Abstract
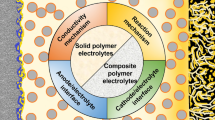
Rechargeable lithium−sulfur (Li−S) batteries are one of the most promising next-generation energy storage systems due to their extremely high energy densities and low cost compared with state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. However, the main obstacles of conventional Li−S batteries arise from the dissolution of lithium polysulfides in organic liquid electrolytes and corresponding safety issues. To address these issues, an effective approach is to replace conventional liquid electrolytes with solid-state electrolytes. In this review, recent progress in the development of solid electrolytes, including solid polymer electrolytes and inorganic glass/ceramic solid electrolytes, along with corresponding all-solid-state Li−S batteries (ASSLSBs) and related interfacial issues at the electrode/electrolyte interface, will be systematically summarized. In addition, the importance of various solid-state lithium ion conductors in ASSLSBs will be discussed followed by detailed presentations on the development of various forms of sulfur-based positive electrode materials (e.g., elemental sulfur, lithium sulfide, metal sulfides, lithium thiophosphates, and lithium polysulfidophosphates) along with key interfacial challenges at the electrode/solid electrolyte interface (cathode/SE and anode/SE). Finally, this review will provide a brief outlook on the future research of ASSLSBs.
Graphical Abstract
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Herbert, D.,Ulam, J.: Electric dry cells and storage batteries. US Patent 3043896A, filed November 24, 1954, and issued July 10, 1962
Manthiram, A., Fu, Y., Chung, S.H., et al.: Rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Chem. Rev. 114, 11751–11787 (2014)
Pang, Q., Liang, X., Kwok, C.Y., et al.: Advances in lithium–sulfur batteries based on multifunctional cathodes and electrolytes. Nat. Energy 1, 16132 (2016)
Mikhaylik, Y.V., Kovalev, I., Schock, R., et al.: High energy rechargeable Li–S cells for EV application. Status, remaining problems and solutions. ECS Trans. 25, 23–34 (2010)
Pan, H., Yang, Y.: Effects of radio-frequency sputtering powers on the microstructures and electrochemical properties of LiCoO2 thin film electrodes. J. Power Sources 189, 633–637 (2009)
Lin, M., Wang, S.H., Gong, Z.L., et al.: A strategy to improve cyclic performance of LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 in a wide voltage region by Ti-doping. J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, A3036–A3040 (2013)
Fu, Y., Su, Y.S., Manthiram, A.: Sulfur–carbon nanocomposite cathodes improved by an amphiphilic block copolymer for high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 6046–6052 (2012)
Ji, X.L., Lee, K.T., Nazar, L.F.: A highly ordered nanostructured carbon-sulphur cathode for lithium-sulphur batteries. Nat. Mater. 8, 500–506 (2009)
Wang, G., Lai, Y., Zhang, Z., et al.: Enhanced rate capability and cycle stability of lithium–sulfur batteries with a bifunctional MCNT@PEG-modified separator. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 7139–7144 (2015)
Ji, X., Nazar, L.F.: Advances in Li–S batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9821–9826 (2010)
Oschatz, M., Thieme, S., Borchardt, L., et al.: A new route for the preparation of mesoporous carbon materials with high performance in lithium–sulphur battery cathodes. Chem. Commun. 49, 5832–5834 (2013)
Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Haibara, M., et al.: Reduced polysulfide shuttle effect by using polyimide separators with ionic liquid-based electrolytes in lithium–sulfur battery. Electrochim. Acta 255, 109–117 (2017)
Li, G.C., Hu, J.J., Li, G.R., et al.: Sulfur/activated-conductive carbon black composites as cathode materials for lithium/sulfur battery. J. Power Sources 240, 598–605 (2013)
Scheers, J., Fantini, S., Johansson, P.: A review of electrolytes for lithium–sulphur batteries. J. Power Sources 255, 204–218 (2014)
Liang, X., Garsuch, A., Nazar, L.F.: Sulfur cathodes based on conductive MXene nanosheets for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 127, 3979–3983 (2015)
Zhang, J., Li, H.Q., Tang, Q., et al.: Improved-performance lithium–sulfur batteries modified by magnetron sputtering. RSC Adv. 6, 114447–114452 (2016)
Pang, Q., Kundu, D., Cuisinier, M., et al.: Surface-enhanced redox chemistry of polysulphides on a metallic and polar host for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat. Commun. 5, 4759 (2014)
