Abstract
Research suggests that training relational operant patterns of behavior can lead to increases in general cognitive ability and educational outcomes. Most studies to date have been under-powered and included proxy measures of educational attainment. We attempted to extend previous findings with increased experimental control in younger children (aged 6.9–10.1 years). Participants (N = 49) were assigned to either a relational training or chess control group. Over 5 months, teachers assigned class time to complete either relational training or play chess. Those who were assigned relational training gained 8.9 non-verbal IQ (NVIQ) points, while those in the control condition recorded no gains (dppc2 = .99). Regression analyses revealed that post-training NVIQ predicted reading test scores (conducted approximately 1 month later) over and above baseline NVIQ in the experimental condition only, consistent with what we might expect in a full test of far transfer towards educational outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Within any given peer group, it is possible to rank individuals intellectually based on their answers to an arbitrary set of questions that require symbolic manipulation to answer correctly. Curiously, their relative peer ranking will tend to be the same across a brand new set of such questions. This score is typically known as an intelligence quotient (IQ), and it, in turn, predicts scores across other tests (Conway & Kovacs, 2015; Van Der Maas et al., 2006). IQ also predicts success regarding other informal tests including educational achievement, occupational progression, healthy habits, and social success (Strenze, 2007). There are some who argue that the general predictive validity of IQ is perhaps one of the most mainstream and robust findings in psychology (Gottfredson & Deary, 2004; Haier, 2016; Ritchie, 2015).
The critical test of whether one has enhanced IQ (cf. Jensen, 1989) is that improvements on the tasks used to train IQ will show near transfer (e.g., to other intellectual tests) and far transfer (e.g., to educational outcomes). Psychologists have generally struggled to train IQ such that it impacts cross-domain outcomes, such as educational attainment. This is compounded by the fact that contemporary intelligence research often focuses on the link between genes and intelligence or proxy measures of intelligence such as attainment (Davies et al., 2018; Hill et al., 2018a; Hill et al., 2018b; Plomin & Von Stumm, 2018; Savage et al., 2018; Smith-Woolley et al., 2018; Zabaneh et al., 2017). Some researchers even believe educators are powerless in terms of improving children’s educational outcomes (e.g., Detterman, 2017). Smith-Woolley et al. (2018) recently noted that differences in state General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) examination performance across the UK public non-selective, public selective, and private schools mirror the genetic differences between them, suggesting that socioeconomic status and social mobility are a reflection of differences in genetic dispositions (cf. also Abdellaoui et al., 2018). While this research endeavor is useful for understanding the biological basis of human cognition, it has, so far, not yielded much insight into how to improve it. This mainstream consensus within the neuroscience/behavioral genetics wings of intelligence research (Haier, 2016) may be disheartening for educators.
Cognitive interventions for improving intelligence have typically attempted to train working memory in recent years (e.g., Buschkuehl, Hernandez-Garcia, Jaeggi, Bernard, & Jonides, 2014; Jaeggi, Buschkuehl, Jonides, & Shah, 2011; Jaeggi, Buschkuehl, Shah, & Jonides, 2014; Jones, Peterson, Blacker, & Berryhill, 2017; Soveri, Karlsson, Waris, Grönholm-Nyman, & Laine, 2017; von Bastian, Langer, Jäncke, & Oberauer, 2013). A meta-analysis conducted by Au et al. (2015) reported that the most notable attempt at raising intelligence with working memory training (N-Back training) yielded a 2–3 point mean rise in IQ across several studies (Au et al., 2015), and even this small increase is disputed (Sala & Gobet, 2017d). Moreover, putative reports of near and far transfer of working memory training have typically failed to replicate under stringent conditions (e.g., Chooi & Thompson, 2012; Colom & Román, 2018; Colom et al., 2013; Fissler et al., 2017; Hilbert et al., 2017; Melby-Lervåg & Hulme, 2013, 2016; Melby-Lervåg, Redick, & Hulme, 2016; Schwaighofer, Fischer, & Bühner, 2015; Shipstead, Redick, & Engle, 2012; Stephenson & Halpern, 2013; Thompson et al., 2013). In a similar fashion, chess (Sala & Gobet, 2017a), video games (Sala et al., 2018; Simons et al., 2016), music (Sala & Gobet, 2017c), and compensatory education (McKey, 1985) are all strategies that have failed to raise general cognitive ability, leading many to the general conclusion that “brain training doesn’t work” (Kassai et al., 2019; Sala & Gobet, 2019). However, one might argue that most of these approaches are quite theoretically imprecise and perhaps unlikely to work in the first place, highlighting the need for a cogent theory of language and cognition when conceptualizing cognitive training interventions.
From a behavior-analytic point of view, latent traits such as IQ are low resolution in that they do not specify the processes through which we adapt to the environment (see Schlinger, 2003). Instead, the shared variance across multiple cognitive tests (hereinafter, g or IQ if also corrected for age) is simply a useful statistical summary of multiple undelineated processes through which we adapt to our environments. Therefore, training more basic and defined patterns of generally adaptive behavior may be a useful way of training the discrete patterns of cognition typically summarized as g. Behavior analysts call these patterns “operants” or ways of operating upon our environments.
One particular behavior-analytic theory, relational frame theory (RFT; Hayes, Barnes-Holmes, & Roche, 2001), conceptualizes language and cognition as operant behavior, specifically the capacity for arbitrarily applicable relational responding (AARR or “relational framing behavior”). AARR is the behavior of responding to one stimulus in terms of another based on their symbolic properties. For example, “here” only exists relative to “there,” “before” relative to “after,” “same” relative to “different,” and so on. Some more straightforward relations are symmetrical. For example, if A = B, then B also = A, or if A is opposite to B, then B is opposite to A. More complex relations are asymmetrical. For example, if A > B, then we do not say that B > A; we need to say that B < A. This linguistic practice is a useful social convention that can be learnt. The key feature of AARR is in deriving novel, untrained relations, as this helps to account for the complexity and generativity associated with human language and cognition. For example, given that A > B and B > C, people can derive the reverse relations (B < A and C < B) and also relations between A and C, which were never previously paired (i.e., A > C and C < A). AARR becomes psychologically relevant when a member of the network is salient. For example, imagine that A means “a dollar,” which you know from your direct experience is valuable. If I then tell you that a dollar (A) < an unknown currency (B), you will treat B as being of greater value having never directly encountered B and its associated functions. We can test this by offering you a choice between having either a dollar or a B.
Operant skills are “go-to” patterns of behavior that get amended based on whether they achieve their intended functions in particular situations. Therefore, they can also be trained by manipulating the environment (see Kishita, Ohtsuki, and Stewart (2013); McLoughlin and Stewart (2017); Moran, Walsh, Stewart, McElwee, and Ming (2015)). Not only can relational operants be trained, but they are strongly associated with IQ (Colbert et al., 2017), and this is congruent with converging consensus from the fields of neuroscience (Davis et al., 2017), linguistics (Everaert et al., 2015; Goldwater, 2017), evolutionary biology (Wilson & Hayes, 2018), and cognitive psychology (Alexander, 2019; Goldwater, Don, Krusche, & Livesey, 2018; Goldwater & Schalk, 2016; Halford, Wilson, & Phillips, 2010; Kaufman, DeYoung, Gray, Brown, & Mackintosh, 2009) that relational reasoning is central to cognition.
