Abstract
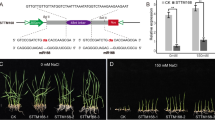
Salinity affects plant in a variety of ways, including ion toxicity, osmotic stress and oxidative damage. Allantoin is a nitrogenous compound derived from purine catabolism that contributes to nitrogen recycling in plants. In rice, accumulation of allantoin in response to salinity stress has been reported. But the role of allantoin under salinity stress is not elucidated till now. Recently, miRNAs have emerged as major regulatory molecules which have been shown to regulate gene expressions during salinity stress condition. To understand the effect of exogenous application of allantoin on miRNAs mediated short-term tolerance of salt sensitive rice genotype IR-29, the relative expression of 10 salinity responsive miRNAs were investigated under salinity stress. The result demonstrates that several miRNA changed their expression pattern in presence of allantoin under salinity. For an example, miRNAs such as osa-miRNA393a, osa-miRNA414, osa-miRNA530 and osa-miR818a were down-regulated under salinity stress condition whereas all these four miRNAs were up-regulated under salinity along with allantoin treated condition indicating that this differential expression under allantoin may play an important role for salinity tolerance of IR-29.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- mM:
-
Millimolar
- nt:
-
Nucleotides
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SnRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- qRT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative transcription PCR
References
Ai B, Chen Y, Zhao M, Ding G, Xie J, Zhang F (2021) Overexpression of miR1861h increases tolerance to salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genet Resour Crop Evol 68:87–92
Alamillo JM, Díaz-Leal JL, Sánchez-Moran MV, Pineda M (2010) Molecular analysis of ureide accumulation under drought stress in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Cell Env 33:1828–1837
Alzahrani SM, Alaraidh IA, Khan MA, Migdadi HM, Alghamdi SS, Alsahli AA (2019) Identification and characterization of salt-responsive microRNAs in Vicia faba by high-throughput sequencing. Genes 10:303
Barakat A, Sriram A, Park J, Zhebentyayeva T, Main D, Abbott A (2012) Genome wide identification of chilling responsive microRNAs in Prunus persica. BMC Genom 13:1–11
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bonilla P, Dvorak J, Mackell D, Deal K, Gregorio G (2002) RFLP and SSLP mapping of salinity tolerance genes in chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombinant inbred lines. Philippine Agricultural Scientist (Philippines)
Brychkova G, Alikulov Z, Fluhr R, Sagi M (2008) A critical role for ureides in dark and senescence-induced purine remobilization is unmasked in the Atxdh1 Arabidopsis mutant. Plant J 54:496–509
Coleto I, Pineda M, Rodiño AP, De Ron AM, Alamillo JM (2014) Comparison of inhibition of N2 fixation and ureide accumulation under water deficit in four common bean genotypes of contrasting drought tolerance. Ann Bot 113:1071–1082
Corpas FJ, Gomez M, Hernandez JA, Luis A (1993) Metabolism of activated oxygen in peroxisomes from two Pisum sativum L. cultivars with different sensitivity to sodium chloride. J Plant Physiol 141:160–165
Deng PC, Wang L, Cui LC, Feng KW, Liu FY, Du XH, Tong W, Nie XJ, Ji WQ, Weining S (2001) Global identification of microRNAs and their targets in barley under salinity stress. PLoS ONE 10:e0137990
Desimone M, Catoni E, Ludewig U, Hilpert M, Schneider A, Kunze R, Tegeder M, Frommer WB, Schumacher K (2002) A novel superfamily of transporters for allantoin and other oxo derivatives of nitrogen heterocyclic compounds in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:847–856
Feng K, Nie X, Cui L, Deng P, Wang M, Song W (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of salinity stress-responsive miRNAs in wild emmer wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. dicoccoides). Genes 8:156
Fukai T, Ushio-Fukai M (2011) Superoxide dismutases: role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid Redox Sign 15:1583–1606
Ganie SA, Molla KA, Henry RJ, Bhat KV, Mondal TK (2019) Advances in understanding salt tolerance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 132:851–870
Gao P, Bai X, Yang L, Lv D, Pan X, Li Y, Zhu Y (2011) osa-MIR393: a salinity-and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene. Mol Biol Rep 38:237–242
Gupta B, Huang B (2014) Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization. Int J Genomics 2014:1–8
Gus’Kov EP, Prokof’ev VN, Kletskii ME, Kornienko IV, Gapurenko OA, Olekhnovich LP, Chistyakov VA, Shestopalov AV, Sazykina MA, Markeev AV, Shkurat TP (2004) Allantoin as a vitamin. Dokl Biochem Biophys 398:320–324
