Abstract
Background
B-box (BBX) genes play important roles in plant growth regulation and responses to abiotic stresses. The plant growth and yield production of allotetraploid rapeseed is usually hindered by diverse nutrient stresses. However, no systematic analysis of Brassicaceae BBXs and the roles of BBXs in the regulation of nutrient stress responses have not been identified and characterized previously.
Results
In this study, a total of 536 BBXs were identified from nine brassicaceae species, including 32 AtBBXs, 66 BnaBBXs, 41 BoBBXs, 43 BrBBXs, 26 CrBBXs, 81 CsBBXs, 52 BnBBXs, 93 BjBBXs, and 102 BcBBXs. Syntenic analysis showed that great differences in the gene number of Brassicaceae BBXs might be caused by genome duplication. The BBXs were respectively divided into five subclasses according to their phylogenetic relationships and conserved domains, indicating their diversified functions. Promoter cis-element analysis showed that BBXs probably participated in diverse stress responses. Protein-protein interactions between BnaBBXs indicated their functions in flower induction. The expression profiles of BnaBBXs were investigated in rapeseed plants under boron deficiency, boron toxicity, nitrate limitation, phosphate shortage, potassium starvation, ammonium excess, cadmium toxicity, and salt stress conditions using RNA-seq data. The results showed that different BnaBBXs showed differential transcriptional responses to nutrient stresses, and some of them were simultaneously responsive to diverse nutrient stresses.
Conclusions
Taken together, the findings investigated in this study provided rich resources for studying Brassicaceae BBX gene family and enriched potential clues in the genetic improvement of crop stress resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
B-box proteins (BBXs) are one of most important zinc finger transcription factors (TFs) owing to their essential roles in plant growth and development [1]. BBXs contain one to two conserved B-box domains [B-box 1 (B1) and B-box 2 (B2)] at the N-terminus, and some of them also share additional CONSTANS, CO-like, and TIMING of CAB1 (CCT) domain at the C-terminus [2]. BBX proteins are classified into five classes according to the number of B-box and CCT. In the classes I and II, BBXs consist of two B-boxes and a CCT, and B2 shows differences in the amino acid sequence between the two types of BBXs. Class III BBXs have one B1 and CCT domains, and class IV have both B1 and B2. However, in the class V BBXs, only B1 is identified [2].
BBXs have been reported to participate in photomorphogenesis, flower induction, shade avoidance, phytohormone signals, and stress responses [3, 4]. The hypocotyls of Arabidopsis bbx4 mutant seedlings are longer than those of wild type under red light [5, 6], and bbx2, bbx20, and bbx21 show long hypocotyls under both red and blue lights [5, 7]. However, the hypocotyl growth is inhibited by red, far red, and blue lights in bbx24, bbx25 and bbx32 [8,9,10]. BBXs are involved in regulating flowering by affecting photoperiodism. In Arabidopsis, AtBBX1 can activate FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) by binding to its promoter under a long day time [11, 12]. AtBBX4 is likely to interact with AtBBX32, and they commonly control the FT expression [13]. Some BBXs are involved in gibberellic acid (GA), cytokinin (6-BA), and sucrose-mediated flowering induction in apples [14]. Shade avoidance usually leads to competitive plant growth, including hypocotyl and stem elongation, leaf angle increase, branch number decrease, and early blooming [15, 16]. AtBBX1, AtBBX2, AtBBX21, and AtBBX22 participate in plant cell elongation under shade [17, 18]. BBXs play important roles in auxin (indoleacetic acid), GA, abscisic acid (ABA), and brassinosteroid (BR) signal transduction [19]. AtBBX21 and ABA insensitive 5 (ABI5) form a protein complex to participate in light-mediated ABA signals [20]. AtBBX18 is reported to increase the GA activity, and then promote hypocotyl growth [21]. BR signal TF BRASSINAZOLE-RESISTANT 1 (BZR1)-mediated hypocotyl elongation is repressed by AtBBX20 [22]. The crosstalk between OsBBX proteins (OsBBX8, OsBBX27, and OsBBX30) and the IAA signal is found in rice [23]. BBX proteins are also involved in the responses of plants to both biotic and abiotic stress stimuli in plants. AtBBX18 can be induced by heat and shares a closed relationship with heat resistance. Overexpressing AtBBX24 increases tolerance of Arabidopsis to salt [24]. A recent study suggested that BBXs are likely to participate in drought, cold, salt, and heavy metal stresses in rice, and several BBXs are involved in responses to hormonal signals [25]. A rice BBX gene, OsCOL9, enhances the resistance of rice to blast by mediating salicylic acid (SA) and ethylene (ETH) signals [26].
N is an essential macronutrient for seed yield and protein synthesis [27]. Nitrate (NO3−) and ammonium (NH4+) are two inorganic forms of N nutrients that can be absorbed by plants. However, most plant species cannot tolerate NH4+ excess, showing toxicity symptoms [28]. In agriculture, P is an essential nutrient for plant growth and development, and it has been widely used as fertilizers. The interaction between P and N can be predicted from the responses of N-responsive genes to P availability [29]. K is involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis and plant photosynthesis, and it can enhance the resistance of crops to drought, disease and cold [30]. Though micronutrients are the trace elements that are required for high plant, micronutrient deficiency can cause undesirable growth. For example, B plays important roles in cell wall synthesis, pollen tube elongation, carbohydrate transport, and N metabolism, and B deficiency often results in decreased crop production [31].
In Brassicaceae, several nutrient-related gene families have been identified, such as amino acid (AA) permease (AAP) and aquaporin (AQP) [32, 33]. However, the information about BBX genes is limited and their roles in nutrient regulation are not identified. In this study, a comprehensive study of BBX genes was performed in nine Brassicaceae species, including Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana), Brassica napus (B. napus), Brassica oleracea (B. oleracea), Brassica rapa (B. rapa), Capsella rubella (C. rubella), Camelina sativa (C. sativa), Brassica nigra (B. nigra), Brassica juncea (B. juncea) and Brassica carinata (B. carinata). The phylogenetic relationships, synteny, genomic structures, conserved domains, promoter sequences and protein protein interaction networks about BBX genes were analyzed. In addition, their responses to N limitation, P starvation, K shortage, and B deficiency, and B excess, NH4+ (A) toxicity, Cd treatment, and salt stress were investigated in allotetraploid rapeseed.
Results
Genome-wide identification of BBX genes and their phylogenetic analysis in Brassicaceae
In the present study, a total of 536 BBX genes were identified (Fig. 1a), including 32, 66, 41, 43, 26, 81, 52, 93 and 102 BBX genes in A. thaliana, B. napus, B. oleracea, B. rapa, C. rubella, C. sativa, B. nigra, B. juncea, and B. carinata, respectively (Fig. 1a). Considering better understanding and consistency, they were named according to their location on chromosomes (Figure S1). The BBX genes were distributed on most chromosomes of each genome. Further, 12 BBX genes were identified in corresponding scaffolds, and the genome of C. rubella was assembled only to the scaffold level. For example, BnaBBX1–26 were present respectively on chromosomes A01–10 and C01–09, but BnaBBX52–66 were located on random chromosomes due to the deficiency of B. napus (allotetraploid rapeseed) genome assembly (Figure S1–1); Each B. oleracea chromosome, except for chromosome10, contained about four BoBBXs, whereas only one gene (BoBBX30) was present on chromosome 08 (Figure S1–2); All B. rapa chromosomes included BrBBX genes, and seven BrBBXs were identified on chromosomes A01 and A07; however, only BrBBX16 in A04 and BrBBX43 in scaffold000467 were found (Figure S1–3); In C. rubella scaffolds 1–4 and 6–8, 26 CrBBXs were found (Figure S1–4); CsBBX1–80 were noted on 19 of 20 chromosomes, and CsBBX81 was present in scaffold00495 (Figure S1–5).