“Strengthening Mental Abilities with Relational Training” (SMART) is a commercial online program that trains relational framing operants (i.e., same/different and more/less relations) via multiple exemplar training in a gamified format. To date, several studies have suggested that training relational framing in this format leads to rises in IQ (Amd & Roche, 2018; Cassidy, Roche, Colbert, Stewart, & Grey, 2016; Cassidy, Roche, & Hayes, 2011; Colbert, Tyndall, Roche, & Cassidy, 2018; McLoughlin, Tyndall, & Pereira, 2018; Parra & Ruiz, 2016; Thirus, Starbrink, & Jansson, 2016; Vizcaíno-Torres et al., 2015) and there are putative indications of improvements in educational outcomes (Cassidy et al., 2016; J. Hayes & Stewart, 2016). Several studies with RFT-based interventions have also reported to enhance performance on specific tests such analogical responding (Ruiz & Luciano, 2011), hierarchical responding (Mulhern et al., 2017, 2018), and statistical learning (Sandoz & Hebert, 2017). These studies are typically too small to be generalizable to the broader population. However, these studies show preliminary evidence for the utility of relational skills training and that operant abilities are skills through which we adapt to our environments (see also O’Hora et al. (2008); O’Hora, Pelaez, and Barnes-Holmes (2005); O’Toole, Barnes-Holmes, Murphy, O’Connor, and Barnes-Holmes (2009); also see Cassidy, Roche, and O’Hora (2010), for a discussion of how relational skills are related to IQ test items).
Hayes and Stewart (2016) attempted to test the differential effects of relational training (n = 14) and an active control condition (computer programming, which requires high cognitive engagement; n = 14) for improving performance on memory, literacy, and numeracy in children aged 10–11 years. Those who completed relational training improved their scores on various educationally relevant IQ subtests, including spelling, reading, and numerical operations. This study was novel in that it employed the Drumcondra Primary Reading Test (DPRT) and Drumcondra Primary Mathematics Test (DPMT) as outcome variables. These are standardized tests of the Irish National Curriculum, thus allowing the researchers to test for improved school performance while controlling for relevant learning opportunities. These tests are also independently assessed such that the effects of teacher biases are reduced. In their study, Hayes and Stewart (2016) recorded correlations between AARR ability and (i) DPRT performance (r = .59) and (ii) DPMT performance (r = .69). Additionally, those who completed relational training had significantly higher DPMT scores, with large effect sizes. This remains the only active-controlled RCT testing the far transfer of relational training effects to date and the only such study to employ a curriculum-appropriate independently designed test of educational achievement as the outcome variable. We sought to conceptually replicate and extend this research in the present study, but with a larger sample.
Of particular relevance to the present study, Amd and Roche (2018) provided relational training to a single sample of 35 socially disadvantaged children in Bangladesh and observed rises in Fluid Intelligence as measured using a standard matrix reasoning test. In typical SMART studies in which large rises in Fluid Intelligence are recorded, participants complete 55 relational training stages. In Amd and Roche (2018), training completion varied. Those who completed greater than 13 stages of relational training demonstrated significantly higher rises in Fluid Intelligence (+ 5 fluid IQ points) than those who completed 7 stages or less (+ 1 point). This study suggests that participants can benefit from relational training quite early on. However, it is not clear whether this depends on their baseline cognitive ability. We sought to explore this further in the present study.
Previous research has found that relational training significantly enhances the full-scale IQ of children as young as 10 or 11 years of age (Cassidy et al., 2011; Hayes & Stewart, 2016). It is not yet clear what are the earliest ages at which it might be deemed to be feasible or appropriate to engage in relational training (e.g., SMART program) in order to observe cognitive enhancements typically reported with older children and adolescents (e.g., Cassidy et al., 2016; Colbert et al., 2018). Derived relational responding (or AARR) has been reported in an infant as young as 27 months (Lipkens et al., 1993) and in preschool children (Smeets et al., 2001), so it is known that very young children can demonstrate stimulus equivalence or relations of sameness. It is less clear how young children fare in experimental preparations designed to train more complex relations such as more than and less than. Furthermore, RFT-based interventions such as the SMART program are labor and time intensive, and we are not yet sure whether younger children would have the capacity, motivation, or will to consistently engage with a relational training intervention over a period of months, even in a gamified format. Thus, two of the key questions the present study aims to examine are whether children as young as 6 or 7 years old will demonstrate the capacity to engage with and benefit from more complex relational training (i.e., more than/less than) and whether they would evidence the motivation to persist with the training program over a prolonged period of time.
Besides IQ, there are also some non-cognitive factors (e.g., Studer-Luethi et al., 2012) that predict cognitive training success and educational attainment. For example, with respect to factor theories of personality, conscientiousness, the proclivity for order and hard work, is positively associated, while neuroticism, or susceptibility towards negative emotion, is broadly negatively associated with educational attainment. Additionally, with limited time for assessment, including measures of both personality and intelligence can help to parsimoniously account for a range of other non-cognitive factors thought to affect educational outcomes: e.g., (i) agreeableness, sex, and cognitive ability explain 65% of the variance in “emotional intelligence” (Schulte et al., 2004); (ii) “grit” does not predict school outcomes after controlling for conscientiousness (Ivcevic & Brackett, 2014); (iii) “emotional regulation strategies” are poorer predictors of depression than neuroticism, but they share common variance (Andrés et al., 2016); (iv) the relationship between cognitive “self-appraisal” and “test anxiety” is fully accounted for by personality (Chamorro-Premuzic et al., 2008); and (v) the inclusion of the big five personality factors reduces the variance explained by learning styles in GPA from 10 to only 3% (Komarraju et al., 2011). While IQ is a stronger predictor of educational attainment than personality factors (Bergold & Steinmayr, 2018), it is still important to account for non-cognitive factors (West et al., 2016). Personality tests measure relatively stable patterns of behavior that have broader scope than other non-cognitive factors that appear to impact educational outcomes. The brevity and generality of the items means that these data can be obtained with lower response burden on participants compared with other factors. In this study, we tested the effects of a behavioral training system on non-verbal IQ (NVIQ; i.e., standardized responses on the non-verbal sub-scale of the Kaufman Brief IQ Test, Second Edition) and educational attainment while accounting for the effects of personality. The only a priori prediction we had about how personality would affect our study outcomes was that neuroticism would be negatively related to training completion; all other analyses involving personality were exploratory.
There remains a dearth of tests of the utility of the relational training programs with large samples and active control conditions, with tests of far transfer of training effects (especially real educational outcomes). The biggest studies to date are Cassidy et al. (2016; N = 30) and Hayes and Stewart (2016; N = 28). Additionally, Hayes and Stewart (2016) is the only study to employ a strong active control condition and include a real educational outcome measure. The overarching aims of this study were to provide a larger, independent, active-controlled test of (i) the effects of SMART training on the ability to learn (i.e., NVIQ) and (ii) whether any gains in NVIQ would explain variance in educational outcomes (i.e., the DPRT and DPMT), in a younger sample than has been tested heretofore. We chose to measure NVIQ instead of a verbal measure (e.g., vocabulary) as we were interested in measuring and training the ability to learn and cognitively manipulate information (NVIQ) rather than the sum total of what someone has learnt, which is dependent on both the ability to learn + exposure to learning opportunities. We chose chess as the control condition as chess has previously been used for cognitive training (cf. Sala & Gobet, 2017a). We hypothesized that training effects would transfer towards examinations that depended on participants’ performance on the day (e.g., reading comprehension) and less so for those that depend more heavily on participants having successfully availed of prior learning opportunities (e.g., mathematics). Additionally, as a “catch-all” indicator of non-cognitive traits, we included a measure of personality to explore their role in relational frame training completion and performance.
