Abstract
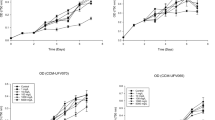
Effects of COD/SO42− and SO42−/NH4+ ratios on simultaneous removal of sulfate- and ammonium-rich synthetic wastewaters were investigated under micro-oxygenated condition (dissolved oxygen concentration at 0.10–0.15 mg/L). Lactate was served as carbon source to generate COD/SO42− ratios of 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 3.5 and 4.0. The batch experimental results indicated that the highest sulfate (72.1%) and ammonium (62.8%) removal efficiencies could be reached at COD/SO42− ratio of 4.0. The main metabolic products were elemental sulfur (0.63 g S0/g SO42−–Sadded) and nitrogen gas (0.57 g N2/g NH4+–Nadded). Subsequently, various SO42−/NH4+ ratios (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 and 2.5) were performed at controlled COD/SO42− ratio of 4.0. The highest SO42−/NH4+ ratio of 2.5 provided 76.6 and 72.8% sulfate and ammonium removal efficiencies, respectively, and also reached the highest yield of elemental sulfur and nitrogen gas of 0.68 g S0/g SO42−–Sadded and 0.66 g N2/g NH4+–Nadded, respectively. Microbial consortium structure providing the highest removal efficiencies was consequently analyzed using Illumina sequencing and polymerase chain reaction-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis approaches. Taxonomic assignments demonstrated that Proteobacteria (46%), Firmicutes (15%), and Bacteroidetes (14%) were the most abundant phyla. Almost core genera analysis with two distinguished approaches demonstrated similar results. Aside from microbial community analysis, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to validate existing abundance of aforementioned seven dominant microorganisms. The nitrous oxide reductase gene was shown the most abundance (~ 108 copies/µL) which plays a crucial role for simultaneous removal of sulfur and nitrogen compounds.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S, Tang K, Nemati M (2010) Simultaneous biodesulphurization and denitrification using oil reservoir microbial culture: effects of sulphide loading rate and sulphide to nitrate loading ratio. Water Res 44:1531–1541
APHA (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Beaumont HJE, Schooten B, Lens SI, Westerhoff HV, Spanning RJM (2004) Nitrosomonas europaea expresses nitric oxide reductase during nitrification. J Bacteriol 186(13):4417–4421
Beller HR, Chain PSG, Letain TE, Chakicherla A, Larimer FW, Richardson PM et al (2006) The genome sequences of the obligately chemolithoautotrophic, facultatively anaerobic bacterium Thiobacillus denitrificans. J Bacteriol 188(4):1473–1488
Beristain-Cardoso R, Gómez J, Méndez-Pampín M (2011) Sulfide and ammonium oxidation, acetate mineralization by denitrification in a multipurpose UASB reactor. Bioresour Technol 102:2549–2554
Bertolino SM, Rodrigues ICB, Guerra-Sá R, Aquino SF, Leão VA (2012) Implications of volatile fatty acids profiles on metabolic pathway during continuous sulfate reduction. J Environ Manag 103:15–23
Brand TPH, Roest K, Brdjanovic D, Chen GH, Loosdrecht MCM (2014) Influence of acetate and propionate on sulphate reducing bacteria activity. J Appl Microbiol 117(6):1839–1847
Chen C, Wang A, Ren N, Lee DJ, Lai JY (2009) High-rate denitrifying sulfide removal process in expanded granular sludge bed reactor. Bioresour Technol 100:2316–2319
Fajardo C, Mora M, Fernández I, Mosquera-Corral A, Campos JL, Méndez R (2014) Cross effect of temperature, pH and free ammonia on autotrophic denitrification process with sulphide as electron donor. Chemosphere 97:10–15
Fotidis IA, Karakashev D, Kotsopoulos TA, Martzopoulos GG, Angelidaki I (2013) Effect of ammonium and acetate on methanogenesis and community composition. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 83(1):1–11
Fuseler K, Krekeler D, Sydow U, Cypionka H (1996) A common pathway of sulfide oxidation by sulfate-reducing bacteria. FEM Microbiol Letters 144:129–134
Geet J, Borremans B, Diels L, Springael D, Vangronsveld J, Lelie DVD, Vanbroekhoven K (2006) DsrB gene-based DGGE for community and diversity surveys of sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 66:194–205
Ghosh W, Dam B (2009) Biochemistry and molecular biology of lithotrophic sulfur oxidation by taxonomically and ecologically diverse bacteria and archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:999–1043
Guo H, Chen C, Lee DJ, Wang A, Re N (2015) Denitrifying sulfide removal by Pseudomonas sp. c27 at excess carbon supply: mechanisms. Bioresour Technol 180:381–385
Hahnke S, Striesow J, Elvert M, Mollar XP, Klocke M (2014) Clostridium bornimense sp. nov., isolated from mesophilic two-phase laboratory scale biogas reactor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2792–2797
Hanson TE, Campbell BJ, Kalis KM, Campbell MA, Klotz MG (2013) Nitrate ammonification by Nautilia profundicola AmH: experimental evidence consistent with a free hydroxylamine intermediate. Front Microbiol 4(180):1–9
Hatamoto M, Nagai H, Sato S et al (2012) Rubber and methane recovery from deproteinized natural rubber wastewater by coagulation pre-treatment and anaerobic treatment. Int J Environ Res 6(3):577–584