Zhang, S., Ueno, K., Dokko, K., et al.: Recent advances in electrolytes for lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500117 (2015)
Ely, T.O., Kamzabek, D., Chakraborty, D., et al.: Lithium–sulfur batteries: state of the art and future directions. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 1783–1814 (2018)
Yue, L., Maa, J., Zhang, J., et al.: All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 5, 139–164 (2016)
Meesala, Y., Jena, A., Chang, H., et al.: Recent advancements in Li-ion conductors for all-solid-state Li-ion batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2, 2734–2751 (2017)
Gao, Z., Sun, H., Fu, L., et al.: Promises, challenges, and recent progress of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Adv. Mater. 30, 1705702 (2018)
Varzi, A., Raccichini, R., Passerini, S., et al.: Challenges and prospects of the role of solid electrolytes in the revitalization of lithium metal batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 17251–17259 (2016)
Bachman, J.C., Muy, S., Grimaud, A., et al.: Inorganic solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: mechanisms and properties governing ion conduction. Chem. Rev. 116, 140–162 (2016)
Yu, X., Manthiram, A.: Electrode-electrolyte interfaces in lithium–sulfur batteries with liquid or inorganic solid electrolytes. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 2653–2660 (2017)
Manthiram, A., Yu, X., Wang, S.: Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 16103 (2017)
Janek, J., Zeier, W.G.: A solid future for battery development. Nat. Energy 1, 16141 (2016)
Sun, C., Liu, J., Gong, Y., et al.: Recent advances in all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. Nano Energy 33, 363–386 (2017)
Tatsumisago, M., Nagao, M., Hayashi, A.: Recent development of sulfide solid electrolytes and interfacial modification for all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 1, 17–25 (2013)
Chen, S., Xie, D., Liu, G., et al.: Sulfide solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries: structure, conductivity, stability and application. Energy Storage Mater. 14, 58–74 (2018)
Judez, X., Zhang, H., Li, C., et al.: Solid electrolytes for safe and high energy density lithium–sulfur batteries: promises and challenges. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, A6008–A6016 (2018)
Sun, Y.Z., Huang, J.Q., Zhao, C.Z., et al.: A review of solid electrolytes for safe lithium–sulfur batteries. Sci. China Chem. 60, 1508–1526 (2017)
Liu, Y., He, P., Zhou, H.: Rechargeable solid-state Li-Air and Li–S batteries: materials, construction, and challenges. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1701602 (2017)
Lei, D., Shi, K., Ye, H., et al.: Progress and perspective of solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1707570 (2018)
Xu, R., Zhang, S., Wang, X., et al.: Recent developments of all-solid-state lithium secondary batteries with sulfide inorganic electrolytes. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 6007–6018 (2018)
Agostini, M., Aihara, Y., Yamada, T., et al.: A lithium–sulfur battery using a solid, glass-type P2S5–Li2S electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 244, 48–51 (2013)
Kamaya, N., Homma, K., Yamakawa, Y., et al.: A lithium superionic conductor. Nat. Mater. 10, 682–686 (2011)
Xiang, Y.X., Zheng, G., Zhong, G., et al.: Toward understanding of ion dynamics in highly conductive lithium ion conductors: some perspectives by solid state NMR techniques. Solid State Ionics 318, 19–26 (2018)
Fu, K.K., Gong, Y., Xu, S., et al.: Stabilizing the garnet solid-electrolyte/polysulfide interface in Li–S batteries. Chem. Mater. 29, 8037–8041 (2017)
Lin, Y., Wang, X., Liu, J., et al.: Natural halloysite nano-clay electrolyte for advanced all-solid-state lithium sulfur batteries. Nano Energy 31, 478–485 (2017)
Chen, L., Fan, Z.: Dendrite-free Li metal deposition in all-solid-state lithium sulfur batteries with polymer-in-salt polysiloxane electrolyte. Energy Storage Mater. 15, 37–45 (2018)
Judez, X., Zhang, H., Li, C., et al.: Polymer-rich composite electrolytes for all-solid-state Li–S cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 3473–3477 (2017)
Fenton, D.E., Parker, J.M., Wright, P.V.: Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 14, 589 (1973)
Jeon, B.H., Yeon, J.H., Chung, I.J.: Preparation and electrical properties of lithium–sulfur-composite polymer batteries. J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 143, 93–97 (2003)