The gene number analysis of Brassicaceae BBX. a The number of BBX genes in Arabidopsis (At), Brassica napus (Bna), Brassica oleracea (Bo), Brassica rapa (Br), Capsella rubella (Cr), and Camelina sativa (Cs). b The number of BBX family gene pair among each Brassicaceae specie. c The number of BBX gene pair between Arabidopsis and each Brassicaceae specie
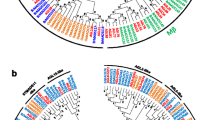
The unrooted maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree classified Brassicaceae BBXs into five subclasses to identify putative orthologs (Fig. 2). Subgroup A comprised 8 CsBBXs, 2 CrBBXs, 10 BnaBBXs, 7 BrBBXs, 5 AtBBXs, 10 BnBBXs, 14 BjBBXs, and 30 BcBBXs. Subgroup B comprised 4 AtBBXs and 61 other species BBXs. A large number of BBXs were clustered together in subgroup C, and most of them were in gene pairs. The maximum number of BBX genes was observed in subfamily D. CrBBX10-CsBBX74-CsBBX2-CsBBX56, CrBBX25-CsBBX42-CsBBX70-CsBBX79, CrBBX4-CsBBX16, CsBBX39-CsBBX41-CsBBX46-CsBBX81, CsBBX3-CsBBX76-CsBBX57-CrBBX11, CsBBX12, CsBBX18- CrBBX16 and CsBBX68, respectively, shared a closed evolutionary relationship with AtBBX7, AtBBX8, AtBBX27, AtBBX9, AtBBX10, AtBBX11, AtBBX12, and AtBBX13 in subclass D. Subgroup E contained about 25% of AtBBXs, 22% of BnaBBXs, 24% of BoBBXs, 25% of BrBBXs, 26% of CrBBXs, 21% of CsBBXs, 36% of BnBBXs, 32% of BjBBXs and 30% of BcBBXs.
Conserved domain and gene structure analysis of BBXs
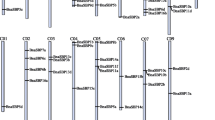
BBXs were thought to be functionally or structurally significant in protein sequences. The output of “Batch Web CD-Search Tool” showed that all BBX proteins contained at least one B-box domain (Figure S2). The length of BBX genes in proteins and coding sequence (CDS) were identified to better analyze the BBX protein structure (Table S1). Proteins and CDSs were respectively from 97 to 876 amino acids (aa) and 294 to 2631 bp, respectively, and most of them were 400 aa long. About half of BnaBBXs contained approximately 400 aa, and these proteins included both B-box and CCT domains. Short BnaBBXs contained one or two B-box domains; Moreover, an SOG2 superfamily domain, which is involved in cell separation and cytokinesis, was identified in BnaBBX36 (Figure S2–1). There were two B-boxes (B1 and B2) and a CCT in most of BoBBXs, whereas the short proteins (such as BoBBX1 and BoBBX2) shared only one B-box. BoBBX5 and BoBBX11 separately included acetyl esterase (Aes) and SOG2 (Figure S2–2). Six BrBBXs (BrBBX1–4, BrBBX10, BrBBX15, BrBBX20, and BrBBX31) shared one B-box, while the other BrBBXs were made up of two domains (two B-boxes or a B-box and a CCT). Also, BrBBX28 shared two other domains [small ubiquitin-like modifier (UbI_SUMO_like) and CCCH-type Zn-finger (CTH1) superfamily] (Figure S2–3). At least two domains were found in all CrBBXs, except for CrBBX12 and CrBBX23; no additional domain was identified in CrBBXs (Figure S2–4). In terms of CsBBXs, the conserved domains of BBXs were also uncovered. Several domains (CsBBX7, CsBBX35 and CsBBX73) included double B-box and CCT; moreover, extra protein of the unknown function (DUF4621) domain was identified in CsBBX22 (Figure S2–5). B-box and CCT domains were identified in all BnBBX, besides, there were UbI_SUMO_like and CTH1 in BnBBX25 (Figure S2–6). Except for B-box and CCT, PLN02929 (PLN02929), Glyco_hydro_47 (Glycosyl hydrolase family 47), and Cupredoxin domains (involved in intermolecular electron transfer reactions) were also found in several BjBBX proteins (Figure S2–7). In terms of BcBBXs, it was worth noting that BCBBX6 contained a bzip_plant_RF2 domain (Figure S2–8). The protein sequences of conserved domains of BBXs were further analyzed in the Pfam database to determine their conserved domains (Figure S3). As predicted, conserved B-boxes and CCT were found in BBXs, but with exceptions. For example, BnaBBX1, BnaBBX4, BoBBX1, BrBBX1–2, CrBBX23, CsBBX43, BnBBX8, BjBBX1, and BcBBX4 contained only a B-box. However, no motifs were identified in many BBX proteins, including BrBBX2, BrBBX8, BoBBX2, BoBBX9, BrBBX3–4, CrBBX4, CrBBX12, CsBBX4, CsBBX10, BnBBX3, BjBBX2, BcBBX1, and so on, in the Pfam database (data not shown). This might be due to the delayed update of the Pfam database.
According to a previous study [2], BBXs could be divided into five types. The protein types of Brassicaceae BBXs are listed in Table S1, and the representatives of each type are shown in Fig. 3. For example, the representatives of type I contained AtBBX1, BnaBBX3, BoBBX3, BrBBX8, CrBBX9, CsBBX1, BnBBX2, BjBBX5 and BcBBX2. Structure I-V comprised 6, 7, 4, 8, and 7 AtBBXs; 5–27 BnaBBXs were classified into five structures; The number of BoBBXs in structures I-V were from 3 to 10;, 5 to 12 BrBBXs were present in each type; The number of each type of CrBBXs was from 2 to 10. In class I-V, 29, 4, 15, 21, and 12 CsBBXs were identified, respectively (Fig. 4a). In Arabidopsis, most (25%) of AtBBX genes were in type IV, and a few ones belonged to type III (Fig. 4b). Most of BBXs among B. napus, B. oleracea, C. rubella, C. sativa, B. nigra, B.juncea and B. carinata, were in type I or IV, while a few BBXs were in type II or III (Fig. 4c-e and g-j). The number of BrBBXs in each type was in the order: IV = I > III > II > V (Fig. 4f).
Gene structures were involved in gene evolution. Therefore, a detailed BBX structure analysis was performed (Figure S4). Most of BnaBBXs shared more than one CDS, with the exceptions of BnaBBX1, BnaBBX3–4, BnaBBX8, BnaBBX24–25, BnaBBX28, BnaBBX33, BnaBBX38, BnaBBX49–50, BnaBBX53, BnaBBX57, BnaBBX59–60, and BnaBBX64 (Figure S4–1). The length of BnaBBXs ranged from 100 to 6500 bp. More than 94% of BoBBX genes contained at least two CDSs. The length of a majority of BoBBXs was from about 800 to 1800 bp, and long BoBBX2 and BoBBX18 were mainly due to their non-CDS (Figure S4–2). About half of BrBBXs were constructed by one or two CDSs, and BrBBX28 was the longest gene (Figure S4–3). Among CrBBXs, long untranslated regions (UTRs) of CrBBX8 and CrBBX18–20 were interesting (Figure S4–4). About 90% of CSBBX genes contained at least one intron (Figure S4–5). Most of BnBBX and BjBBX genes were less than 2.0 kb in length, while BnBBX14, BnBBX25, BjBBX7, BjBBX31, BjBBX45, BjBBX67, BjBBX71, and BjBBX73 contained long introns (Figures S4–6 and S4–7). All BcBBXs, except for BcBBX18, BcBBX20, BcBBX28, BcBBX29, BcBBX34, BcBBX37, BcBBX52, BcBBX53, BcBBX56, and so on, shared one to six introns (Figure S4–8).
