Abstract
Background
The eastern edge of the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau (QTP) and subtropical China have various regions where plant species originate and thrive, but these regions have been the focus of very few integrative studies. Here, we elucidated the phylogeographic structure of a continuous and widespread Akebia trifoliata population across these two regions.
Results
Sixty-one populations consisting of 391 genotypes were examined to assess population diversity and structure via network distribution analysis, maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree reconstruction, divergence time estimation, demographic history inference, and ancestral area reconstruction of both conserved internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and chloroplast (rps16) DNA sequences. The results showed that the ITS region was more variable than the rps16 region and could be suitable for studying intraspecific phylogeography. The A. trifoliata population displayed high genetic diversity, genetic differentiation and obvious phylogeographical structure, possibly originating on the eastern QTP, expanding during the last glacial-interglacial cycle, diverging in the early Pleistocene and middle Pleistocene, and extensively migrating thereafter. The migration route from west to east along rivers could be largely responsible for the long-distance dispersal of this species, while three main refuges (Qinba Mountains, Nanling Mountains and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau) with multiple ice shelters facilitated its wide distribution.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that the from west to east long migration accompanying with the minor short reciprocal migration in the south-north direction, and the three main refuges (the Qinba Mountains, Nanling Mountains and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau) contributed to the extant geographical distribution of A. trifoliata. In addition, this finding also strongly reduced the discrepancy between glacial contraction and postglacial expansion and the in situ survival hypothesis by simultaneously considering the existence of many similar climate-related ecological niches and migration influences.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
China’s present-day topography is well known for being elevated in the west and low in the east, which could have resulted from the rapid uplift of the Tibetan Plateau (TP) during the Quaternary Period [1]. As a main driving force of eco-environmental evolution, rapid changes have led to corresponding alternations in both geomorphic and climate types and consequently generated various sources and reservoirs of biological diversity in the region surrounding the TP [2]. Further analysis supported that the climate oscillations accompanying this process resulted in alternation between contraction and expansion due to cyclical variations in glacial intervals, which had an important influence on the current distributions of extant species [3]. Recently, many glacial refugia found in mainland China during the species conservation process also well supported this view [4]. For sedentary and/or special species, populations close to glacier refugia generally have greater genetic diversity than those far from them [5]. Therefore, scientists can infer the evolutionary history of a given species according to the distribution of its genetic information.
In the region of the eastern edge of the TP, the alternating distribution of a series of spectacular north‒south trending mountains and rapidly rushing rivers results in various deep valleys, in which numerous species occur due to the large variation in altitudes. Regions harbouring both ancient and newly originated species are the most famous biodiversity cradles in the world [6]. Studies have suggested that many species retreated here for shelter during the ice ages but migrated to other places after the ice ages since the beginning of the Quaternary [7,8,9], which indicated that the area was a major shelter and possibly an important centre of species origin. In addition, the migration of species, especially vascular plants, directly across the TP would have been impeded by various high mountains with perennial frozen earth [10], indicating that subtropical China, both south of the Qinling Mountains and Huaihe River Line and east of the TP [11], is also an ideal geographical area for investigating species’ refuge locations and migration routes.
Species in these areas are useful for biologists studying evolutionary events [12], and there have been various reports on the evolution of species in the region. Based on the evidence from both ancient vegetation and systematic geography, two main models have been proposed to describe the refugia and postglacial population dynamics of plant species in subtropical China [13]. One is the glacial contraction and postglacial expansion model (CE model) [14], which asserts that species experienced sharp contraction during glacial periods and quick expansion after glacial periods. For example, reconstruction of the palaeontological community showed that the subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in China retreated c. 1000 km to the south during the last glacial maximum (LGM, c. 0.021 − 0.018 Ma), while large-scale expansion occurred in the northern high-latitude area after that period [14, 15], which provided direct evidence supporting the CE model. In addition, comparative analysis revealed that southern populations usually had greater genetic diversity than northern populations, possibly resulting from the greater accumulation of ancient and private alleles during the longer evolutionary history compared with that of the northern population [16, 17]. The other is the in situ survival model (ISS model), which considers that there are many shelters during glacial periods and relatively few local expansion events after glacial periods [18,19,20]. Most of the evidence supporting this model mainly comes from research on deciduous broad-leaved forest plants [6, 13, 21,22,23]. In fact, the CE model ignores the possibility of many ecological niches with similar climate conditions, while the ISS model poorly accounts for migration effects.
In addition, different plant types can have different evolutionary histories. Thus, further studies of population evolutionary histories across the eastern edge of the TP and in subtropical China with new plant types would be valuable for understanding species history. However, few studies have simultaneously considered populations across the two regions [24, 25]. Broad-leaved forest trees have received little attention because there are very few with wide and continuous distributions in the two regions due to large variations in climate, elevation, and landforms [26], while other plant types, such as vines, have not received much attention in phylogeographic research due to their weakened role in forests compared with that of tall, large woody trees. Furthermore, the two regions together account for one-third of China’s land area [27], so it is difficult to simultaneously sample at this large scale due to a shortage of available ex situ conservation genetic resources. In addition, underdeveloped road networks on the eastern edge of the TP due to natural barriers are also an important reason for the few samples collected in the past. With the establishment of living germplasm banks of various woody perennial plants and the improvement of transportation infrastructure, systemically studying evolutionary history by integrating samples from the two regions is becoming feasible.
Akebia trifoliata (three-leaf Akebia) is a woody perennial climbing vine in the family Lardizabalaceae [28]. Various studies have suggested that A. trifoliata has many advantages for elucidating the phylogeography of mainland China. First, according to the records from the Plants for a Future database (www.pfaf.org), it originated in China (https://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx? LatinName = Akebia + trifoliata), although South Korea and Japan also have populations of A. trifoliata [29], and it is continuously distributed from the eastern edge of the TP to the eastern coast of mainland China; therefore, A. trifoliata is a typical species of the region spanning the eastern edge of the TP and subtropical China [28]. In addition, characteristics such as a small genome [30], a relatively short juvenile stage, a large breeding coefficient, cross-pollination and numerous discernible phenotypic traits make A. trifoliata an ideal model plant, especially for perennial woody species [31, 32]. Third, the availability of sufficient wild germplasm from the whole mainland of China [33] is highly advantageous for systemically studying the phylogeography of A. trifoliata. There have been few reports on the genetic diversity of A. trifoliata, but the employed samples were narrow in scope and usually small in size [34]. Therefore, further study of phylogenetic relationships will be valuable for understanding the evolutionary history of A. trifoliata. In the present study, conserved DNA sequences, including those of the maternally inherited chloroplast gene rps16 and the biparentally inherited nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer (ITS), were used to explore the genetic diversity and population structure of A. trifoliata in the region across the eastern edge of the TP and subtropical China. Our objectives were to determine the locations of the main shelters of A. trifoliata, to infer the migration route, and to identify the evolutionary model responsible for the distribution of extant A. trifoliata populations.
