The engineered strains produced ethanol at 75 °C, near the ethanol boiling point. The AdhB expressing strain produced ethanol (1.4 mM on Avicel, 0.4 mM on switchgrass) as well as acetate (13.0 mM on Avicel, 15.7 mM on switchgrass). The AdhE expressing strain produced more ethanol (2.3 mM on Avicel, 1.6 mM on switchgrass) and reduced levels of acetate (12.3 mM on Avicel, 15.1 mM on switchgrass). These engineered strains produce cellulosic ethanol at the highest temperature of any microorganism to date. In addition, the addition of 40 mM MOPS to the growth medium increased the maximal growth yield of C. bescii by approximately twofold.
Conclusions
The utilization of thermostable enzymes will be critical to achieving high temperature CBP in bacteria such as C. bescii. The ability to produce ethanol at 75 °C, near its boiling point, raises the possibility that process optimization could allow in situ product removal of this end product to mitigate ethanol toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Production of renewable and sustainable biofuels from lignocellulosic biomass using thermophilic bacteria has attracted increasing attention because of the potential advantages of using high temperature fermentation, including improved kinetics, increased mixing rate, lower oxygen solubility, reduced risk of microbial contamination, reduced costs for cooling and heating during the bioconversion process, and providing the possibility of ethanol separation in continuous cultures [1–6]. Fermentative thermophilic anaerobic bacteria have been used to convert plant biomass into ethanol without added lignocellulose-degrading enzymes using a process called consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) [7–9]. Much of the CBP research to date has focused on Clostridium thermocellum [10–12], which grows at 60 °C and produces ethanol, acetate, lactate, formate, CO2, H2, and amino acids as major fermentation products [8, 13]. Increased ethanol production and tolerance of this microorganism have been achieved by extensive metabolic engineering [14–21]. However, while C. thermocellum has the ability to deconstruct crystalline cellulose and catabolize hexose sugars, it cannot utilize hemicellulosic pentose sugars such as xylose and arabinose for growth and its optimal growth temperature is 60 °C [8, 12]. To fully realize the potential of thermophilic CBP, several major improvements over the state of the art will be needed, including increased ethanol yield and titer, co-utilization of hemicellulosic sugars, and ethanol production near or above the boiling point of ethanol (~78 °C).
Caldicellulosiruptor bescii, previously known as “Anaerocellum thermophilum”, is an anaerobic, Gram-positive bacterium originally isolated from the hot springs of Kamchatka, Russia [22–24]. This microorganism has been reported to grow on cellulose up to 83 °C with an optimum temperature of 78 °C at pH 7 and is among the most thermophilic cellulolytic organisms discovered to date [23, 24]. It is able to efficiently ferment crystalline cellulose, hemicellulosic sugars, xylan, and un-pretreated plant biomass, such as hardwood poplar, switchgrass and Napier grasses, producing acetate, lactate, and H2 [12, 23]. These characteristics could provide unique advantages over existing CBP approaches, avoiding costly lignocellulose pretreatment and allowing separation of ethanol from continuously growing cultures [25, 26].
Recently, new genetic tools have been successfully used for insertion, deletion, and heterologous/homologous expression of genes in C. bescii [26–29]. Like other near-maximal H2-yielding anaerobic microbes, C. bescii does not encode either AdhE (bi-functional acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase) or ALDH (acetaldehyde dehydrogenase) [30]; thus, no ethanol production is detected in this strain [23]. However, its chromosome encodes two AdhAs (alcohol dehydrogenase), Cbes0928 and Cbes0224 [31]. Introduction of a heterologous ethanol production pathway via expression of the NADH-dependent AdhE from C. thermocellum (Fig. 1a) in a C. bescii ldh mutant strain resulted in production of ethanol from both model substrates and un-pretreated switchgrass [26]. Although neither the ethanol yield nor titer was sufficient to meet requirements for economic product recovery, the bioethanol production directly from real-world substrates opens the door to development of the next generation of CBP. In addition, because of the insufficient thermostability of the C. thermocellum AdhE, this engineered strain was only able to produce ethanol up to 65 °C [26], which is far below the C. bescii optimum growth temperature and the ethanol boiling temperature.
To overcome this issue, we sought to identify a more thermostable ethanol pathway to introduce into C. bescii. T. pseudethanolicus 39E is a Gram-positive, anaerobic thermophile that produces ethanol as a major fermentation product and grows up to 70 °C [32–34]. It encodes two bi-functional alcohol dehydrogenases, adhB and adhE [4, 35]. The bi-functional acetyl-CoA thioesterase/alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhB) is NADPH-dependent and proposed as a key terminal enzyme for ethanol production in T. pseudethanolicus based on microarray data [4, 32]. The other bi-functional acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase (AdhE) showed NADH-dependent ALDH activity and weak NADPH-dependent ADH activity [32, 36]. Utilization of more thermostable enzymes such as these will be critical to achieving high temperature CBP in C. bescii. Here, we explore the use of these more thermostable enzymes from T. pseudethanolicus to develop ethanol production pathways that function near the optimal growth temperature in C. bescii. Further, we explore optimization of culture medium buffering capacity as a means of improving growth and fermentation in engineered C. bescii strains under batch conditions.
