Abstract
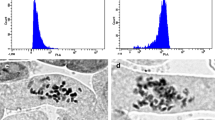
Chromosome and morphological variations of embryogenic calli-derived plants of gynogenic haploid, diploid, triploid and tetraploid asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) were investigated. Artificial tetraploids were produced using colchicine treatment of seeds of diploid cultivar, ‘Poultom’. ‘Haidel’ (2X) was crossed with the artificial tetraploids, from which one gynogenic haploid, one diploid, 6 triploid, 3 mixoploids were obtained. Embryogenic calli were first obtained from crown buds, subsequently induced to form somatic embryos, and after 30 days, induced to germinate. Chromosome variation in embryogenic calli-derived plants increased with increasing duration of subculture, particularly when low ploidy levels of plants such as haploid and diploid were used as explants. Approximately 80% of haploid-derived plants showed morphological variations such as dwarfness and abnormal morphological characteristics, although no differences were observed in cladodes and stem characteristics between other polyploid-derived plants and their parents. The data presented here would supply important fundamental information for commercial mass-propagation using somatic embryogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Araki, H., H. Shimazaki, Y. Hirata, T. Oridate, T. Harada & T. Yakuwa, 1992. Chromosome number variation of callus cells and regenerated plants in Asparagus officinalisL., Plant Tissue Culture Lett 9 (3): 169-175.
Dan, Y. & C.T. Stephens, 1991. Studies of protoplast culture types and plant regeneration from callus-derived protoplasts of Asparagus officinalisL. cv. Lucullus 234. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 27: 321-331.
Dore, C., 1995. Asparagus anther culture and field trials of dihaploids and F1 hybrids. In: Y.P.S. Bajaj (Ed.), Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestory, Vol. 12. Haploids in Crop Improvement I, pp. 322-345. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Elmer, W.H., T. Ball, M. Volokita, C.T. Stephens & K.C. Sink, 1989. Plant regeneration from callus-derived protoplasts of asparagus. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 114 (6): 1019-1024.
Falavigna, A., M.G. Tacconi & P.E. Casali, 1985. Asparagus breeding through anther culture technique for asparagus breeding in Italy. Proc 6th Int Asparagus Symp, Guelph, pp. 31-40.
Feng, X.R. & D.J. Wolyn, 1991. High frequency production of haploid embryos in asparagus anther culture. Plant Cell Rep 10: 574-578.
Feng, X.R. & D.J. Wolyn, 1993a. Genotype, temperature, and sampling date affect embryogenesis in asparagus anther culture. Hort Sci 28 (3): 216-217.
Feng, X.R. & D.J. Wolyn, 1993b. Development of haploid asparagus embryos from liquid cultures of anther-derived calli is enhanced by ancymidol. Plant Cell Rep 12: 281-285.
Harada, H., 1973. Differentiation of shoots, roots and somatic embryos in asparagus tissue culture. Proc. of 4th Eucarpia Congr. on asparagus breeding held at CHRA, INRA, Versailles, France, pp. 163-170.
Kohmura, H., S. Chokyu & Y. Ikeda, 1991. Micropropagation of Asparagus officinalisL. through somatic embryogenesis. 3. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from spear of field crop. Bull Hiroshima Pref Agr Exp Sta 54: 33-40.
Kohmura, H., S. Chokyu & T. Harada, 1994. An effective micropropagation system using embryogenic calli induced from bud clusters in Asparagus officinalisL. J Jpn Soc Hort Sci 63 (1): 51-59.
Kunitake, H. & M. Mii, 1990. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from protoplasts of asparagus (Asparagus officinalisL.). Plant Cell Rep 8: 706-710.
Kunitake, H., T. Nakashima, K. Mori & M. Tanaka, 1996. Production of interspecific somatic hybrid plant between Asparagus officinalisL. and A. macowaniithrough electrofusion. Plant Sci 116: 213-222.
Kunitake, H., T. Nakashima, K. Mori & M. Tanaka, 1997. Normalization of asparagus somatic embryogenesis using a maltose-containing medium. J Plant Physiol 150: 458-461.
Kuwahara, K., T. Nakashima & M. Tanaka, 1989. The development of utilization method of embryoid and shoot primordia. 1. Induction of somatic embryogenesis from immature embryo. Bull Saga Pref Agri Exp Stn 25: 59-64.
Levi, A. & K.C. Sink, 1991. Somatic embryogenesis in asparagus: The role of explant and growth regulators. Plant Cell Rep 9: 14-16.
Levi, A. & K.C. Sink, 1992. Asparagus somatic embryos: Production in suspension culture and conversion to plantlets on solidified medium as influenced by carbohydrate regime. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 31: 115-122.
Li, B. & D.J. Wolyn, 1995. The effects of ancymidol, abscisic acid, uniconazole and paclobutrazol on somatic embryogenesis of asparagus. Plant Cell Reports 14: 529-533.
Mukhopadhyay, S. & Y. Desjardins, 1994. Plant regeneration from protoplast-derived somatic embryos of Asparagus officinalisL. J Plant Physiol 144: 94-99.
Murashige, T. & F. Skoog, 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473-497.
Nakashima, T., H. Kunitake, K. Mori & M. Tanaka, 1993. The development of utilization method of embryoid and shoot primordia. 5. In vitromass-propagation of asparagus (Asparagus officinalisL.). Bull Saga Pref Agri Exp Stn 28: 12-29.
Odake, Y., A. Udagawa, H. Saga & M. Mii, 1993. Somatic embryogenesis of tetraploid plants from internodal segments of a diploid cultivar of Asparagus officinalisL. grown in liquid culture. Plant Sci 94: 173-177.
Parrot, W.A., S.A. Merkle & E.G. Williams, 1991. Somatic embryogenesis: Potential for use in propagation and gene transfer system. Adv Methods Plant Biotechnol 4: 158-200.
Reuther, G., 1977. Adventitious organ formation and somatic embryogenesis in callus of asparagus and iris and its possible application. Acta Hort 78: 217-224.
Saito, T., S. Nishizawa & S. Nishimura, 1991. Improved culture conditions for somatic embryogenesis from Asparagus officinalisL. using an aseptic ventilative filter. Plant Cell Rep 10: 230-234.
Torrey, D. & L. Peirce, 1983. Production of haploid plantlets from anthers of asparagus. Hort Sci 18 (4): 569.
Tsay, H.S. & J.Y. Hsu, 1985. The breeding of all-male asparagus plants by means of anther culture. Proc 6th Int Asparagus Symp, Guelph, pp. 22-30.
Vasil, I.K., 1988. Progress in the regeneration and genetic manipulation of cereal crops. Bio/Technology 6: 397-402.
Wilmar, C. & M. Hellendoorn, 1968. Growth and morphogenesis of asparagus cells cultured in vitro. Nature 217: 369-370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunitake, H., Nakashima, T., Mori, K. et al. Somaclonal and chromosomal effects of genotype, ploidy and culture duration in Asparagus officinalis L.. Euphytica 102, 309–316 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018371004374
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018371004374