Methods
Plant genotypes
A total of 391 genotypes of 61 populations from the A. trifoliata ex situ conservation germplasm bank located at the Chongzhou Research Station of Sichuan Agricultural University [31] were chosen for the study. These genotypes originated from a large geographical area spanning from 99°57′E to 120°11′E and from 24°49′N to 34°42′N in mainland China.
DNA extraction, amplification and sequencing
Total genomic DNA was extracted according to the previously published CTAB method. The rps16 chloroplast gene and ITS were selected as maternally and biparentally inherited molecular markers, respectively [35, 36]. The corresponding primers were synthesized and then subjected to polymerase chain reaction (PCR) according to a previously described reaction system and program [31]. Sequencing reactions were conducted with corresponding forward and reverse primers commercially provided by Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China).
Population genetic diversity and genetic differentiation
For the rps16 and ITS data, the sequence was first manually edited using BioEdit 7.0.1 [37] and then aligned with MAFFT 7.2.2 software [38]. Finally, the conserved region of the aligned sequence was extracted using Gblock v 0.91b [39]. We used DnaSP 5.10 software to calculate genetic information statistics, including haplotype number, Hd and π, of the conserved sequence [40]. In addition, we used PERMUT 2.0 [41] to calculate the hT and hS between populations with 1,000 repeats and to assess the difference between the GST and NST of distinct populations, excluding populations with sample sizes less than 3. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) and correlation analysis between genetic distance and geographical distance were performed by Arlequin 3.0 [42] and by GenAlEx 6.5 [43], respectively.
Phylogenetic analyses and molecular dating
The haplotype (ITS haplotypes and rps16 haplotypes) network diagram was constructed using PopART 1.7 [44], and a sampling distribution map was constructed using ArcGIS 10.2 [45]. ML trees were reconstructed according to conserved haplotype sequences using PhyloSuite 1.2.2 [46] with the best-fit models (TPM3 + F + I and TIM3 + F + R2 for rps16 and ITS, respectively) produced from the AIC program of ModelFinder software [47], in which Archakebia apetala was used as the outgroup.
The divergence time of the haplotype lineages of A. trifoliata was determined with a secondary calibration method by BEAST 2 [48]. The first step was to determine the crown age of A. trifoliata. Four matK gene sequences of A. trifoliata and 15 matK gene sequences of 15 different species were employed by searching GenBank (Table S2), consisting of six from Lardizabalaceae, five from Menispermaceae, two from Berberidaceae, one from Eupteleaceae and one from Ranunculaceae. In addition, four calibrated time points, Ranzania-Mahonia-Berberis (45.0 Ma) [49], Chasmanthera-Odontocarya (33.9 Ma) [50], Tinospora-Chasmanthera-Odontocarya (55.2 Ma) [51, 52], and Stephania-Menispermum-Chasmanthera-Tinospora-Odontocarya (89.3 Ma) [53], were used. The chronogram of Ranunculales was produced using BEAST2 with the Yule model, an uncorrelated lognormal relaxed clock [54] and the TVM + F + G4 best-fit model selected by the BIC approach in ModelFinder software [47]. For each BEAST2 analysis, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) was run for 1 × 108 generations, sampling once every 1000 generations, and the first 10% of the samples were removed as burn-in. The sufficiency and convergence of the sampling results were checked by Tracer 1.7.2.
In the second step, chronograms of A. trifoliata haplotypes were further derived using a method similar to that used to date intraspecific nodes, in which the root nodes were corrected by using the above estimated crown group age (median value) of A. trifoliata in the first step, and A. apetala was still an outgroup. GTR + F + G4 and F81 + F + G4 were the best-fit models for the ITS and rps16 haplotypes, respectively. A. apetala was still an outgroup.
Demographic history
The values of Tajima’s [55], Fu and Li’s [56] and Fu and Li’s [57] of all sequences were calculated by DnaSP 5.10 software [40], and the observed paired difference pattern (mismatch distribution) was also analysed using the same software with a constant population size model. Both the sum of squared deviations (SSD) and Harpending’s raggedness index (HRag) were analysed by Arlequin 3.0, and we further analysed population expansion only when the corresponding p value was greater than the 0.05 level. The expansion time was calculated using the formula T = τ/2µkg, where µ, k and g refer to the replacement rate (s s− 1 yr− 1) of each site in the ITS every year, the length of the sequence and the age of the first reproduction, respectively. In this study, a mean value of µ for shrubs and herbal plants ranging from 3.46 to 8.69 × 10− 9 (s s− 1 yr− 1) [58] was used as the µ value of the A. trifoliata ITS sequence. The g value of A. trifoliata is usually three years.
Ancestral area reconstructions
Based on the chronograms of the ITS and rps16 haplotypes, the geographical diversification of A. trifoliata was further reconstructed via Bayesian binary MCMC (BBM) analysis in RASP 4.x [59]. During this process, the distribution of A. trifoliata was divided into four regions according to natural geographical boundaries: A (the eastern Tibetan Plateau), B (central northern China), C (central China) and D (eastern China). MCMC trees were constructed with 5000 randomly chosen trees from all post-burn-in trees from BEAST2 analysis. The parameters of the BBM analyses were set as follows: null for the root distribution, 10 chains for optimization with the fixed JC model for 5 × 105 cycles, the posterior distribution sampled every 100 generations, and four regions for the permitted maximum value.