Method
Participants
We recruited from three cohorts of pupils in a rural Irish primary school, aged 6.7–10.1 years (M = 8.67, SD = .91) and then assigned them to one of two conditions (see Design for details). To ensure equal opportunity to participate, those who were allocated to the control condition were given access to the training after the study. No participants were purposefully excluded. To be included in this study, participants needed to be students at the school in question, participating in the standard curriculum. We began with 55 participants; however, due to attrition (one child moved schools and four were absent for testing), we analyzed data from 49 participants in our final analysis of the effects of SMART training on NVIQ, leaving us with an 89% retention rate. Thirty were in the experimental condition (SMART training; 20 girls), and 19 were in the control condition (chess; 13 girls). Participants were treated in accordance with the British Psychological Society Code of Human Research Ethics and were allowed to withdraw at any point.
Materials
We chose NVIQ, DPRT, and DPMT as our three main outcome variables, as they all differed substantially from the experimental and control condition training tasks. Additionally, any improvements in performance on NVIQ are not dependent on the learning opportunities participants receive in the curriculum; this was a performance-based measure. For the most part, the DPRT and DPMT test the degree to which pupils avail of learning opportunities presented by the teacher, whose job is to teach these tests; these are largely knowledge-based measures. However, the reading comprehension subtest of the DRPT involves making sense of previously unseen material and is arguably better characterized as a performance outcome measure.
Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test-2 (Kaufman & Kaufman, 2004)
We measured NVIQ using the non-verbal sub-scale of the KBIT-2. This is a 46-item standardized test of abstract matrix reasoning ability that is suitable for ages 4–90 years. During each trial, a series of abstract geometric/colored shapes were required to complete a sequence of patterns by selecting the correct image from an array of possible alternatives.
Drumcondra Tests
The Drumcondra tests are standardized tests of educational attainment in relation to the Irish National Curriculum for primary schools (see Hayes and Stewart (2016)). These tests were group administered during school time by school staff.
Drumcondra Primary Reading Test—Revised
There are three main sub-scales of this reading test: (i) vocabulary, (ii) reading comprehension, and (iii) word analogies. We also recorded total reading scores across the vocabulary and comprehension subtests. All questions were in multiple-choice format. For each scale, there were four different indices of performance: (i) raw scores, (ii) standard scores (i.e., scores relative to others the same age), (iii) Sten scores (a ranked score from 1 to 10 in which “5” represents the mean), and (iv) percentile ranks. According to the Educational Research Centre (2007), using the Kuder-Richardson Formula (KR20), the DPRT has an internal consistency of .93.
Drumcondra Primary Mathematics Test—Revised
This test is based on the 1999 Primary School Mathematics Curriculum. About half of the questions were in multiple-choice format, while the rest involved written work such as short-answer questions or drawing diagrams. Similar to the DPRT, there were four different indices of performance: (i) raw scores, (ii) standard scores, (iii) Sten scores, and (iv) percentile ranks. According to the Educational Research Centre (2006), the KR20 coefficient for the DPRT is .93.
Big Five Scale for Children (Gaio, 2012)
We measured personality factors using the BFC. The BFC is a 65-item self-report scale that assesses five different dimensions of children’s non-cognitive behavioral preferences/temperaments. These are negative emotionality, agreeableness, conscientiousness, extraversion, and openness. The BFC is answered on a 5-point Likert scale (almost never-almost always). Gaio (2012) reported alpha values ranging from .78 to .88 for the BFC; however, our alpha values ranged from .58 to .88, suggesting that this measure may not have as much internal reliability as we expected. Tentatively, this measure does also have good test-retest reliability, with coefficients ranging from .62 to .84 in the Spanish version (De Oviedo et al., 2005). Nonetheless, we retained this baseline measure as a potentially useful “catch-all” indicator of children’s traits.
Procedure
Allocation to Conditions
Participants were allocated to one of two conditions based on timetabling convenience for their respective classes. A series of Mann Whitney U tests were conducted to test for differences in median scores in age, NVIQ, and personality across the experimental and control conditions at time 1 (using a Bonferroni correction). There was no evidence of differences in age, NVIQ, nor any of the big five personality traits across conditions at time 1. Additionally, a Pearson’s chi square analysis indicated that boys and girls were also not differentially distributed across conditions. Therefore, it appears that, although we employed convenience allocation to each condition, key traits were not differentially distributed across conditions at baseline.
Conditions
Those in the experimental condition were given access to the training over a 4-month period during the school year, in which they received a minimum of 240 min of supervised training during their class under their teacher’s supervision (see Fig. 1 for a full timeline). During this period, participants were differentially reinforced for making progress on a weekly basis with tokens for completing training at home. Tokens gained students entry to an end-of-year prize draw. For completing each of the first 10 stages, students gained one ticket. From stages 11–20, they gained two tickets per stage. From stages 21–30, they gained three tickets per stage. From stages 31–40, they gained four tickets per stage. Finally, from stages 41–47 (the highest stage reached), they gained five tickets per stage. At the same time, those in the control condition were allowed to play online chess on the school iPads during the same period, as this was already part of the school curriculum and was previously hypothesized to be a useful cognitive training in its own right (Sala & Gobet, 2017a). We measured all participants’ NVIQ before and after SMART/chess training. We also measured personality traits at baseline and literacy (DPRT) and numeracy (DPMT) approximately 1 month after training. This procedure is summarized in Fig. 1.
SMART Experimental Condition
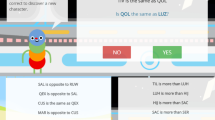
Participants received training in the general ability to derive relations between arbitrary nonsense syllables based on English language cues. This program trained the receptive ability to derive relations of sameness/opposition (symmetrical relations) and more than/less than (asymmetrical relations). The training consisted of up to 70 stages, which started at an “easy” level (see Fig. 2, upper left) and became progressively more difficult (see Fig. 2, upper right for a stage representing the median highest stage completed, lower left for the highest stage completed, and lower right for a later stage representing the highest possible complexity level currently available).
Participants unlocked new stages of slightly increased complexity upon demonstrating that they had mastered the previous stage. As seen in Fig. 2, early stages involve simply deriving relations based on short A-B networks (e.g., Fig. 2, upper left), while a more complex network might involve A-C networks (e.g., Fig. 2, lower left). More advanced stages involved more/less relations, which are more difficult because they are asymmetrical. That is, if A = B, then B simply = A, while on the other hand, if A > B, B is not > A; we need a new symbol to represent the reverse of a > relationship. In this case, the appropriate symbol is physically the reverse of “>” (i.e., “<”), but this is not always the case. For example, the cue “more than” does not physically resemble the cue “less than,” but it is functionally opposite. Users were only allowed to complete up to five new stages per day. During training blocks, participants received corrective feedback after each response by way of a progress bar. Participants were required to answer 16 trials consecutively correct to proceed to the testing phase and the progress bar reset following each wrong answer. Participants received an array of 16 trials of a similar type/complexity during test blocks, only this time without corrective feedback. The overall probability of passing any testing phase by chance was approximately .000015. Before proceeding to a new stage, participants were required to pass the testing block of each stage. If they did not pass, they would have to repeat the training block. Participants were also allowed to revisit previous trials. To ensure that each trial was unique, participants were never allowed to see the same nonsense syllable more than once on each training account. As such, participants were trained in the domain-general act of deriving stimulus relations and not in simply remembering particular relations from one trial to the next. The software recorded an incorrect response and presented a new trial after a 30-s time limit had elapsed. Participants were allowed to adjust the time limit for each trial if they wished to challenge themselves further. Participants were not required to complete a specified number of stages.