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Biol 51:463–499
Hauck OK, Scharnberg J, Escobar NM, Wanner G, Giavalisco P, Witte CP (2014) Uric acid accumulation in an Arabidopsis urate oxidase mutant impairs seedling establishment by blocking peroxisome maintenance. Plant Cell 26:3090–3100
Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (2010) Research on plant abiotic stress responses in the post-genome era: past, present and future. Plant J 61:1041–1052
Iglesias MJ, Terrile MC, Windels D, Lombardo MC, Bartoli CG, Vazquez F, Estelle M, Casalongue CA (2001) Mir393 regulation of auxin signaling and redox-related components during acclimation to salinity in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 9:e107678
Irani S, Todd CD (2016) Ureide metabolism under abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 199:87–95
Irani S, Todd CD (2018) Exogenous allantoin increases Arabidopsis seedlings tolerance to NaCl stress and regulates expression of oxidative stress response genes. J Plant Physiol 221:43–50
Irani S, Lobo JM, Gray GR, Todd CD (2018) Allantoin accumulation in response to increased growth irradiance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biol Plant 62:181–187
Jin Q, Xu Y, Mattson N, Li X, Wang B, Zhang X, Jiang H, Liu X, Wang Y, Yao D (2017) Identification of submergence-responsive microRNAs and their targets reveals complex miRNA-mediated regulatory networks in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn). Front Plant Sci 8:6–20
Khadri M, Pliego L, Soussi M, Lluch C, Ocana A (2001) Ammonium assimilation and ureide metabolism in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) nodules under salt stress. Agronomie 21:635–643
Khadri M, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2006) Alleviation of salt stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by exogenous abscisic acid supply. J Plant Growth Regul 25:110–119
Khan N, Bano A, Rahman MA, Rathinasabapathi B, Babar MA (2019) UPLC-HRMS-based untargeted metabolic profiling reveals changes in chickpea (Cicer arietinum) metabolome following long-term drought stress. Plant Cell Env 42:115–132
Kramer MF (2011) Stem-loop RT-qPCR for miRNAs. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 95:15
Kumar K, Kumar M, Kim SR, Ryu H, Cho YG (2013) Insights into genomics of salt stress response in rice. Rice 6:1–15
Lee DK, Redillas MC, Jung H, Choi S, Kim YS, Kim JK (2018) A nitrogen molecular sensing system, comprised of the ALLANTOINASE and UREIDE PERMEASE 1 genes, can be used to monitor N status in rice. Front Plant Sci 9:444
Lescano CI, Martini C, Gonzalez CA, Desimone M (2016) Allantoin accumulation mediated by allantoinase down regulation and transport by Ureide Permease 5 confers salt stress tolerance to Arabidopsis plants. Plant Mol Biol 91:581–595
Li W, Jia Y, Liu F, Wang F, Fan F, Wang J, Zhu J, Xu Y, Zhong W, Yang J (2019) Integration analysis of small RNA and degradome sequencing reveals MicroRNAs responsive to Dickeyazeae in resistant rice. Int J Mol Sci 20:222
Liu J, Shabala S, Zhang J, Ma G, Chen D, Shabala L, Zhao Q (2020) Melatonin improves rice salinity stress tolerance by NADPH oxidase-dependent control of the plasma membrane K+ transporters and K+ homeostasis. Plant Cell Env 43:2591–2605
Macovei A, Tuteja N (2012) microRNAs targeting DEAD-box helicases are involved in salinity stress response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 12:1–12
Mittal D, Sharma N, Sharma V, Sopory SK, Sanan-Mishra N (2016) Role of microRNAs in rice plant under salt stress. Ann Appl Biol 168:2–18
Mondal S, Borromeo TH (2016) Screening of salinity tolerance of rice at early seedling stage. J Biosci Agric Res 10:843–847
Mondal TK, Ganie SA, Debnath AB (2015) Identification of novel and conserved miRNAs from extreme halophyte, Oryza coarctata, a wild relative of rice. PLoS ONE 10:e0140675
Mondal TK, Panda AK, Rawal HC, Sharma TR (2018) Discovery of microRNA-target modules of African rice (Oryza glaberrima) under salinity stress. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Mosaad IS, Serag AH, Moustafa-Farag M, Seadh AK (2020) Effect of exogenous proline application on maize yield and the optimum rate of mineral nitrogen under salinity stress. J Plant Nutr 43:354–370
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nam MH, Bang E, Kwon TY, Kim Y, Kim EH, Cho K, Park WJ, Kim BG, Yoon IS (2015) Metabolite profiling of diverse rice germplasm and identification of conserved metabolic markers of rice roots in response to long-term mild salinity stress. Int J Mol Sci 16:21959–21974
Nikovics K, Blein T, Peaucelle A, Ishida T, Morin H, Aida M, Laufs P (2006) The balance between the MIR164A and CUC2 genes controls leaf margin serration in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:2929–2945