Results
Sequence variation, genetic diversity, and genetic structure
The lengths of the rps16 and ITS sequences obtained from 391 samples of A. trifoliata were 744 bp with a 33.9% G + C content and 695 bp with a 63% G + C content, respectively. We first identified a total of 22 rps16 haplotypes (C1 ∼ C22) and 75 ITS haplotypes (R1 ∼ R75) according to 59 and 88 polymorphic sites in the rps16 and ITS sequences, respectively. ITS sequences had greater haplotype diversity (Hd) (0.86), nucleotide diversity (π) (3.07 × 10− 3), total genetic diversity (hT) (0.88), average genetic diversity (hS) (0.31) and fixation index (FST) (0.64) values among the 61 small populations than did rps16 sequences (Table S1). In addition, we also found that for the ITS dataset, the GST (0.44) was lower than the NST (0.68), while for the rps16 dataset, the GST (0.44) was larger than the NST (0.31), which indicated that the ITS dataset had an obvious phylogeographic structure, while the rps16 dataset did not.
In fact, the results of the Mantel test suggested that for the rps16 dataset, there was no obvious correlation between genetic distance and geographical distance among populations (R2 = 0.0005, p = 0.17) (Fig. 1a), while for the ITS dataset, the relationship was significant at the p = 0.05 level, although R2 was only 0.21 (Fig. 1b). Furthermore, the AMOVA results showed that the variation in the ITS region mainly occurred among populations, while that in the rps16 region mainly occurred within populations (Table 1).
Network and distribution of haplotypes
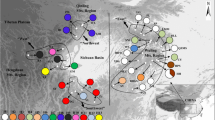
The TCS network diagrams of the ITS haplotypes exhibited a multiple star-shaped radial pattern, and the haplotypes clearly corresponded to distinct geographical regions (Fig. 2a). In contrast, the distribution of rps16 haplotypes showed a single star-shaped radial pattern (Fig. 2b), which indicated that there was no geographical structure. According to the geographical distribution of the ITS haplotypes (Fig. 2a), no haplotype was common to all regions, while 63 (84%) of the haplotypes were region specific. Among the 63 region-specific haplotypes, 12 (R3 ∼ R10, R33, R73 ∼ R75), 13 (R27 ∼ R32, R36, R38, R39, R41, R67 ∼ R69), 28 (R14 ∼ R16, R21 ∼ R26, R42 ∼ R56, R63 ∼ R66) and 10 (R18 ∼ R20, R57 ∼ R60, R70 ∼ R72) haplotypes were specific to the A, B, C and D regions, respectively (Fig. 2c and Table S1). We further found that 26 haplotypes, including 12 of the A region-specific haplotypes, 13 of the B region-specific haplotypes and one (R11) haplotype common to the A, B and C regions, were derived from R2 by one to ten steps of mutation; 28 of the C region-specific haplotypes were derived from R12 by one to four steps of mutation; and 10 of the D region-specific haplotypes were derived from R61 by one to three steps of mutation. Obviously, R2 is the ancestral haplotype because of its large proportion and wide distribution.
(a) TCS-derived network of genealogical relationships between the 75 ITS haplotypes. (b) TCS-derived network of genealogical relationships between the 22 haplotypes (rps16). The circle size of the two network diagrams is proportional to the sample size of each haplotype. Black filled dots indicate missing haplotypes. The haplotypes from the four regions are represented by four different colours. The dashes on the straight line represent the number of abrupt steps. (c) Sampling distribution map of 61 populations of Akebia trifoliata. Red, yellow, green and blue represent the different geographical locations of A (the eastern Tibetan Plateau), B (central northern China), C (central China) and D (eastern China), respectively
Moreover, we detected 22 rps16 haplotypes, 16 (72.7%) of which were region specific, while three (13.6%) rps16 haplotypes (C1, C4 and C6) were common to all four lineages. We also found that C1 produced four B region-specific rps16 haplotypes (C10-C12 and C21), two C region-specific rps16 haplotypes (C8 and C9) and one D region-specific rps16 haplotype (C19) via one mutation step and directly produced two A region-specific rps16 haplotypes (C2 and C22) via multiple steps of mutation. Moreover, all rps16 haplotypes of the D region were simply derived from C1 by only one mutation step. The results suggested that C1 was the ancestral rps16 haplotype. Overall, the distributions of both the ITS and rps16 haplotypes revealed obvious ITS sequence divergence, while the rps16 sequence lacked such divergence across geographical regions.
ML phylogenetic tree of A. trifoliata haplotypes
The maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of all 75 A. trifoliata ITS haplotypes with A. apetala as an outgroup had three major branches: I, II and III (Fig. 3a). Branch I mainly consisted of all (12) specific haplotypes from the A region, most (nine out of 13) specific haplotypes from the B region, four specific haplotypes (R21, R22, R46 and R56) from the C region and five other common haplotypes (R1, R2, R11, R35 and R40) in two or three regions; branch II mainly consisted of all (10) specific haplotypes from the D region, two specific haplotypes (R32 and R67) from the B region, four specific haplotypes (R45, R65, R50 and R51) from the C region and one common haplotype (R61) in the B and D regions; and branch III mainly consisted of almost all (24 out of 28) specific haplotypes from the C region, two B region-specific haplotypes (R27 and R31) and six other common haplotypes (R12, R13, R17, R34, R37 and R62) in two or three regions. In contrast, there was no obvious branch on the ML phylogenetic tree of all 22 A. trifoliata rps16 haplotypes (Fig. 3b), in which the haplotypes were evenly distributed among the four regions.
Maximum likelihood tree for A. trifoliata based on (a) ITS haplotypes and (b)rps16 haplotypes; Archakebia apetala was the outgroup. Bootstrap probabilities are indicated on the branches. Red, yellow, green and blue in colour represent A (the eastern Tibetan Plateau), B (central northern China), C (central China) and D (eastern China) region-specific haplotypes, while others in grey represent haplotypes from two to four different regions. I, II and III are the three major branches of the ITS haplotype ML tree (a)
Divergence time of A. trifoliata haplotypes
The BEAST2-derived matK chronogram showed that the crown group age of A. trifoliata was 2.06 Ma (Fig. 4), and when it was used as a root prior, the coalescence times of 75 haplotypes (node f in Fig. 5a) and 22 haplotypes (node g in Fig. 5b) were 2.82 Ma and 2.12 Ma, respectively.