Chess Active Control Condition
We chose this control activity because teachers at this school reported children being motivated to work harder at school for chess time in previous years. This activity was led by their classroom teacher on a weekly basis. Those in the control condition received a minimum of 240 min of chess (Dora Logic Ltd., 2018) on the school iPads from February to June of the school year, analogous to the experimental condition. Just as the training group were able to increase their difficulty by progressing through new stages and adjusting their time limits, those who played chess could challenge themselves by availing of three different CPU opponent difficulty settings. In accordance with RFT, the game of chess involves the complex manipulation of symbols for pragmatic purposes but theoretically with less precision than SMART training.
Results
Descriptive Statistics
Preliminary descriptive statistics (including means, standard deviations, and confidence intervals) for our main variables of interest can be found in Table 1. We then explored the intercorrelations between our main variables of interest, using a Bonferroni correction to control for multiple comparisons (see Table 2).
Training Completion
In the experimental condition, the mean number of training stages completed was 14.57 (SD = 11.20, Mdn = 9) out of the 70 stages available. We examined the relationship between the number of relational training stages that those in the experimental condition completed and all our other baseline measures to understand who, in our sample, was more likely to engage in training. There was a strong negative relationship between susceptibility to negative emotion and the number of training stages completed (r[22] = − .64, p = .001). We found no other relationships between personality traits nor NVIQ and training completion. NVIQ change was not linearly related to the number of training stages completed (see Fig. 3).
NVIQ
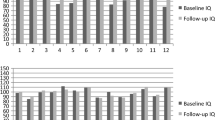
We used a mixed-design analysis of variance to assess the effects of one between-subjects factor (conditions: SMART and chess) and one repeated measures factor (time: time 1 and time 2) on NVIQ (see Fig. 4).
We observed a main effect of condition on NVIQ (F[1, 47] = 7.23, MSE = 273.87, p = .010, ƞp2 = .13). We did not observe an overall effect of time on NVIQ (F[1, 47] = .84, MSE = 153.13, p > .05). There was an interaction effect between condition and time on NVIQ (F[1, 47] = 6.53, MSE = 153.13, p = .014, ƞp2 = .12). This interaction was such that when observing the simple effects in the experimental condition, we found significant increases in NVIQ from time 1 (M = 99.57, SD = 12.32) to time 2 (M = 108.47, SD = 14.30) indicating that the training was successful in the experimental condition (ΔNVIQ = 8.90; F[1, 47] = 7.76, p = .008, CI = 2.47–15.33, ƞp2 = .14). However, in the chess condition, there was no significant change in NVIQ from time 1 (M = 96.90, SD = 14.05) to time 2 (M = 92.68, SD = 18.54). The overall effect size in the experimental condition, in accordance with Morris’ (2008) guidelines was dppc2 = .99, with power of 1-β = .779. We calculated the Reliable Change Index (Zahra et al., 2016) at 3.50, suggesting that the observed change in the experimental condition is not accounted for by test-retest unreliability.
Which Participants Improved with Training?
We attempted to find out who gained the most NVIQ within the experimental condition. There was a moderate negative relationship between baseline NVIQ and the degree to which participants in the experimental group’s NVIQ scores changed from time 1 to time 2 (r[29] = − .37, p = .042).
Relationships Between NVIQ and Educational Outcomes
It was not possible to conduct pre- and post-training curriculum-appropriate educational achievement tests to probe for far transfer of training effects. However, the purpose of these analyses was to test whether NVIQ at time 2 would predict test results once we controlled for NVIQ at time 1. This would allow us to adjudicate between two competing hypotheses. H0: NVIQ at time 2 does not predict educational outcomes once controlling for NVIQ at time 1. This outcome would imply that there is no evidence for far transfer of relational training effects. H1: NVIQ at time 2 predicts educational outcomes even when controlling for NVIQ at time 1. This outcome would be consistent with what we might expect to observe in a direct test of far transfer. It appeared that, once controlling for baseline NVIQ, there were strong relationships between post-training NVIQ and reading comprehension outcomes in the experimental condition only (see Table 3, upper right). Table 3 presents several partial correlations in which time 2 NVIQ correlated with reading outcomes over and above time 1 NVIQ.
Follow-up multiple regression analyses revealed that time 2 NVIQ predicted performance on reading comprehension tests conducted approximately 1 month later over and above time 1 NVIQ, explaining 7% (Comp RS) and 14% (Comp SS) additional variance, respectively (see Fig. 5 for a summary; however, these results are presented in more detail in Table 4).
Unique variance explained by time 2 NVIQ in reading examination scores approximately 1 month later in the SMART condition. See Table 4 for detailed regression analyses
Discussion
In this study, we replicated and extended previous tests of the efficacy of relational training, employing a larger and much younger sample. Participants in previous relational (i.e., SMART) training studies typically completed 55 training stages, compared with just under 15 stages on average in the current study. It is notable that this low training dosage yielded a NVIQ increase (of 8.9 points) that was about three times as large as the most recent popular working memory training (see Au et al. (2015)), with a large effect size. Additionally, the observed NVIQ gains following SMART training explained a substantial amount of variance in independently assessed curriculum-appropriate test results.
We also found that those who were less susceptible to negative emotion completed more relational training. This suggests that this training, as expected, is cognitively challenging and that those who generally tend to react to challenging situations by withdrawing or by getting frustrated will complete less training, all things being equal. We found no evidence to suggest that those who were “smarter” in the first place found training easier from the beginning and subsequently entered into a positive feedback loop that allowed them to achieve the highest NVIQ gains. Instead, those who had lower NVIQ at baseline appeared to benefit more from this lower-complexity training (M = 14.57 stages completed). It is possible that those with higher baseline ability were not challenged enough, cognitively speaking, as they may have reached the later stages; this will be important to test in future research. SMART allows users to make small, gradual steps up in difficulty (see Fig. 2) informed by findings from an established research program in the experimental analysis of human behavior (see Dymond and Roche (2013), for a book-length review), which may benefit those who require smaller steps up in difficulty to make progress.
We did not find a linear relationship between training completion and NVIQ change, as might be expected given the negative relationship between NVIQ change and baseline NVIQ. In the future, more highly powered studies may be able to test for a non-linear relationship between training completion and NVIQ change. We predict that the relationship between NVIQ change and training completion will be higher for those who have lower NVIQ at baseline. Additionally, in future studies with larger samples, it will be important to test whether training completion mediates the change in NVIQ from time 1 to time 2.
