Abstract
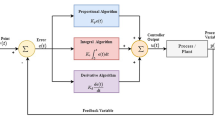
This paper investigates the application of conventional and neural adaptive control schemes to Gas Metal Arc (GMA) welding. The goal is to produce welds of high quality and strength. This can be achieved through proper on-line control of the geometrical and thermal characteristics of the process. The welding process is variant in time and strongly nonlinear, and is subject to many defects due to improper regulation of parameters like arc voltage and current, or travel speed of the torch. Adaptive control is thus naturally a very good candidate for the regulation of the geometrical and thermal characteristics of the welding process. Here four adaptive control techniques are reviewed and tested, namely: model reference adaptive control (MRAC), pseudogradient adaptive control (PAC), multivariable self-tuning adaptive control (STC), and neural adaptive control (NAC). Extensive numerical results are provided, together with a discussion of the relative merits and limitations of the above techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hunt, V. D.: Industrial Robotics Handbook, Industrial Press Inc., New York, 1983.
Tzafestas, S. G. (ed.): Intelligent Robotic Systems, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1991.
Tzafestas, S. G. (ed.): Applied Control: Current Trends and Modern Methodologies, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1993.
Tzafestas, S. G. and Verbruggen, H. B. (eds): Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Decision Making, Control and Automation, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht/Boston, 1995.
Doumanidis, C. and Hardt, D. E.: A model for in-process control of thermal properties during welding, ASME J. Dynamic Syst. Meas. and Control 111(1989), 40–50.
Doumanidis, C. and Hardt, D. E.: Multivariable adaptive control of thermal properties during welding, ASME J. Dynamic Syst. Meas. and Control 113(1991), 82–92.
Doumanidis, C.: Multiplexed and distributed control of automated welding, IEEE Control Systems Magaz., August (1994), 13–24.
Nishar, D. V., Schiano, J. L., Perkins, W. R., and Weber, R. A.: Adaptive control of temperature in arc welding, IEEE Control Systems Magaz., August (1994), 4–12.
Henderson, D. E., Kokotovitch, P. V., Schiano, J. L., and Rhode, D. S.: Adaptive control of an arc welding process, in: Proc. 1991 American Control Conference, Vol. 1, 1991, pp. 723–728.
Rhode, D. S. and Kokotovitch, P. V.: Parameter convergence conditions independent of plant order, in: Proc. 1989 American Control Conference, Vol. 1, 1989, pp. 981–986.
Lightbody, G. and Irwin, G. W.: Direct neural model reference adaptive control, IEE Proc.–Control Theory and Appl. 142(1995), 31–43.
Slotine, J. and Welping, L.: Applied Nonlinear Control, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 1991.
Narendra, K. S. and Lin, Y.: Stable adaptive control, IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, AC-25(3) (June 1980).
Suzuki, A., Hardt, D. E., and Valavani, L.: Application of adaptive control theory to GTA weld geometry regulation, ASME J. Dynamic Syst. Meas. and Control 113(1991), 93–103.
Song, J. B. and Hardt, D. E.: Dynamic modeling and adaptive control of the gas metal arc welding process, ASME J. Dynamic Syst. Meas. and Control 116(1994), 405–413.
Haykin, S.: Adaptive Filter Theory, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, 1991.
Tzafestas, S. G.: Digital PID and self-tuning control, in: S. G. Tzafestas (ed.), Applied Digital Control, North Holland, Amsterdam, 1985, pp. 1–49.
Haykin, S: Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, Macmillan College Publishing Company, Toronto, 1994.
Miller, W. T., Sutton, R. S., and Werbos, P. J.: Neural Networks for Control, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1990.
Tzafestas, S. G.: Neural networks in robot control, in: Artificial Intelligence in Industrial Decision Making, Control and Automation, Kluwer, Dordrecht/Boston, 1995, pp. 327–387.
Kawato, M. Furukawa, K., and Suzuki, R.: A Hierarchical neural network model for control and learning of voluntary movement, Biol. Cybern. 57(1987), 169–185.
Kawato, M., Uno, Y., Isobe, M., and Suzuki, R.: A Hierarchical neural network model for voluntary movement with application to robotics, IEEE Control Systems Magaz., April (1988), 8–16.
Ramaswamy, K., Cook, G. E., Andersen, K., and Karsai, G.: Neural networks in GTA weld modeling and control, in: Proc. American Control Conference, Vol. 1, 1989, pp. 62–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzafestas, S.G., Rigatos, G.G. & Kyriannakis, E.J. Geometry and Thermal Regulation of GMA Welding via Conventional and Neural Adaptive Control. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems 19, 153–186 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007968630038
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007968630038