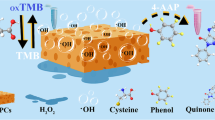
Abstract
The controllable growth of metal nanoparticles on nanomaterials is becoming an effective strategy for developing nanocomposites with designated performance. Herein, a simple and mild strategy for the in situ growth of Pt–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles on covalent organic frameworks (COFs) to regulate the nanozyme activity was designed for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and glutathione (GSH). The COFs not only offer sufficient loading sites for the uniform dispersion of Pt–Pd bimetallic nanoparticles, but also increase the adsorption of substrate to promote the catalytic reaction. With the bimetallic synergistic effect of Pt–Pd nanoparticles, the prepared multifunctional nanozyme (Pt–Pd/COFs nanozyme) simultaneously exhibited superior peroxidase (POD)-like activity and oxidase (OXD)-like activity. Using the multifunctional nanozyme, a colorimetric sensing system was constructed for sensitive detection of H2O2 and GSH, with the wide linear ranges of 5–1000 µmol/L and 1–40 µmol/L, and the detection limits were 1.14 μmol/L and 0.43 μmol/L, respectively. It was successfully used for the detection of real samples in environmental water and serum, providing a simple method for disease diagnosis and environmental monitoring.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data is available upon reasonable request.
References
Wu JX, Wang XY, Wang Q, Lou ZP, Li SR, Zhu YY, Qin L, Wei H. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48:1004–76.
Filizola M, Loew GH. Role of protein environment in horseradish peroxidase compound I formation: molecular dynamics simulations of horseradish peroxidase−HOOH complex. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122(1):18–25.
An MY, He MQ, Lin CS, Wu YB, Ai YJ, Xin HB, Liang QL. Recent progress of nanozymes with different spatial dimensions for bioanalysis. Mater Today Nano. 2023;22:100330.
Lin YY, Ren JS, Qu XG. Catalytically active nanomaterials: a promising candidate for artificial enzymes. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47(4):1097–105.
Chen QM, Liang CH, Zhang XD. High oxidase-mimic activity of Fe nano-particles embedded in an N-rich porous carbon and their application for sensing of dopamine. Talanta. 2018;182:476–83.
Liu H, Ding YN, Bian B, Li L, Li RM. Rapid colorimetric determination of dopamine based on the inhibition of the peroxidase mimicking activity of platinum loaded CoSn(OH)6 nanocubes. Microchim Acta. 2019;186:755.
Gao LZ, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang JB, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang TH, Feng J, Yang DL, Perrett S, Yan XY. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:577–83.
Mu JS, Zhang L, Zhao M, Wang Y. Catalase mimic property of Co3O4 nanomaterials with different morphology and its application as a calcium sensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(10):7090–8.
Wang XL, Yang Q, Cao YX, Hao HB, Zhao JH, Hao JC. Metallosurfactant ionogels in imidazolium and protic ionic liquids as precursors to synthesize nanoceria as catalase mimetics for the catalytic decomposition of H2O2. Chem Eur J. 2016;22(49):17857–65.
Natalio F, Andre R, Hartog AF, Stoll B, Jochum KP, Wever R, Tremel W. Vanadium pentoxide nanoparticles mimic vanadium haloperoxidases and thwart biofilm formation. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012;7:530–5.
Xi XX, Wang JH, Wang YZ, Xiang HY, Chen MM, Wu Z, Zhang XH, Wang SF, Wen W. Preparation of Au/Pt/Ti3C2Cl2 nanoflakes with self-reducing method for colorimetric detection of glutathione and intracellular sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Carbon. 2022;197:476–84.
Ye QY, Dai T, Shen J, Xu Q, Hu XY, Shu Y. Incorporation of fluorescent carbon quantum dots into metal–organic frameworks with peroxidase-mimicking activity for high-performance ratiometric fluorescent biosensing. J Anal Test. 2023;7:16–24.
Li S, Wei ZY, Xiong L, Xu Q, Yu L, Xiao YX. In situ formation of o-phenylenediamine cascade polymers mediated by metal-organic framework nanozymes for fluorescent and photothermal dual-mode assay of acetylcholinesterase activity. Anal Chem. 2022;94(49):17263–71.
Dai XH, Liu H, Cai B, Liu Y, Song KP, Chen J, Ni SQ, Kong LS, Zhan JH. A bioinspired atomically thin nanodot supported single-atom nanozyme for antibacterial textile coating. Small. 2023;19(47):2303901.
Wu SL, Wu WW, Zhu XY, Li MH, Zhao JG, Dong SJ. Atomically dispersed hierarchically ordered porous Fe–N–C single-atom nanozymes for dyes degradation. Nano Res. 2023;16:10840–7.
Chen JQ, Liu XY, Zheng GZ, Fang W, Wang P, Gao J, Liu JB, Wang MZ, Wang QY. Detection of glucose based on noble metal nanozymes: mechanism, activity regulation, and enantioselective recognition. Small. 2022;19(8):2205924.
Cai SF, Duan HH, Liang XX, Wang C, Yang R, Li YD. Single-layer Rh nanosheets with ultrahigh peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric biosensing. Nano Res. 2018;11:6304–16.
Dong C, Yu Q, Ye RP, Su PP, Liu J, Wang GH. Hollow carbon sphere nanoreactors loaded with PdCu nanoparticles: void-confinement effects in liquid-phase hydrogenations. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59(42):18374–9.
Liu YY, He Q, Li YR, Li YQ, He CY. Synthesis of copper-based nanoparticles confined in a pyridine N-containing COF and their catalytic applications. Micropor Mesopor Mater. 2024;364:112868.
Qian C, Teo WL, Gao Q, Wu HW, Liao YZ, Zhao YL. Polycrystalline covalent organic frameworks. Mater Today. 2023;71:91–107.