Post-training NVIQ predicted reading comprehension performance (on the DPRT) over and above pre-training NVIQ. Perhaps, this should not be surprising, given that reading comprehension involves manipulating symbols/language given previously unseen information, which is what relational training aims to strengthen. Similarly, it is unsurprising that the residual NVIQ did not explain variance in other aspects of reading performance such as vocabulary because vocabulary scores are dependent on both (i) participants’ abilities and (ii) having had the learning opportunities to learn new words in the first place. It is possible that the vocabulary learning opportunities were not presented after experimental participants had gained an increased ability to learn (i.e., NVIQ). We would only expect vocabulary and other measures of crystallized knowledge to improve if relational skills were improved prior to learning opportunities being presented. With the ability to semantically relate and differentiate words in complex relational networks (cf. McLoughlin & Stewart, 2017), vocabulary may expand thereafter, subject to appropriate learning opportunities. Reading comprehension may be considered to be a purer performance measure of literacy, rather than a task that requires prior learning opportunities.
On the other hand, we did not find that residual NVIQ in the relational training condition explained variance in mathematics outcomes, however. This might, at first glance, appear somewhat surprising given the findings of Hayes and Stewart (2016), who reported that completing relational training led to improved DPMT scores but not improved DPRT scores. However, this discrepancy may likely be partially due to the large difference in the numbers of training stages completed (14.57 in present study versus 55 in Hayes and Stewart (2016)). Importantly, the first 29 stages of the program involve training same/different relations (i.e., equivalence and non-equivalence), and the remaining 26 stages focus on establishing more than/less than relations. Thus, with an average of just under 15 training stages completed, it is likely that a substantial portion of the sample did not reach the more than/less than relational training trials. Mathematics largely involves symbolic manipulation of quantities (e.g., which has the greater value—7 × 3 or 2 × 10?; If Sarah has 4 apples, 6 pears, and 2 oranges and Maria has 7 apples, 1 pear, and 6 oranges, who has the most fruit?). The present data suggest that it might be necessary to complete at least a certain number of more than/less than relational training trials to substantively impact subsequent performance on indices of mathematics aptitude or ability, although simpler symmetrical relations may still be useful for learning new mathematical terminology (cf. Sandoz & Hebert, 2017).
It was not possible for us to conduct a double-blind study, and so there is a possibility that the changes in NVIQ observed herein were partially the result of placebo effects or motivational differences across conditions. On the other hand, the magnitude of the increase in NVIQ in the experimental condition (8.90 NVIQ points or two-thirds of an IQ standard deviation) is not easily explained by motivational and expectancy effects. In particular, the acid test of whether one has really raised NVIQ (rather than simply motivation/expectations) is achieving far transfer towards unrelated real-world outcomes over a period of time. Given that the exams were conducted a month after the time 2 NVIQ test, far transfer is arguably the most likely explanation as to why time 2 NVIQ predicted exam performance over and above time 1 NVIQ in the experimental condition only. Disentangling the active components of SMART training is of course beyond the scope and aims of the present study, but we hope that this will be tested further in either a large-scale randomized controlled trial or in appropriate component studies. One possible future direction might be to systematically provide different SMART training dosages across experimental conditions so that motivation and the potential for expectancy effects are more equal across conditions. This would allow the effect of training completion be more clearly delineated. When dosage and possible engagement issues are addressed, then a substantially larger-N trial to estimate the potential public health value of the SMART intervention would be justified.
The increase in NVIQ is considerably less than was reported in several other SMART studies. However, participants in our study completed a mean of 27% of the training stages reported in other SMART studies (e.g., Cassidy et al., 2016, 2011; Colbert et al., 2018; Hayes & Stewart, 2016). The degree to which our participants’ NVIQ increased is roughly congruent with those studies, assuming that increases in intelligence due to relational training are linearly related to the amount of training completed (see also Amd and Roche (2018)).
In hindsight, the low average number of relational training trials completed in the present study as compared with previous studies referred to above is somewhat unsurprising. Due to time pressures to cover the content of the school curriculum, this particular school could only agree to allocate 240 min of class time to pupils in both conditions. This is a very low training dosage compared with those studies cited above, where participants typically engaged in relational training for 30–40 min per session, for three or four sessions per week, over a period of 3 or 4 months. Even allowing for the fact that participants could engage with the relational training program in their own time if they wished, the total number of hours of exposure to training is much less than in some studies. Amd and Roche (2018) also employed a similar measure of NVIQ (i.e., Matrices) and correspondingly noted a possible relationship between number of stages of training completed and NVIQ gain. Furthermore, targeting a sample with such a youthful age range (6–10 years) was ambitious for this kind of intensive cognitive training. The comparatively low training completion in this study is notable for researchers who wish to embark on a demanding program of relational frame training with young children of this age range in the future.
The present study is only the second test of the efficacy of relational operant training to employ an active control condition, and it is also the largest to date. While the inclusion of an active control condition is a useful addition to research in this domain, we acknowledge some methodological weaknesses with the control condition itself. Due to the nature of the school’s curriculum, the children were assigned 240 h to playing online chess as per their class schedule. However, there was no real way of measuring or recording their active engagement in this condition over that period, unlike the experimental condition where the program recorded the number of relational training trials completed and points gained. Moreover, participants in the experimental condition were encouraged to engage with the SMART program in their own free time on an ad hoc basis outside of the assigned 240 min within class time at school. Thus, the conditions were not evenly matched in terms of time spent on the two different tasks. Notwithstanding, a key difference between the groups, and what underpins successful engagement with relational training, is frequent behavioral reinforcement (i.e., after each trial). This core feature of multiple exemplar training is not as prominent in the control condition, meaning we expected both disproportional engagement and gains in the experimental condition.
Future research should consider including an active control condition that more closely mirrors an RFT-based relational training intervention. With the SMART program, this might currently be difficult or expensive in practice as it likely would involve developing a whole new control website that looks somewhat similar to the SMART website and incorporates similar features such as gamified characters and points gained. However, Cassidy et al. (2011) did include a control condition that were only exposed to equivalence training (i.e., same/different) and not more than/less than training, whereas the experimental group was exposed to both types of relational training. The gains observed in full-scale WISC IQ in the experimental group over and above the control group could be attributable to exposure to more than/less than relational training. It is possible that researchers could develop offline versions of such an experimental and control condition to provide a more robust scientific test of the potential of RFT-based intervention programs to demonstrate a stronger evidence-base of cognitive and educational enhancement.
We did not randomly assign participants to each condition. This was largely due to a stipulation from the institutional ethics committee that all children in the same class should have equal access to the relational training program. This led to unbalanced condition numbers of 30 (experimental; three classes) and 19 (control; two classes). Nonetheless, our key traits were not differently distributed across conditions at time 1, which is what a full randomized controlled trial aims to achieve (cf. Kaptchuk, 2001). However, we acknowledge that this, of course, does not equate to randomization and thus is an important methodological limitation to address in future studies in this area. Ideally, in the future, researchers will conduct double-blind experiments in which participants receive greater dosages of training and in larger samples wherein clustered randomization is possible. We see the present study as an important bridge between early small-N studies and the studies we would like to conduct, arguing that previous studies are not sufficient justification for a full-scale clustered randomized controlled trial.