Results and discussion
Higher buffering capacity of culture medium improves C. bescii growth
The pH of cultures during growth is important for anaerobic microorganisms, particularly at higher growth yields [37, 38]. C. bescii has a narrow optimal pH range, pH 6.8–7.3, in culture media in closed bottles [24, 39] and the production of acetic and lactic acid have been shown to inhibit growth, especially at late growth phases [23, 37]. While fed-batch cultivation with pH control in a fermentor, such as that used in industrial processes, can solve this problem, pH control in bench-scale genetic experiments is not practical [40]. An alternative approach is to use high initial buffering capacity to prevent excessive pH changes [41, 42]. This has enabled higher growth yields and rates in other microorganisms [43, 44]. To systematically investigate the influence of increased buffer concentrations on the growth yield, metabolite production, and final pH values of C. bescii fermentations; 3-(N-morpholino) propane sulfonic acid (MOPS) was used as a buffering reagent in addition to the 2.4 mM phosphate normally used in this medium supplemented with 1 % cellobiose as the carbon source [39]. Growth was tested with MOPS concentrations ranging from 0 to 200 mM to determine if pH was limiting bioconversion (Fig. 2). At 160 mM MOPS, growth was severely inhibited, and virtually no growth was observed at 200 mM MOPS. At lower MOPS concentrations, however, a clear improvement was observed. The maximal growth yield of C. bescii increased approximately twofold as measured by optical density at 680 nm (OD680) when the MOPS concentration in the medium was increased from 0 to 40 mM (Fig. 2a). At 80 and 120 mM MOPS, a similar final OD was attained, but only after a lag period. Because C. bescii can grow at relatively high osmotic pressure (>550 mOsmol) [37, 45], the longer lag phase at MOPS concentrations of 80 mM and above suggests a mechanism other than osmotic stress to explain this difference (Fig. 2a) [40, 46]. The final pH of the culture medium increased from 4.5 to 5.8 as the MOPS concentration was increased from 0 to 120 mM (Fig. 2d). These results are consistent with previous results in pH-controlled fermenters; the decrease in pH during fermentation is a limiting factor for growth and limits the ability to reach higher cell densities [37]. Substrate conversion into products also increased with MOPS concentration (Fig. 2b–d). H2 (Fig. 2d) and acetate production (Fig. 2b) showed a steady increase with increased buffer concentrations up to 120 mM MOPS. H2 production increased 62 % (from 13.9 to 22.6 mM) and acetate production increased 149 % (from 7.2 to 17.9 mM) on 120 mM MOPS compared to the culture without MOPS. The maximum yield of lactate was obtained on 80 mM MOPS (Fig. 2c). In this analysis, 40 mM MOPS was sufficient to sustain exponential growth to maximal growth yield and the fastest doubling time (~2.3 h) with a final pH ~5.1. We, therefore, used 40 mM MOPS for subsequent analyses.
Effect of buffer (MOPS) concentrations during the cultivation of wild-type C. bescii in closed-serum bottles without pH control. a Growth properties measured by optical density at 680 nm, b acetate production, and c lactate production as a function of increasing MOPS concentration. Black, 0 mM; green, 20 mM; dark red, 40 mM; light red, 80 mM; blue, 120 mM; purple, 160 mM, gray, 200 mM. d Final pH of media (blue bars) and hydrogen production (red bars) after 36 h cultivation
Heterologous expression of the thermostable AdhE and AdhB from T. pseudethanolicus in C. bescii
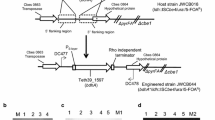
The T. pseudethanolicus adhE gene (bifunctional secondary ADH/aldehyde hydrogenase, Teth39_0206) and adhB gene (bifunctional secondary ADH/Acetyl-CoA thioesterase, Teth39_0218) were cloned from T. pseudethanolicus 39E under the transcriptional control of the C. bescii S-layer protein (Cbes2303) promoter (PS-layer) [26, 29] (Additional file 1: Figures S1, S2; Table 1). Both the PS-layerTeth39_0206 (adhE) and PS-layerTeth39_0218 (adhB) expression cassettes contain a Rho-independent transcription terminator and C-terminal 6X His-tag to facilitate protein purification and Western blotting. These genes were each inserted into the inter-cistronic region between Cbes0863 and Cbes0864 of the chromosome in C. bescii strain JWCB017 (ΔpyrFA Δldh) (Fig. 3a). Uracil prototrophic transformants were serially passaged as described [26] to allow segregation of merodiploids containing a mixture of the integrated adhE expression cassette and the wild-type genomes. This resulted in strains JWCB049 (ΔpyrFA Δldh CIS1:: PS-layerTeth39_0206), and JWCB054 (ΔpyrFA Δldh CIS1:: PS-layerTeth39_0218) (Table 1). Verification of JWCB049 and JWCB054 was performed using PCR amplification with primers DC477 and DC478 (Fig. 3b), and sequencing the PCR products. The parent strain, JWCB017, produced the expected wild type 2.44-kb band, whereas amplification of JWCB049 and JWCB054 produced ~5.0-kb and ~ 3.5-kb bands, respectively, indicating an insertion of the adhE and adhB expression cassettes within the targeted region (Fig. 3b). The previous deletion of the ldh gene in JWCB017, JWCB049, and JWCB054 was also confirmed (Additional file 1: Figure S3).