BEAST2-derived chronogram of Ranunculales based on matK sequences with calibration points denoted by nodes a-d. The blue bars indicate the 95% HPD credibility intervals for node ages (in Myr ago, Ma). The age estimate (Ma) (mean 95% highest posterior density: HPD) for each node is shown beside the nodes. The posterior probability values are labelled on each branch in turn
BEAST2-derived chronograms of ITS haplotypes (a) and rps16 haplotypes (b) calibrated by the crown time of Akebia trifoliata. The age estimate (Ma) (HPD) for each node is shown beside the node. The regions with a greater than 95% posterior probability are indicated by thick branches. The red, yellow, green and blue branches represent haplotypes from the A (the eastern Tibetan Plateau), B (central Northern China), C (central China) and D (eastern China) regions, respectively, and the other black branches except those of the outgroup represent haplotypes from two to four different regions
In the ITS chronogram, four nodes (f1-f4) covered 37 haplotypes: 12 specific to the A region, 10 specific to the B region, seven specific to the C region and eight non-region specific; node f5 covered 38 haplotypes: three specific to the B region, 21 specific to the C region, 10 specific to the D region, and four that were non-region specific.
The coalescence time of the five nodes varied from 2.27 Ma to 1.25 Ma, which falls within the early Pleistocene (2.58–0.78 Ma) (Fig. 5a), during which the divergence of all 22 ITS haplotypes and five rps16 haplotypes occurred. However, the remaining 53 (70.67%) ITS haplotypes and 17 (77.27%) rps16 haplotypes originated during the middle Pleistocene (0.78 − 0.12 Ma).
Demographic history
All neutrality test values, including Tajima’s D, Fu and Li’s D and Fu and Li’s F, of all ITS and rps16 datasets in the whole population and all four regions were negative, although those of the rps16 haplotypes were not significant in the D region (Table 2). The mismatch distribution of the ITS haplotypes was unimodal in the A and D regions (Fig. 6), while that of the rps16 dataset was peak free in the whole population and each region (Fig. S1). The results of the fit test using the sudden expansion model showed that the SSD (0.0267) and HRag (0.322) values of the ITS haplotypes in the whole population were not significant at the p = 0.05 level, which suggested the occurrence of one expansion event (possibly 150 Ka). However, the rps16 haplotypes of A. trifoliata mainly experienced balancing selection throughout their evolutionary history because there were no detectable SSD or HRag values in the whole population or any of the four geographical regions.
Ancestral area reconstructions
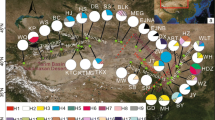
According to the topology of the reconstructed ancestral area of the ITS region, the marginal probabilities of the A region at h1, h2, h4 and h8 were 0.64, 0.45, 0.52 and 0.77, respectively (Fig. 7a). The populations of other regions, especially the C region, colonized from the A region. The marginal probability of B at h3 was the largest (0.25), which suggested that region C was also partly colonized by the population from region B. The marginal probabilities of C at h5, h6 and h7 were 0.97, 0.97 and 0.95, respectively, indicating that the population of the D region was largely derived from the C region.
Ancestral area reconstructions based on the Bayesian binary Markov chain Monte Carlo (BBM) method performed in the RASP using the BEAST2-derived chronogram of Akebia trifoliata based on (a) ITS and (b)rps16 haplotypes (see Fig. 5a and b). The circle at each node represents the marginal probability of each alternative ancestral region derived from the BBM analysis. The results are based on a maximum area of four. Inferred dispersal events are indicated by blue arrows. (c) Distribution area map of Akebia trifoliata: A (the eastern Tibetan Plateau), B (central northern China), C (central China) and D (eastern China). (d) Speculative diagram of expansion or propagation events in Akebia trifoliata, with bold solid lines representing the main expansion or propagation events
Similarly, the marginal probability of the A region at i1 was 0.97 in the rps16 topology (Fig. 7b), also suggesting that the A region was the ancient distribution area of A. trifoliata. The value (0.40) at i2 indicated that the populations of both the B and C regions could have colonized from the A region. The marginal probability of the C region at i4 was 0.39, suggesting that the population of the D region mainly colonized the C region. We also noticed that the information at both i3 and i5 was confusing, which could result from the unclear pedigree of rps16.
BBM analyses showed the potential for many seed dispersal events (see the blue arrow in Fig. 7), with only the absence of directional dispersal events from the population in the D region to the A region. Generally, the species migration route was from the ancestral distribution A region simultaneously to the B and C regions, then from the B region to the C region, and finally from the C region to the D region (Fig. 7c and d).
Discussion
The characteristics of the population and conserved DNA sequences help elucidate the phylogeographic structure of A. trifoliata
Genetic diversity parameters such as the hT, Hd and π of conserved DNA sequences provide the best evidence for elucidating the phylogeographic structure of a given species or a larger classification unit, such as genus, family and even order [40]; however, population characteristics, including geographical distribution, breeding system and effective size, also have an important influence on genetic diversity [60]. Whether we can accurately detect phylogeographic structure is largely dependent on two key factors: population characteristics and DNA sequence conservation.
Previous studies demonstrated that A. trifoliata originated in China and exhibited a constrained continuous distribution from the eastern edge of the TP to the eastern coast of mainland China and even to South Korea and Japan [28, 29]. In addition, the biological characteristics [30] and availability of sufficient germplasms via the ex situ living conservation method [31] have been reported. The 391 genotypes employed in this study originated from various places in mainland China, and there was a small geographic interval between adjacent samples (Fig. 2c), providing an ideal population for deducing the evolutionary history of species, especially climbing vine plants, in mainland China.
Molecular markers based on conserved DNA elements, including maternal chloroplast and biparental nuclear genomic markers, have been widely employed to investigate population genetic diversity. In this study, a previously reported chloroplast gene (rps16) and a nuclear DNA marker (ITS) were used to determine the genetic diversity of the A. trifoliata population [35, 36]. We first checked 22 and 75 haplotypes from 59 to 88 polymorphic sites in the rps16 and ITS sequences, respectively (Table S1). Based on the haplotypes, the genetic diversity (hT=0.881, π × 10− 3=3.07) of A. trifoliata at the nuclear DNA level (Table S1) was greater than that of Zingiber officinale [61], Pinus attenuata [62] and Antirrhinum charidemi [63]. We found that the genetic diversity (hT=0.313, π × 10− 3=0.90) of the A. trifoliata population at the chloroplast sequence level was lower than that at the nuclear DNA level (Table S1), which could result from the low variation rate of the chloroplast compared with the nuclear DNA sequence [64]. This also provides a reasonable explanation for why the ITS and rps16 sequences are used to determine the genetic structure of intraspecific and interspecific populations, respectively [63, 65]. To obtain more information on different DNA sequences, we simultaneously used rps16 and ITS markers to determine genetic diversity in the present study, which would be beneficial for elucidating phylogeographic structure.