Armand, M.B.: Polymer solid electrolytes—an overview. Solid State Ionics 9, 745–754 (1983)
Takeda, Y., Yamamoto, O., Imanishi, N.: Lithium dendrite formation on a lithium metal anode from liquid, polymer and solid electrolytes. Electrochemistry 84, 210–218 (2016)
Jeong, S.S., Lim, Y.T., Choi, Y.J., et al.: Electrochemical properties of lithium sulfur cells using PEO polymer electrolytes prepared under three different mixing conditions. J. Power Sources 174, 745–750 (2007)
Hassoun, J., Scrosati, B.: Moving to a solid-state configuration: a valid approach to making lithium–sulfur batteries viable for practical applications. Adv. Mater. 22, 5198–5201 (2010)
Zhang, C., Lin, Y., Liu, J.: Sulfur double locked by a macro-structural cathode and a solid polymer electrolyte for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 10760–10766 (2015)
Marceau, H., Kim, C.S., Paolella, A., et al.: In operando scanning electron microscopy and ultraviolet visible spectroscopy studies of lithium/sulfur cells using all solid-state polymer electrolyte. J. Power Sources 319, 247–254 (2016)
Huang, B., Yao, X., Huang, Z., et al.: Li3PO4-doped Li7P3S11 glass–ceramic electrolytes with enhanced lithium ion conductivities and application in all-solid-state batteries.J. Power Sources 284, 206–211 (2015)
Liu, D., Zhu, W., Feng, Z., et al.: Recent progress in sulfide-based solid electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 213, 169–176 (2016)
Kanno, R., Murayama, M.: Lithium Ionic Conductor Thio-LISICON the Li2S–GeS2–P2S5 system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148, A742–A746 (2001)
Bron, P., Johansson, S., Zick, K., et al.: Li10SnP2S12: an affordable lithium superionic conductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 15694–15697 (2013)
Kato, Y., Hori, S., Saito, T., et al.: High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 1, 16030 (2016)
Deiseroth, H.J., Kong, S.T., Eckert, H., et al.: Li6PS5X: a class of crystalline Li-rich solids with an unusually high Li + mobility. Angew.Chem Int. Ed. 47, 755–758 (2008)
Chen, M., Adams, S.: High performance all-solid-state lithium/sulfur batteries using lithium argyrodite electrolyte. J. Solid State Electrochem. 19, 697–702 (2015)
Wang, D., Zhong, G., Pang, W.K., et al.: Toward understanding the lithium transport mechanism in garnet-type solid electrolytes: Li+ ion exchanges and their mobility at octahedral/tetrahedral sites. Chem. Mater. 27, 6650–6659 (2015)
Wang, S., Ding, Y., Zhou, G., et al.: Durability of the Li1+xTi2-xAlx(PO4)3 solid electrolyte in lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 1, 1080–1085 (2016)
Whiteley, J.M., Woo, J.H., Hu, E., et al.: Empowering the lithium metal battery through a silicon-based superionic conductor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161, A1812–A1817 (2014)
Bonanos, N., Knight, K.S., Ellis, B.: Perovskite solid electrolytes: structure, transport properties and fuel cell applications. Solid State Ionics 79, 161–170 (1995)
Xu, R.C., Xia, X.H., Zhang, S.Z., et al.: Interfacial challenges and progress for inorganic all-solid-state lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 284, 177–187 (2018)
Seino, Y., Ota, T., Takada, K., et al.: A sulphide lithium super ion conductor is superior to liquid ion conductors for use in rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 7, 627–631 (2014)
Wang, C., Yang, Y., Liu, X., et al.: Suppression of lithium dendrite formation by using LAGP–PEO (LiTFSI) composite solid electrolyte and lithium metal anode modified by PEO (LiTFSI) in all-solid-state lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 13694–13702 (2017)
Blanga, R., Goor, M., Burstein, L., et al.: The search for a solid electrolyte, as a polysulfide barrier, for lithium/sulfur batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 20, 3393–3404 (2016)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Sulfur–carbon composite electrode for all-solid state Li/S battery with Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 56, 6055–6059 (2011)
Nagata, H., Chikusa, Y.: Transformation of P2S5 into a solid electrolyte with ionic conductivity at the positive composite electrode of all-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries. Energy Technol. 2, 753–756 (2014)
Yao, X., Huang, N., Han, F., et al.: High-performance all-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries enabled by amorphous sulfur-coated reduced graphene oxide cathodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602923 (2017)