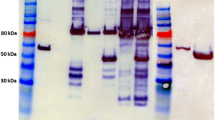
Targeted insertion and expression of the T. pseudethanolicus 39E adhE (Teth39_0206) and adhB (Teth39_0218) in C. bescii. a A diagram of the integration vector pDCW180 (Additional file 1: Figure S1), which contains the PS-layerTeth39_0206 expression cassette and pyrF cassette [27] for selection of transformants. Homologous recombination can occur at the upstream- or downstream-targeted chromosomal regions (inter-cistronic region between Cbes0863 and Cbes0864), integrating the plasmid into the genome and generating uracil prototroph strain. Counter selection with 5-FOA selects for loss of the plasmid sequences but not the adhE expression cassette. Bent arrows depict primers used for verification of the integrated expression cassette. Apr apramycin resistance gene cassette. b Gel depicting PCR products amplified from the targeted chromosome region in JWCB001 (wild-type; lane 1), JWCB017 (ΔpyrFA Δldh; lane 2), JWCB049 (ΔpyrFA Δldh CIS1:: PS-layerTeth39_0206; lane 3), and JWCB054 (ΔpyrFA Δldh CIS1:: PS-layerTeth39_0218; lane 4) amplified by primers DC477 and DC478. M1: 1-kb DNA ladder (New England Biolabs). c Total cell protein lysates (75 µg) isolated from mid-log phase cultures grown at 75 °C were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE gels, followed by Western blot analysis probed with anti-His-tag antibody as described in “Methods”. Lane 1: JWCB017; lane 2: JWCB049; lane 3: JWCB054; M2: MagicMark™ XP Western Protein Standard (Invitrogen)
To test expression of the T. pseudethanolicus AdhE and AdhB proteins in C. bescii, JWCB049 and JWCB054 were grown in low osmolarity defined (LOD) medium [39] to mid-log phase at 75 °C (Fig. 3c). Cell extracts were then examined by Western hybridization using monoclonal anti-His antibodies (Fig. 3c). An approximately 100 kDa protein from the AdhE strain (lane 2 in Fig. 3c) and an approximately 40 kDa protein from the AdhB strain (lane 3 in Fig. 3c) were detected, which correspond to the predicted molecular weights for the His-tagged proteins. No proteins were detected by the anti-His antibodies in the parental strain (JWCB017, lane 1 in Fig. 3c). Interestingly, the AdhE protein (lane 2) was less abundant than AdhB (lane 3). The AdhE protein contains a linker region between the ALDH and ADH domains [47] and this kind of linker region has been observed to be susceptible to proteolysis in various multi-domain proteins, which may explain the lower abundance of T. pseudethanolicus AdhE relative to AdhB in C. bescii. Alternatively, even small differences in T. pseudethanolicus codon usage could decrease translational efficiency in C. bescii, which would suggest codon optimization as a future strategy to increase expression.
Engineered C. bescii strains produce ethanol from cellobiose at 75 °C
In previous work to engineer ethanol production in C. bescii, mutation of the lactate dehydrogenase gene (ldh) was obtained in the C. bescii chromosome [48] and an adhE gene from C. thermocellum was introduced [26]. Deletion of the ldh gene resulted in a strain, JWCB017 that produced no lactate and more acetate and hydrogen than the wild type [49]. Addition of the adhE gene to the ldh mutant strain resulted in a strain that produced ethanol and less acetate, presumably because carbon was channeled from acetate to ethanol [26]. The introduction of new fermentation pathways could affect growth and product formation due to potential redox imbalances. To investigate the functionality of T. pseudethanolicus AdhE and AdhB in C. bescii, strains were characterized in LOD medium supplemented with 40 mM MOPS and 1 % (wt/vol) cellobiose. We first compared growth rate of the strains expressing AdhE (JWCB049) and AdhB (JWCB054) to the parent strain (JWCB017) at 75 °C (Fig. 4). There was no obvious difference in growth rate, with calculated doubling times of 2.0, 1.9, and 1.9 h for JWCB017, JWCB049 and JWCB054, respectively. Further, all three strains reached similar maximal optical densities (~0.8 at OD680 nm) after 15 h incubation (Fig. 4a), suggesting that heterologous expression of these genes is not detrimental to C. bescii.
Growth and product formation of the mutant strains on cellobiose. a Growth properties measured by optical density (OD680nm), b acetate production, and c ethanol production of C. bescii mutant strains on 1 % cellobiose as a sole carbon source at 75 °C; black circles, JWCB017; red squares, JWCB049; blue triangles, JWCB054. d Hydrogen produced by each strain at the end of fermentation (48 h); black bars, JWCB017; red bars, JWCB049; blue bars, JWCB054. Error bars based on two biologically independent experiments
Fermentation products were also monitored into the stationary growth phase by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (Fig. 4b–d), and final product yields were calculated (Table 2). As expected, none of the strains produced lactate because they contain a deletion of the lactate dehydrogenase gene. C. bescii JWCB017 (ΔpyrFA Δldh) produced 17.0 mM acetate, 23.9 mM H2, and no ethanol (Fig. 4b, c), representing 12.9 % conversion of cellobiose into acetate and 91 % carbon recovery overall without accounting for microbial cell mass. The AdhB expressing strain JWCB054 produced 1.4 mM ethanol in addition to 15.5 mM acetate and 23.2 mM H2 from cellobiose (Fig. 4b–d), representing 11.6 % conversion of cellobiose into acetate and 1.1 % into ethanol with an overall 88 % carbon recovery (Table 2). The AdhE expressing strain JWCB049 produced approximately twice as much ethanol (2.9 mM) as strain JWCB054 and showed reduced production of acetate (14.1 mM) and H2 (22.5 mM) (Fig. 4b, c; Table 2) compared to the parental stain JWCB017, indicating redirection of carbon flow from pyruvate away from acetate and toward ethanol. JWCB049 showed 10.7 % conversion of cellobiose into acetate and 2.2 % to ethanol with 81 % overall carbon recovery. Interestingly, H2 production is reduced in strain JWCB049, but not in strain JWCB054. This may be explained by the fact that H2 production in C. bescii is likely catalyzed by an NADH- and ferredoxin-dependent electron bifurcating [FeFe] hydrogenase (Cbes1297-1299) [50]. Thus, the AdhE pathway, which utilizes one NADH and one NADPH, partially competes with the hydrogenase for electrons, while the strictly NADPH-dependent AdhB does not.
