Abstract
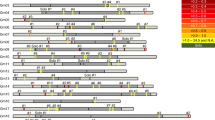
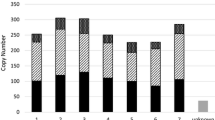
The BARE-1 retrotransposon is a major, active component of the genome of barley (Hordeum vulgareL.) and other Hordeum species. Copia-like in its organization, it consists of 1.8-kb long terminal repeats bounding an internal domain of 5275bp which encodes a predicted polyprotein of 1301 residues. The polyprotein contains the key residues, structural motifs, and conserved regions associated with retroviral and retrotransposon GAG, aspartic proteinase, integrase, reverse transcriptase, and RNaseH polypeptides. BARE-1 is actively transcribed and translated. As part of our effort to understand the evolution and function of BARE-1, we have examined its copy number and localization. Full-length members of the BARE-1 family constitute 2.8% of the barley genome. Globally, they are dispersed throughout the genome, excepting the centromeric, telomeric, and NOR regions. Locally, BARE-1 occurs more commonly in repetitive DNA than in coding regions, forming clusters of nested insertions. Both barley and other Hordeum genomes contain a high proportion of BARE-1 solo LTRs. New techniques have been developed which exploit the insertion site polymorphism generated by -1 integration to produce molecular markers for breeding, biodiversity, and mapping applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennetzen, J.L., 1996. The contributions of retroelements to plant genome organization, function and evolution. Trends Microb. 4: 347–353.
Bevan, M., I. Brancroft, E. Bent, K. Love, H. Goodman et al., 1998. Analysis of 1.9 Mb of contiguous sequence from chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 391: 485–488.
Boeke, J.D. & V.G. Corces, 1989. Transcription and reverse transcription of retrotransposons. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 43: 403–434.
Boeke, J.D. & K.B. Chapman, 1991. Retrotransposition mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 3: 502–507.
Chavanne, F., D.X. Zhang, M.F. Liaud & R. Cerff, 1998. Structure and evolution of Cyclops: a novel giant retrotransposon of the Ty3/Gypsy family highly amplified in pea and other legume species. Plant Mol. Biol. 37: 363–375.
Chen, M., P. SanMiguel & J.L. Bennetzen, 1998. Sequence organization and conservation in sh2/a1-homologous regions of sorghum and rice. Genetics 148: 435–443.
Day, A.M., M. Schimer-Rahire, M.R. Kuchka, S.P. Mayfield & J.D. Rochaix, 1988. A transposon with an unusual arrangement of long terminal repeats in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 7: 1917–1927.
Deragon, J.M., B.S. Landry, T. Pelissier, S. Tutois, S. Tourmente & G. Picard, 1994. An analysis of retroposition in plants of SINEs from Brassica napus. J. Mol. Evol. 39: 378–386.
Ellis, T.H.N., S.J. Poyser, M.R. Knox, A.V. Vershinin & M.J. Ambrose, 1998. Polymorphism of insertion sites of Ty1-copia class retrotransposons and its use for linkage and diversity analysis in pea. Mol. Gen. Genet. 260: 9–19.
Faustinella, F., H. Kwon, F. Serrano, J.W. Belmont, C.T. Caskey et al., 1994. A new family of murine retroviral vectors with extended multiple cloning sites for gene insertion. Hum. Gene Ther. 5: 307–312.
Flavell, A.J., D.B. Smith & A. Kumar, 1992. Extreme heterogeneity of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in plants. Mol. Gen. Genet. 231: 233–242.
Flavell, A.J., M.R. Knox, S.R. Pearce & T.H.N. Ellis, 1998. Retrotransposon-based insertion polymorphisms (RBIP) for high throughput marker analysis. Plant J. 16: 643–650.
Goff, S.P., 1990. Retroviral reverse transcriptase: synthesis, structure and function. J. Acquire. Immune Defic. Syn. Dr. 3: 817–831.
Grandbastien, M.A., 1992. Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet. 8: 103–108.
Gribbon, B.M., S.R. Pearce, R. Kalendar, A.H. Schulman, L. Paulin, P. Jack, A. Kumar & A.J. Flavell, 1999. Phylogeny and transpositional activity of Ty-copia group retrotransposons in cereal genomes. Mol. Gen. Genet. 261: 883–891.
Heyman, T., B. Agouti, S. Riant, D.X. Wilhelm & M.L. Wilhelm, 1995. Plus-strand DNA synthesis of yeast retrotransposon Ty1 is initiated at two sites: PPT1 next to the 3′ and PPT2 within the pol gene. PPT1 is sufficient for Ty1 transposition. J. Mol. Biol. 253: 291–303.
Hirochika, H., 1993. Activation of tobacco retrotransposons during tissue culture. EMBO J. 12: 2521–2528.
Hirochika, H. & R. Hirochika, 1993. Ty1-copia group retrotransposons as ubiquitous components of plant genomes. Jpn. J. Genet. 68: 35–46.