Nagata, H., Chikusa, Y.: An all-solid-state lithium sulfur battery using two solid electrolytes having different functions. J. Power Sources 329, 268–272 (2016)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: High-capacity Li2S-nanocarbon composite electrode for all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 10015–10020 (2012)
Suzuki, K., Mashimo, N., Ikeda, Y., et al.: High cycle capability of all-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries using composite electrodes by liquid-phase and mechanical mixing. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 1, 2373–2377 (2018)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Electrochemical performance of all-solid-state Li/S batteries with sulfur-based composite electrodes prepared by mechanical milling at high temperature. Energy Technol. 1, 186 (2013)
Nagao, M., Imade, Y., Narisawa, H., et al.: All-solid-state Li–sulfur batteries with mesoporous electrode and thio-LISICON solid electrolyte. J. Power Sources 222, 237–242 (2013)
Kobayashi, T., Imade, Y., Shishihara, D., et al.: All solid-state battery with sulfur electrode and thio-LISICON electrolyte. J. Power Sources 182, 621–625 (2008)
Roggenbuck, J., Koch, G., Tiemann, M.: Synthesis of mesoporous magnesium oxide by CMK-3 carbon structure replication. Chem. Mater. 18, 4151–4156 (2006)
Kinoshita, S., Okuda, K., Machida, N., et al.: All-solid-state lithium battery with sulfur/carbon composites as positive electrode materials. Solid State Ionics 256, 97–102 (2014)
Yu, C., van Eijck, L., Ganapathy, S., et al.: Synthesis, structure and electrochemical performance of the argyrodite Li6PS5Cl solid electrolyte for Li-ion solid state batteries. Electrochim. Acta 215, 93–99 (2016)
Xu, R.C., Xia, X.H., Wang, X.L., et al.: Tailored Li2S–P2S5 glass–ceramic electrolyte by MoS2 doping, possessing high ionic conductivity for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 2829–2834 (2017)
Xu, R.C., Xia, X.H., Li, S.H., et al.: All-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries based on a newly designed Li7P2.9Mn0.1S10.7I0.3 superionic conductor. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 6310–6317 (2017)
Rao, C.N.R., Sood, A.K., Voggu, R., et al.: Some novel attributes of graphene. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1, 572–580 (2010)
Xu, R.C., Wu, Z., Zhang, S.Z., et al.: Construction of all-solid-state batteries based on a sulfur–graphene composite and Li9.54Si1.74P1.44S11.7Cl0.3 solid electrolyte. Chem. Eur. J. 23, 13950–13956 (2017)
Hao, Y., Wang, S., Xu, F., et al.: A design of solid-state Li–S cell with evaporated lithium anode to eliminate shuttle effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 33735–33739 (2017)
Liang, X., Wen, Z., Liu, Y., et al.: Highly dispersed sulfur in ordered mesoporous carbon sphere as a composite cathode for rechargeable polymer Li/S battery. J. Power Sources 196, 3655–3658 (2011)
Gracia, I., Youcef, H.B., Judez, X., et al.: S-containing copolymer as cathode material in poly(ethylene oxide)-based all-solid-state Li–S batteries. J. Power Sources 390, 148–152 (2018)
Eshetu, G.G., Judez, X., Li, C., et al.: Ultrahigh performance all solid-state lithium sulfur batteries: salt anion’s chemistry-induced anomalous synergistic effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 9921–9933 (2018)
Tao, X., Liu, Y., Liu, W., et al.: Solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries operated at 37 °C with composites of nanostructured Li7La3 Zr2O12/carbon foam and polymer. Nano Lett. 17, 2967–2972 (2017)
Sheng, O., Jin, C., Luo, J., et al.: Ionic conductivity promotion of polymer electrolyte with ionic liquid grafted oxides for all solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 12934–12942 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Zhao, Y., Gosselink, D., et al.: Synthesis of poly(ethylene-oxide)/nanoclay solid polymer electrolyte for all solid-state lithium/sulfur battery. Ionics 21, 381–385 (2015)
Nan, C., Lin, Z., Liao, H., et al.: Durable carbon-coated Li2S core-shell spheres for high performance lithium/sulfur cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4659–4663 (2014)
Son, Y.K., Lee, J.S., Son, Y., et al.: Recent advances in lithium sulfide cathode materials and their use in lithium sulfur batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 5, 1500110 (2015)
