Abstract
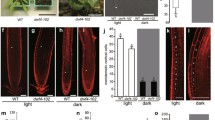
Double B-box 1a (DBB1a) belongs to the zinc-finger family proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Transcriptional analysis uncovered that the DBB1a gene expression was blue light-dependently regulated, and the transcript level of DBB1a in cry1cry2 was decreased but not in phyAphyB compared to wild type under blue light conditions. Transgenic plants containing pDBB1a:GUS (β-glucuronidase) displayed GUS activity in the vascular system of leaves and petioles. Green fluorescent protein (GFP)-fused DDB1a (DBB1a-GFP) protein was found in the nucleus in transient transformation assays with onion epidermal cells as well as in stable transgenic Arabidopsis plants. To investigate the function of DBB1a, we generated DBB1a over-expressing and under-expressing transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Analysis of hypocotyl growth of these lines indicated that DBB1a promoted hypocotyl elongation under blue light condition. The phenotype of transgenic plants with DBB1a over-expression could be impaired by a gibberellin (GA)-biosynthesis inhibitor. Moreover, the expression analysis of GA metabolic and catabolic genes in DBB1a transgenic lines indicated that the DBB1a suppressed GA2-oxidase1 (GA2ox1) and GA2-oxidase8 (GA2ox8) expression, but induced GA3β-hydroxygenase1 (GA3ox1) and GA20-oxidase1 (GA20ox1) expression under blue light. Taken together, we concluded that DBB1a promotes hypocotyl elongation under blue light condition through an increase in bioactive GA levels in Arabidopsis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COP1:
-
Constitutive photomorphogenic 1
- DBB1a:
-
Double B-box 1a
- GA(s):
-
Gibberellin(s)
- GA3 :
-
Gibberellic acid
- GA2ox:
-
GA2-oxidase1
- GA3ox:
-
GA3β-hydroxygenase
- GA20ox:
-
GA20-oxidase
- HY5:
-
Long hypocotyl 5
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Ahmad M, Cashmore AR (1993) HY4 gene of A. thaliana encodes a protein with characteristics of a blue-light photoreceptor. Nature 366:162–166
Alabadí D, Blázquez M (2009) Molecular interactions between light and hormone signaling to control plant growth. Plant Mol Biol 69:409–417
Alabadi D, Gil J, Blazquez MA, Garcia-Martinez JL (2004) Gibberellins repress photomorphogenesis in darkness. Plant Physiol 134:1050–1057
Briggs WR, Olney MA (2001) Photoreceptors in plant photomorphogenesis to date. Five phytochromes, two cryptochromes, one phototropin, and one superchrome. Plant Physiol 125:85–88
Carol RA, Steve AK (1998) COP1 and HY5 interact to mediate light-induced gene expression. BioEssays 20:445–448
Chen M, Chory J, Fankhauser C (2004) Light signal transduction in higher plants. Annu Rev Genetics 38:87–117
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Datta S, Hettiarachchi C, Johansson H, Holm M (2007) SALT TOLERANCE HOMOLOG2, a B-box protein in Arabidopsis that activates transcription and positively regulates light-mediated development. Plant Cell 19:3242–3255
Datta S, Johansson H, Hettiarachchi C, Irigoyen ML, Desai M, Rubio V, Holm M (2008) LZF1/SALT TOLERANCE HOMOLOG3, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, involved in light-dependent development and gene expression, undergoes COP1-mediated ubiquitination. Plant Cell 20:2324–2338
de Lucas M, Daviere J-M, Rodriguez-Falcon M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blazquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008) A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451:480–484
Elmayan T, Balzergue S, Beon F, Bourdon V, Daubremet J, Guenet Y, Mourrain P, Palauqui J-C, Vernhettes S, Vialle T, Wostrikoff K, Vaucheret H (1998) Arabidopsis mutants impaired in cosuppression. Plant Cell 10:1747–1758
Endo M, Mochizuki N, Suzuki T, Nagatani A (2007) CRYPTOCHROME2 in vascular bundles regulates flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:84–93
Eriksson S, Bohlenius H, Moritz T, Nilsson O (2006) GA4 is the active gibberellin in the regulation of LEAFY transcription and Arabidopsis floral initiation. Plant Cell 18:2172–2181
Hedden P, Philips AL (2000) Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed by genes. Trends Plant Sci 5:523–530
Indorf M, Cordero J, Neuhaus G, Rodríguez-Franco M (2007) Salt tolerance (STO), a stress-related protein, has a major role in light signalling. Plant J 51:563–574
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Bio Rep 5:387–450
Jiao Y, Lau OS, Deng XW (2007) Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nat Rev Genet 8:217–230
Kumagai T, Ito S, Nakamichi N, Niwa Y, Murakami M, Yamashino T, Mizuno T (2008) The common function of a novel subfamily of B-box zinc finger proteins with reference to circadian-associated events in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci Biotech Biochem 72:1539–1549
Lee LY, Fang MJ, Kuang LY Gelvin SB (2008) Vectors for multi-color bimolecular fluorescence complementation to investigate protein–protein interaction in living plant cells. Plant Methods 4. doi:10.1186/1746-4811-4-24
Lester DR, Ross JJ, Smith JJ, Elliott RC, Reid JB (1999) Gibberellin 2-oxidation and the SLN gene of Pisum sativum. Plant J 19:65–73
Lin C (2002) Blue light receptors and signal transduction. Plant Cell 14:S207–S225
Liu H, Yu X, Li K, Klejnot J, Yang H, Lisiero D, Lin C (2008) Photoexcited CRY2 interacts with CIB1 to regulate transcription and floral initiation in Arabidopsis. Science 322:1535–1539
