Abstract
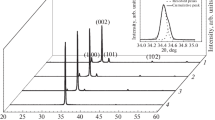
This study has extensively described the fabrication and characterization of sisal-like ZnO microstructures. HMT aqueous solution containing zinc nitrate tetrahydrate as crystalline zinc source has been utilized to synthesize sisal-like ZnO samples via a controlled hydrothermal route. A variety of characterization techniques including FESEM, XRD, FT-IR, and Raman spectroscopy have been employed to investigate the effects related to varying annealing temperatures on morphological and structural properties. The FESEM observations have revealed a transition from hexagonal microrods to modified microrods and then to pointed microrods for sisal-like ZnO architectures as the annealing temperature increases. XRD results have indicated a considerably high purity for as-synthesized ZnO microstructures. The crystalline quantities of ZnO samples have been estimated using various X-ray line-broadening analysis methods including Debye-Scherrer and Williamson-Hall techniques. UV-Vis DRS measurements have been carried out to study optical properties. Results have shown improved light harvesting related to both enhanced absorption intensities and decreased band-gap energies with the increase of annealing temperatures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
da Silva, L.F., Mastelaro, V.R., Catto, A.C., Escanhoela Jr., C.A., Bernardini, S., Zílio, S.C., Longo, E., Aguir, K.: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide gas sensor based on a nanostructured SrTi0. 85Fe0. 15O3 thin film. J. Alloys Compd. 638, 374–379 (2015)
Brian, O., Michael, G.: A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature. 353(6346), 737–740 (1991)
Minne, S., Manalis, S., Quate, C.: Parallel atomic force microscopy using cantilevers with integrated piezoresistive sensors and integrated piezoelectric actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67(26), 3918–3920 (1995)
Karimi, T., Haghighatzadeh, A.: Enhanced photocatalytic activity of SnO2 NPs by chromium (Cr) concentration. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42(4), 158 (2019)
Efimov, A.A., Volkov, I.A., Ivanov, V., Vasiliev, A.A., Varfolomeev, A., Pislyakov, A.V., Lagutin, A.S., Maeder, T.: Spark discharge synthesis of semiconductor nanoparticles for thick-film metal oxide gas sensors. Proc. Eng. 168, 1036–1039 (2016)
Li, Y., Wang, S., Wu, J., Ma, J., Cui, L., Lu, H., Sheng, Z.: One-step hydrothermal synthesis of hybrid core-shell Co3O4@ SnO2–SnO for supercapacitor electrodes. Ceram. Int. (2020)
Acharyulu, N., Srinivasu, C., Babavali, S.F.: Synthesis of carbon nano spherical structures and nano composite oxide [TiO2/SnO2 (2: 1)] hollow spheres by hydrothermal method and study of characterization with photo catalytic activity. Materials Today, Proceedings (2020)
Suvith, V., Devu, V., Philip, D.: Facile synthesis of SnO2/NiO nano-composites: Structural, magnetic and catalytic properties. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 786–794 (2020)
Asadi, A., Akbarzadeh, R., Eslami, A., Jen, T.-C., Oviroh, P.O.: Effect of synthesis method on NS-TiO2 photocatalytic performance. Energy Procedia. 158, 4542–4547 (2019)
Mahmoudabadi, Z.D., Eslami, E.: One-step synthesis of CuO/TiO2 nanocomposite by atmospheric microplasma electrochemistry–its application as photoanode in dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Alloys Compd. 793, 336–342 (2019)
Xiao, Q.: Synthesis and characterization of 3D ZnO superstructures via a template-free hydrothermal method. Powder Technol. 189(1), 103–107 (2009)
Kumar, V., Singh, R., Purohit, L., Singh, F.: Effect of swift heavy ion on structural and optical properties of undoped and doped nanocrystalline zinc oxide films. Adv. Mater. Lett. 4(6), 423–427 (2013)
Koao, L., Dejene, F., Swart, H.: Properties of flower-like ZnO nanostructures synthesized using the chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 27, 33–40 (2014)
Worasawat, S., Masuzawa, T., Hatanaka, Y., Neo, Y., Mimura, H., Pecharapa, W.: Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorods by hydrothermal method. Mater. Today: Proc. 5(5), 10964–10969 (2018)
Agarwal, S., Rai, P., Gatell, E.N., Llobet, E., Güell, F., Kumar, M., Awasthi, K.: Gas sensing properties of ZnO nanostructures (flowers/rods) synthesized by hydrothermal method. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 292, 24–31 (2019)
Singh, R., Singh, F., Kanjilal, D., Agarwal, V., Mehra, R.: White light emission from chemically synthesized ZnO–porous silicon nanocomposite. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 42(6), 062002 (2009)
Kumar, V., Singh, R., Purohit, L., Mehra, R.: Structural, transport and optical properties of boron-doped zinc oxide nanocrystalline. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27(6), 481–488 (2011)
Wager, J.F.: Transparent electronics. science 300(5623), 1245-1246 (2003).