A. trifoliata populations exhibited clear phylogeographic structure
Usually, molecular variation [66], the relationship between GGD and GD [67], the number of regional private haplotypes [19] and the relative sizes of GST and NST [20] are important information for describing population structure. First, we found that there was large molecular variation in the ITS sequence among different regional populations, while the variation in the rps16 sequence was small (Table 1). Second, we also found a significant positive relationship between GGD and GD based on the ITS sequence, while there was no obvious relationship between them based on the rps16 sequence (Fig. 1); in this study, the weak relationship could partly result from uneven samples from various regions (Table S1). Third, some regional private haplotypes of both ITS and rps16 existed in each region (Fig. 2a and b; Table S1) and even on each branch of the ML tree (Fig. 3), possibly related to the high differentiation of different regions (Table 1). Finally, for the ITS sequence, the GST (0.437) was obviously lower than the NST (0.677). Taken together, these findings suggest that there was no obvious geographical structure at the chloroplast DNA level, possibly resulting from different inheritance modes [64], dispersal strategies [68] and slow variation rates because of their high conservation [65]; however, the clear phylogeographic structure of the A. trifoliata population at the nuclear DNA level is beyond all reasonable doubt.
Multiple historical ice shelters could have affected the current distribution status of A. trifoliata
Studies have shown that plant populations around glacial habitats usually have high genetic diversity and many private alleles or haplotypes [17, 69]. Here, we found that many haplotypes of both ITS and rps16 were region-specific (Figs. 2a and b and 3), which indicated that there were multiple refuge regions. According to the number of haplotypes, Hd and π, three putative main refuge regions (the Qinba Mountains, Nanling Mountains and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau) can be suggested.
First, the Qinba Mountains could be the main refugia region of A. trifoliata because the populations, including Bazhong from the A region and both Ankang and Xian from the B region, had many ITS haplotypes, high Hd and large π, and they commonly showed the ancestral haplotype R2 (Fig. 2a), which was also well supported by the high polymorphism of A. trifoliata resources previously reported in the region [34]. Second, the Nanling Mountains, as representative mountains in the subtropical region and one of the major biodiversity hotspots in China [70], could also be a refuge region because the Hezhou, Yongzhou, Guilin, and Ganzhou populations from the C or D region had similarly many haplotypes and high Hd and π values (Fig. 2b), and R12 was their common haplotype. Various studies have suggested that the Nanling Mountains provide shelter for many plants [71], such as Castanopsis eyrie [72] and Loropetalum chinense [73], which supports the Nanling Mountains as a historically important refuge region for A. trifoliata. Third, the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau is still a refuge region because of the very high π values for the rps16 sequence in addition to the ITS sequence in both the Bijie and Zunyi populations from the C region [74, 75].
At present, the CE and ISS models represent two prevalent views about the contraction and expansion of plant species in the subtropical region of China during the ice age cycle [14, 20]. Unfortunately, the CE model largely ignores the existence of many similar ecological niches, while the ISS model overlooks the effects of migration on species distributions. In this study, among the 61 populations, 55 had a sample size larger than two, of which 26 populations had an Hd value of ITS greater than 0.6 (Table S1). Of these 26 populations, 12 were geographically close to the three main refuge regions, while 14 were far from the main refuge regions, which clearly showed that the three main refuge regions (the Qinba Mountains, Nanling Mountains and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau) harboured many independent, small ice shelters. In addition, many haplotypes, including 53 ITS haplotypes and 17 rps16 haplotypes, originated during the middle Pleistocene (0.78 − 0.12 Ma), while the other haplotypes were produced before this stage, which indicated that whole or partial population expansion occurred in the past. The results of the neutrality test and ITS mismatch distribution analysis clearly demonstrated that population expansion events occurred in at least the A and D regions. The view of three main refuge regions with some independent, small ice shelters provides a reasonable explanation for the continuous and wide distribution of A. trifoliata in many regions of mainland China.
Putative migration route and differentiation events of A. trifoliata
Molecular dating can provide information about the differentiation time of conserved DNA sequences, which is helpful for inferring population differentiation processes [76]. In this study, molecular dating revealed that the differentiation times of the common ITS and rps16 haplotypes in A. trifoliata were 2.82 Ma and 2.12 Ma, respectively (Fig. 5a and b), and both occurred during the period spanning the late Pliocene to early Pleistocene. During this period, the third uplift of the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau [77], the Asian monsoon [78] and the Asian drought [79] gradually intensified, causing habitat fragmentation and species differentiation [80]. For example, the Hainan Island population of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum differentiated at 2.78 Ma [22]. Second, most (72.2%) of the haplotypes of A. trifoliata differentiated in the middle Pleistocene (0.78 − 0.12 Ma), which is similar to the haplotype differentiation time of Sargentodoxa cuneata in this region [76], but the remaining 27.8% of the A. trifoliata haplotypes differentiated before this period (Fig. 5a and b). Hence, the putative divergence times of the common ITS and rps16 haplotypes in A. trifoliata could be reasonable. In addition, both the frequency and distribution of haplotypes (Fig. 2a and b) suggested that region A was the ancestral region because of the high frequency and wide distribution of the ancestral haplotypes R2 and C1 (Table S1).
The results of further BBM analysis revealed the putative migration route (Fig. 7c and d), and in this model, the route from the ancestral A region simultaneously from both the B and C regions, from the B region to the C region, and then from the C region to the D region was the main route of A. trifoliata migration, and the corresponding reverse route could be a minor migration route. In fact, this hypothesis of species migration off the Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau [81] also agreed well with the putative migration model. In addition, we also found minor migration from the ancestral A region to the D region, while there was no reverse route. Finally, migration from west to east could be a major direction, while reciprocal migration between the south and the north could be minor, which could have resulted from climate oscillation in the past [17]. The main route and direction of A. trifoliata migration could be closely related to its natural spread through west-east-flowing rivers, especially the Yangtze River [31], animals such as birds [82] and even commercial action [83]. Moreover, incomplete coverage of glaciers during this process [84] may also explain the widespread differentiation of A. trifoliata.
