Abstract
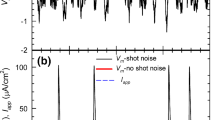
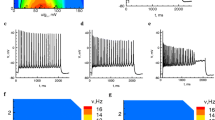
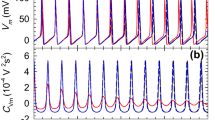
THE experimental results of voltage noise analyses for the potassium channel system in frog nerve membranes are inconsistent with the theoretical expectations: the measured noise intensity should decrease at positive membrane potentials, where an increase is found1,2. The theories3–7 are based upon the empirical Hodgkin–Huxley equations, and therefore “…cover only the short term responses of the membrane…”8. Our noise experiments were made in the stationary state. A recent report suggests Hodgkin–Huxley kinetics for potassium noise currents measured earlier after changes in membrane potential9. Taken together these results suggest, however, that the potassium channel system changes its behaviour in time with respect to its noise pattern, which implies the occurrence of structural changes in time. We show here that the potassium channel system does indeed change structurally during long duration voltage steps.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siebenga, E., de Goede, J., and Verveen, A. A., Pflügers Arch., 351, 25–34 (1974).
Van den Berg, R. J., de Goede, J., and Verveen, A. A., Pflügers Arch., 360, 17–23 (1975).
Stevens, C. F., Biophys. J., 12, 1028–1047 (1972).
Hill, T. L., and Chen, Y., Biophys. J., 12, 948–959 (1972).
Verveen, A. A., DeFelice, L. J., Progr. Biophys. molec. Biol., 28, 189–265 (1974).
Conti, F., and Wanke, E., Q., Rev. Biophys., 8, 4, 451–506 (1975).
Chen, Y., Biophys. J., 16, 965–971 (1976).
Hodgkin, A. L., and Huxley, A. F., J. Physiol., Lond., 117, 500–544 (1952).
Begenisich, T., and Stevens, C. F., Biophys. J., 15, 843–846 (1975).
Dodge, F., thesis, The Rockefeller Institute, New York (1963).
Frankenhaeuser, B., J. Physiol., Lond., 169, 424–430 (1963).
Schwarz, J. R., and Vogel, W., Pflügers Arch., 330, 61–73 (1971).
Frankenhaeuser, B., J. Physiol., Lond., 135, 550–559 (1957).
Van den Berg, R. J., Abstracts 17th Dutch Federative Meeting, Amsterdam (1976).
Van der Ziel, A., Noise: Sources, Characterization and Measurement (Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 1970).
Siebenga, E., Meyer, A. W. A., and Verveen, A. A., Pflügers Arch., 341, 87–96 (1973).
Hille, B., J. gen. Physiol., 50, 1287–1302 (1967).
Koppenhöfer, E., Pflügers Arch., 293, 34–55 (1967).
Fishman, H. M., Moore, L. E., and Poussart, D. J. M., J. membr. Biol., 24, 305–328 (1975).
Conti, F., DeFelice, L. J., and Wanke, E., J. Physiol., Lond., 248, 45–82 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VAN DEN BERG, R., SIEBENGA, E. & BRUIN, G. Potassium ion noise currents and inactivation in voltage-clamped node of Ranvier. Nature 265, 177–179 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/265177a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/265177a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Relationship in Pacemaker Neurons Between the Long-Term Correlations of Membrane Voltage Fluctuations and the Corresponding Duration of the Inter-Spike Interval
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2017)
-
Noise analysis of the K+ current through the apical membrane ofNecturus gallbladder
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1981)
-
Noise analysis of the K+ current through the apical membrane ofNecturus gallbladder
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1981)
-
Burst noise: Electrical breakdowns in myelinated nerve membrane
Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism (1980)
-
Differences between K channels in motor and sensory nerve fibres of the frog as revealed by fluctuation analysis
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1980)