Engineered C. bescii strains produce ethanol from Avicel and lignocellulose at 75 °C
To demonstrate the utility of this ethanol-producing pathway for high temperature CBP, we also investigated the ability of the engineered strains to produce ethanol from the model substrate crystalline cellulose (2 % Avicel) and the real-world cellulosic substrate switchgrass (2 %). Results were similar to those observed for cellobiose (Fig. 5). As expected, parent strain JWCB017 produced acetate (13.8 mM from Avicel, 16.1 mM from switchgrass) but no ethanol. The AdhB expressing strain, JWCB054, produced ethanol (1.4 mM on Avicel, 0.4 mM on switchgrass) as well as acetate (13.0 mM on Avicel, 15.7 mM on switchgrass). The AdhE expressing strain, JWCB049, produced more ethanol (2.3 mM on Avicel, 1.6 mM on switchgrass) than strain JWCB054 and reduced levels of acetate (12.3 mM on Avicel, 15.1 mM on switchgrass). To date, these strains represent the maximum temperature at which cellulosic ethanol production has been engineered into a microorganism.
Fermentation product analysis of C. bescii mutant strains on Avicel and switchgrass. Analysis of fermentation products acetate (a, c), and ethanol (b, d) after growth on Avicel [2 % (wt/vol)] (a, b) and switchgrass [2 % (wt/vol)] (c, d) at 75 °C. Black circles, JWCB0017; red squares, JWCB049; blue triangles, JWCB054. Error bars based on two biologically independent experiments
On all substrates, cofactor specificity of the ethanol synthesis pathway likely limits ethanol formation. Previous work focused on expression of C. thermocellum adhE in C. bescii [26], which utilizes NADH as an electron donor for both acetyl-CoA reduction to acetaldehyde (ALDH activity) and acetaldehyde reduction to ethanol (ADH activity). The T. pseudethanolicus AdhB and AdhE enzymes, on the other hand, both utilize NADPH for ADH activity, and AdhB also utilizes NADPH for its Acetyl-CoA thioesterase activity (Fig. 1b). While diverse pathways for NADPH generation are known, the mechanism by which C. bescii generates NADPH is not known. C. bescii does not encode an obvious Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, suggesting it does not utilize the non-oxidative Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP), nor does it encode a malate dehydrogenase that would be necessary for a “malate shunt” as is seen in C. thermocellum [51]. C. bescii does encode a putative NADH:Ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase (NfnAB; Athe_0644-0645) [31, 52], that would take electrons from NADH and reduced ferredoxin to generate two NADPH, but the in vivo importance of NfnAB in C. bescii is unknown.
We hypothesize that low electron flux through NADPH could be limiting ethanol production. The AdhE pathway requires one NADPH per ethanol, while the AdhB pathway requires two NADPH per ethanol (Fig. 1b). If NADPH were limiting, we would expect the AdhE pathway to produce twice as much ethanol as the AdhB pathway. Indeed, this is exactly what is observed. The ethanol yield per mole of consumed cellobiose in the adhE expression strain was twice that of the adhB expression strain (0.54 and 0.28 mol ethanol/mol cellobiose for the AdhE and AdhB strains, respectively) (Table 2). Furthermore, both strains produced substantially less ethanol compared to our previous study in which we expressed the NADH-dependent C. thermocellum AdhE (15.3 mM) [26], again supporting the idea that NADPH availability is limiting ethanol production when utilizing these NADPH-dependent pathways in C. bescii. Future engineering efforts to increase NADPH availability or alter cofactor specificity have the potential to further increase ethanol yields. By producing ethanol at 75 °C, this work lays the foundations for further metabolic engineering and process optimization that could lead to in situ ethanol removal during fermentation to enhance recovery and decrease product toxicity.
Conclusions
To gain the most value from high temperature CBP, both C5 and C6 sugars will need to be converted into fuel at high yield and titer at a temperature near or above the boiling point of ethanol. Here we report metabolically engineered strains that produce ethanol in vivo near the ethanol boiling point by introducing thermostable AdhB and AdhE proteins from T. pseudethanolicus into C. bescii. The yield and titer of ethanol are still low, but the prospect of further strain modification to improve NADPH availability or alter co-factor specificity of the enzymes has the potential to further improve upon this strain. Further, this work provides insights into mechanisms of redox balancing within C. bescii that will assist future metabolic engineering efforts.