Nourimand M, Todd CD (2016) Allantoin increases cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis via activation of antioxidant mechanisms. Plant Cell Physiol 57:2485–2496
Nourimand M, Todd CD (2017) Allantoin contributes to the stress response in cadmium-treated Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol Biochem 119:103–109
Phillips JR, Dalmay T, Bartels D (2007) The role of small RNAs in abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 581:3592–3597
Sagi M, Omarov RT, Lips SH (1998) The Mo-hydroxylases xanthine dehydrogenase and aldehyde oxidase in ryegrass as affected by nitrogen and salinity. Plant Sci 135:125–135
Shabala L, Zhang J, Pottosin I, Bose J, Zhu M, Fuglsang AT, Velarde- Buendia A, Massart A, Hill CB, Roessner U, Bacic A (2016) Cell-type-specific H+- ATPase activity in root tissues enables K+ retention and mediates acclimation of barley (Hordeum vulgare) to salinity stress. Plant Physiol 172:2445–2458
Sun Y, Mu C, Zheng H, Lu S, Zhang H, Zhang X, Liu X (2018) Exogenous Pi supplementation improved the salt tolerance of maize (Zea mays L.) by promoting Na+ exclusion. Sci Rep 8:1–13
Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK (2007) Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12:301–309
Sunkar R, Zhou X, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Zhu JK (2008) Identification of novel and candidate miRNAs in rice by high throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol 8:1–17
Tabatabaei SJ (2006) Effects of salinity and N on the growth, photosynthesis and N status of olive (Olea europaea L.) trees. Sci Hortic 108:432–438
Varkonyi-Gasic E, Wu R, Woo M, Walton EF, Hellens RP (2007) Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3:1–12
Ventura Y, Myrzabayeva M, Alikulov Z, Omarov R, Khozin-Goldberg I, Sagi M (2014) Effects of salinity on flowering, morphology, biomass accumulation and leaf metabolites in an edible halophyte. AoB Plants 6:1–11
Wang JW (2014) Regulation of flowering time by the miR156-mediated age pathway. J Exp Bot 65:4723–4730
Wang YC, Qu GZ, Li HY, Wu YJ, Wang C, Liu GF, Yang CP (2010) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic poplar plants expressing a manganese superoxide dismutase from Tamarix androssowii. Mol Biol Rep 37:1119–1124
Watanabe S, Kounosu Y, Shimada H, Sakamoto A (2014) Arabidopsis xanthine dehydrogenase mutants defective in purine degradation show a compromised protective response to drought and oxidative stress. Plant Biotech 14:0117–0131
Werner AK, Witte CP (2011) The biochemistry of nitrogen mobilization: purine ring catabolism. Trends Plant Sci 16:381–387
Xia KF, Wang R, Ou XJ, Fang ZM, Tian CG, Duan J, Wang YQ, Zhang MY (2001) OsTIR1 and osAFB2 down regulation via osmir393 overexpression leads to more tillers, early flowering and less tolerance to salt and drought in rice. PLoS ONE 7:364–373
Yang Z, Zhu P, Kang H, Liu L, Cao Q, Sun J, Dong T, Zhu M, Li Z, Xu T (2020) High-throughput deep sequencing reveals the important role that microRNAs play in the salt response in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). BMC Genom 21:1–16
Yoshida S, Forno AD, Cook JH, Gomes KA(1976) Routine procedure for growing rice plants in culture solution. In: Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice, 3rd edn. The International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines, pp 61–65
You S, Zhu B, Wang F, Han H, Sun M, Zhu H, Yao Q (2017) A Vitis vinifera xanthine dehydrogenase gene, VvXDH, enhances salinity tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Biotech Rep 11:147–160
Zhao B, Ge L, Liang R, Li W, Ruan K, Lin H, Jin Y (2009) Members of miR-169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription factor. BMC Mol Biol 10:1–10
Zhou LG, Liu YH, Liu ZC, Kong DY, Duan M, Luo LJ (2010) Genome wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J Exp Bot 61:4157–4168
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Director, National Institute for Plant Biotechnology (NIPB), New Delhi for providing all the facility. JN is thankfully acknowledges the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for providing the fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TKM conceived the idea and monitored the progress. CN guided JN to do the wet lab work. AKP helped to design the primers. SC and JN developed the manuscript. All contributed to improve the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishad, J., Panda, A.K., Chowrasia, S. et al. Allantoin mediated regulation of miRNAs for short term salinity stress tolerance in Oryza sativa L. cv. IR-29. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 31, 953–960 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-022-00774-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-022-00774-5