Synteny and promoter analysis of BBX genes
Gene expansion occurs during the evolution of species. This study investigated their segment duplication in duplicated blocks within each genome to identify the expansion patterns of BBX genes in Brassicaceae species. A total of 495 pairs of BBXs were identified within nine genomes, including 11 pairs of AtBBXs, 29 pairs of BnaBBXs, 9 pairs of BoBBXs, 17 pairs of BrBBXs, 56 pairs of CsBBXs, 7 pairs of CrBBXs, 50 pairs of BnBBXs, 162 pairs of BjBBXs, and 154 pairs of BcBBXs (Fig. 1b). The duplicated BBXs in gene pairs were evenly distributed on most of chromosomes in each species (Figure S5). For example, almost all of B. napus chromosomes contained BnaBBX genes, and several chromosomes (chrA01, chrA03, chrA04, chrA07, chrC01, chrA02_random, chrA07_random, and chrC01_random) shared only one gene pair (Figure S5–2). Seven of nine B. oleracea chromosomes contained BoBBX genes in pairs, and 2, 1, 3, 2, 3, 1, and 1 BoBBXs were, respectively, found on chromosomes C01, C02, C03, C05, C07, C08, and C09 (Figure S5–3). The values of nonsynonymous (Ka) and synonymous substitution (Ks) were calculated to understand selection pressure among the aforementioned BBX gene pairs during the evolutionary process (Table S2). The Ka values of BBX gene pairs ranged from 0 (CsBBX50-CsBBX31, CsBBX63-CsBBX34, and BjBBX17-BjBBX44) to 0.45 (CsBBX37-CsBBX33) with an average of 0.14, and their Ks values ranged from 0.0086 (CsBBX43-CsBBX6) to 5.02 (CsBBX37-CsBBX33) with an average of 0.65. Then, Ka/Ks values of these gene pairs were calculated. They were all found to be less than 1.0, indicating that these genes might experience negative selection.
Besides, the syntenic maps of AtBBXs and each of Brassicaceae BBXs were also created. Further, 20, 19, 24, 28, 23, 77, 129, and 125 gene pairs were identified in A. thaliana-B. napus, A. thaliana-B. oleracea, A. thaliana-B. rapa, A. thaliana-C. sativa, A. thaliana-C. rubella, A. thaliana-B. nigra, A. thaliana-B.juncea, and A. thaliana-B. carinata (Fig. 1c). More than 60% AtBBXs were identified to be orthologous of BnaBBXs, which were distributed over 11 B. napus chromosomes (Figure S6–1). About half of AtBBXs and 14 BoBBXs were found in 19 gene pairs, and A. thaliana chromosome C09 and B. oleracea chromosome 4, respectively, contained most of AtBBXs and BnaBBXs (Figure S6–2). Twenty-four A. thaliana-B. rapa BBX gene pairs were identified from 13 chromosomes of two species. The duplicated AtBBXs were located on chromosomes 1–5, and the duplicated BrBBXs were located on chromosomes A01, A04, and A05–10 (Figure S6–3). Also, 23 AtBBXs and 15 CrBBXs were localized to duplicated genomic regions on five chromosomes and six scaffolds, respectively (Figure S6–4). Eighteen CrBBX genes on seven chromosomes and 28 AtBBX genes on five chromosomes were identified as syntenic genes (Figure S6–5). All genes in A. thaliana-B. nigra, A. thaliana-B.juncea, and A. thaliana-B. carinata BBX pairs were distributed over all their chromosomes (Figures S6–7, S6–8, and S6–9). The ratios of Ka/Ks were calculated to understand the divergence among orthologous gene pairs of B. napus and Arabidopsis, B. oleracea and Arabidopsis, B. rapa and Arabidopsis, C. rubella and Arabidopsis, C. sativa and Arabidopsis, B. nigra and A. thaliana, B.juncea and A. thaliana, and B. carinata and A. thaliana (Table S3). The values of Ka/Ks were less than 0.7, and the average Ka/Ks ratio of gene pairs between two species was 0.21, which was smaller than that between single species. This indicated that negative selection dominated the evolution of Brassicaceae BBX genes.
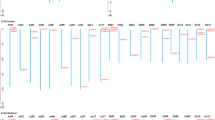
The promoters of BnaBBXs, BoBBXs, BrBBXs, CrBBXs, CsBBXs, BnBBXs, BjBBXs, and BcBBXs were analyzed. Stress-related elements [i.e., methyl jasmonate (MeJA)-responsiveness element, defense and stress responsiveness element, ABA responsiveness element, low-temperature responsiveness element, SA responsiveness element and drought-inducibility element] were found (Figure S7). For example, in BnaBBXs and BoBBXs, most of cis-elements were related to abscisic acid and salicylic acid responsiveness; and other stress-related elements were also identified (Figures S7–1 and 7–2). Further, 2 to 17 ABA responsiveness elements were observed in BrBBXs, except for BrBBX3, BrBBX11, BrBBX27, and BrBBX28 (Figure S7–3).
Protein–protein interaction analysis of BnaBBXs and their responses to B
Protein–protein interactions have been proved to be effective in uncovering biochemical functions of targets [34]. Many BnaBBX proteins potentially interacted with each other, with exceptions of BnaBBX52, BnaBBX65, BnaBBX12, and BnaBBX55 (Fig. 5). Besides, other partners of BnaBBXs that were also identified included gigantea protein (GI), flavin-binding kelch repeat f box 1 (FKF1), FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT), MADS-box protein AGAMOUS-LIKE 20 (AGL20), FLOWERING LOCUS C (FLC), phytochrome B (PHYB), transducin/WD40 repeat-like superfamily protein constitutive photomorphogenesis protein 1 (COP1), basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor [Hypocotyl5 (HY5)], MADS-box transcription factor APETALA1 (AP1), and C2H2-like zinc finger protein LATE FLOWERING (LATE) (Fig. 5). Most of these patterns were involved in flowering. For example, FT is a mobile flower-promoting signal that promotes the transition of a plant from vegetative growth to flowering; In long days, CO interacting with FT promotes flowering; AGL20 acts downstream of FT to regulate growth phase transitions. LATE acts as a transcriptional repressor of flowering. AP1 is indispensable for the normal development of sepals and petals in flowers. The remaining patterns (FKF1, PHYB, COP1, and HY5) take part in light-dependent circadian cycles. In addition, AtCO (BnaBBX26 and BnaBBX51) can strongly interact with 11 proteins (GI, HY5, COP1, FT, FKF1, LATE, BBX19, AGAL20, AP1, PHYB, and FLC).
B deficiency retards leaf and root growth but increases the number and length of root hairs in root tips [35]; and B toxicity is involved in leaf necrosis and primary root growth [35]. However, whether BnaBBXs take part in B-mediated plant growth is unknown. Differentially expressed BnaBBXs were identified under deficient- and excess-B conditions to elucidate the effects of B on BnaBBX gene expression (Fig. 6). In the roots, six BnaBBXs, especially BnaBBX7, were induced after low B treatment in cluster 1, while nine BnaBBXs, especially BnaBBX15, BnaBBX43, and BnaBBX45, were obviously repressed in cluster 2 (Fig. 6a). Six BnaBBXs were differentially expressed in shoots after B deficiency treatment; half of them were upregulated in cluster 1, while others were downregulated in cluster 2 (Fig. 6b). B toxicity also influenced BnaBBX expression (Fig. 6c and d). Only BnaBBX56 was repressed by excess B in the roots (Fig. 6c). After B toxicity treatment, BnaBBX24, BnaBBX27, BnaBBX4 and BnaBBX38 were induced in the shoots, while another four BnaBBXs were inhibited (Fig. 6d).