Yu, C., Ganapathy, S., de Klerk, N.J.J., et al.: Unravelling Li-ion transport from pico-seconds to seconds: bulk versus interfaces in an argyrodite Li6PS5Cl–Li2S all solid state Li-ion battery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 11192–11201 (2016)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M., et al.: Li2S nanocomposites underlying high-capacity and cycling stability in all-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 274, 471–476 (2015)
Choi, S., Yoon, I., Nichols, W.T., et al.: Carbon-coated Li2S cathode for improving the electrochemical properties of an all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery using Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 44, 7450–7453 (2018)
Yu, C., Ganapathy, S., van Eck, E.R.H., et al.: Revealing the relation between the structure, Li-ion conductivity and solid-state battery performance of the argyrodite Li6PS5Br solid electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 21178–21188 (2017)
Takeuchi, T., Kageyama, H., Nakanishi, K., et al.: Application of graphite–solid electrolyte composite anode in all-solid-state lithium secondary battery with Li2S positive electrode. Solid State Ionics 262, 138–142 (2014)
Hakari, T., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Highly utilized lithium sulfide active material by enhancing conductivity in all-solid-state batteries. Chem. Lett. 44, 1664–1666 (2015)
Hakari, T., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Li2S-based solid solutions as positive electrodes with full utilization and superlong cycle life in all-solid-state Li/S batteries. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 1, 1700017 (2017)
Nishio, Y., Kitaura, H., Hayashi, A., et al.: All-solid-state lithium secondary batteries using nanocomposites of NiS electrode/Li2S–P2S5 electrolyte prepared via mechanochemical reaction. J. Power Sources 189, 629–632 (2009)
Yao, X., Liu, D., Wang, C., et al.: High-energy all-solid-state lithium batteries with ultralongcycle life. Nano Lett. 16, 7148–7154 (2016)
Zhang, Q., Mwizerwa, J.P., Wan, H., et al.: Fe3S4@Li7P3S11nanocomposites as cathode materials for all-solid-state lithium batteries with improved energy density and low cost. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 23919–23925 (2017)
Matsuyama, T., Deguchi, M., Mitsuhara, K., et al.: Structure analyses using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and X-ray absorption near edge structure for amorphous MS3 (M: Ti, Mo) electrodes in all-solid-state lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 313, 104–111 (2016)
Matsuyama, T., Hayashi, A., Ozaki, T., et al.: Electrochemical properties of all-solid-state lithium batteries with amorphous MoS3 electrodes prepared by mechanical milling. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 14142–14147 (2015)
Shin, B.R., Nam, Y.J., Kim, J.W., et al.: Interfacial architecture for extra Li+storage in all-solid-state lithium batteries. Sci. Rep. 4, 5572 (2014)
Wan, H., Peng, G., Yao, X., et al.: Cu2ZnSnS4/graphene nanocomposites for ultrafast, long life all-solid-state lithium batteries using lithium metal anode. Energy Storage Mater. 4, 59–65 (2016)
Ulissi, U., Ito, S., Hosseini, S.M., et al.: High capacity all-solid-state lithium batteries enabled by pyrite-sulfur composites. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1801462 (2018)
Hakari, T., Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., et al.: All-solid-state lithium batteries with Li3PS4 glass as active material. J. Power Sources 293, 721–725 (2015)
Hakari, T., Sato, Y., Yoshimi, S., et al.: Favorable carbon conductive additives in Li3PS4 composite positive electrode prepared by ball-milling for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 164, A2804–A2811 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Chen, R., Liu, T., et al.: High capacity and superior cyclic performances of all-solid-state lithium batteries enabled by a glass-ceramics solo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 10029–10035 (2018)
Hakari, T., Deguchi, M., Mitsuhara, K., et al.: Structural and electronic-state changes of a sulfide solid electrolyte during the Li deinsertion–insertion processes. Chem. Mater. 29, 4768–4774 (2017)
Hayashi, A., Ohtsubo, R., Nagao, M., et al.: Characterization of Li2S–P2S5–Cu composite electrode for all-solid-state lithium secondary batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 377–381 (2010)
Yue, J., Yan, M., Yin, Y.X., et al.: Progress of the interface design in all-solid-state Li–S batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1707533 (2018)