We also found that those who completed more training were less susceptible to negative emotion, suggesting that relational operant training may be emotionally taxing. This is an important finding as it suggests that propensity towards negative emotion might be a key variable to consider when designing intensive cognitive training programs. Given that personality dispositions are both highly heritable and also difficult to change without intensive therapy (Jang et al., 1996; Roberts et al., 2017; Viken et al., 1994), future contextual behavioral research could focus on tailoring interventions to those with differing underlying personality characteristics who might be inclined to give up on training more readily than others. This might be achieved by including higher-quality reinforcers within SMART to improve sustained engagement, especially in populations who tend to be higher in trait negative emotion that may be at a disadvantage.
Conclusion
This study is one of the largest controlled tests of the efficacy of relational operant training to date, but researchers must attempt to conduct even larger scale studies in the future with a view to implementing the intervention on a much broader scale. In the present study, even with a low training dosage and a sample of young children aged from just 6 to 10 years, we yielded an increase in NVIQ that is three times that of the most popular cognitive training intervention to date (cf. Au et al. (2015); though also Sala and Gobet (2017b)). Therefore, relational operant skills training is a strong candidate to be a viable intervention for accelerating children’s progress towards developmental milestones. Furthermore, these data corroborate RFT’s core hypothesis that tests of cognitive ability and educational attainment may indeed be indirect tests of more fundamental relational operant skills.
Data Availability
Data and code (SPSS) are available upon request by contacting the corresponding author.
References
Abdellaoui, A., Hugh-Jones, D., Kemper, K. E., Holtz, Y., Nivard, M. G., Veul, L., Yengo, L., Zietsch, B. P., Frayling, T. M., Wray, N., Yang, J., Verweij, K. J. H., & Visscher, P. M. (2018). Genetic consequences of social stratification in Great Britain. BioRxiv, 457515. https://doi.org/10.1101/457515.
Alexander, P. A. (2019). Individual differences in college-age learners: the importance of relational reasoning for learning and assessment in higher education. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(3), 416–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12264.
Amd, M., & Roche, B. (2018). Assessing the effects of a relational training intervention on fluid intelligence among a sample of socially disadvantaged children in Bangladesh. The Psychological Record, 68(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40732-018-0273-4.
Andrés, M. L., Richaud De Minzi, M. C., Castañeiras, C., Canet-Juric, L., & Rodríguez-Carvajal, R. (2016). Neuroticism and depression in Children: The Role of Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies. Journal of Genetic Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221325.2016.1148659.
Au, J., Sheehan, E., Tsai, N., Duncan, G. J., Buschkuehl, M., & Jaeggi, S. M. (2015). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory: a meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(2), 366–377.
Bergold, S., & Steinmayr, R. (2018). Personality and intelligence interact in the prediction of academic achievement. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence6020027.
Buschkuehl, M., Hernandez-Garcia, L., Jaeggi, S. M., Bernard, J. A., & Jonides, J. (2014). Neural effects of short-term training on working memory. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(1), 147–160.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., Colbert, D., Stewart, I., & Grey, I. M. (2016). A relational frame skills training intervention to increase general intelligence and scholastic aptitude. Learning and Individual Differences, 47, 222–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2016.03.0011041-6080.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., & Hayes, S. C. (2011). A relational frame training intervention to raise intelligence quotients: a pilot study. The Psychological Record, 61(2), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395755.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., & O’Hora, D. (2010). Relational frame theory and human intelligence. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 11(1), 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2010.11434333.
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Ahmetoglu, G., & Furnham, A. (2008). Little more than personality: dispositional determinants of test anxiety (the big five, core self-evaluations, and self-assessed intelligence). Learning and Individual Differences, 18(2), 258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2007.09.002.
Chooi, W.-T., & Thompson, L. A. (2012). Working memory training does not improve intelligence in healthy young adults. Intelligence, 40(6), 531–542.
Colbert, D., Dobutowitsch, M., Roche, B., & Brophy, C. (2017). The proxy-measurement of intelligence quotients using a relational skills abilities index. Learning and Individual Differences, 57, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.03.010.
Colbert, D., Tyndall, I., Roche, B., & Cassidy, S. (2018). Can SMART training really increase intelligence? A replication study. Journal of Behavioral Education, 27(4), 509–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-018-9302-2.
Colom, R., & Román, F. J. (2018). Enhancing intelligence: from the group to the individual. Journal of Intelligence, 6(1), 11.
Colom, R., Román, F. J., Abad, F. J., Shih, P. C., Privado, J., Froufe, M., Escorial, S., Martínez, K., Burgaleta, M., & Quiroga, M. A. (2013). Adaptive n-back training does not improve fluid intelligence at the construct level: gains on individual tests suggest that training may enhance visuospatial processing. Intelligence, 41(5), 712–727.
Conway, A. R. A., & Kovacs, K. (2015). New and emerging models of human intelligence. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 6(5), 419–426.
Davies, G., Lam, M., Harris, S. E., Trampush, J. W., Luciano, M., Hill, W. D., Hagenaars, S. P., Ritchie, S. J., Marioni, R. E., Fawns-Ritchie, C., Liewald, D. C. M., Okely, J. A., Ahola-Olli, A. V., Barnes, C. L. K., Bertram, L., Bis, J. C., Burdick, K. E., Christoforou, A., DeRosse, P., et al. (2018). Study of 300,486 individuals identifies 148 independent genetic loci influencing general cognitive function. Nature Communications, 9(1), 2098. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04362-x.
Davis, T., Goldwater, M., & Giron, J. (2017). From concrete examples to abstract relations: the rostrolateral prefrontal cortex integrates novel examples into relational categories. Cerebral Cortex, 27(4), 2652–2670. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw099.
De Oviedo, U., Carrasco Ortiz, E., Ángel, M., Tello, H., Pablo, F., Gandara, D. B., & Victoria, M. (2005). Dimensionalidad del cuestionario de los cinco grandes (BFQ-N) en población infantil española [Big five questionnaire dimensions in Spanish children (BFQ-C)]. Psicothema, 17(2), 286–291 http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=72717216.
Detterman, D. K. (2017). Education and intelligence: pity the poor teacher because student characteristics are more significant than teachers or schools. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, 19, E93. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2016.88.
Dymond, S., & Roche, B. (2013). Advances in relational frame theory: research and application. Context Press.
Everaert, M. B. H., Huybregts, M. A. C., Chomsky, N., Berwick, R. C., & Bolhuis, J. J. (2015). Structures, not strings: linguistics as part of the cognitive sciences. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(12), 729–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2015.09.008.
Fissler, P., Müller, H.-P., Küster, O. C., Laptinskaya, D., Thurm, F., Woll, A., Elbert, T., Kassubek, J., von Arnim, C. A. F., & Kolassa, I.-T. (2017). No evidence that short-term cognitive or physical training programs or lifestyles are related to changes in white matter integrity in older adults at risk of dementia. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 11, 110.
Gaio, V. (2012). Psychometric Properties of the Big Five Questionnaire-Children (BFQ-C) in American Adolescents [Arizona State University]. https://repository.asu.edu/attachments/93558/content//tmp/package-It1sWU/Gaio_asu_0010N_11584.pdf
Goldwater, M. B. (2017). Grammatical constructions as relational categories. Topics in Cognitive Science. https://doi.org/10.1111/tops.12272.
Goldwater, M. B., Don, H. J., Krusche, M. J. F., & Livesey, E. J. (2018). Relational discovery in category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 147(1), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000387.