Methods
Strains, media and culture conditions
C. bescii and E. coli strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. All C. bescii strains were grown anaerobically in liquid or on solid media in low osmolality defined (LOD) medium [39], final pH 7.0, with maltose [0.5 % (wt/vol); catalog no. M5895, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO] used as the sole carbon source for routine growth and transformation experiments. Liquid cultures were grown at 75 °C in anaerobic culture serum bottles with five gassing cycles with argon. For uracil auxotrophs, the LOD medium was supplemented with 40 µM uracil. E. coli strain DH5α was used for plasmid DNA construction and preparation. Standard techniques for E. coli were performed as described [53]. E. coli cells were grown in LB broth supplemented with apramycin (50 μg/mL) and plasmid DNA was isolated using a Qiagen Miniprep Kit. Chromosomal DNA from C. bescii strains was extracted using the Quick-gDNA MiniPrep (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) or the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Vector construction for the knock-in of Teth39_0206 (adhE) and Teth39_0218 (adhB) into C. besci
The plasmids described below were generated using Q5 High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) for PCR reactions, restriction enzymes (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA, USA), and the Fast-link DNA Ligase kit (Epicentre Biotechnologies, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Plasmid pDCW180 (Fig. 1a; Additional file 1: Figure S1) was constructed by inserting the Teth39_0206 open reading frame into pDCW142 [26], which contains the regulatory region of Cbes2303, a C-terminal 6X Histidine-tag and a Rho-independent transcription terminator. The 6.3 kb DNA fragment was amplified with primers DC464 containing a BamHI cut site and DC466 containing a SphI cut site using pDCW142 as a template. A 2.62 kb DNA fragment containing the coding sequence of Teth39_0206 was amplified with DC597 containing a BamHI site and DC598 containing a SphI site using T. pseudethanolicus 39E genomic DNA as a template. The two linear DNA fragments were then digested with BamHI and SphI, and ligated to construct pDCW180 (8.9 kb) (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Plasmid pDCW183 (Additional file 1: Figure S2) is identical to pDCW180 except for the cloning of Teth39_0218. To make this change, a 1.06-kb DNA fragment containing the coding sequence of Teth39_0218 was amplified by PCR using DC621 (with BamHI site) and DC622 (with SphI site) using T. pseudethanolicus 39E genomic DNA as a template. The 6.3-kb of backbone fragment was amplified from pDCW142 [26] by PCR using DC619 (with BamHI site) and DC620 (with SphI site). DNA sequences of the primers are shown in Additional file 1: Table S1. E. coli strain DH5α cells were transformed by electroporation in a 2-mm gap cuvette at 2.5 V and transformants were selected for apramycin resistance. The sequences of all plasmids were verified by Automatic sequencing (Macrogen USA, Rockville, MD, USA). All plasmids are available on request.
C. bescii transformation, screening, purification, and sequence verification of engineered strains
To construct strain JWCB049, one microgram of M.Cbe1 methylated pDCW180 DNA was used to electrotransform JWCB017 (C. bescii ΔpyrFA Δldh) as described [28] and cells were plated onto solid LOD medium. Uracil prototrophic transformants were selected and used to inoculate into liquid medium for subsequent genomic DNA extraction and confirmation of the pDCW180 knock-in into the targeted chromosome via PCR screening. The insertion was targeted to base pair coordinates 962290 to 964604 in the C. bescii chromosome, designated CIS1 (chromosomal integration site one). Confirmed transformants were inoculated into nonselective liquid defined medium, with 40 μM uracil, and incubated overnight at 75 °C to allow loop-out of the plasmid prior to plating onto 5-FOA (8 mM) containing solid medium. After the initial screening, transformants containing the expected knock-in were further purified by one additional passage under selection on solid medium and screened a second time by PCR to check for segregation of the PS-layerTeth39_0206 insertion. The insertion of Teth39_0206 at the targeted chromosome region was verified by PCR amplification and sequence analysis using primers DC462, DC463, DC477, DC478 DC599, DC600, DC601 and DC602. A PCR product was generated from genomic DNA using primers DC477 and DC478 targeting outside the homologous regions used to construct the knock-in. Construction of JWCB054 was the same as JWCB049 except that pDCW183 (Table 1) was used to electrotransform JWCB017. All primers and sequences used in this study are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1.
Preparation of cell lysates and western blotting
Five hundred mL cultures of C. bescii strains (JWCB017, 049, and 054) were grown to mid-log phase at 75 °C, harvested by centrifugation at 6000×g at 4 °C for 15 min and resuspended in Cell-Lytic B cell lysis reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Cells were lysed by a combination of 4× freeze-thawing and sonication on ice. Protein concentrations were determined using the Bio-Rad protein assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) with bovine serum albumin as the standard. Cell free extracts (75 µg) were electrophoresed in 4–15 % gradient Mini-Protean TGX gels, which were either stained using Coomassie blue or were transferred to PVDF membranes (ImmobilonTM-P; EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) using a Bio-Rad Mini-Protean 3 electrophoretic apparatus. The membrane was then probed with His-tag (6xHis) monoclonal antibody (1:5000 dilution; Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY, USA) using the ECL Western Blotting substrate Kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) as specified by the manufacturer.