Luo, C., Ji, X., Chen, J., et al.: Solid-state electrolyte anchored with a carboxylatedazo compound for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 8567–8571 (2018)
Aso, K., Sakuda, A., Hayashi, A., et al.: All-solid-state lithium secondary batteries using NiS-carbon fiber composite electrodes coated with Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolytes by pulsed laser deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 686–690 (2013)
Choi, H.U., Jin, J.S., Park, J.Y., et al.: Performance improvement of all-solid-state Li–S batteries with optimizing morphology and structure of sulfur composite electrode. J. Alloys Comput. 723, 787–794 (2017)
Suzuki, K., Kato, D., Hara, K., et al.: Composite sulfur electrode prepared by high-temperature mechanical milling for use in an all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery with a Li3.25Ge0.25P0.75S4 electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 258, 110–115 (2017)
Hayashi, A., Ohtomo, T., Mizuno, F., et al.: All-solid-state Li/S batteries with highly conductive glass-ceramic electrolytes. Electrochem. Commun. 5, 701–705 (2003)
Busche, M.R., Weber, D.A., Schneider, Y., et al.: In situ monitoring of fast Li-ion conductor Li7P3S11 crystallization inside a hot-press setup. Chem. Mater. 28, 6152 (2016)
Lin, Z., Liu, Z., Fu, W., et al.: Lithium polysulfidophosphates: a family of lithium-conducting sulfur-rich compounds for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 7460–7463 (2013)
Han, F., Gao, T., Zhu, Y., et al.: A battery made from a single material. Adv. Mater. 27, 3473 (2015)
Han, F., Yue, J., Fan, X., et al.: High-performance all-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery enabled by a mixed-conductive Li2S Nanocomposite. Nano Lett. 16, 4521 (2016)
Lin, Z., Liu, Z., Dudney, N.J., et al.: Lithium superionic sulfide cathode for all-solid lithiumsulfur batteries. ACS Nano 7, 2829–2833 (2013)
Eom, M., Son, S., Park, C., et al.: High performance all-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery using a Li2S–VGCF nanocomposite. Electrochim. Acta 230, 279–284 (2017)
Xu, R.C., Wang, X.L., Zhang, S.Z., et al.: Rational coating of Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte on MoS2 electrode for all-solid state lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 374, 107–112 (2018)
Long, P., Xu, Q., Peng, G., et al.: NiS nanorods as cathode materials for all-solid-state lithium batteries with excellent rate capability and cycling stability. ChemElectroChem 3, 764–769 (2016)
Wenzel, S., Leichtweiss, T., Krüger, D., et al.: Interphase formation on lithium solid electrolytes—an in situ approach to study interfacial reactions by photoelectron spectroscopy. Solid State Ionics 278, 98–105 (2015)
Shin, B.R., Nam, Y.J., Oh, D.Y., et al.: Comparative study of TiS2/Li−In all-solid-state lithium batteries using glass-ceramic Li3PS4 and Li10GeP2S12 solid electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 146, 395–402 (2014)
Eshetu, G.G., Judez, X., Li, C., et al.: Lithium azide as an electrolyte additive for all-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 15368–15372 (2017)
Wu, B., Wang, S., Lochala, J., et al.: The role of solid electrolyte interphase layer in preventing Li dendrite growth in solid-state batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 11, 1803–1810 (2018)
Zheng, B., Zhu, J., Wang, H., et al.: Stabilizing Li10SnP2S12/Li Interface via an in-situ formed solid electrolyte interphase layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 25473–25482 (2018)
Wu, B., Wang, S., Evans, W.J., et al.: Interfacial behaviours between lithium ion conductors and electrode materials in various battery systems. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 15266–15280 (2016)
Thangadurai, V., Weppner, W.: Li6ALa2Ta2O12 (A = Sr, Ba): novel garnet-like oxides for fast lithium ion conduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 107 (2005)
Sakuma, M., Suzuki, K., Hirayama, M., Kanno, R.: Reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface of all-solid-state lithium batteries incorporating Li-M (M = Sn, Si) alloy electrodes and sulfide-based solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 285, 101–105 (2016)
Leite, M.S., Ruzmetov, D., Li, Z., et al.: Insights into capacity loss mechanisms of all-solid-state Li-ion batteries with Al anodes. J. Mater Chem. A 2, 20552–20559 (2014)
Wenzel, S., Randau, S., Leichtweiß, T., et al.: Direct observation of the interfacial instability of the fast ionic conductor Li10GeP2S12 at the lithium metal anode. Chem. Mater. 28, 2400–2407 (2016)