Goldwater, M. B., & Schalk, L. (2016). Relational categories as a bridge between cognitive and educational research. Psychological Bulletin, 142(7), 729–757. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000043.
Gottfredson, L. S., & Deary, I. J. (2004). Intelligence predicts health and longevity, but why? Current Directions in Psychological Science, 13(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.01301001.x.
Haier, R. J. (2016). The neuroscience of intelligence. Cambridge University Press.
Halford, G. S., Wilson, W. H., & Phillips, S. (2010). Relational knowledge: the foundation of higher cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14, 497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.08.005.
Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86(3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114.
Hayes, S. C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2001). Relational frame theory: a post-Skinnerian account of human language and cognition. Plenum Press.
Hilbert, S., Schwaighofer, M., Zech, A., Sarubin, N., Arendasy, M., & Bühner, M. (2017). Working memory tasks train working memory but not reasoning: a material- and operation-specific investigation of transfer from working memory practice. Intelligence, 61, 102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTELL.2017.01.010.
Hill, W. D., Marioni, R. E., Maghzian, O., Ritchie, S. J., Hagenaars, S. P., McIntosh, A. M., Gale, C. R., Davies, G., & Deary, I. J. (2018b). A combined analysis of genetically correlated traits identifies 187 loci and a role for neurogenesis and myelination in intelligence. Molecular Psychiatry, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-017-0001-5.
Hill, W. D., Arslan, R. C., Xia, C., Luciano, M., Amador, C., Navarro, P., Hayward, C., Nagy, R., Porteous, D. J., McIntosh, A. M., Deary, I. J., Haley, C. S., & Penke, L. (2018a). Genomic analysis of family data reveals additional genetic effects on intelligence and personality. Molecular Psychiatry, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-017-0005-1.
Ivcevic, Z., & Brackett, M. (2014). Predicting school success: comparing conscientiousness, grit, and emotion regulation ability. Journal of Research in Personality, 52(10), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2014.06.005.
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., & Shah, P. (2011). Short-and long-term benefits of cognitive training. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(25), 10081–10086.
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Shah, P., & Jonides, J. (2014). The role of individual differences in cognitive training and transfer. Memory & Cognition, 42(3), 464–480.
Jang, K. L., Livesley, W. J., & Vemon, P. A. (1996). Heritability of the big five personality dimensions and their facets: a twin study. Journal of Personality, 64(3), 577–592.
Jensen, A. R. (1989). Raising IQ without increasing g? A review of the Milwaukee project: preventing mental retardation in children at risk the Milwaukee project: preventing mental retardation in children at risk. By. Developmental Review, 9, 234–258. http://arthurjensen.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/Raising-IQ-Without-Increasing-g-Review-of-Howard-L.-Garbers-The-Milwaukee-Project-Preventing-Mental-Retardation-in-Children-at-Risk-1989-by-Arthur-Robert-Jensen.pdf
Jones, K. T., Peterson, D. J., Blacker, K. J., & Berryhill, M. E. (2017). Frontoparietal neurostimulation modulates working memory training benefits and oscillatory synchronization. Brain Research, 1667, 28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BRAINRES.2017.05.005.
Kaptchuk, T. J. (2001). The double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial: Gold standard or golden calf? In Journal of Clinical Epidemiology (Vol. 54). https://www.medschool.lsuhsc.edu/internal_medicine/residency/docs/JC 2015-03 gold standard or golden calf_Nesh.PDF.
Kassai, R., Futo, J., Demetrovics, Z., & Takacs, Z. K. (2019). A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence on the near- and far-transfer effects among children’s executive function skills. Psychological Bulletin, 145(2), 165–188. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000180.
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (2004). Kaufman brief intelligence test. Wiley Online Library.
Kaufman, S. B., DeYoung, C. G., Gray, J. R., Brown, J., & Mackintosh, N. (2009). Associative learning predicts intelligence above and beyond working memory and processing speed. Intelligence, 37(4), 374–382.
Kishita, N., Ohtsuki, T., & Stewart, I. (2013). The training and assessment of relational precursors and abilities (TARPA): a follow-up study with typically developing children. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 2(1–2), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2013.01.001.
Komarraju, M., Karau, S. J., Schmeck, R. R., & Avdic, A. (2011). The big five personality traits, learning styles, and academic achievement. Personality and Individual Differences, 51(4), 472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2011.04.019.
Lipkens, R., Hayes, S. C., & Hayes, L. J. (1993). Longitudinal study of the development of derived relations in an infant. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.1993.1032.
West, M. R., Kraft, M. A., Finn, A. S., Martin, R. E., Duckworth, A. L., Gabrieli, C. F. O., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2016). Promise and Paradox: Measuring Students’ Non-Cognitive Skills and the Impact of Schooling. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis. https://doi.org/10.3102/0162373715597298.
McKey, R. H. (1985). The impact of head start on children, families and communities. Synthesis and Utilization Project: Final Report of the Head Start Evaluation. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED263984.pdf.
McLoughlin, S., & Stewart, I. (2017). Empirical advances in studying relational networks. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 6(3), 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCBS.2016.11.009.
McLoughlin, S., Tyndall, I., & Pereira, A. (2018). Piloting a brief relational operant training program: analyses of response latencies and intelligence test performance. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 19(2), 228–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2018.1507087.
Melby-Lervåg, M., & Hulme, C. (2013). Is working memory training effective? A meta-analytic review. Developmental Psychology, 49(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028228.
Melby-Lervåg, M., & Hulme, C. (2016). There is no convincing evidence that working memory training is effective: A reply to Au et al.(2014) and Karbach and Verhaeghen (2014). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(1), 324–330. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0862-z.
Melby-Lervåg, M., Redick, T. S., & Hulme, C. (2016). Working memory training does not improve performance on measures of intelligence or other measures of “far transfer” evidence from a meta-analytic review. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 11(4), 512–534. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616635612.
Moran, L., Walsh, L., Stewart, I., McElwee, J., & Ming, S. (2015). Correlating derived relational responding with linguistic and cognitive ability in children with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 19, 32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2014.12.015.
Morris, S. B. (2008). Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organizational Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059.
Mulhern, T., Stewart, I., & Elwee, J. M. (2017). Investigating relational framing of categorization in young children. Psychological Record, 67(4), 519–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40732-017-0255-y.
Mulhern, T., Stewart, I., & McElwee, J. (2018). Facilitating relational framing of classification in young children. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 8, 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2018.04.001.
O’Hora, D., Pelaez, M., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2005). Derived relational responding and performance in verbal subtests of the WAIS-III. The Psychological Record, 55, 155–175.
O’Hora, D., Peláez, M., Barnes-Holmes, D., Rae, G., Robinson, K., & Chaudhary, T. (2008). Temporal relations and intelligence: correlating relational performance with performance on the WAIS-III. The Psychological Record, 58(1), 569–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395638.
O’Toole, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., Murphy, C., O’Connor, J., & Barnes-Holmes, Y. (2009). Relational flexibility and human intelligence: extending the remit of skinner’s verbal behavior. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 9(1), 1–17.
Parra, I., & Ruiz, F. J. (2016). The effect on intelligence quotient of training fluency in relational frames of coordination. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 16(1), 1–12.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics, 19(3), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.104.