The expression patterns of BnaBBX genes under low and high B levels. a Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under low and normal B supply levels. b Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under low and normal B supply levels. c Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under excess and normal B supply levels. d Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under excess and normal B supply levels. Chart legend indicates the values of log2(fold-change)
Effect of N, P, and K on the expression of BnaBBX genes
N nutrients are highly demanded in rapeseed, but N use efficiency is low [36]. N limitation affects leaves, roots, nitrate (NO3−), total N and anthocyanin concentrations, and glutamine synthetase activity in B. napus [37]. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the use of nitrogen by plants have not been fully understood, and the information about BnaBBX involvement in N metabolism is limited. The transcript levels of BnaBBX genes after low-N treatment were investigated to better understand the potential roles of BnaBBXs in assimilating N. Under N stress, the expression of eight BnaBBXs was significantly altered in the roots; BnaBBX33, BnaBBX8, and BnaBBX32 were downregulated, but the remaining ones were upregulated (Fig. 7a). In the shoots, eight BnaBBXs responded to N stress; only BnaBBX62 was controlled in the N-treated group, and seven BnaBBXs (BnaBBX49, BnaBBX53, BnaBBX61, BnaBBX11, BnaBBX51, BnaBBX38, and BnaBBX64) were obviously induced (Fig. 7b).
The expression patterns of BnaBBX genes under different N, P and K levels. a Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under low and normal N supply levels. b Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under low and normal N supply levels. c Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under low and normal P supply levels. d Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under low and normal K supply levels. e Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under low and normal K supply levels. f Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under low and normal K supply levels. Chart legend indicates the values of log2(fold-change)
P is widely present in most fertilizers and is required for normal plant growth [38]. The expression of three BnaBBXs (BnaBBX43, BnaBBX6, and BnaBBX32) clearly increased in the roots after P stress treatment, but the expression of eleven, especially BnaBBX20, BnaBBX25, and BnaBBX35, was suppressed (Fig. 7c). In the shoots, more BnaBBXs were affected by P stress. The expression of BnaBBX33, BnaBBX25, BnaBBX20, and BnaBBX50 was inhibited by P in cluster 1, while 20 BnaBBXs, especially BnaBBX44 and BnaBBX51, showed higher expression levels under P deficiency in cluster 2 (Fig. 7d).
K is an important macronutrient for plant vegetative and reproductive growth [39]. In low K treated group, BnaBBX27 was induced in the roots, but the expression of 14 BnaBBXs (BnaBBX32, BnaBBX43, BnaBBX63, BnaBBX58, BnaBBX5, BnaBBX30, BnaBBX49, BnaBBX51, BnaBBX10, BnaBBX56, BnaBBX3, BnaBBX13, BnaBBX52 and BnaBBX55) were significantly decreased (Fig. 7e). In the shoots, K deficiency resulted in an obvious decrease in the expression of BnaBBXs; especially the expression of BnaBBX51–52, expressions in cluster 1 and 2 and that of 14 BnaBBX genes in cluster 3, particularly BnaBBX31, were increased (Fig. 7f).
Effects of a, cd, and salt on the expression of BnaBBX genes
At proper supplies, A is a major inorganic N source for plant growth, whereas it causes toxicity at excess external supplies [40]. BnaBBX expression profiles were evaluated to understand their potential involvement in responses to A toxicity. A total of 14 BnaBBXs were differentially expressed in the roots relative to the condition of excess A (Fig. 8a). BnaBBX37, BnaBBX53, BnaBBX25 and BnaBBX51 were upregulated by A, while the expression levels of other genes were decreased. In the shoots, among differentially expressed 12 BnaBBXs, the expression of four BnaBBXs (BnaBBX20, BnaBBX54, BnaBBX10 and BnaBBX28) were decreased after A toxicity, but eight BnaBBXs showed higher expression levels under A toxicity compared with the control condition (Fig. 8b).
The expression patterns of BnaBBX genes under A, Cd and salt toxicity. a Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under A toxicity and A free. b Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under A toxicity and A free. c Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under Cd toxicity and Cd free. d Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in SHoot under Cd toxicity and Cd free. e Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in root under salt toxicity and salt free. f Expression analysis of BnaBBXs in shoot under salt toxicity and salt free. Chart legend indicates the values of log2(fold-change)
Cd is a harmful heavy metal for plant growth and development. Rapeseed has been widely used to restore cadmium-contaminated soils. After Cd treatment, necrotic spots on the young leaves of seedlings were observed, and root hair growth was also affected [41]. However, the molecular mechanism underlying Cd toxicity resistance has not been fully revealed. In the roots, seven and 17 BnaBBXs exhibited higher or lower expression, respectively, in the Cd-treated group compared with the control group (Fig. 8c). In the shoots, nine BnaBBXs were significantly elevated under Cd toxicity in cluster 1, while Cd repressed the expression of BnaBBX62, BnaBBX20, BnaBBX52, BnaBBX35, and BnaBBX59 in cluster 2 (Fig. 8d).
Salt stress constrains plant growth and clearly reduces rapeseed yield [42, 43]. The salt altered the expression of 25 BnaBBXs in the roots and shoots (Fig. 8e and f). Under salt stress, BnaBBX58 showed a low expression level in the roots in cluster 1, but 11 BnaBBXs shared higher expression levels in cluster 2 (Fig. 8e). After salt treatment, the expression of BnaBBX30, BnaBBX37, BnaBBX18, and BnaBBX42 was distinctly upregulated in the shoots, while the expression of nine BnaBBXs was obviously downregulated (Fig. 8f).
Diverse responses of BnaBBXs to various nutrient stress signals
A Venn diagram was constructed to investigate whether BnaBBXs were responsive to diverse nutrient stresses simultaneously (Fig. 9a and b). Many BnaBBX genes were affected by more than one stress signal at the same time, and several ones only responded to only single nutrient stress (Fig. 9a and b, and Tables S4, and S5). For example, one (BnaBBX10) and three (BnaBBX20, BnaBBX51 and BnaBBX37) BnaBBXs were separately regulated by five nutrient stresses in the roots and shoots at once. Six and one BnaBBXs were, respectively, responsive to four signals in roots and shoots. A total of 28 BnaBBXs simultaneously responded to three nutrient stresses in two tissues. About 26 BnaBBXs were simultaneously regulated by two stresses. However, some BnaBBXs (BnaBBX44, BnaBBX38, BnaBBX55, BnaBBX54, BnaBBX41, BnaBBX53, BnaBBX64, and so on) were only controlled by a single stress in the roots or shoots.
Venn diagram showing the transcriptional responses of BnaBBXs under diverse nutrient stresses. a The number of differentially expressed BnaBBX genes in root of Brassica napus under diverse nutrient stresses. b The number of differentially expressed BnaBBX genes in shoot of Brassica napus under diverse nutrient stresses. Chart legend indicates the values of log2(fold-change)
Discussion
BBX family members have been reported to play critical roles in plant growth and stress responses [1, 5, 6]. However, the information about Brassicaceae BBXs is limited so far. In this study, 536 BBX genes were identified, including 32 AtBBXs, 66 BnaBBXs, 41 BoBBXs, 43 BrBBXs, 26 CrBBXs, 81 CsBBXs, 52 BnBBXs, 93 BjBBXs, and 102 BcBBXs. Their conserved domain, gene structure, gene phylogeny, promoter, and synteny analyses were completed. The BnaBBX protein-protein interaction network was constructed. Moreover, differential expression profiles of BnaBBX genes under N limitation, P shortage, K deficiency, B starvation, A excess, Cd toxicity, and salt stress were delineated. These results might provide an integrated insight into BBX family genes.