Grätzel, M.: Conversion of sunlight to electric power by nanocrystalline dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 164(1-3), 3–14 (2004)
Johnson, J.C., Yan, H., Yang, P., Saykally, R.J.: Optical cavity effects in ZnO nanowire lasers and waveguides. J. Phys. Chem. B. 107(34), 8816–8828 (2003)
Kim, I.-D., Hong, J.-M., Lee, B.H., Kim, D.Y., Jeon, E.-K., Choi, D.-K., Yang, D.-J.: Dye-sensitized solar cells using network structure of electrospun ZnO nanofiber mats. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(16), 163109 (2007)
Rabenau, A.: The role of hydrothermal synthesis in preparative chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 24(12), 1026–1040 (1985)
Huang, J., Matsunaga, N., Shimanoe, K., Yamazoe, N., Kunitake, T.: Nanotubular SnO2 templated by cellulose fibers: synthesis and gas sensing. Chem. Mater. 17(13), 3513–3518 (2005)
Yadav, A., Prasad, V., Kathe, A., Raj, S., Yadav, D., Sundaramoorthy, C., Vigneshwaran, N.: Functional finishing in cotton fabrics using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 29(6), 641–645 (2006)
Izu, N., Murayama, N., Shin, W., Itoh, T., Matsubara, I.: Preparation of SnO2 nanoparticles less than 10 nm in size by precipitation using hydrophilic carbon black powder. Mater. Lett. 62(2), 313–316 (2008)
El-Desoky, M., Ali, M., Afifi, G., Imam, H.: Annealing effects on the structural and optical properties of growth ZnO thin films fabricated by pulsed laser deposition (PLD). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25(11), 5071–5077 (2014)
Ray, P.G., Das, M., Wan, M., Jacob, C., Roy, S., Basak, P., Dhara, S.: Surfactant and catalyst free facile synthesis of Al-doped ZnO nanorods–An approach towards fabrication of single nanorod electrical devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 512, 145732 (2020)
Lingmin, Y., Lei, C., Chun, L., Mingli, Y., Xinhui, F.: Resistive-type UV–visible photodetector based on CdS NWs/ZnO nanowalls heterostructure fabricated using in-situ synthesis method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 154090 (2020).
de Almeida, W.L., Rodembusch, F.S., Ferreira, N.S.: de Sousa. V.C, Eco-friendly and cost-effective synthesis of ZnO nanopowders by Tapioca-assisted sol-gel route. Ceramics International (2020)
Dhandapani, P., Prakash, A.A., AlSalhi, M.S., Maruthamuthu, S., Devanesan, S., Rajasekar, A.: Ureolytic bacteria mediated synthesis of hairy ZnO nanostructure as photocatalyst for decolorization of dyes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 122619 (2020)
Dong, P., Hou, G., Liu, C., Zhang, X., Tian, H., Xu, F., Xi, X., Shao, R.: Origin of activity and stability enhancement for Ag3PO4 photocatalyst after calcination. Materials. 9(12), 968 (2016)
Reunchan, P., Boonchun, A., Umezawa, N.: Electronic properties of highly-active Ag 3 AsO 4 photocatalyst and its band gap modulation: an insight from hybrid-density functional calculations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(33), 23407–23411 (2016)
Duan, X., Huang, Y., Agarwal, R., Lieber, C.M.: Single-nanowire electrically driven lasers. Nature. 421(6920), 241–245 (2003)
Mayers, B., Xia, Y.: Formation of tellurium nanotubes through concentration depletion at the surfaces of seeds. Adv. Mater. 14(4), 279–282 (2002)
Huang, M.H., Mao, S., Feick, H., Yan, H., Wu, Y., Kind, H., Weber, E., Russo, R., Yang, P.: Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science. 292(5523), 1897–1899 (2001)
Qiu, Y., Yang, S.: ZnO nanotetrapods: controlled vapor-phase synthesis and application for humidity sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17(8), 1345–1352 (2007)
Long, T., Yin, S., Takabatake, K., Zhnag, P., Sato, T.: Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanorods and nanodisks from zinc chloride aqueous solution. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 4(3), 247 (2009)
Lao, J., Huang, J., Wang, D., Ren, Z.: ZnO nanobridges and nanonails. Nano Lett. 3(2), 235–238 (2003)
Wang, Z.L.: Zinc oxide nanostructures: growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 16(25), R829 (2004)
Wang, Z., Qian, X.-f., Yin, J., Zhu, Z.-k.: Large-scale fabrication of tower-like, flower-like, and tube-like ZnO arrays by a simple chemical solution route. Langmuir. 20(8), 3441–3448 (2004)