Growth properties and end product analysis on various MOPS concentrations, growth curve analysis, and fermentation conditions
Growth experiments testing buffering capacity were conducted with wild type C. bescii in stoppered 125-mL serum bottles containing 50 mL LOD medium supplemented with 10 g/L cellobiose (catalog no. M5895; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), 1 mM uracil and 3-morpholino-propanesulfonic acid (MOPS: catalog no. RDD003, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) ranging from 0 to 200 mM. Duplicate bottles were inoculated with a fresh 1 % (vol/vol) inoculum and incubated at 75 °C with shaking at 150 rpm. Optical cell density was monitored using a SmartSpec™ Plus spectrophotometer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA), measuring absorbance at 680 nm. When testing bioconversion by engineered strains, growth was performed in LOD media supplemented with 40 mM of MOPS. Batch fermentations were performed at 75 °C in the same culture conditions, except using 10 g/L cellobiose, 20 g/L Avicel (catalog no. 11365, Fluka, Swedesboro, NJ, USA), or 20 g/L unpretreated switchgrass [sieved −20/+80-mesh fraction; washed with warm water but no additional pretreatment (note that the biomass samples were not autoclaved before use); provided by Brian Davison, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, USA] as carbon sources. Fermentation products were measured for 120 h, but all fermentations were complete within 48 h.
Analytical techniques for determining fermentation end products
On the fermentation experiments, cellobiose, glucose, acetate, lactate, and ethanol, were monitored and analyzed on an Agilent 1200 Infinity HPLC system (Agilent Tech., Santa Clara, CA, USA) fitted with a Micro-Guard Cation H+ guard column and an Aminex HPX-87H column (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). All separations were performed under isocratic conditions with a temperature of 50 °C and a flow rate of 0.6 mL/min in 5.0 mM H2SO4, and then passed through a refractive index detector (Agilent 1200 Infinity Refractive Index Detector; Agilent Tech., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The total peak areas were integrated and compared to peak areas and retention times of known standards for each compound of interest. For H2 production at the end of the fermentation, H2 was measured using a GC8A Gas chromatograph (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). Gas separations were performed on a Molecular Sieve packed column 5A (80/100 mesh; Alltech, Columbia, MD, USA) with a 70 °C oven temperature and detection with a Thermal Conductivity Detector at 120 °C. The samples were prepared from the headspace of stoppered 125-mL serum-bottle cultures using a gas-tight glass syringe (Hamilton, Reno, NV). The standards were also prepared from identical bottles with the same medium with known amounts of H2 in the headspace. H2 was calculated as moles produced per liter liquid phase to facilitate comparison to soluble fermentation products. Based on ideal gas law, pure H2 is assumed as 1 mol of H2 at 298 k (25 °C) and 1 atmosphere in 24.5 litters [54].
Abbreviations
- CBP:
-
consolidated bioprocessing
- C. bescii :
-
Caldicellulosiruptor bescii
- T. pseudethanolicus 39E:
-
Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus 39E
- C. thermocellum :
-
Clostridium thermocellum
- 5-FOA:
-
5-fluoroorotic acid
- ADH:
-
alcohol dehydrogenase
- ALDH:
-
acetaldehyde dehydrogenase
- AdhE:
-
bifunctional acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase
- AdhB:
-
bifunctional acetyl CoA thioesterase/alcohol dehydrogenase
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- LOD:
-
low osmolarity defined
- MOPS:
-
3-(N-morpholino) propane sulfonic acid
- OD:
-
optical density
- PPP:
-
pentose phosphate pathway
References
Himmel ME, Ding SY, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD. Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science. 2007;315(5813):804–7.
Lynd LR, Laser MS, Bransby D, Dale BE, Davison B, Hamilton R, Himmel M, Keller M, McMillan JD, Sheehan J, et al. How biotech can transform biofuels. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(2):169–72.
Solomon BD. Biofuels and sustainability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1185:119–34.
Burdette D, Zeikus JG. Purification of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenases from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus 39E and characterization of the secondary-alcohol dehydrogenase (2 degrees Adh) as a bifunctional alcohol dehydrogenase–acetyl-CoA reductive thioesterase. Biochem J. 1994;302(Pt 1):163–70.
Taylor MP, Eley KL, Martin S, Tuffin MI, Burton SG, Cowan DA. Thermophilic ethanologenesis: future prospects for second-generation bioethanol production. Trends Biotechnol. 2009;27(7):398–405.
Wiegel J. Ethanol from cellulose. Experientia. 1982;38(2):151–6.
Frock AD, Kelly RM. Extreme Thermophiles: moving beyond single-enzyme biocatalysis. Current Opin Chem Eng. 2012;1(4):363–72.
Olson DG, McBride JE, Shaw AJ, Lynd LR. Recent progress in consolidated bioprocessing. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012;23(3):396–405.
Olson DG, Sparling R, Lynd LR. Ethanol production by engineered thermophiles. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015;33C:130–41.
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS. Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev MMBR. 2002;66(3):506–77 (table of contents).
Blumer-Schuette SE, Brown SD, Sander KB, Bayer EA, Kataeva I, Zurawski JV, Conway JM, Adams MW, Kelly RM. Thermophilic lignocellulose deconstruction. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2013;38(3):393–448.
Blumer-Schuette SE, Kataeva I, Westpheling J, Adams MW, Kelly RM. Extremely thermophilic microorganisms for biomass conversion: status and prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008;19(3):210–7.
Ellis LD, Holwerda EK, Hogsett D, Rogers S, Shao X, Tschaplinski T, Thorne P, Lynd LR. Closing the carbon balance for fermentation by Clostridium thermocellum (ATCC 27405). Bioresour Technol. 2012;103(1):293–9.