Hirochika, H., K. Sugimoto, Y. Otsuki, H. Tsugawa & M. Kanda, 1996. Autonomous transposition of the tobacco retrotransposon Tto1 in rice. Plant Cell 8: 725–734.
Jääskeläinen, M., A.H. Mykkänen, T. Arna, C. Vicient, A. Suoniemi, R. Kalendar, H. Savilahti & A.H. Schulman, 1999. Retrotransposon BARE-1: expression of encoded proteins and formation of virus-like particles in barley cells. Plant J. 20: 413–422.
Jordan, I.K. & J.F. McDonald, 1999. Tempo and mode of Ty element evolution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 151: 1341–1351.
Joseph, J.L., J.W. Sentry & D.R. Smyth, 1990. Interspecies distribution of abundant DNA sequences in Lilium. J. Mol. Evol. 30: 146–154.
Kalendar, R., T. Grob, M. Regina, A. Suoniemi & A.H. Schulman, 1999. IRAP and REMAP: Two new retrotransposon-based DNA fingerprinting techniques. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 704–711.
Kankaanpää, J., L. Mannonen & A.H. Schulman, 1996. The genome sizes of Hordeum species show considerable variation. Genome 39: 730–735.
Kim, A., C. Terzian, P. Santamaria, A. Pelisson, N. Prud'homme & A. Bucheton, 1994. Retroviruses in invertebrates: the gypsy retrotransposon is apparently an infectious retrovirus of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1285–1289.
Kim, J.M., S. Vanguri, J.D. Boeke, A. Gabriel & D.F. Voytas, 1998. Transposable elements and genome organization: A comprehensive survey of retrotransposons revealed by the complete Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome sequence. Genome Res. 8: 464–478.
Kumar, A. & J. Bennetzen, 1999. Plant Retrotransposons. Annu. Rev. Genet. 33: 479–532.
Laten, H., A. Majumdar & E.A. Gaucher, 1998. SIRE-1, a copia/Ty1-like retroelement from soybean, encodes a retroviral envelope-like protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 6897–6902.
Lauermann, V., M. Hermankova & J.D. Boeke, 1997. Increased length of long terminal repeats inhibits Ty1 transposition and leads to the formation of tandem multimers. Genetics 145: 911–922.
Lucas, H., F. Feuerbach, K. Kunert, M.-A. Grandbastien & M. Caboche, 1995. RNA-mediated transposition of the tobacco retrotransposon Tnt1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J. 14: 2364–2373.
Lucas, H., G. Moore, G. Murphy & R.B. Flavell, 1992. Inverted repeats in the long-terminal repeats of the wheat retrotransposon Wis2–1A. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9: 716–728.
Manninen, O., R. Kalendar, J. Robinson & A.H. Schulman. Application of BARE-1 retrotransposon markers to map a major resistance gene for net blotch in barley. Submitted.
Manninen, I. & A.H. Schulman, 1993. BARE-1, a copia-like retroelement in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 22: 829–846.
Marillonnet, S. & S.R. Wessler, 1998. Extreme structural heterogeneity among the members of a maize retrotransposon family. Genetics 150: 1245–1256.
Matsuoka, Y. & K. Tsunewaki, 1999. Evolutionary dynamics of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in grass shown by reverse transcriptase domain analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16: 208–217.
Noma, K., R. Nakajima, H. Ohtsubo & E. Ohtsubo, 1997. RIRE1, a retrotransposon from wild rice Oryza australiensis. Genes Genet. Syst. 72: 131–140.
Pearce, S.R., G. Harrison, J.S. Heslop-Harrison, A.J. Flavell & A. Kumar, 1997. Characterization and genomic organisation of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in rye (Secale cereale). Genome 40: 617–625.
Pearce, S.R., G. Harrison, D. Li, J.S. Heslop-Harrison, A. Kumar & A.J. Flavell, 1996. The Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in Vicia species: copy number, sequence heterogeneity and chromosomal localisation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 250: 305–315.
Pearce, SR, C. Stuart-Rogers, M.R. Knox, A. Kumar, T.H.N. Ellis & A.J. Flavell, 1999. Rapid isolation of plant Ty1-copia group retrotransposon LTR sequences for molecular marker studies. Plant J. 19: 711–717.
Pelisson, A., L. Teysset, F. Chalvet, A. Kim, N. Prud'homme, C. Terzian & A. Bucheton, 1997. About the origin of retroviruses and the co-evolution of the gypsy retrovirus with the Drosophila flamenco host gene. Genetica 100: 29–37.
Pimpinelli, S., M. Berloco, L. Fanti, P. Demitri, E. Bonaccorsi et al., 1995. Transposable elements are stable components of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 3804–3808.
Pouteau, S., E. Huttner, M.A. Grandbastien & M. Caboche, 1991. Specific expression of the tobacco Tnt1 retrotransposon in protoplasts. EMBO J. 10: 1911–1918.
Reamon-Buttner, S.M., T. Schmidt & C. Jung, 1999. AFLPs represent highly repetitive sequences in Asparagus officinalis L. Chrom. Res. 7: 297–304.