The last concern was the origin of the A. trifoliata distributed in Korea and Japan, and in our opinion, these A. trifoliata possibly migrated from the D region of mainland China, which could be resolved by a future study with samples from these two countries.
Conclusions
Both conserved DNA sequences and continuously and widely distributed large populations provide a valuable opportunity to elucidate the evolutionary history of a given species. In this study, a maternally inherited chloroplast gene (rps16) and a biparentally inherited nuclear ITS sequence were simultaneously employed to assess the phylogeographic structure of A. trifoliata populations in the region across the QTP eastern edge and subtropical China, where more than 90% of publications about the species originated. Our results suggested that A. trifoliata originated on the eastern edge of the QTP and then migrated eastwards to the east coast of mainland China, even to Korea and Japan, and that multiple ice shelters in the Qinba Mountains, Nanling Mountains and Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau region supported its proliferation throughout subtropical China. Overall, the unique origin, long-distance migration, high intraspecific divergence, multiple ice shelters and regional expansion of A. trifoliata resulted in its continuous and wide distribution.
Data availability
All the original DNA data, including the rps16 and ITS sequences of A. trifoliata used in this study, were uploaded to the GenBase of the Chinese National Genomics Data Center (NGDC) under the accession numbers C_AA025186.1 ∼ C_AA025576.1 for the ITS dataset and C_AA024795.1 ∼ C_AA025185.1 for the rps16 dataset.
Abbreviations
- A. trifoliata :
-
Akebia trifoliata
- BBM:
-
Bayesian binary MCMC
- CE model:
-
Contraction and postglacial expansion model
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- ISS model:
-
In situ survival model
- ITS:
-
Internal transcribed spacer
- LGM:
-
Last glacial maximum
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- QTP:
-
Qinghai‒Tibet Plateau
- rps16 :
-
Ribosomal protein S16
- SSD:
-
Sum of squared deviations
- TP:
-
Tibetan Plateau
References
Zhang D, Fengquan L, Jianmin B. Eco-environmental effects of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau uplift during the Quaternary in China. Environ Geol. 2000;39:1352–8.
Liu Y, Dietrich CH, Wei C. Genetic divergence, population differentiation and phylogeography of the cicada Subpsaltria Yangi based on molecular and acoustic data: an example of the early stage of speciation? BMC Evol Biol. 2019;19:1–17.
Wang LY, Ikeda H, Liu TL, Wang YJ, Liu JQ. Repeated range expansion and glacial endurance of Potentilla glabra (Rosaceae) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J Integr Plant Biol. 2009;51:698–706.
Yu H, Deane DC, Zhang Y, Li S, Miao S, Xie G, et al. Integrating multiple indices of geobiodiversity reveals a series of regional species-rich areas worthy of conservation in the region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Biol Conserv. 2021;261:109238.
Patricelli D, Sielezniew M, Ponikwicka-Tyszko D, Ratkiewicz M, Bonelli S, Barbero F, et al. Contrasting genetic structure of rear edge and continuous range populations of a parasitic butterfly infected by Wolbachia. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:1–14.
Liu JQ, Sun YS, Ge XJ, Gao LM, Qiu YX. Phylogeographic studies of plants in China: advances in the past and directions in the future. J Syst Evol. 2012;50:267–75.
Chen S, Wu G, Zhang D, Gao Q, Duan Y, Zhang F, et al. Potential refugium on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau revealed by the chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the alpine species Metagentiana striata (Gentianaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2008;157:125–40.
Xiong Q, Halmy MWA, Dakhil MA, Pandey B, Zhang F, Zhang L, et al. Concealed truth: modeling reveals unique quaternary distribution dynamics and refugia of four related endemic keystone Abies taxa on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol Evol. 2019;9:14295–316.
Zhang Q, Chiang TY, George M, Liu JQ, Abbott RJ. Phylogeography of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau endemic Juniperus przewalskii (Cupressaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence variation. Mol Ecol. 2005;14:3513–24.
Sierra-Almeida A, Cavieres LA, Bravo LA. Warmer temperatures affect the in situ freezing resistance of the Antarctic vascular plants. Front Plant Sci. 2018;9:1456.
Chen XD, Yang J, Feng L, Zhou T, Zhang H, Li HM, et al. Phylogeography and population dynamics of an endemic oak (Quercus Fabri Hance) in subtropical China revealed by molecular data and ecological niche modeling. Tree Genet Genomes. 2020;16:1–13.
Ye JW, Li DZ. Diversification of east Asian subtropical evergreen broadleaved forests over the last 8 million years. Ecol Evol. 2022;12:e9451.
Qiu YX, Fu CX, Comes HP. Plant molecular phylogeography in China and adjacent regions: tracing the genetic imprints of quaternary climate and environmental change in the world’s most diverse temperate flora. Mol Phylogenetics Evol. 2011;59:225–44.
Qian H, Ricklefs RE. Palaeovegetation (communications arising): diversity of temperate plants in East Asia. Nature. 2001;413:130–1.
Ni J, Yu G, Harrison SP, Prentice IC. Palaeovegetation in China during the late quaternary: biome reconstructions based on a global scheme of plant functional types. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol. 2010;289:44–61.
Tiffney BH, Manchester SR. The use of geological and paleontological evidence in evaluating plant phylogeographic hypotheses in the Northern Hemisphere Tertiary. Int J Plant Sci. 2001;162:S3–17.
Hewitt G. The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature. 2000;405:907–13.
Bai WN, Wang WT, Zhang DY. Contrasts between the phylogeographic patterns of chloroplast and nuclear DNA highlight a role for pollen-mediated gene flow in preventing population divergence in an east Asian temperate tree. Mol Phylogenetics Evol. 2014;81:37–48.
Chen SC, Zhang L, Zeng J, Shi F, Yang H, Mao YR, et al. Geographic variation of chloroplast DNA in Platycarya strobilacea (Juglandaceae). J Syst Evol. 2012;50:374–85.
Xu J, Deng M, Jiang XL, Westwood M, Song YG, Turkington R. Phylogeography of Quercus glauca (Fagaceae), a dominant tree of east Asian subtropical evergreen forests, based on three chloroplast DNA interspace sequences. Tree Genet Genomes. 2015;11:1–17.
