Summary
1. The experiments were carried out on single Ranvier nodes of Xenopus laevis. The influence of tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA) on the membrane currents was studied under voltage clamp conditions. The node under investigation was continuously superfused with the test solutions.
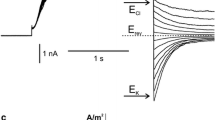
2. 5 mM TEA reduced the delayed currents (i.e. the potassium outward current I K and the non-specific current I p) to almost zero. The effect was fully reversible. The peak sodium current I Na and the leakage current I L were barely influenced.
3. The delayed potassium inward current seen with high external potassium concentrations was also eliminated by 5 mM TEA.
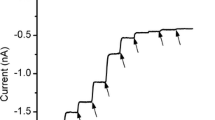
4. 0.3 mM TEA reduced I K to about two thirds of its normal value and delayed the onset of the potassium outward current. The time constant determining the change of potassium permeability was reversibly increased by a factor of 1.7.
5. The effect of TEA on the kinetics of the sodium system was comparatively small. 5 mM TEA altered the time constants for the turning on and for the inactivation of the sodium permeability by a factor of 0.9 and 1.4 respectively.
6. It was concluded that TEA mainly affects the delayed permeability increase. The described effects of TEA on the membrane currents qualitatively explain the prolongation of the action potential in TEA-treated nodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Armstrong, C. M., and L. Binstock: Anomalous rectification in the squid axon injected with tetraethylammonium chloride. J. gen. Physiol. 48, 859–872 (1965).
Blaustein, M. P., and D. E. Goldman: Competitive action of calcium and procaine on lobster axon. A study of the mechanism of action of certain local anesthetics. J. gen. Physiol. 49, 1043–1062 (1966).
Cole, K. S., and J. W. Moore: Potassium ion current in the squid axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys. J. 1, 1–14 (1960).
Dettbarn, W. D., H. Higman, P. Rosenberg, and D. Nachmansohn: Rapid and reversible block of electrical activity by powerful marine toxins. Science 132, 300 (1960).
Dodge, F. A.: A study of ionic permeability changes underlying excitation in myelinated nerve fibers of the frog. Thesis. The Rockefeller Institute, New York 1963.
—, and B. Frankenhaeuser: Membrane currents in isolated frog nerve fibre under voltage clamp conditions. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 143, 76–90 (1958).
Fitzhugh, R.: Thresholds and plateaus in the Hodgkin-Huxley nerve equations. J. gen. Physiol. 43, 867–896 (1960).
Frankenhaeuser, B.: Steady-state inactivation of sodium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 148, 671–676 (1959).
— Quantitative description of sodium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 151, 491–501 (1960).
— Delayed currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis investigated with voltage clamp technique. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 40–45 (1962a).
— Instantaneous potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 46–53 (1962b).
— Potassium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 54–61 (1962c).
— A quantitative description of potassium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 424–430 (1963a).
— Inactivation of the sodium-carrying mechanism in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus leavis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 445–451 (1963b).
—, and A. L. Hodgkin: The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 137, 218–244 (1957).
—, and A. F. Huxley: The action potential in the myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 171, 302–315 (1964).
—, and L. E. Moore: The effect of temperature on the sodium and potassium permeability changes in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 431–437 (1963a).
— The specificity of the initial current in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Voltage clamp experiments. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 438–444 (1963b).
Goldman, D. E.: Potential, impedance, and rectification in membranes. J. gen. Physiol. 27, 37–60 (1943).
Hagiwara, S., and N. Saito: Voltage-current relations in nerve cell membrane of Onchidium verruculatum. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 148, 161–179 (1959).
Hille, B.: Common mode of action of three agents that decrease the transient change in sodium permeability in nerves. Nature (Lond.) 210, 1220–1222 (1966).
Hodgkin, A. L., and A. F. Huxley: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 117, 500–544 (1952).
Kilb, H., u. R. Stämpfli: Ein Vielweghahn zur raschen Umschaltung auf verschiedene Durchströmungsflüssigkeiten. Helv. physiol. pharmacol. Acta 13, 191–194 (1955).
Koppenhöfer, E.: TEA-Wirkung auf die Ionenströme markhaltiger Nervenfasern von Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 289, R 9 (1966).
Meissner, H. P.: Das Verhalten der Schnürringsmembran unter dem Einfluß starker depolarisierender Impulse. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 283, 213–221 (1965).
Moore, J. W.: Voltage clamp studies in internally perfused axons. J. gen. Physiol. 48, suppl. 11–17 (1965).
Nakajima, S.: Analysis of K-inactivation and TEA action in the supramedullar cells of puffer. J. gen. Physiol. 49, 629–640 (1966).
Nakamura, Y., S. Nakajima, and H. Grundfest: Selective block of Na-activation in voltage clamped squid giant axon and eel electroplaque by Tetrodotoxin. Biol. Bull. 127, 382 (1964).
Narahashi, T., J. W. Moore, and W. R. Scott: Tetrodotoxin blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axons. J. gen. Physiol. 47, 965–974 (1964).
Schmidt, H.: Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf das Membranpotential und den Membranwiderstand von Bündeln markhaltiger Nervenfasern. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 282, 351–361 (1965).
—, u. R. Stämpfli: Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf den einzelnen Ranvierschen Schnürring. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 287, 311–325 (1966).
Shanes, A. M.: Electrochemical aspects of physiological and pharmacological action in excitable cells. Pharmacol. Rev. 10, 59–273 (1958).
Takata, M., J. W. Moore, C. Y. Kao, and F. A. Fuhrman: Blockage of sodium conductance increase in lobster giant axon by Tarichatoxin (Tetrodotoxin). J. gen. Physiol. 49, 977–987 (1966).
Tasaki, I.: Demonstration of two stable states of the nerve membrane in potassiumrich media. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 148, 306–331 (1959).
—, and S. Hagiwara: Demonstration of two stable potential states in the squid giant axon under tetraethylammonium chloride. J. gen. Physiol. 40, 859–885 (1957).
Taylor, R. E.: Effect of procaine on electrical properties of squid axon membrane. Amer. J. Physiol. 196, 1071–1078 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koppenhöfer, E. Die Wirkung von Tetraäthylammoniumchlorid auf die Membranströme Ranvierscher Schnürringe von Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Archiv 293, 34–55 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362660
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00362660