Henry S, Bru D, Stres B, Hallet S, Philippot L (2006) Quantitative detection of the nosZ gene, encoding nitrous oxide reductase, and comparison of abundance of 16 s rRNA, narG, nirK, and nosZ genes in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(8):5181–5189
Huang C, Zhao Y, Li Z et al (2015) Enhanced elementary sulfur recovery with sequential sulfate-reducing, denitrifying sulfide-oxidizing process in a cylindrical-type anaerobic baffled reactor. Bioresour Technol 192:478–485
Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2003) Azoarcus sp. strain BH72 model for nitrogen-fixing grass endophytes. J Biotechnol 106:169–178
Janssen AJH, Lettinga G, Keizer A (1999) Removal of hydrogen sulphide from wastewater and waste gases by biological conversion to elemental sulphur Colloidal and interfacial aspects of biologically produced sulphur particles. Colloids Surf A 151:389–397
Jiang Y, Wei L, Zhang H, Yang K, Wang H (2016) Removal performance and microbial communities in a sequencing batch reactor treating hypersaline phenol-laden wastewater. Bioresour Technol 218:146–152
Kim DJ, Ahn DH, Lee DI (2005) Effects of free ammonia and dissolved oxygen on nitrification and nitrite accumulation in a biofilm airlift reactor. Korean J Chem Eng 22(1):85–90
Koo T, Shin SG, Lee J, Han G, Kim W, Cho K, Hwang S (2017) Identifying methanogen community structures and their correlations with performance parameters in four full scale anaerobic sludge digesters. Bioresour Technol 228:368–373
Kuo HW, Huang CY, Chang CN, Lee PL, Chen YW, Huang CF, Chang HH et al (2016) Identification of diverse bacterial communities for potential bio-aids capable of troubleshooting for wastewater biological treatment processes. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14(4):743–754
Li W, Zhao QL, Liu H (2009) Sulfide removal by simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic desulfurization-denitrification process. J Hazard Mater 162:848–953
Liamleam W, Annachhatre AP (2007) Research review paper: electron donors for biological sulfate reduction. Biotechnol Adv 25:452–463
Limpiyakorn T, Shinohara Y, Kurisu F, Yagi O (2005) Communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge of various sewage treatment plants in Tokyo. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:205–217
Liu B, Zhang F, Feng X, Liu Y, Yan X, Zhao L (2006) Thauera and Azoarcus as functionally important genera in a denitrifying quinoline-removal bioreactors as revealed by microbial community structure comparison. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:274–286
Liu C, Zhao D, Ma W, Guo Y, Wang A, Wang Q, Lee DJ (2015) Denitrifying sulfide removal process on high-salinity wastewaters in the presence of Halomonas sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(3):421–1426
Liu J, Wei Z, Zhang J, Li H, Li L, Tian Y (2017) Shifts in microbial community structure and diversity in a MBR combined with worm reactors treating synthetic wastewater. J Environ Sci 54:246–255
Lu XM, Lu PZ (2014) Characterization of bacterial communities in sediments receiving various wastewater effluents with high-throughput sequencing analysis. Microb Ecol 67(3):612–623
Mayumi D, Mochimaru H, Yoshioka H et al (2010) Evidence for syntrophic acetate oxidation coupled to hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis in the high-temperature petroleum reservoir of yabase oil field (Japan). Environ Microbiol 13(8):1995–2006
Meyer B, Imhof JF, Kuever J (2007) Molecular analysis of distribution and phylogeny of soxB gene among sulfur oxidizing bacteria evolution of Sox enzyme system. Environ Microbiol 9(12):2957–2977
Oren A (2014) The family Rhodocyclaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryote. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 975–998
Oyekola OO, van Hile RP, Harrison STL (2009) Study anaerobic lactate metabolism under biosulfidogenic conditions. Water Res 43:3345–3354
Prosser JI, Embley TM (2012) Cultivation-based and molecular approaches to characterization of terrestrial and aquatic nitrifiers. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81:165–179
Ren NQ, Chua H, Chan SY, Tsang YF, Sin N (2007) Effects of COD/SO4 2− ratios on an acidogenic sulfate-reducing reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:1661–1666
Reyes-Avila J, Razo-Flores E, Gomez J (2004) Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen, carbon and sulfur by denitrification. Water Res 38(14–15):3313–3321
Rincón B, Portillo MC, González JM, Borja R (2013) Microbial community dynamics in the two-stage anaerobic digestion process of two-phase olive mill residue. Int J Environ Sci Technol 10:635–644
Ruiz G, Jeison D, Chamy R (2003) Nitrification with high nitrite accumulation for treatment of wastewater with high ammonia concentration. Water Res 37:1371–1377
Sahinkaya E, Dursan N (2012) Sulfur oxidizing autotrophic and mixotrophic denitrification processes for drinking water treatment: elimination of excess sulfate production and alkalinity requirement. Chemosphere 89:144–149