Wang XR, Han X, Zhang J, Wu XW, Liu Y, Cui Y. Homochiral 2D porous covalent organic frameworks for heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(38):12332–5.
Nguyen HL, Gropp C, Ma YH, Zhu CH, Yaghi OM. 3D covalent organic frameworks selectively crystallized through conformational design, and functions. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;142(48):20335–9.
Zhang M, Meng L, Yang MY, Liao JP, Liu YF, Yan HJ, Chang JN, Yu TY, Li SL, Lan YQ. Ultrafine Cu nanoclusters confined within covalent organic frameworks for efficient electroreduction of CO2 to CH4 by synergistic strategy. eScience. 2023;3(3):100116.
Xin Y, Liu XJ, Wang CL, Liu NZ, Jiang QT, Duan JZ. Electrochemical detection of copper ions with covalent organic frame material modified carbon paste electrode. Chin J Anal Lab. 2023;42(9):1199–204.
Liu XY, Wang F, Meng Y, Zhao LP, Shi WJ, Wang X, He ZK, Chao J, Li CL. Electrochemical/visual microfluidic detection with a covalent organic framework supported platinum nanozyme-based device for early diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;207:114208.
Yuan RR, Li HK, He HM. Recent advances in metal/covalent organic framework-based electrochemical aptasensors for biosensing applications. Dalton Trans. 2021;50:14091–104.
Li GR, Wu YJ, Zhong C, Yang YX, Lin ZA. Predesigned covalent organic framework with sulfur coordination: anchoring Au nanoparticles for sensitive colorimetric detection of Hg(II). Chin Chem Lett. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108904.
Zhang C, Wang P, Yin X, Liu H, Yang Y, Cheng L, Song G, Zhang X. Two-photon supramolecular nanoplatform for ratiometric bioimaging. Anal Chem. 2019;91(9):6371–7.
Lai X, Shen Y, Gao SB, Chen YJ, Cui YS, Ning DX, Ji XB, Liu ZW, Wang LG. The Mn-modified porphyrin metal-organic framework with enhanced oxidase-like activity for sensitively colorimetric detection of glutathione. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;213:114446.
Li G, Hu GX, Chen B, Gu Y, Yang JY, Yang HB, Hu FX, Li CM, Guo CX. Boosting photo-electro-fenton process via atomically dispersed iron sites on graphdiyne for in vitro hydrogen peroxide detection. Small. 2023;19(33):2301540.
Zhu ZM, Yan DP, Huang ZH, Zhong XL, Shen Y. Detection of glutathione based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a fluorescence probe. Chin J Anal Lab. 2023;42(11):1508–15.
Ganganboina AB, Doong R. The biomimic oxidase activity of layered V2O nanozyme for rapid and sensitive nanomolar detection of glutathione. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;273:1179–86.
Li JZ, Li YH, Gao ZF. Polydopamine-based colorimetric superwettable biosensor for highly sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. J Anal Test. 2023;7:118–27.
Liang Y, Liu YY, Zhao P, Chen YY, Lei JC, Hou JZ, Hou CJ, Hou DQ. An electrochemical sensor based on FeCo bimetallic single-atom nanozyme for sensitive detection of H2O2. Anal Chim Acta. 2023;1281:341867.
Liang N, Ge XY, Zhao Y, Xia L, Song ZL, Kong RM, Qu FL. Promoting sensitive colorimetric detection of hydroquinone and Hg2+ via ZIF-8 dispersion enhanced oxidase-mimicking activity of MnO2 nanozyme. J Hazard Mater. 2023;454:131455.
Wang HS, Wu FL, Wu LF, Guan JQ, Niu XD. Nanozyme colorimetric sensor array based on monatomic cobalt for the discrimination of sulfur-containing metal salts. J Hazard Mater. 2023;456:131643.
Feng SN, Yan MX, Xue Y, Huang JS, Yang XR. Electrochemical immunosensor for cardiac troponin I detection based on covalent organic framework and enzyme-catalyzed signal amplification. Anal Chem. 2021;93(40):13572–9.
Peng XL, Zhu JL, Wu Z, Wen W, Zhang XH, Chen MM, Wang SF. High-efficient Pt@COF nanospheres-based electrochemical-chemical-chemical redox cycling for ultrasensitive microRNAs biosensing. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2023;392:134074.
Zhang T, Chen YL, Huang W, Wang Y, Hu XY. A novel AuNPs-doped COFs composite as electrochemical probe for chlorogenic acid detection with enhanced sensitivity and stability. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;276:362–9.
Kang X, Cao GJ, Wang JP, Wang J, Zhu X, Fu MY, Yu DH, Hua L, Gao FL. Synergistic action of cavity and catalytic sites in etched Pd-Cu2O octahedra to augment the peroxidase-like activity of Cu2O nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of isoniazid and ascorbic acid. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024;246:115880.
Zhou LL, Guan Q, Li YA, Zhou Y, Xin YB, Dong YB. One-pot synthetic approach toward porphyrinatozinc and heavy-atom involved Zr-NMOF and its application in photodynamic therapy. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(6):3169–76.
Zhuang YX, Zhang XD, Chen QM, Li SQ, Cao HY, Huang YM. Co3O4/CuO hollow nanocage hybrids with high oxidase-like activity for biosensing of dopamine. Biomater Adv. 2019;94:858–66.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22076041, 22076042) and the Key Research and Development Program of Hubei Province, China (2023BAB134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, Y., Xi, X., Bao, T. et al. Integrating Bimetallic Nanoparticles with Covalent Organic Frameworks as Multifunctional Nanozyme for Colorimetric Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide and Glutathione. J. Anal. Test. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-024-00298-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41664-024-00298-y