Comparison of BBX genes among nine Brassicaceae species
The identification of 32 BBX genes has been systematically reported in Arabidopsis [2]. In this study, 66 BnaBBXs, 41 BoBBXs, 43 BrBBXs, 26 CrBBXs, 81 CsBBXs, 52 BnBBXs, 93 BjBBXs, and 102 BcBBXs were respectively identified (Fig. 1a). The number of BnaBBXs, BoBBXs, BrBBXs, CrBBXs, CsBBXs, BnBBXs, BjBBXs, and BcBBXs was nearly 2-, 1.2-, 1.3-, 0.8-, 2.5-, 1.6-, 2.9-, and 3.1-fold of AtBBXs, rspectively. Generally, gene duplication results in gene family expansion [44]. Then, orthologous BBX genes were detected in the syntenic maps. The 11 pairs of AtBBXs, 29 pairs of BnaBBXs, 9 pairs of BoBBXs, 17 pairs of BrBBXs, 7 pairs of CrBBXs, 56 pairs of CsBBXs, 50 pairs of BnBBXs, 162 pairs of BjBBXs and 154 pairs of BcBBXs were respectively identified (Fig. 1b). The result indicated that segmental gene duplication was likely to increase the expression of BnaBBXs, BrBBXs, CsBBXs, BnBBXs, BjBBXs, and BcBBXs. In addition, genome-wide duplication events that occurred million years ago contributed to chromosome reduplication. Therefore, whole-genome duplications were predicted to mainly induce the expansion and evolution of BBX family in B. oleracea and C. rubella.
These BBXs were belonged to six different subfamilies, and the gene number of each subfamily varied, indicating their different evolutionary patterns (Fig. 2). The syntenies between duplicated blocks in Arabidopsis-B. napus, Arabidopsis-B. oleracea, Arabidopsis-B. rapa, Arabidopsis-C. rubella, Arabidopsis-C. sativa, Arabidopsis-B. nigra, Arabidopsis-B.juncea, and Arabidopsis-B. carinata were also determined to predict the unknown functions of the BnaBBXs, BoBBXs, BrBBXs, CrBBXs, CsBBXs, BnBBXs, BjBBXs and BcBBXs according to AtBBXs. The 20, 19, 24, 28, 23, 77, 129 and 125 gene pairs were respectively found in Arabidopsis-B. napus, Arabidopsis-B. oleracea, Arabidopsis-B. rapa, Arabidopsis-C. rubella, Arabidopsis-C. sativa, Arabidopsis-B. nigra, Arabidopsis-B.juncea, and Arabidopsis-B. carinata, respectively (Fig. 1c). These BnaBBX, BoBBX, BrBBX, CrBBX, CsBBX, BnBBX, BjBBX and BcBBX genes in pairs were considered to originate from common ancestors with AtBBXs, indicating their similar functions with corresponding Arabidopsis ones. For example, AtBBX4, AtBBX20, AtBBX24 and AtBBX32 were involved in red-, far-red- or blue light-mediated photomorphogenesis [8, 10, 13, 18, 19]; Therefore, their homologous genes (BrBBX40-BnBBX2-BjBBX17-BcBBX30-BcBBX43, CsBBX19-CrBBX15-BnBBX17-BjBBX68-BcBBX39-BcBBX9-BcBBX98, BnaBBX39-BnBBX7-BjBBX18-BcBBX11, and BoBBX16-BrBBX16-CsBBX35-CrBBX20-BnaBBX36-BoBBX24-BrBBX32-CsBBX33-CrBBX22- BnBBX4-BjBBX21-BcBBX18) were likely to take part in plant photomorphogenesis.
Conserved domains were always associated with gene functions. Therefore, typical domains were investigated in BBX gene families. According to a previous study [2], BBX genes were divided into classes I-V (Fig. 3). BBXs in type IV shared the largest proportion among AtBBXs, BrBBXs, CrBBXs, BnBBXs, BjBBXs, and BcBBXs, while most of BnaBBX, BoBBX, CrBBXs, and CsBBXs were in type I (Fig. 4). Moreover, double B-boxes or CCT domains were found in CsBBX7, CsBBX35 and CsBBX73 (Figure S2–5). Different types of BBX genes showed different biological functions [2]. Therefore, the main roles of BBX genes may vary among different Brassicaceae species. Except for B-boxes and CCT domains, other domains were also found in several BBXs (Figure S2). For example, SOG2 superfamily was in BnaBBX36 and BoBBX11, Aes in BoBBX5, Ubl_SUMO_like and CTH1 superfamily in BrBBX28 and BnBBX25, and DUF4621 superfamily in CsBBX22. Also, some unknown domains were found in AtBBX proteins [5, 11, 45]. This result suggested that BoBBX5, BoBBX11, CsBBX22, BrBBX28, BnaBBX36, and BnBBX25 shared other functions associated with these additional motifs.
Putative functions of BnaBBXs in stress responses and flower induction
Large numbers of MeJA-responsiveness, defense and stress responsiveness, abscisic acid responsiveness, low-temperature responsiveness, SA responsiveness or drought-inducibility elements were found in five Brassicaceae BBXs, and ABA responsiveness elements were mainly present in all BBXs (Figure S7); ABA was involved in seed dormancy and germination, root growth, abiotic and biotic stress response, and inducing stomatal closure [1, 46, 47]. These findings indicated that BBXs were involved in stress tolerance, especially ABA-mediated biological processes.
The expression patterns of BnaBBXs were investigated to identify their functions in regulating various nutrient stresses. B, N, P, and K were nutrients required for plant growth; they had essential roles in diverse plant physiological pathways and oxidative stresses [33, 35, 36]. In the roots and shoots, 21 BnaBBXs were upregulated or downregulated by B limitation, and 9 genes were affected by B toxicity (Fig. 6). Eight BnaBBXs were altered in the upper and lower parts of allotetraploid rapeseed seedlings after N stress (Fig. 7a and b). Thirty-eight BnaBBXs were differentially expressed in response to P insufficiency (Fig. 7c and d). In the roots and shoots, many BnaBBXs were influenced by K stress (Fig. 7e and f). These results provided valuable information about BnaBBXs involvement in regulating nutrient assimilation; these genes were candidate regulators in the roots or shoots.
Various adverse environmental factors, including drought, salinity, heat, and cold, negatively affect plant growth and development [48, 49]. This study found that many BnaBBX genes were sensitive to A, Cd, and salt, and their expression was greatly altered by these stresses in the roots or shoots (Fig. 8). The transcriptional activity of some OsBBX genes was reported to be greatly affected by Cd [25]. The expression patterns of three OsBBXs were altered by salt stress [25]. AtBBX24 promoted root growth under a high-salinity condition [24]. However, few studies focused on BBX-mediated A adaptation. The results of the present study indicated that, like AtBBXs and OsBBXs, BnaBBXs might be involved in response to Cd and salt stresses; also, they might possibly participate in A metabolism. Future studies should focus on the exact roles of the BnaBBX gene family in adaptation to these stresses.