Cun YZ, Wang XQ. Phylogeography and evolution of three closely related species of Tsuga (hemlock) from subtropical eastern Asia: further insights into speciation of conifers. J Biogeogr. 2015;42:315–27.
Wang YH, Jiang WM, Comes HP, Hu FS, Qiu YX, Fu CX. Molecular phylogeography and ecological niche modelling of a widespread herbaceous climber, Tetrastigma hemsleyanum (Vitaceae): insights into Plio–pleistocene range dynamics of evergreen forest in subtropical China. New Phytol. 2015;206:852–67.
Zhang ZY, Wu R, Wang Q, Zhang ZR, López-Pujol J, Fan DM, et al. Comparative phylogeography of two sympatric beeches in subtropical China: species‐specific geographic mosaic of lineages. Ecol Evol. 2013;3:4461–72.
Wang Z, Zhong C, Li D, Yan C, Yao X, Li Z. Cytotype distribution and chloroplast phylogeography of the Actinidia chinensis complex. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21:1–15.
Zhang YH, Volis S, Sun H. Chloroplast phylogeny and phylogeography of stellera chamaejasme on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in adjacent regions. Mol Phylogenetics Evol. 2010;57:1162–72.
Ren Z, Zuo Y, Ma Y, Zhang M, Smith L, Yang L, et al. The natural environmental factors influencing the spatial distribution of marathon event: a case study from China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:2238.
Song YC. The essential characteristics and main types of the broad-leaved evergreen forest in China. Phytocoenologia. 1988;16:105–23.
Li L, Yao X, Zhong C, Chen X, Huang H. Akebia: a potential new fruit crop in China. HortScience. 2010;45:4–10.
Huang P, Zang F, Li C, Lin F, Zang D, Li B, et al. The Akebia genus as a novel forest crop: a review of its genetic resources, nutritional components, biosynthesis, and biological studies. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:936571.
Zhong S, Li B, Chen W, Wang L, Guan J, Wang Q, et al. The chromosome-level genome of Akebia trifoliata as an important resource to study plant evolution and environmental adaptation in the cretaceous. Plant J. 2022;112:1316–30.
Guan J, Fu P, Wang X, Yu X, Zhong S, Chen W, et al. Assessment of the breeding potential of a set of genotypes selected from a natural population of Akebia trifoliata (three–leaf Akebia). Horticulturae. 2022;8:116.
Matsumoto D, Shimizu S, Shimazaki A, Ito K, Taira S. Effects of self-pollen contamination in artificial pollination on fruit set of ‘Fuji Murasaki’ Akebia Trifoliata. Hortic J. 2022;91:431–6.
Yang H, Chen W, Fu P, Zhong S, Guan J, Luo P. Developmental stages of Akebia trifoliata fruit based on volume. Hortic Sci Technol. 2021;39:823–31.
Zhang Z, Yang Q, Niu Y, Zhang Y, Dong S, Zhang W, et al. Diversity analysis and establishment of core collection among Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. In Qinba mountain area of China using ISSR and SRAP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2021;68:1085–102.
Kitaoka F, Kakiuchi N, Long C, Itoga M, Yoshimatsu H, Mitsue A, et al. Difference of ITS sequences of Akebia plants growing in various parts of Japan. J Nat Med. 2009;63:368–74.
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J. Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol. 1991;17:1105–9.
Hall TA. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1999;41:95–8.
Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:772–80.
Castresana J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol. 2000;17:540–52.
Librado P, Rozas J. DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1451–2.
Pons O, Petit RJ. Measwring and testing genetic differentiation with ordered versus unordered alleles. Genetics. 1996;144:1237–45.
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform. 2005;1:117693430500100003.
Peakall R, Smouse PE. GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes. 2006;6:288–95.
Leigh JW, Bryant D. POPART: full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol Evol. 2015;6:1110–6.
Johnston K, Ver Hoef JM, Krivoruchko K, Lucas N. Using ArcGIS geostatistical analyst (GIS by ESRI company, 380 New York Street, Redlands, CA 92373); Esri 2001.
Zhang D, Gao F, Jakovlić I, Zou H, Zhang J, Li WX, et al. PhyloSuite: an integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol Ecol Resour. 2020;20:348–55.
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TK, Von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods. 2017;14:587–9.
Bouckaert R, Heled J, Kühnert D, Vaughan T, Wu CH, Xie D, et al. BEAST 2: a software platform for bayesian evolutionary analysis. Plos Comput Biol. 2014;10:e1003537.
Manchester SR. Biogeographical relationships of north American tertiary floras. Ann Mo Bot Gard. 1999;86:472–522.
Jacques FMB, Guo SX. Palaeoskapha Sichuanensis gen. et sp. nov. (Menispermaceae) from the Eocene relu formation in Western Sichuan, West China. J Syst Evol. 2007;45:576.
Jacques FMB, De Franceschi D. Endocarps of Menispermaceae from Le Quesnoy outcrop (sparnacian facies, lower eocene, Paris Basin). Rev Palaeobot Palynol. 2005;135:61–70.
Reid EM, Chandler MEJ. The London clay flora. London: British Museum; 1933.
Knobloch E. Fossile früchte und samen Aus Der Flyschzone Der Mährischen Karpaten. Sb Geol Ved Paleontol. 1971;13:7–43.
Drummond AJ, Nicholls GK, Rodrigo AG, Solomon W. Estimating mutation parameters, population history and genealogy simultaneously from temporally spaced sequence data. Genetics. 2002;161:1307–20.
Tajima F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics. 1989;123:585–95.
Fu YX, Li WH. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations. Genetics. 1993;133:693–709.
Fu YX. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics. 1997;147:915–25.
Richardson JE, Pennington RT, Pennington TD, Hollingsworth PM. Rapid diversification of a species-rich genus of neotropical rain forest trees. Science. 2001;293:2242–5.
Yu Y, Blair C, He X. RASP 4: ancestral state reconstruction tool for multiple genes and characters. Mol Biol Evol. 2020;37:604–6.
Wu J, Wang W, Deng D, Zhang K, Peng S, Xu X, et al. Genetic diversity and phylogeography of Daphnia similoides sinensis located in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Ecol Evol. 2019;9:4362–72.