Schmidt I, Sliekers O, Schmid M et al (2003) New concepts of microbial treatment processes for the nitrogen removal in wastewater. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:481–492
Sierra-Alvarez R, Beristain-Cardoso R, Salazar M, Go̍mez J, Razo-Flores E, Field JA (2007) Chemolithotrophic denitrification with elemental sulfur for groundwater treatment. Water Res 41:1253–1262
Song B, Palleroni NJ, Kerkhof LJ, Häggblom MM (2010) Characterization of halobenzoate-degrading denitrifying Azoarcus and Thaeura isolates and description of Thaeura chlorobenzoica sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:589–602
Strous M, Gerven E, Zheng P, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1997) Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res 31(8):1955–1962
Strous M, Pelletier E, Mangenot S, Rattei T, Lehner A, Taylor MW, Horn M et al (2006) Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anammox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 440(7085):790–794
Su JF, Zheng SC, Huang TL et al (2015) Characterization of the anaerobic denitrification bacterium Acinetobacter sp. sz28 and its application for groundwater treatment. Bioresour Technol 192:654–659
Thoungnueakhaeng W, Chaiprasert P (2015) Effect of dissolved oxygen concentrations on specific microbial activities and their metabolic products in simultaneous sulfur and nitrogen removal. Int J Environ Sci Dev 6(4):235–240
Villahermosa D, Corzo A, González JM, Portillo MC, Garcia-Robledo E, Papspyrou S (2013) Reduction of net sulfide production rate by nitrate in wastewater bioreactors. Kinetics and changes in the microbial community. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1738–1751
Wang AJ, Gao S, Yuan Y, Chen C (2013) Influence of sulfide to nitrate ratios on denitrifying sulfide removal and elemental sulfur reclamation from wastewater containing high organic carbon concentration. Adv Mate Res 726–731:2186–2190
Xu XJ, Chen C, Wang AJ, Fang N, Yuan Y, Ren NQ, Lee DJ (2012) Enhanced elementary sulfur recovery in integrated sulfate-reducing, sulfur-producing reactor under micro-aerobic condition. Bioresour Technol 116:517–521
Xu X, Liu G, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang H, Qi L, Wang H (2018) Analysis of key microbial community during the start-up of anaerobic ammonium oxidation process with paddy soil as inoculated sludge. J Environ Sci 64:317–327
Yu Y, Lee C, Hwang S (2005) Analysis of community structures anaerobic processes using quantitative real-time PCR method. Water Sci Technol 52(1–2):85–91
Yuan Y, Chen C, Zhao Y et al (2015) Influence of COD/sulfate ratios on integrated reactor system for simultaneous removal of carbon, sulfur and nitrogen. Water Sci Technol 71(5):709–716
Zhang T, Ye L, Tong AMY, Shao MF, Lok S (2011) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in six full-scale wastewater treatment bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1215–1225
Zhao Y, Zhang B, Feng C, Huang F, Zhang P, Zhang Z, Yang Y et al (2012) Behavior of autotrophic denitrification and heterotrophic denitrification in an intensified biofilm-electrode reactor for nitrate-contaminated drinking water treatment. Bioresour Technol 107:159–165
Zhi W, Ji G (2014) Quantitative response relationships between nitrogen transformation rates and nitrogen functional genes in tidal flow constructed wetland under C/N ratio constraints. Bioresour Technol 64:32–41
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. App Environ Microbiol 62(2):316–322
Zhu L, Dai X, Xu X, Lv M, Cao D (2013) Microbial community analysis for aerobic granular sludge reactor treating high-level 4-chloroaniline wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(7):1845–1854
Zhu X, Mengqi L, Wei Z, Rui L, Chen L (2017) Performance and microbial community of membrane bioreactor system—treating wastewater from ethanol fermentation of food waste. J Environ Sci 53:284–292
Zhuo M, Ye H, Zhao X (2014) Isolation and Characterization of novel heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying Pseudomonas stutzeri KTB for bioremediation of wastewater. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19:231–238
Ziganshin AM, Schmidt T, Scholwin F, Ill’inskaya ON, Harms H, Kleinsteuber S (2011) Bacteria and archaea involved in anaerobic digestion of distillers grains with solubles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:2039–2052
Acknowledgements
This research was facilitated by Excellent Center of Waste Utilization and Management (ECoWaste) and King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi through “KMUTT 55th Anniversary Commemorative Fund” with Grant No. KMUTT-6001004790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Borghei.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charoensuk, P., Thongnueakhaeng, W. & Chaiprasert, P. Performance and microbial consortium structure in simultaneous removal of sulfur and nitrogen compounds under micro-oxygenated condition. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 5767–5782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2132-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2132-x