In addition, this study investigated that many BnaBBXs were simultaneously responsive to diverse stresses (Fig. 9, Tables S4, and S5). For example, the expression of BnaBBX10, BnaBBX37, BnaBBX51, and BnaBBX20 was affected by five nutrient stresses in the shoots or roots at the same time. Also, several BnaBBX genes were involved in four, three, or two stress signals in two parts of B. napus. According to the phylogenetic analysis, BoBBX36 and BcBBX42 were the homologous genes of BnaBBX10; BnaBBX37, BnaBBX51, and BnaBBX20, respectively, got together with BrBBX17, BcBBX54, and BcBBX38 (Fig. 2). However, some genes were only under the control of a single nutrient stress. The afore-mentioned findings indicated that many BnaBBXs and their homologs played core roles in response to various nutrient stresses; and some were only particular in a specific stress. However, these need to be verified in the near future.
Conclusions
This study was novel in performing the genome-wide analysis of genes belonging to the Brassicaceae BBX family. The information regarding their chromosomal location, conserved domain, gene structure, synteny, promoter sequence, and protein-protein interaction network was identified. BnaBBX expression profiles in response to B deficiency and toxicity, N limitation, P shortage, K starvation, A excess, Cd toxicity, and salt stress were delineated. A large number of BnaBBXs were involved in improving rapeseed resistance to nutrient stresses in the roots or shoots; some of them were identified as the core regulators in this process. The data generated in this study provided a comprehensive understanding of BBX gene family evolution and involvement of BnaBBX genes in stress responses and flower induction. Future studies should focus on validating the functions of BBXs.
Methods
Identification, conserved domain, chromosome location, phylogenetic relationship, and gene structure of BBX genes
Using known AtBBX protein sequences as queries, B. napus, B. oleracea, B. rapa, C. rubella, C. sativa, B. nigra, B.juncea, and B. carinata protein databases were searched using “Blast Several Sequences to a Big Database” in TBtools software [50], with an expected value (e-value) of e− 5. The conserved domains in BBXs were confirmed in Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/) and Batch Web CD-Search Tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi) databases and, respectively, visualized using “Visualize Pfam Domain Pattern” and “Visualize NCBI CDD Domain Pattern” tools [50]. The candidates lacking characteristic domains were eliminated from further analyses. With chromosome length and gene position files, BBXs genes were mapped onto chromosomes using “Gene Location Visualize (Advanced)” of TBtools [50].
For phylogenetic analysis, MEGA X was used to construct the phylogenetic tree by the maximum likelihood method. Protein sequences were aligned with default parameters using the ClustalW program. With generic feature format version 3 (gff3) files of BBXs, a Visualize Gene Structure (Basic) tool [50] was used to draw the gene structure diagram.
Homology and synteny analysis, identification of cis-acting elements in promoters of BBX genes, BnaBBXs protein-protein interaction networks, and heatmap analyses
“One Step MCScanX” of TBtools [50] was used to analyze BBX duplication events with genome sequences and gff3 files. “Table Row Extract Or Filter”, “File Transformat For Microsyteny Viewer And Advanced Circos”, “Fasta stats”, and “File Merge For MCScanX” tools of TBtools software were used to visualize the synteny of BBX gene pairs according to a previous study [51]. Nonsynonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitutions of each BBX gene pair were calculated using a Simple Ka/Ks Calculator (NG) [50]. The cis-elements in the 3000-bp genomic sequence upstream of the start codon were analyzed in the PlantCARE online tool (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/), and “Simple Biosequence Viewer” of TBtools [50] was used for visualization. STRING 10 (http://string-db.org/) (option value > 0.800) was used to construct an interaction network, with interolog proteins from Arabidopsis, to analyze the relationship of BnaBBXs with other proteins. The heat maps were generated with the “HeatMap” tool of TBtools [50].
Plant materials and treatments
Uniform B. napus (Zhongshuang 11) seedlings of 7-d old were transplanted into black plastic containers containing Hoagland nutrient solution (5.0 mM KNO3, 1.0 mM KH2PO4, 2.0 mM MgSO4·7H2O, 5.0 mM Ca (NO3)2·4H2O, 0.10 μM Na2MoO4·2H2O, 0.050 mM EDTA-Fe, 0.80 μM ZnSO4·7H2O, 9.0 μM MnCl2·4H2O, 0.30 μM CuSO4·5H2O, and 46 μM H3BO3). Before use for treatments, B. napus seedlings were cultivated for 10 days (d) in a chamber under a light intensity of 300–320 μmol m− 2 s− 1, a temperature of 25 °C daytime/22 °C night, a light period of 16-h photoperiod/8-h dark, and relative humidity of 70%.
B deficiency and toxicity treatments
Seventeen-day-old rapeseed seedlings were, respectively, cultivated in 0.25 μM and 1500 μM H3BO3 for 10 d in B deficiency- and excess-treated groups.
N, P, and K depletion treatments
B. napus seedlings, 17-d old, were cultivated in Hoagland nutrient solution, including 0.30 mM N, 5mΜ P, and 0.30 mM K for 3 d.
NH4+ toxicity treatment
Uniform Zhongshuang 11 seedlings, 7 d old, were first cultivated in Hoagland nutrient solution containing normal nitrate for 10 d. Subsequently, they were transferred to an N-free solution for 3 d. Finally, the plants were subjected to 9.0 mM NH4+ (excess NH4+) for 6 h.
Cd toxicity and salt treatments
The Cd- and salt-treated 17-day-old Zhongshuang 11 seedlings were, respectively, grown in a solution containing 10 μM CdCl2 for 12 h and 200 mM NaCl for 1 d. The seedlings in the control groups were cultivated in a normal solution for appropriate times based on the aforementioned treatments. Comparative transcriptomes were performed using roots and shoots from control and stress-treated plants in previous studies [27, 33, 35, 41, 52, 53]; the transcriptome data can be found in published studies. Differentially expressed genes are defined as those with P value < 0.05, false-discovery rate less than 0.05, and |log2(fold-change)| ≥ 1.
Availability of data and materials
All the data and materials that are required to reproduce these findings can be shared by contacting the corresponding author, Dr. Ying-peng Hua (yingpenghua@zzu.edu.cn).
Abbreviations
- BBX:
-
B-box
- B:
-
Boron
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- Pi:
-
Phosphate
- K:
-
Potassium
- A. thaliana :
-
Arabidopsis thaliana
- B. napus :
-
Brassica napus
- B. oleracea :
-
Brassica oleracea
- B. rapa :
-
Brassica rapa
- C. rubella :
-
Capsella rubella
- C. sativa :
-
Camelina sativa
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- A:
-
Ammonium (NH4+)
- NO3 − :
-
Nitrate
- DEGs:
-
Differentially expressed genes
References
Cutler SR, Rodriguez PL, Finkelstein RR, Abrams SR. Abscisic acid: emergence of a core signaling network. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61(1):651–79. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112122.
Khanna R, Kronmiller B, Maszle DR, Coupland G, Holm M, Mizuno T, et al. The Arabidopsis B-box zinc finger family. Plant Cell. 2009;21(11):3416–20. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.069088.
Chen S, Jiang W, Yin J, Wang S, Fang Z, Ma D, et al. Genome-wide mining of wheat B-BOX zinc finger (BBX) gene family provides new insights into light stress responses. Crop Pasture Sci. 2021;72(1):17–37. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP20342.
Mbambalala N, Panda SK, van der Vyver C. Overexpression of AtBBX29 improves drought tolerance by maintaining photosynthesis and enhancing the antioxidant and osmolyte capacity of sugarcane plants. Plant Mol Biol Reporter. 2021;39:419-33.
Datta S, Hettiarachchi GH, Deng XW, Holm M. Arabidopsis CONSTANS-LIKE3 is a positive regulator of red light signaling and root growth. Plant Cell. 2006;18(1):70–84. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.038182.