Tan, L., Gao, H., Andriamitantsoa, R.S., Hu, B.-t.: Facial fabrication of hierarchical 3D Sisal-like CuO/ZnO nanocomposite and its catalytic properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 708, 77–80 (2018)
Iwan, S., Zhao, J., Tan, S., Sun, X.: Enhancement of UV photoluminescence in ZnO tubes grown by metal organic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD). Vacuum. 155, 408–411 (2018)
Bao, Y., Gao, L., Feng, C., Ma, J., Zhang, W., Liu, C., Simion, D.: Hollow flower-like ZnO: Synthesis, growth mechanism and application in polyacrylate. Adv. Powder Technol. (2020)
Lam, S.-M., Sin, J.-C., Hua, L., Haixiang, L., Wei, L.J., Zeng, H.: A Z-scheme WO3 loaded-hexagonal rod-like ZnO/Zn photocatalytic fuel cell for chemical energy recuperation from food wastewater treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 145945 (2020).
Yu, Q., Fu, W., Yu, C., Yang, H., Wei, R., Li, M., Liu, S., Sui, Y., Liu, Z., Yuan, M.: Fabrication and optical properties of large-scale ZnO nanotube bundles via a simple solution route. J. Phys. Chem. C. 111(47), 17521–17526 (2007)
Ranjitha, A., Muthukumarasamy, N., Thambidurai, M., Agilan, S., Balasundaraprabhu, R.: Effect of hydrothermal growth temperature on structural and optical properties of TiO 2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(2), 553–558 (2013)
Liu, S.-Y., Chen, T., Wan, J., Ru, G.-P., Li, B.-Z., Qu, X.-P.: The effect of pre-annealing of sputtered ZnO seed layers on growth of ZnO nanorods through a hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A. 94(4), 775–780 (2009)
El-Desoky, M., Ali, M., Afifi, G., Imam, H., Al-Assiri, M.: Effects of annealing temperatures on the structural and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Silicon. 10(2), 301–307 (2018)
Raoufi, D.: Synthesis and microstructural properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by precipitation method. Renew. Energy. 50, 932–937 (2013)
Pudukudy, M., Hetieqa, A.: Yaakob, Z: Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of annealing dependent quasi spherical and capsule like ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 319, 221–229 (2014)
Umar, A., Kumar, R., Kumar, G., Algarni, H., Kim, S.H.: Effect of annealing temperature on the properties and photocatalytic efficiencies of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 648, 46–52 (2015)
Uthirakumar, P., Hong, C.-H.: Effect of annealing temperature and pH on morphology and optical property of highly dispersible ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Charact. 60, 1305–1310 (2009)
Sahu, K., Kar, A.K.: Morphological, optical, photocatalytic and electrochemical properties of hydrothermally grown ZnO nanoflowers with variation in hydrothermal temperature. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 104, 104648 (2019)
Rekha, K., Nirmala, M., Nair, M.G., Anukaliani, A.: Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 405(15), 3180–3185 (2010)
Singh, P., Kumar, A., Kaushal, A., Kaur, D., Pandey, A., Goyal, R.: In situ high temperature XRD studies of ZnO nanopowder prepared via cost effective ultrasonic mist chemical vapour deposition. Bull. Mater. Sci. 31(3), 573–577 (2008)
Sivakami, R., Dhanuskodi, S., Karvembu, R.: Estimation of lattice strain in nanocrystalline RuO2 by Williamson–Hall and size–strain plot methods. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 152, 43–50 (2016)
Lee, J.S., De Angelis, R.: X-ray diffraction patterns from nanocrystalline binary alloys. Nanostruct. Mater. 7(7), 805–812 (1996)
Mote, V., Purushotham, Y., Dole, B.: Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6(1), 6 (2012)
Ataie Dil, M., Haghighatzadeh, A., Mazinani, B.: Photosensitization effect on visible-light-induced photocatalytic performance of TiO2/chlorophyll and flavonoid nanostructures: kinetic and isotherm studies. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42(5), 248 (2019)
Chittan, M.V., Kumar, C.M., Sowjanya, K., Kumar, B.R.: Estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized alumina doped ZnO ceramics by X-ray peak profile analysis. Mater. Today: Proc. 4(8), 9237–9245 (2017)
Prabhu, Y.T., Rao, K.V., Kumar, V.S.S., Kumari, B.S.: X-ray analysis by Williamson-Hall and size-strain plot methods of ZnO nanoparticles with fuel variation. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2014 (2014).