Nayak S, Naik PK, Acharya L, Mukherjee AK, Panda PC, Das P. Assessment of genetic diversity among 16 promising cultivars of ginger using cytological and molecular markers. Z Naturforsch C. 2005;60:485–92.
Wu J, Krutovskii KV, Strauss SH. Nuclear DNA diversity, population differentiation, and phylogenetic relationships in the California closed-cone pines based on RAPD and allozyme markers. Genome. 1999;42:893–908.
Forrest A, Escudero M, Heuertz M, Wilson Y, Cano E, Vargas P. Testing the hypothesis of low genetic diversity and population structure in narrow endemic species: the endangered Antirrhinum charidemi (Plantaginaceae). Bot J Linn Soc. 2017;183:260–70.
Álvarez I, Wendel JF. Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol Phylogenetics Evol. 2003;29:417–34.
Downie SR, Katz-Downie DS. Phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast rps16 intron sequences reveals relationships within the woody southern African Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae. Can J Bot. 1999;77:1120–35.
Li Q, Guo X, Niu J, Duojie D, Li X, Opgenoorth L, et al. Molecular phylogeography and evolutionary history of the endemic species Corydalis Hendersonii (Papaveraceae) on the Tibetan Plateau inferred from chloroplast DNA and ITS sequence variation. Front Plant Sci. 2020;11:436.
Lu M, Zhang H, An H. Chloroplast DNA-based genetic variation of Rosa roxburghii in Southwest China: phylogeography and conservation implications. Hortic Plant J. 2021;7:286–94.
Caron H, Molino JF, Sabatier D, Léger P, Chaumeil P, Scotti-Saintagne C, et al. Chloroplast DNA variation in a hyperdiverse tropical tree community. Ecol Evol. 2019;9:4897–905.
Comes HP, Kadereit JW. The effect of quaternary climatic changes on plant distribution and evolution. Trends Plant Sci. 1998;3:432–8.
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Da Fonseca GA, Kent J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature. 2000;403:853–8.
Tian S, Kou Y, Zhang Z, Yuan L, Li D, López-Pujol J, et al. Phylogeography of Eomecon Chionantha in subtropical China: the dual roles of the Nanling Mountains as a glacial refugium and a dispersal corridor. BMC Evol Biol. 2018;18:20.
Denk T, Grimm GW. The biogeographic history of beech trees. Rev Palaeobot Palynol. 2009;158:83–100.
Gong W, Liu W, Gu L, Kaneko S, Koch MA, Zhang D. From glacial refugia to wide distribution range: demographic expansion of Loropetalum chinense (Hamamelidaceae) in Chinese subtropical evergreen broadleaved forest. Org Divers Evol. 2016;16:23–38.
Chen JM, Liu F, Gituru WR, Wang QF. Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the Chinese endemic alpine quillwort Isoetes Hypsophila Hand.-Mazz. (Isoetaceae). Int J Plant Sci. 2008;169:792–8.
Fang F, Sun H, Zhao Q, Lin C, Sun Y, Gao W, et al. Patterns of diversity, areas of endemism, and multiple glacial refuges for freshwater crabs of the genus Sinopotamon in China (Decapoda: Brachyura: Potamidae). PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e53143.
Tian S, Lei SQ, Hu W, Deng LL, Li B, Meng QL, et al. Repeated range expansions and inter-/postglacial recolonization routes of Sargentodoxa Cuneata (Oliv.) Rehd. Et Wils. (Lardizabalaceae) in subtropical China revealed by chloroplast phylogeography. Mol Phylogenetics Evol. 2015;85:238–46.
Zhou S, Wang X, Wang J, Xu L. A preliminary study on timing of the oldest pleistocene glaciation in Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Quat Int. 2006;154:44–51.
Kou Y, Cheng S, Tian S, Li B, Fan D, Chen Y, et al. The antiquity of Cyclocarya paliurus (Juglandaceae) provides new insights into the evolution of relict plants in subtropical China since the late early miocene. J Biogeogr. 2016;43:351–60.
Dao K, Chen J, Jin P, Dong C, Yang Y, Xu X, et al. A new material of Lindera (Lauraceae) of the late Pliocene from Tengchong, Yunnan and the Genus’ biogeography significance. Acta Geol Sin Ed. 2013;87:690–706.
Donoghue MJ, Bell CD, Li J. Phylogenetic patterns in Northern Hemisphere plant geography. Int J Plant Sci. 2001;162:S41–52.
Jia DR, Abbott RJ, Liu TL, Mao KS, Bartish IV, Liu JQ. Out of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: evidence for the origin and dispersal of eurasian temperate plants from a phylogeographic study of Hippophaë rhamnoides (Elaeagnaceae). New Phytol. 2012;194:1123–33.
Takahashi K, Kamitani T. Effect of dispersal capacity on forest plant migration at a landscape scale. J Ecol. 2004;92:778–85.
Sauer JD. Plant migration: the dynamics of geographic patterning in seed plant species. California: University of California Press; 1988.
Tang CQ, Matsui T, Ohashi H, Dong YF, Momohara A, Herrando-Moraira S, et al. Identifying long-term stable refugia for relict plant species in East Asia. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4488.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to Huazhong You for providing help in managing the wild germplasms.
Funding
This study was supported by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (24QYCX0256, 24NSFSC7732, 2022ZHXC0044, 2022ZHXC0002 and 2022ZHXC0028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QD designed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. YZ, SZ, QZ, H(ao)Y, H(uai)Y, and XY collected the samples and performed the experiments. FT and CC managed the project and revised the manuscript. PL conceived the study and procured funding. All the authors read and agreed with the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1:
Locations of populations of Akebia trifoliata sampled, sample sizes(n), the cpDNA haplotype and ITS haplotype frequency, haplotype distribution type, haplotype (gene) diversity (Hd) and nucleotide diversity (π × 10 − 3) of each population
Supplementary Table S2:
The taxa of Ranunculales used for estimating the crown group age of Akebia trifoliata
Supplementary Figure 1:
Mismatch distribution analyses of the five rps16 clades consisting of both four regional populations and the whole population, in which the observed mismatch frequencies and best-fit curves of the sudden expansion model are shown
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhong, S. et al. Conserved DNA sequence analysis reveals the phylogeography and evolutionary events of Akebia trifoliata in the region across the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau and subtropical China. BMC Ecol Evo 24, 52 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-024-02243-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-024-02243-0