Fan XY, Sun Y, Cao DM, Bai MY, Luo XM, Yang HJ, et al. BZS1, a B-box protein, promotes photomorphogenesis downstream of both brassinosteroid and light signaling pathways. Mol Plant. 2012;5(3):591–600. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sss041.
Datta S, Hettiarachchi C, Johansson H, Holm M. SALT TOLERANCE HOMOLOG2, a B-box protein in Arabidopsis that activates transcription and positively regulates light-mediated development. Plant Cell. 2007;19(10):3242–55. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.054791.
Gangappa SN, Crocco CD, Johansson H, Datta S, Hettiarachchi C, Holm M, et al. The Arabidopsis B-BOX protein BBX25 interacts with HY5, negatively regulating BBX22 expression to suppress seedling photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell. 2013;25(4):1243–57. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.109751.
Kumagai T, Ito S, Nakamichi N, Niwa Y, Murakami M, Yamashino T, et al. The common function of a novel subfamily of B-box zinc finger proteins with reference to circadian-associated events in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72(6):1539–49. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.80041.
Holtan HE, Bandong S, Marion CM, Adam L, Tiwari S, Shen Y, et al. BBX32, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, functions in light signaling by suppressing HY5-regulated gene expression and interacting with STH2/BBX21. Plant Physiol. 2011;156(4):2109–23. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.177139.
Tiwari SB, Shen Y, Chang HC, Hou Y, Harris A, Ma SF, et al. The flowering time regulator CONSTANS is recruited to the FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter via a unique cis-element. New Phytol. 2010;187(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03251.x.
Cao S, Kumimoto RW, Gnesutta N, Calogero AM, Mantovani R, Holt BR. A distal CCAAT/NUCLEAR FACTOR Y complex promotes chromatin looping at the FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter and regulates the timing of flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2014;26(3):1009–17. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.120352.
Tripathi P, Carvallo M, Hamilton EE, Preuss S, Kay SA. Arabidopsis B-BOX 32 interacts with CONSTANS-LIKE3 to regulate flowering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(1):172–7. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1616459114.
Shalmani A, Fan S, Jia P, Li G, Muhammad I, Li Y, et al. Genome identification of B-BOX gene family members in seven rosaceae species and their expression analysis in response to flower induction in Malus domestica. Molecules. 2018;23(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071763.
Casal JJ. Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2013;64(1):403–27. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120221.
Pierik R, de Wit M. Shade avoidance: phytochrome signalling and other aboveground neighbour detection cues. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(11):2815–24. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert389.
Crocco CD, Holm M, Yanovsky MJ, Botto JF. Function of B-BOX under shade. Plant Signal Behav. 2011;6(1):101–4. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.1.14185.
Crocco CD, Locascio A, Escudero CM, Alabadi D, Blazquez MA, Botto JF. The transcriptional regulator BBX24 impairs DELLA activity to promote shade avoidance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun. 2015;6(1):6202. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7202.
Vaishak KP, Yadukrishnan P, Bakshi S, Kushwaha AK, Ramachandran H, Job N, et al. The B-box bridge between light and hormones in plants. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019;191:164–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.12.021.
Xu D, Li J, Gangappa SN, Hettiarachchi C, Lin F, Andersson MX, et al. Convergence of light and ABA signaling on the ABI5 promoter. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(2):e1004197. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004197.
Wang Q, Zeng J, Deng K, Tu X, Zhao X, Tang D, et al. DBB1a, involved in gibberellin homeostasis, functions as a negative regulator of blue light-mediated hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Planta. 2011;233(1):13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1274-y.
Sun Y, Fan XY, Cao DM, Tang W, He K, Zhu JY, et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell. 2010;19(5):765–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.010.
Huang J, Zhao X, Weng X, Wang L, Xie W. The rice B-box zinc finger gene family: genomic identification, characterization, expression profiling and diurnal analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048242.
Nagaoka S, Takano T. Salt tolerance-related protein STO binds to a Myb transcription factor homologue and confers salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot. 2003;54(391):2231–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erg241.
Shalmani A, Jing XQ, Shi Y, Muhammad I, Zhou MR, Wei XY, et al. Characterization of B-BOX gene family and their expression profiles under hormonal, abiotic and metal stresses in Poaceae plants. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5336-z.
Liu H, Dong S, Sun D, Liu W, Gu F, Liu Y, et al. CONSTANS-like 9 (OsCOL9) interacts with receptor for activated C-kinase 1(OsRACK1) to regulate blast resistance through salicylic acid and ethylene signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e166249.
Zhang GB, Meng S, Gong JM. The expected and unexpected roles of nitrate transporters in plant abiotic stress resistance and their regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3535.
Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ. NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: a critical review. J Plant Physiol. 2002;159(6):567–84. https://doi.org/10.1078/0176-1617-0774.
Hu B, Jiang Z, Wang W, Qiu Y, Zhang Z, Liu Y, et al. Nitrate-NRT1.1B-SPX4 cascade integrates nitrogen and phosphorus signalling networks in plants. Nat Plants. 2019;5(4):401–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-019-0384-1.
Krapp A. Plant nitrogen assimilation and its regulation: a complex puzzle with missing pieces. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2015;25:115–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.010.
Takano J, Noguchi K, Yasumori M, Kobayashi M, Gajdos Z, Miwa K, et al. Arabidopsis boron transporter for xylem loading. Nature. 2002;420(6913):337–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01139.
Yuan D, Li W, Hua Y, King GJ, Xu F, Shi L. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the aquaporin gene family and transcriptional responses to boron deficiency in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01336.
Zhou T, Yue CP, Huang JY, Cui JQ, Liu Y, Wang WM, et al. Genome-wide identification of the amino acid permease genes and molecular characterization of their transcriptional responses to various nutrient stresses in allotetraploid rapeseed. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02367-7.
Wei W, Hu Y, Han YT, Zhang K, Zhao FL, Feng JY. The WRKY transcription factors in the diploid woodland strawberry Fragaria vesca: identification and expression analysis under biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016;105:129–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.014.
Hua Y, Feng Y, Zhou T, Xu F. Genome-scale mRNA transcriptomic insights into the responses of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) to varying boron availabilities. Plant Soil. 2017;416:205–25.
Clement G, Moison M, Soulay F, Reisdorf-Cren M, Masclaux-Daubresse C. Metabolomics of laminae and midvein during leaf senescence and source-sink metabolite management in Brassica napus L. leaves. J Exp Bot. 2018;69(4):891–903. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx253.
Zhang ZH, Zhou T, Liao Q, Yao JY, Liang GH, Song HX, et al. Integrated physiologic, genomic and transcriptomic strategies involving the adaptation of allotetraploid rapeseed to nitrogen limitation. BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18(1):322. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1507-y.
Tang H, Niu L, Wei J, Chen X, Chen Y. Phosphorus limitation improved salt tolerance in maize through tissue mass density increase, osmolytes accumulation, and Na(+) uptake inhibition. Front Plant Sci. 2019;10:856. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00856.
Huertas R, Rubio L, Cagnac O, Garcia-Sanchez MJ, Alche JD, Venema K, et al. The K+/H+ antiporter LeNHX2 increases salt tolerance by improving K+ homeostasis in transgenic tomato. Plant Cell Environ. 2013;36(12):2135–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12109.
Liu Y, von Wiren N. Ammonium as a signal for physiological and morphological responses in plants. J Exp Bot. 2017;68(10):2581–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx086.
Zhang ZH, Zhou T, Tang TJ, Song HX, Guan CY, Huang JY, et al. A multiomics approach reveals the pivotal role of subcellular reallocation in determining rapeseed resistance to cadmium toxicity. J Exp Bot. 2019;70(19):5437–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz295.