Yogamalar, R., Srinivasan, R., Vinu, A., Ariga, K., Bose, A.C.: X-ray peak broadening analysis in ZnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 149(43-44), 1919–1923 (2009)
Ramasamy, V., Vijayalakshmi, G.: Effect of Zn doping on structural, optical and thermal properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Superlattice. Microst. 85, 510–521 (2015)
Bindu, P., Thomas, S.: Estimation of lattice strain in ZnO nanoparticles: X-ray peak profile analysis. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 8(4), 123–134 (2014)
Suresh, R., Ponnuswamy, V., Mariappan, R.: Effect of annealing temperature on the microstructural, optical and electrical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 273, 457–464 (2013)
Al-Assiri, M., Mostafa, M., Ali, M., El-Desoky, M.: Synthesis, structural and electrical properties of annealed ZnO thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition (PLD). Superlattice. Microst. 75, 127–135 (2014)
Sharma, A., Rai, V., Mani, S., Chawade, S.: A study of structural parameters and photoluminescence of Tb doped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. (2019)
Wahab, R., Ansari, S., Seo, H.-K., Kim, Y.S., Suh, E.-K., Shin, H.-S.: Low temperature synthesis and characterization of rosette-like nanostructures of ZnO using solution process. Solid State Sci. 11(2), 439–443 (2009)
Selvi, N., Sankar, S.: Effect of shells ZnO; SiO2 on SnO2 hybrid core-shell nanospheres and their structural, morphological and magnetic properties. Int. J. Chem. Technol. Res. 6(14), 5665–5671 (2014)
BANAVATU, L., RAO, D.S., Basavaiah, K.: Synthesis of γ-Bi2MoO6 by Co-precipitation Method and Evaluation for Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B, Crystal Violet and Orange II Dyes Under Visible Light Irradiation. Asian J. Chem. 30(1), 97–102 (2018)
Jang, M., Ryu, M., Yoon, M., Lee, S., Kim, H., Onodera, A., Kojima, S.: A study on the Raman spectra of Al-doped and Ga-doped ZnO ceramics. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(3), 651–657 (2009)
Zolfaghari, M.: Propose for Raman mode position for Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 555, 1–8 (2019)
Zhang, R., Yin, P.-G., Wang, N., Guo, L.: Photoluminescence and Raman scattering of ZnO nanorods. Solid State Sci. 11(4), 865–869 (2009)
Peng, Z., Dai, G., Chen, P., Zhang, Q., Wan, Q., Zou, B.: Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of star-like ZnO nanostructures. Mater. Lett. 64(8), 898–900 (2010)
Lv, J., Sun, Y., Cao, L., Zhao, M., Shang, F., Mao, S., Jiang, Y., Xu, J., Wang, F., Zhou, Z.: Effect of reaction temperature on surface morphology and photoelectric properties of ZnO grown by hydrothermal method in mixed solvent. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(7), 5518–5523 (2015)
Sahu, S., Nanda, K.: Semiconductor nanoparticles: physics and applications. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 103 (2001)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank the Research Council for their generous support of this work.
Funding
The current study was partially supported by the Ahvaz Branch of Islamic Azad University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghighatzadeh, A., Hosseini, M., Haghighi, S. et al. The effect of annealing temperature on hydrothermally grown sisal-like ZnO microstructures. J Aust Ceram Soc 57, 993–1002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-021-00602-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-021-00602-4