Shao X, Raman B, Zhu M, Mielenz JR, Brown SD, Guss AM, Lynd LR. Mutant selection and phenotypic and genetic characterization of ethanol-tolerant strains of Clostridium thermocellum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;92(3):641–52.
Rani KS, Swamy MV, Sunitha D, Haritha D, Seenayya G. Improved ethanol tolerance and production in strains of Clostridium thermocellum. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 1996;12(1):57–60.
Brown SD, Guss AM, Karpinets TV, Parks JM, Smolin N, Yang S, Land ML, Klingeman DM, Bhandiwad A, Rodriguez M Jr, et al. Mutant alcohol dehydrogenase leads to improved ethanol tolerance in Clostridium thermocellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(33):13752–7.
Biswas R, Zheng T, Olson DG, Lynd LR, Guss AM. Elimination of hydrogenase active site assembly blocks H2 production and increases ethanol yield in Clostridium thermocellum. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2015;8:20.
Argyros DA, Tripathi SA, Barrett TF, Rogers SR, Feinberg LF, Olson DG, Foden JM, Miller BB, Lynd LR, Hogsett DA, et al. High ethanol titers from cellulose by using metabolically engineered thermophilic, anaerobic microbes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(23):8288–94.
Rydzak T, Lynd LR, Guss AM. Elimination of formate production in Clostridium thermocellum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;42(9):1263–72.
Tripathi SA, Olson DG, Argyros DA, Miller BB, Barrett TF, Murphy DM, McCool JD, Warner AK, Rajgarhia VB, Lynd LR, et al. Development of pyrF-based genetic system for targeted gene deletion in Clostridium thermocellum and creation of a pta mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(19):6591–9.
Biswas R, Prabhu S, Lynd LR, Guss AM. Increase in ethanol yield via elimination of lactate production in an ethanol-tolerant mutant of Clostridium thermocellum. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e86389.
Svetlichnyi VA, Svetlichnaya TP, Chernykh NA, Zavarzin GA. Anaerocellum Thermophilum Gen. Nov Sp. Nov. an extremely thermophilic cellulolytic Eubacterium isolated from hot-springs in the valley of Geysers. Microbiology. 1990;59(5):598–604.
Yang SJ, Kataeva I, Hamilton-Brehm SD, Engle NL, Tschaplinski TJ, Doeppke C, Davis M, Westpheling J, Adams MW. Efficient degradation of lignocellulosic plant biomass, without pretreatment, by the thermophilic anaerobe “Anaerocellum thermophilum” DSM 6725. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(14):4762–9.
Yang SJ, Kataeva I, Wiegel J, Yin Y, Dam P, Xu Y, Westpheling J, Adams MW. Classification of ‘Anaerocellum thermophilum’ strain DSM 6725 as Caldicellulosiruptor bescii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010;60(Pt 9):2011–5.
Bhalla A, Bansal N, Kumar S, Bischoff KM, Sani RK. Improved lignocellulose conversion to biofuels with thermophilic bacteria and thermostable enzymes. Bioresour Technol. 2013;128:751–9.
Chung D, Cha M, Guss AM, Westpheling J. Direct conversion of plant biomass to ethanol by engineered Caldicellulosiruptor bescii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(24):8931–6.
Chung D, Cha M, Farkas J, Westpheling J. Construction of a stable replicating shuttle vector for Caldicellulosiruptor species: use for extending genetic methodologies to other members of this genus. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e62881.
Chung D, Farkas J, Westpheling J. Overcoming restriction as a barrier to DNA transformation in Caldicellulosiruptor species results in efficient marker replacement. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6(1):82.
Chung D, Young J, Bomble YJ, Vander Wall TA, Groom J, Himmel ME, Westpheling J. Homologous expression of the Caldicellulosiruptor bescii CelA reveals that the extracellular protein is glycosylated. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119508.
Carere CR, Rydzak T, Verbeke TJ, Cicek N, Levin DB, Sparling R. Linking genome content to biofuel production yields: a meta-analysis of major catabolic pathways among select H2 and ethanol-producing bacteria. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:295.
Kataeva IA, Yang SJ, Dam P, Poole FL 2nd, Yin Y, Zhou F, Chou WC, Xu Y, Goodwin L, Sims DR, et al. Genome sequence of the anaerobic, thermophilic, and cellulolytic bacterium “Anaerocellum thermophilum” DSM 6725. J Bacteriol. 2009;191(11):3760–1.
Hemme CL, Fields MW, He Q, Deng Y, Lin L, Tu Q, Mouttaki H, Zhou A, Feng X, Zuo Z, et al. Correlation of genomic and physiological traits of thermoanaerobacter species with biofuel yields. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(22):7998–8008.
Lee Y-E, Jain MK, Lee C, Zeikus JG. Taxonomic distinction of saccharolytic thermophilic anaerobes: description of Thermoanaerobacterium xylanolyticum gen. nov., sp. nov., and Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum gen. nov., sp. nov.; reclassification of Thermoanaerobium brockii, Clostridium thermosulfurogenes, and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum E100-69 as Thermoanaerobacter brockii comb. nov., Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes comb. nov., and Thermoanaerobacter thermohydrosulfuricus comb. nov., respectively; and transfer of Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum 39E to Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993;43(1):41–51.
Onyenwoke RU, Kevbrin VV, Lysenko AM, Wiegel J. Thermoanaerobacter pseudethanolicus sp. nov., a thermophilic heterotrophic anaerobe from Yellowstone National Park. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2007;57(Pt 10):2191–3.