Reddy, S.J., J.V. Degregori, H. von Melchinger & E. Ruley, 1991. Retrovirus promoter trap vector to induce lacZ gene fusion in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 65: 1507–1515.
Royo, J., N. Nass, D.P. Matton, S. Okamoto, A.E. Clarke & E. Newbigin, 1996. A retrotransposon-like sequence linked to the S-locus of Nicotiana alata is expressed in styles in response to touch. Mol. Gen. Genet. 250: 180–188.
SanMiguel, P., A. Tikhonov, Y.K. Jin, N. Motchoulskaia, D. Zakharov, A. Melake-Berhan, P.S. Springer, K.J. Edwards, M. Lee, Z. Avramova & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Nested retrotransposons in the intergenic regions of the maize genome. Science 274: 765–768.
Schmidt, T., 1999. LINEs, SINEs and repetitive DNA: non-LTR retrotransposons in plant genomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 40: 903–910.
Scortecci, K.C., R. Raina, N.V. Fedoroff & M.A. van Sluys, 1999. Negative effect of the 5′-untranslated leader sequence on Ac transposon promoter expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 40: 935–944.
Shepherd, N.S., Z. Schwarz-Sommer, J. Blumberg vel Spalve, M. Gupta, U. Wienand & H. Saedler, 1984. Similarity of the Cin1 repetitive family of Zea mays to eukaryotic transposable elements. Nature 307: 185–187.
Shimamura, M., H. Yasue, K. Ohshima, H. Abe, H. Kato, T. Kishiro, M. Goto, I. Munechika & N. Okada, 1997. Molecular evidence from retrotransposons that whales form a clade within even-toed ungulates. Nature 388: 666–670.
Suoniemi, A., K. Anamthawat-Jonsson, T. Arna & A.H. Schulman, 1996. Retrotransposon BARE-1 is a major, dispersed component of the barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genome. Plant Mol. Biol. 30: 1321–1329.
Suoniemi, A., A. Narvanto & A.H. Schulman, 1996. The BARE-1 retrotransposon is transcribed in barley from an LTR promoter active in transient assays. Plant Mol. Biol. 31: 295–306.
Suoniemi, A., D. Schmidt & A.H. Schulman, 1997. BARE-1 insertion site preferences and evolutionary conservation of RNA and cDNA processing sites. Genetica 100(1–3): 219–230.
Suoniemi, A., J. Tanskanen, O. Pentikäinen, M.S. Johnson & A.H. Schulman, 1998. The core domain of retrotransposon integrase in Hordeum: predicted structure and evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 15: 1135–1144.
Suoniemi, A., J. Tanskanen & A.H. Schulman, 1998. Gypsy-like retrotransposons are widespread in the plant kingdom. Plant J. 13: 699–705.
Temin, H.W., 1981. Structure, variation and synthesis of retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell 27: 1–3.
VanderWiel, P.L., D.F. Voytas & J.F. Wendel, 1993. Copia-like retrotransposable element evolution in diploid and polyploid cotton (Gossypium L.). J. Mol. Evol. 36: 429–447.
van Gent, D.C., A.M.M. Oude Groeneger & R.H.A. Plasterk, 1992. Mutational analysis of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 9598–9602.
Varmus, H. & P. Brown, 1989. Retroviruses, pp. 53–108 in Mobile DNA, edited by D.E. Berg and M.M. Howe. Am. Soc. Microbiol. Washington, DC.
Vicient, C.M., A. Suoniemi, K. Anamthawat-Jonsson, J. Tanskanen, A. Beharav, E. Nevo & A.H. Schulman, 1999. Retrotransposon BARE-1 and its role in genome evolution in the genus Hordeum. Plant Cell 11: 1769–1784.
Voytas, D.F., M.P. Cummings, A. Koniczny, F.M. Ausubel & S.R. Rodermel, 1992. Copia-like retrotransposons are ubiquitous among plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 7124–7128.
Wang, R.R. & J.Z. Wein, 1995. Variations of two repetitive DNA sequences in several Triticeae genomes revealed by polymerase chain reaction and sequencing. Genome 38: 1221–1229.
Waugh, R., K. McLean, A.J. Flavell, S.R. Pearce, A. Kumar, B.B. Thomas & W. Powell, 1997. Genetic distribution of BARE-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol. Gen. Genet. 253: 687–694.
Wright, D.A. & D.F. Voytas, 1998. Potential retroviruses in plants: Tat1 is related to a group of Arabidopsis thaliana Ty3/gypsy retrotransposons that encode envelope-like proteins. Genetics 149: 703–715.
Xiong, Y. & T.H. Eickbush, 1992. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their novel reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 9: 3353–3362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vicient, C.M., Kalendar, R., Anamthawat-Jónsson, K. et al. Structure, functionality, and evolution of the BARE-1 retrotransposon of barley. Genetica 107, 53–63 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003929913398
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003929913398