Abstract
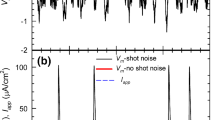
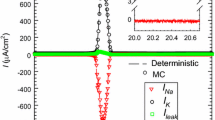
The role played by ion channel noise and ion shot noise around the threshold conditions for spiking activity in biological membranes is studied by means of a stochastic model based on the Hodgkin–Huxley equations, considering membrane voltage-dependent gating channels for sodium and potassium cations, and leakage channels. Ion channel noise, that is, the noise linked to the random opening and closing of the ion channels, is included by means of Langevin sources. Ion shot noise, associated with the random passage of ions through the cell membrane, is considered by using the Gillespie’s method, in terms of the probabilities for different ions to cross the membrane. The threshold for spiking activity is reached by applying increasing values of an external excitation Iapp in a large membrane patch S, for which the strength of channel noise is insufficient for the onset of spikes in the absence of Iapp. On the other hand, since by decreasing S the strength of both noise sources increases, spiking activity is also achieved for small enough values of S when Iapp = 0. The noise behavior of this biological system is analyzed in terms of the autocorrelation function and the spectral density of the membrane voltage fluctuations. Even if ion shot noise is typically considered as negligible when other electrical sources of neural noise are taken into account, the results indicate that, particularly around the onset of instabilities, the signature of shot noise, by the interplay with channel noise, is evident in the spectral density of the membrane voltage fluctuations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisenberg, B.: Ion channels as devices. J. Comput. Electron. 2, 245–249 (2003)
Ha, S.D., Ramanathan, S.: Adaptive oxide electronics: a review. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 071101 (2011)
Kaneko, Y., Nishitani, Y., Ueda, M.: Ferroelectric artificial synapses for recognition of a multishaded image. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 61, 2827–2833 (2014)
Prezioso, M., Merrikh-Bayat, F., Hoskins, B.D., Adam, G.C., Likharev, K.K., Strukov, D.B.: Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature 512, 61–64 (2015)
Romeo, A., Dimonte, A., Tarabella, G., D'Angelo, P., Erokhin, V., Iannotta, S.: A bio-inspired memory device based on interfacing physarum polycephalum with an organic semiconductor. APL Mater. 3, 014909 (2015)
Faisal, A.A., Selen, L.P.J., Wolpert, D.M.: Noise in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. 9, 292–303 (2008)
Kilinc, D., Demir, A.: Noise in neuronal and electronic circuits: a general modeling framework and non-Monte Carlo simulation techniques. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 11, 958–974 (2017)
Kilinc, D., Demir, A.: Spike timing precision of neuronal circuits. J. Comput. Neurosci. 44, 341–362 (2018)
Chein, W.R., Midtgaard, J., Shepherd, G.M.: Forward and backward propagation of dendritic impulses and their synaptic control in mitral cells. Science 278, 463–467 (1997)
Chua, L.: Memristor, Hodgkin–Huxley and edge of chaos. IOP Nanotechnol. 24, 383001 (2013)
Hodgkin, L.A., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–544 (1952)
Steinmetz, P.N., Manwani, A., Koch, C.: Subthreshold voltage noise due to channel fluctuations in active neuronal membranes. J. Comput. Neurosci. 9, 113–148 (2000)
Jacobson, G.A., Diba, K., Yaron-Jakoubovitch, A., Oz, Y., Koch, C., Segev, I., Yaron, Y.: Subthreshold voltage noise of rat neocortical pyramidal neurones. J. Physiol. 564, 145–160 (2005)
Linaro, D., Storace, M., Giugliano, M.: Accurate and fast simulation of channel noise in conductance-based model neurons by diffusion approximation. Plos Comput. Biol. 7, e1001102 (2011)
Schmid, G., Goychuk, I., Hänggi, P.: Stochastic resonance as a collective property of ion channel assemblies. Europhys. Lett. 56, 22–28 (2001)
Vasallo, B.G., Pardo-Galán, F., Mateos, J., González, T., Hedayat, S., Hoel, V., Cappy, A.: Stochastic model for action potential simulation including ion shot noise. J. Comput. Electron. 16, 419–430 (2017)
Vasallo, B.G., Mateos, J., González, T.: Ion shot noise in Hodgkin and Huxley neurons. J. Comput. Electron. 17, 1790–1796 (2018)
Vasallo, B.G., Mateos, J., González, T.: Stochastic model for ion shot noise in Hodgkin and Huxley neurons. In: IEEE Proceedings of International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF), 2017. DOI: 10.1109/icnf.2017.7985975 (2017)
Vasallo, B.G., Mateos, J., González, T.: Interplay between channel and shot noise in subthreshold voltage fluctuations of neural membranes. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Noise and Fluctuations (ICNF), 2019. DOI: 10.5075/epfl-ICLAB-ICNF-269293 (2019)
Schmid, G., Goychuk, I., Hänggi, P.: Channel noise and synchronization in excitable membranes. Phys. A 325, 165–175 (2003)
Schmid, G., Goychuk, I., Hänggi, P., Zeng, S., Jung, P.: Effect of channel block on the spiking activity of excitable membranes in a stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley model. Phys. Biol. 1, 61–66 (2004)
Adair, R.K.: Noise and stochastic resonance in voltage-gated ion channels. PNAS 100, 12099–12104 (2003)
Faisal, A.A., White, J.A., Laughlin, S.B.: Ion-channel noise places limits on the miniaturization of the brain’s wiring. Curr. Biol. 15, 1143–1149 (2005)
Gillespie, D.T.: A general method for numerically simulating the stochastic time evolutions of coupled chemical reactions. J. Comput. Phys. 22, 403–434 (1976)
Gillespie, D.T.: Exact stochastic simulation of coupled chemical reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 81, 2340–2361 (1977)
Brunetti, R., Affinito, F., Jacoboni, C., Piccinini, E., Rudan, M.: Shot noise in single open ion channels: a computational approach based on atomistic simulations. J. Comput. Electron. 6, 391–394 (2007)
Piccinini, E., Affinito, F., Brunetti, R., Jacoboni, C., Rudan, M.: Computational analysis of current and noise properties of a single open ion channel. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 3, 248–255 (2007)
Kuang, S., Wang, J., Zeng, T.: Intrinsic rhythmic fluctuation of membrane voltage evoked by membrane noise in the Hodgkin–Huxley system. Acta Phys. Pol. A 117, 435–438 (2010)
García-Pérez, O., Alimi, Y., Song, A., Íñiguez-de-la-Torre, I., Pérez, S., Mateos, J., González, T.: Experimental assessment of anomalous low-frequency noise increase at the onset of Gunn oscillations in InGaAs planar diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 105(1–4), 113502 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasallo, B.G., Mateos, J. & González, T. Interplay between channel and shot noise at the onset of spiking activity in neural membranes. J Comput Electron 19, 792–799 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01482-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-020-01482-w