Ritchie, S. (2015). Intelligence: all that matters. Hodder & Stoughton.
Roberts, B. W., Luo, J., Briley, D. A., Chow, P. I., Su, R., & Hill, P. L. (2017). A systematic review of personality trait change through intervention. Psychological Bulletin, 143(2), 117–141. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000088.
Ruiz, F. J., & Luciano, C. (2011). Cross-domain analogies as relating derived relations among two separate relational networks. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 95(3), 369–385. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.2011.95-369.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017a). Does chess instruction improve mathematical problem-solving ability? Two experimental studies with an active control group. Learning & Behavior, 45(4), 414–421. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13420-017-0280-3.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017b). Does far transfer exist? Negative evidence from chess, music, and working memory training. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 26(6), 515–520. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721417712760.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017c). When the music’s over. Does music skill transfer to children’s and young adolescents’ cognitive and academic skills? A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review, 20, 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.005.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017d). Working memory training in typically developing children: a meta-analysis of the available evidence. Developmental Psychology, 53(4), 671–685. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000265.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2019). Cognitive training does not enhance general cognition. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 23(1), 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2018.10.004.
Sala, G., Tatlidil, K. S., & Gobet, F. (2018). Video game training does not enhance cognitive ability: a comprehensive meta-analytic investigation. Psychological Bulletin, 144(2), 111–139. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000139.
Sandoz, E. K., & Hebert, E. R. (2017). Using derived relational responding to model statistics learning across participants with varying degrees of statistics anxiety. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 18(1), 113–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2016.1146552.
Savage, J. E., Jansen, P. R., Stringer, S., Watanabe, K., Bryois, J., de Leeuw, C. A., Nagel, M., Awasthi, S., Barr, P. B., Coleman, J. R. I., Grasby, K. L., Hammerschlag, A. R., Kaminski, J. A., Karlsson, R., Krapohl, E., Lam, M., Nygaard, M., Reynolds, C. A., Trampush, J. W., et al. (2018). Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269,867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence. Nature Genetics, 1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0152-6.
Schlinger, H. D. (2003). The myth of intelligence. In The Psychological Record (Vol. 53, pp. 15–32).
Schulte, M. J., Ree, M. J., & Carretta, T. R. (2004). Emotional intelligence: not much more than g and personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 37(5), 1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2003.11.014.
Schwaighofer, M., Fischer, F., & Bühner, M. (2015). Does working memory training transfer? A meta-analysis including training conditions as moderators. Educational Psychologist, 50(2), 138–166.
Shipstead, Z., Redick, T. S., & Engle, R. W. (2012). Is working memory training effective? Psychological Bulletin, 138(4), 628.
Simons, D. J., Boot, W. R., Charness, N., Gathercole, S. E., Chabris, C. F., Hambrick, D. Z., & Stine-Morrow, E. A. L. (2016). Do “brain-training” programs work? Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 17(3), 103–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100616661983.
Smeets, P. M., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2001). Derived stimulus-response and stimulus-stimulus relations in children and Adults: Assessing Training Order Effects. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.2000.2563.
Smith-Woolley, E., Pingault, J.-B., Selzam, S., Rimfeld, K., Krapohl, E., von Stumm, S., Asbury, K., Dale, P. S., Young, T., Allen, R., Kovas, Y., & Plomin, R. (2018). Differences in exam performance between pupils attending selective and non-selective schools mirror the genetic differences between them. Npj Science of Learning, 3(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-018-0019-8.
Soveri, A., Karlsson, E., Waris, O., Grönholm-Nyman, P., & Laine, M. (2017). Pattern of near transfer effects following working memory training with a dual n-back task. Experimental Psychology, 64(4), 240.
Stephenson, C. L., & Halpern, D. F. (2013). Improved matrix reasoning is limited to training on tasks with a visuospatial component. Intelligence, 41(5), 341–357.
Strenze, T. (2007). Intelligence and socioeconomic success: a meta-analytic review of longitudinal research. Intelligence, 35(5), 401–426.
Studer-Luethi, B., Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., & Perrig, W. J. (2012). Influence of neuroticism and conscientiousness on working memory training outcome. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 44–49.
Thirus, J., Starbrink, M., & Jansson, B. (2016). Relational frame theory, mathematical and logical skills: a multiple exemplar training intervention to enhance intellectual performance. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 16(2), 141–155.
Thompson, T. W., Waskom, M. L., Garel, K.-L. A., Cardenas-Iniguez, C., Reynolds, G. O., Winter, R., Chang, P., Pollard, K., Lala, N., & Alvarez, G. A. (2013). Failure of working memory training to enhance cognition or intelligence. PLoS One, 8(5), e63614.
Van Der Maas, H. L. J., Dolan, C. V, Grasman, R. P. P. P., Wicherts, J. M., Huizenga, H. M., & Raijmakers, M. E. J. (2006). A dynamical model of general intelligence: the positive manifold of intelligence by mutualism. Psychological Review, 113(4), 842.
Viken, R. J., Rose, R. J., Kaprio, J., & Koskenvuo, M. (1994). A developmental genetic analysis of adult personality: extraversion and neuroticism from 18 to 59 years of age. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 66(4), 722–730. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.66.4.722.
Vizcaíno-Torres, R. M., Ruiz, F. J., Luciano, C., López-López, J. C., Barbero-Rubio, A., & Gil, E. (2015). The effect of relational training on intelligence quotient: a case study. Psicothema, 27, 120–127. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2014.149.
von Bastian, C. C., Langer, N., Jäncke, L., & Oberauer, K. (2013). Effects of working memory training in young and old adults. Memory & Cognition, 41(4), 611–624.
Wilson, D. S., & Hayes, S. C. (2018). Evolution and contextual behavioral science: an integrated framework for understanding, predicting, and influencing human behavior. New Harbinger: Context Press.
Zabaneh, D., Krapohl, E., Gaspar, H. A., Curtis, C., Lee, S. H., Patel, H., Newhouse, S., Wu, H. M., Simpson, M. A., Putallaz, M., Lubinski, D., Plomin, R., & Breen, G. (2017). A genome-wide association study for extremely high intelligence. Molecular Psychiatry, April, 2017, 1226–1232. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.121.
Zahra, D., Hedge, C., Pesola, F., & Burr, S. (2016). Accounting for test reliability in student progression: the reliable change index. Medical Education, 50(7), 738–745. https://doi.org/10.1111/medu.13059.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Bryan Roche for allowing us access to SMART software for this research study at no cost, and we commend his openness to having this training independently tested.
Funding
This project was funded by the University of Chichester Doctoral Research Bursary.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics
This project was approved by the University of Chichester Research Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• SMART relational operant training raised non-verbal IQ (NVIQ) by 8.9 points, with no rise in the chess control condition.
• Post-training NVIQ explained variance in several national exam outcomes over and above Pre-training NVIQ in the relational operant training condition only.
• Children with lower NVIQ at baseline benefitted most from the training.
• This study has the largest and youngest sample of any test of SMART to date and is the second active-controlled trial by an independent lab.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
McLoughlin, S., Tyndall, I., Pereira, A. et al. Non-verbal IQ Gains from Relational Operant Training Explain Variance in Educational Attainment: An Active-Controlled Feasibility Study. J Cogn Enhanc 5, 35–50 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-020-00187-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-020-00187-z