Wenzel, S., Weber, D.A., Leichtweiss, T., et al.: Interphase formation and degradation of charge transfer kinetics between a lithium metal anode and highly crystalline Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 286, 24–33 (2016)
Zhang, Z., Chen, S., Yang, J., et al.: Interface re-engineering of Li10GeP2S12 electrolyte and lithium anode for all-solid-state lithium batteries with ultralong cycle life. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 2556–2565 (2018)
Hartmann, P., Leichtweiss, T., Busche, M.R., et al.: Degradation of NASICON-type materials in contact with lithium metal: formation of mixed conducting interphases (MCI) on solid electrolytes. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 21064–21074 (2013)
Kato, A., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M., et al.: Enhancing utilization of lithium metal electrodes in all-solid-state batteries by interface modification with gold thin films. J. Power Sources 309, 27–32 (2016)
Wenzel, S., Sedlmaier, S.J., Dietrich, C., et al.: Interfacial reactivity and interphase growth of argyrodite solid electrolytes at lithium metal electrodes. Solid State Ionics 318, 102–112 (2018)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M., et al.: In situ SEM study of a lithium deposition and dissolution mechanism in a bulk-type solid-state cell with a Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolyte. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 18600–18606 (2013)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Fabrication of favorable interface between sulfide solid electrolyte and Li metal electrode for bulk-type solid-state Li/S battery. Electrochem. Commun. 22, 177–180 (2012)
Sang, L., Haasch, R.T., Gewirth, A.A., et al.: Evolution at the solid electrolyte/gold electrode interface during lithium deposition and stripping. Chem. Mater. 29, 3029–3037 (2017)
Nagao, M., Hayashi, A., Tatsumisago, M.: Bulk-type lithium metal secondary battery with indium thin layer at interface between Li electrode and Li2S–P2S5 solid electrolyte. Electrochemistry 80, 734–736 (2012)
Kato, A., Kowada, H., Deguchi, M., et al.: XPS and SEM analysis between Li/Li3PS4 interface with Au thin film for all solid-state lithium batteries. Solid State Ionics 322, 1–4 (2018)
Sharafi, A., Meyer, H.M., Nanda, J., et al.: Characterizing the LieLi7La3Zr2O12 interface stability and kinetics as a function of temperature and current density. J. Power Sources 302, 135–139 (2016)
Sudo, R., Nakata, Y., Ishiguro, K., et al.: Interface behavior between garnet-type lithium-conducting solid electrolyte and lithium metal. Solid State Ionics 262, 151–154 (2014)
Luo, W., Gong, Y., Zhu, Y., et al.: Transition from superlithiophobicity to superlithiophilicity of garnet solid-state electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 12258–12262 (2016)
Han, X., Gong, Y., Fu, K., et al.: Negating interfacial impedance in garnet-based solid-state Li metal batteries. Nat. Mater. 16, 572 (2016)
Fu, K.K., Gong, Y., Liu, B., et al.: Toward garnet electrolyte-based Li metal batteries: an ultrathin, highly effective, artificial solid-state electrolyte/metallic Li interface. Sci. Adv. 3, e1601659 (2017)
Fu, K.K., Gong, Y., Fu, Z., et al.: Transient behavior of the metal interface in lithium metal–garnet batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 14942–14947 (2017)
Luo, W., Gong, Y., Zhu, Y., et al.: Reducing interfacial resistance between garnet-structured solid-state electrolyte and Li-metal anode by a germanium layer. Adv. Mater. 29, 1606042 (2017)
Wang, C., Gong, Y., Liu, B., et al.: Conformal, nanoscale ZnO surface modification of garnet-based solid-state electrolyte for lithium metal anodes. Nano Lett. 17, 565–571 (2017)
Shao, Y., Wang, H., Gong, Z., et al.: Drawing a soft interface: an effective interfacial modification strategy for garnet-type solid-state Li batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 3, 1212–1218 (2018)
Liu, J., Liu, T., Pu, Y., et al.: Facile synthesis of NASICON-type Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolyte and its application for enhanced cyclic performance in lithium ion batteries through the introduction of an artificial Li3PO4 SEI layer. RSC Adv. 7, 46545–46552 (2017)
Tan, S.J., Zeng, X.X., Ma, Q., et al.: Recent advancements in polymer-based composite electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 1, 113–138 (2018)