Ma L, Li J, Qu L, Hager J, Chen Z, Zhao H, Deng XW (2001) Light control of Arabidopsis development entails coordinated regulation of genome expression and cellular pathways. Plant Cell 13:2589–2607
Mallappa C, Yadav V, Negi P, Chattopadhyay S (2005) A basic leucine zipper transcription factor, G-box-binding factor 1, regulates blue light-mediated photomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 281:22190–22199
Mallappa C, Singh A, Ram H, Chattopadhyay S (2008) GBF1, a transcription factor of light signaling in Arabidopsis, is degraded in the dark by a proteasome-mediated pathway independent of COP1 and SPA1. J Biol Chem 283:35772–35782
Mandy J, Dowson-Day AJM (1999) Circadian dysfunction causes aberrant hypocotyl elongation patterns in Arabidopsis. Plant J 17:63–71
Mockler TC, Guo H, Yang H, Duong H, Lin C (1999) Antagonistic actions of Arabidopsis cryptochromes and phytochrome B in the regulation of floral induction. Development 126:2073–2082
Morel J-B, Mourrain P, Béclin C, Vaucheret H (2000) DNA methylation and chromatin structure affect transcriptional and post-transcriptional transgene silencing in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 10:1591–1594
Neff MM, Chory J (1998) Genetic interactions between phytochrome A, phytochrome B, and cryptochrome 1 during Arabidopsis development. Plant Physiol 118:27–35
Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Wei N, Deng XW (2000) Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405:462–466
Reid JB, Symons GM, Ross JJ (2004) Regulation of gibberellin and brassinosteroid biosynthesis by genetic, environmental and hormonal factors. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones, vol 3, 3rd edn. Springer-Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 179–203
Sakamoto T, Kobayashi M, Itoh H, Tagiri A, Kayano T, Tanaka H, Iwahori S, Matsuoka M (2001) Expression of a gibberellin 2-oxidase gene around the shoot apex is related to phase transition in rice. Plant Physiol 125:1508–1516
Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (1999) Molecular cloning and functional expression of gibberellin 2-oxidases, multifunctional enzymes involved in gibberellin deactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4698–4703
Vandenbussche F, Verbelen JP, Van der Straeten D (2005) Of light and length: regulation of hypocotyl growth in Arabidopsis. BioEssays 27:1–10
Wang Q, Tu X, Deng K, Zeng J, Zhao X, Tang D, Liu X (2009a) A defect in zinc finger protein double B-box 1a (DBB1a) causes abnormal floral development in Arabidopsis. J Plant Biol 52:543–549
Wang Q, Tu X, Zhao X, Tang D, Liu X (2009b) Transcription of Zinc finger protein DBB (Double B-Box) subfamily responds to light in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Comm 45:785–790
Weller JL, Hecht V, Vander Schoor JK, Davidson SE, Ross JJ (2009) Light regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis in pea is mediated through the COP1/HY5 pathway. Plant Cell 21:800–813
Xiao C, Chen F, Yu X, Lin C, Fu Y-F (2009) Over-expression of an AT-hook gene, AHL22, delays flowering and inhibits the elongation of the hypocotyl in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 71:39–50
Yadav V, Mallappa C, Gangappa SN, Bhatia S, Chattopadhyay S (2005) A basic Helix-Loop-Helix transcription factor in Arabidopsis, MYC2, acts as a repressor of blue light-mediated photomorphogenic growth. Plant Cell 17:1953–1966
Yamaguchi S (2008) Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:225–251
Yang J, Lin R, Sullivan J, Hoecker U, Liu B, Xu L, Deng XW, Wang H (2005) Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:804–821
Yu X, Sayegh R, Maymon M, Warpeha K, Klejnot J, Yang H, Huang J, Lee J, Kaufman L, Lin C (2009) Formation of nuclear bodies of Arabidopsis CRY2 in response to blue light is associated with its blue light-dependent degradation. Plant Cell 108:061663
Zhao X, Yu X, Foo E, Symons GM, Lopez J, Bendehakkalu KT, Xiang J, Weller JL, Liu X, Reid JB, Lin C (2007) A study of gibberellin homeostasis and cryptochrome-mediated blue light inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiol 145:106–118
Zhou Y, Ni M (2010) Short hypocotyl under blue1 truncations and mutations alter its association with a signaling protein complex in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:703–715
Acknowledgments
We thank C. Lin for providing cry1cry2, phyAphyB and sgs mutant seeds. Our thanks are also due to Drs.Bekir Ulker and Jane Parker for kindly providing pJawohl8-RNAi and CaMV35S::pENSG-GFP-GW vectors, and Dr Ying Ruan and Wenhui Shen for their critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770200), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (755228001) and the 211/985 Higher Education Enhancement Funds to Hunan University.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qiming Wang and Jianxin Zeng contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zeng, J., Deng, K. et al. DBB1a, involved in gibberellin homeostasis, functions as a negative regulator of blue light-mediated hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis . Planta 233, 13–23 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1274-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1274-y