Burdette DS, Vieille C, Zeikus JG. Cloning and expression of the gene encoding the Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus 39E secondary-alcohol dehydrogenase and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1996;316(Pt 1):115–22.
Pei J, Zhou Q, Jiang Y, Le Y, Li H, Shao W, Wiegel J. Thermoanaerobacter spp. control ethanol pathway via transcriptional regulation and versatility of key enzymes. Metab Eng. 2010;12(5):420–8.
Basen M, Rhaesa AM, Kataeva I, Prybol CJ, Scott IM, Poole FL, Adams MW. Degradation of high loads of crystalline cellulose and of unpretreated plant biomass by the thermophilic bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor bescii. Bioresour Technol. 2014;152:384–92.
Lynd LR, Baskaran S, Casten S. Salt accumulation resulting from base added for pH control, and not ethanol, limits growth of Thermoanaerobacterium thermosaccharolyticum HG-8 at elevated feed xylose concentrations in continuous culture. Biotechnol Prog. 2001;17(1):118–25.
Farkas J, Chung D, Cha M, Copeland J, Grayeski P, Westpheling J. Improved growth media and culture techniques for genetic analysis and assessment of biomass utilization by Caldicellulosiruptor bescii. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;40(1):41–9.
Scheidle M, Dittrich B, Klinger J, Ikeda H, Klee D, Buchs J. Controlling pH in shake flasks using polymer-based controlled-release discs with pre-determined release kinetics. BMC Biotechnol. 2011;11:25.
Jeude M, Dittrich B, Niederschulte H, Anderlei T, Knocke C, Klee D, Büchs J. Fed-batch mode in shake flasks by slow-release technique. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;95(3):433–45.
Kumar S, Wittmann C, Heinzle E. Minibioreactors. Biotechnol Lett. 2004;26(1):1–10.
Jensen PR, Hammer K. Minimal requirements for exponential growth of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59(12):4363–6.
Neidhardt FC, Bloch PL, Smith DF. Culture medium for Enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974;119(3):736–47.
van Niel EW, Claassen PA, Stams AJ. Substrate and product inhibition of hydrogen production by the extreme thermophile, Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003;81(3):255–62.
Record MT Jr, Courtenay ES, Cayley DS, Guttman HJ. Responses of E. coli to osmotic stress: large changes in amounts of cytoplasmic solutes and water. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23(4):143–8.
Zheng T, Olson DG, Tian L, Bomble YJ, Himmel ME, Lo J, Hon S, Shaw AJ, van Dijken JP, Lynd LR. Cofactor Specificity of the bifunctional alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase (AdhE) in wild-type and mutant Clostridium thermocellum and Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum. J Bacteriol. 2015;197(15):2610–9.
Cha M, Wang H, Chung D, Bennetzen JL, Westpheling J. Isolation and bioinformatic analysis of a novel transposable element, ISCbe4, from the hyperthermophilic bacterium, Caldicellulosiruptor bescii. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013;40(12):1443–8.
Cha M, Chung D, Elkins JG, Guss AM, Westpheling J. Metabolic engineering of Caldicellulosiruptor bescii yields increased hydrogen production from lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2013;6(1):85.
Schut GJ, Adams MW. The iron-hydrogenase of Thermotoga maritima utilizes ferredoxin and NADH synergistically: a new perspective on anaerobic hydrogen production. J Bacteriol. 2009;191(13):4451–7.
Rydzak T, McQueen PD, Krokhin OV, Spicer V, Ezzati P, Dwivedi RC, Shamshurin D, Levin DB, Wilkins JA, Sparling R. Proteomic analysis of Clostridium thermocellum core metabolism: relative protein expression profiles and growth phase-dependent changes in protein expression. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:214.
Wang S, Huang H, Moll J, Thauer RK. NADP+ reduction with reduced ferredoxin and NADP+ reduction with NADH are coupled via an electron-bifurcating enzyme complex in Clostridium kluyveri. J Bacteriol. 2010;192(19):5115–23.
Sambrook J, Russell D. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 2001.
Lipscomb GL, Schut GJ, Thorgersen MP, Nixon WJ, Kelly RM, Adams MW. Engineering hydrogen gas production from formate in a hyperthermophile by heterologous production of an 18-subunit membrane-bound complex. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(5):2873–9.
Authors’ contributions
DC, MC, JGE and JW conceived and designed the study. DC, MC and ENS performed experiments and analyzed the data. DC, MC, JGE, AMG and JW interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
We thank Sidney Kushner for expert technical advice, Joe Groom for critical review of the manuscript, and Gina Lipscomb and Michael W. W. Adams for Gas chromatography analysis. This work was supported by the BioEnergy Science Center, US DOE Bioenergy Research Center supported by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research in the DOE Office of Science. Oak Ridge National Laboratory is managed by UT-Battelle, LLC, for the US DOE under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Daehwan Chung and Minseok Cha contributed equally to this study
Additional file
13068_2015_346_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Additional file 1: Figure S1. The diagram for Teth39_0206 (adhE) expression cassette integration vector in C. bescii. Figure S2. The diagram for Teth39_0218 (adhB) expression cassette integration vector in C. bescii. Table S1. List of primers used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, D., Cha, M., Snyder, E.N. et al. Cellulosic ethanol production via consolidated bioprocessing at 75 °C by engineered Caldicellulosiruptor bescii . Biotechnol Biofuels 8, 163 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0346-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0346-4