Shokri-Gharelo R, Noparvar PM. Molecular response of canola to salt stress: insights on tolerance mechanisms. Peer J. 2018;6:e4822. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4822.
Feng YN, Cui JQ, Zhou T, Liu Y, Yue CP, Huang JY, et al. Comprehensive dissection into morpho-physiologic responses, ionomic homeostasis, and transcriptomic profiling reveals the systematic resistance of allotetraploid rapeseed to salinity. BMC Plant Biol. 2020;20(1):534. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02734-4.
Ohno S. Gene duplication and the uniqueness of vertebrate genomes circa 1970-1999. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1999;10(5):517–22. https://doi.org/10.1006/scdb.1999.0332.
Crocco CD, Botto JF. BBX proteins in green plants: insights into their evolution, structure, feature and functional diversification. Gene. 2013;531(1):44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.037.
Hirayama T, Shinozaki K. Research on plant abiotic stress responses in the post-genome era: past, present and future. Plant J. 2010;61(6):1041–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04124.x.
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57(1):781–803. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105444.
Rengasamy P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J Exp Bot. 2006;57(5):1017–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj108.
Cramer GR, Urano K, Delrot S, Pezzotti M, Shinozaki K. Effects of abiotic stress on plants: a systems biology perspective. BMC Plant Biol. 2011;11(1):163. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-163.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020;13(8):1194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009.
Li P, Chai Z, Lin P, Huang C, Huang G, Xu L, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum L.). BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):685. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07076-x.
Cui JQ, Hua YP, Zhou T, Liu Y, Huang JY, Yue CP. Global landscapes of the Na(+)/H(+) antiporter (NHX) family members uncover their potential roles in regulating the rapeseed resistance to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103429.
Zhou T, Hua Y, Zhang B, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Shi L, et al. Low-boron tolerance strategies involving pectin-mediated cell wall mechanical properties in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017;58(11):1991–2005. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx130.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Major collaborative innovation project of Zhengzhou (Key discipline construction project of Zhengzhou University) (xkzdjc201905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZLW and HYP was involved in data analysis. MSJ, ZT and YCP made the experiments. ZLW, HYP and HJY designed the study, and ZLW, HYP and HJY wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In this study, all the seeds of rapeseed plants were obtained from our research group led by Prof. Jin-yong Huang (jinyhuang@zzu.edu.cn, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, 45000, Henan Province, China). This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. No specific permits were required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Chromosomal location of BBX genes on Brassicaceae chromosomes. Figure S1–1 The location of BBX genes on B. napus chromosomes. Figure S1–2 The location of BBX genes on B. oleracea chromosomes. Figure S1–3 The location of BBX genes on B. rapa chromosomes and scaffold. Figure S1–4 The location of BBX genes on C. rubella scaffolds. Figure S1–5 The location of BBX genes on C. sativa chromosomes and scaffold. Figure S1–6 Chromosomal location of B. nigra BBX genes. Figure S1–7 Chromosomal location of B.juncea BBX genes. Figure S1–8 Chromosomal location of B. carinata BBX genes.
Additional file 2: Fig
ure S2. Identification and characterization of conserved domains in BBXs in NCBI database. Figure S2–1 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BnaBBXs. Figure S2–2 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BoBBXs. Figure S2–3 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BrBBXs. Figure S2–4 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in CrBBXs. Figure S2–5 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in CsBBXs. Figure S2–6 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BnBBXs. Figure S2–7 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BjBBXs. Figure S2–8 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BcBBXs.
Additional file 3: Fig
ure S3. Identification and characterization of conserved domains in BBXs in pfam database. Figure S3–1 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BnaBBXs. Figure S3–2 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BoBBXs. Figure S3–3 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BrBBXs. Figure S3–4 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in CrBBXs. Figure S3–5 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in CsBBXs. Figure S3–6 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BnBBXs. Figure S3–7 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BjBBXs. Figure S3–8 Identification and characterization of the conserved domains in BcBBXs.
Additional file 4: Fig
ure S4. Structure analysis of BBX genes. Figure S4–1 Exon–intron structures of BnaBBX genes. Figure S4–2 Exon–intron structures of BoBBX genes. Figure S4–3 Exon–intron structures of BrBBX genes. Figure S4–4 Exon–intron structures of CrBBX genes. Figure S4–5 Exon–intron structures of CsBBX genes. Figure S4–6 Exon–intron structures of BnBBX genes. Figure S4–7 Exon–intron structures of BjBBX genes. Figure S4–8 Exon–intron structures of BcBBX genes.
Additional file 5: Fig
ure S5. Synteny of BBX genes in each Brassicaceae genome. Figure S5–1 Synteny of AtBBX genes in A. thaliana genome. Figure S5–2 Synteny of BnaBBX genes in B. napus genome. Figure S5–3 Synteny of BoBBX genes in B. oleracea genome. Figure S5–4 Synteny of BrBBX genes in B. rapa genome. Figure S5–5 Synteny of CrBBX genes in C. rubella genome. Figure S5–6 Synteny of CsBBX genes in C. sativa genome. Figure S5–7 Synteny of BnBBX genes in B. nigra genome. Figure S5–8 Synteny of BjBBX genes in B.juncea genome. S109, C668, C1065 and C306 respectively indicates Super_scaffold_109_3169392_4351964_52914_567609, Contig668_1_483987, Contig1065 and Contig306 in the B.juncea genome. Figure S5–9 Synteny of BcBBX genes in B. carinata genome. J0021.1, J1585.1, J1599.1 and J1604.1 respectively indicates JAAMPC010000021.1, JAAMPC0100001585.1, JAAMPC0100001599.1 and JAAMPC0100001604.1 in the B. carinata genome.
Additional file 6: Fig
ure S6. Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and each other Brassicaceae. Figure S6–1 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B. napus. Figure S6–2 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B. oleracea. Figure S6–3 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B. rapa. Figure S6–4 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and C. rubella. Figure S6–5 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and C. sativa. Figure S6–6 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B. nigra. Figure S6–7 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B.juncea. S109, C668, C1065 and C306 respectively indicates Super_scaffold_109_3169392_4351964_52914_567609, Contig668_1_483987, Contig1065 and Contig306 in the B.juncea genome. Figure S6–8 Synteny of BBX genes between A. thaliana and B. carinata. J0021.1, J1585.1, J1599.1 and J1604.1 respectively indicates JAAMPC010000021.1, J AAMPC010001585.1, J AAMPC010001599.1 and J AAMPC010001604.1 in B. carinata genome.
Additional file 7: Fig
ure S7. Promoter analysis of BBX genes. Figure S7–1 Cis-element identified in promoters of BnaBBXs. Figure S7–2 Cis-element identified in promoters of BoBBXs. Figure S7–3 Cis-element identified in promoters of BrBBXs. Figure S7–4 Cis-element identified in promoters of CrBBXs. Figure S7–5 Cis-element identified in promoters of CsBBXs. Figure S7–7 Cis-element identified in promoters of BjBBXs. Figure S7–8 Cis-element identified in promoters of BcBBXs.
Additional file 8: Table S1.
Information about identified BBX genes. Table S2. Synteny analysis of Brassicaceae BBX genes. Table S3. Synteny analysis of Arabidopsis and each other Brassicaceae BBX genes. Table S4. Common DEGs in root among different classes. Table S5. Common DEGs in root among different classes.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Lw., Ma, Sj., Zhou, T. et al. Genome-wide identification of Brassicaceae B-BOX genes and molecular characterization of their transcriptional responses to various nutrient stresses in allotetraploid rapeseed. BMC Plant Biol 21, 288 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03043-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03043-0