Chien, P.H., Feng, X., Tang, M., et al.: Li Distribution heterogeneity in solid electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 upon electrochemical cycling probed by 7Li MRI. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 9, 1990–1998 (2018)
Fu, K.K., Gong, Y., Dai, J., et al.: Flexible, solid-state, ion-conducting membrane with 3D garnet nanofiber networks for lithium batteries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 7094–7099 (2016)
Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Chen, S., et al.: An advanced construction strategy of all-solid state lithium batteries with excellent interfacial compatibility and ultralong cycle life. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 16984–16993 (2017)
Fu, K.K., Gong, Y., Hitz, G.T., et al.: Three-dimensional bilayer garnet solid electrolyte based high energy density lithium metal–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 10, 1568–1575 (2017)
Li, Y., Xu, B., Xu, H., et al.: Hybrid polymer/garnet electrolyte with a small interfacial resistance for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 753 (2017)
Yamada, T., Ito, S., Omoda, R., et al.: All solid-state lithium–sulfur battery using a glass-type P2S5–Li2S electrolyte: benefits on anode kinetics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, A646–A651 (2015)
Hayashi, A., Ohtsubo, R., Ohtomo, T., et al.: All-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries with Li2S as a positive electrode material. J. Power Sources 183, 422–426 (2008)
Machida, N., Kobayashi, K., Nishikawa, Y., et al.: Electrochemical properties of sulfur as cathode materials in a solid-state lithium battery with inorganic solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 175, 247–250 (2004)
Kinoshita, S., Okuda, K., Machida, N., et al.: Additive effect of ionic liquids on the electrochemical property of a sulfur composite electrode for all-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery. J. Power Sources 269, 727–734 (2014)
Suzuki, K., Kato, D., Hara, K., et al.: Composite sulfur electrode for all-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery with Li2S–GeS2–P2S5-based thio-LISICON solid electrolyte. Electrochemistry 86, 1–5 (2018)
Tanibata, N., Tsukasaki, H., Deguchi, M., et al.: A novel discharge-charge mechanism of a S–P2S5 composite electrode without electrolytes in all solid- state Li/S batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 11224–11228 (2017)
Trevey, J.E., Gilsdor, J.R., Stoldt, C.R., et al.: Electrochemical investigation of all-solid-state lithium batteries with a high capacity sulfur-based electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, A1019–A1022 (2012)
Zhang, Y., Chen, K., Shen, Y., et al.: Synergistic effect of processing and composition x on conductivity of xLi2S-(100-x)P2S5 electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 305, 1–6 (2017)
Nagata, H., Chikusa, Y.: All-solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries using a conductive composite containing activated carbon and electroconductive polymers. Chem. Lett. 43, 1335–1336 (2014)
Marmorstein, D., Yu, T.H., Striebel, K.A., et al.: Electrochemical performance of lithium-sulfur cells with three different polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources 89, 219–226 (2000)
Zhang, C., Lin, Y., Zhu, Y., et al.: Improved lithium-ion and electrically conductive sulfur cathode for all-solid-state lithium–sulfur batteries. RSC Adv. 7, 19231–19236 (2017)
Zhu, Y., Li, J., Liu, J.: A bifunctional ion-electron conducting interlayer for high energy density all-solid-state lithium–sulfur battery. J. Power Sources 351, 17–25 (2017)
Judez, X., Zhang, H., Li, C., et al.: Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide/poly(ethylene oxide) polymer electrolyte for all solid-state Li–S cell. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 8, 1956–1960 (2017)
Zhu, X., Wen, Z., Gu, Z., et al.: Electrochemical characterization and performance improvement of lithium/sulfur polymer batteries. J. Power Sources 139, 269–273 (2005)
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFB0905400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21473148, 21621091, 21761132030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umeshbabu, E., Zheng, B. & Yang, Y. Recent Progress in All-Solid-State Lithium−Sulfur Batteries Using High Li-Ion Conductive Solid Electrolytes. Electrochem. Energ. Rev. 2, 199–230 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41918-019-00029-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41918-019-00029-3