Abstract
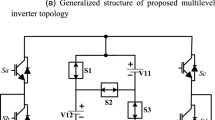
Multilevel inverter (MLI) has grown rapidly in recent years to achieve higher voltage levels, lower voltage stress of the power switches, and lower harmonic distortion of the inverter voltage. The proposed work emphasizes the design of a generalized multilevel inverter using symmetrical and asymmetrical DC sources at the input. The merit of the proposed MLI can efficiently reduce the power electronic devices to produce the output voltage and generate seven-level using 7 power switches, whereas generating 11, 13, and 15-level using ten power switches only. Proposed MLI can be expanded in a cascaded fashion, reducing complexity, and size and thus significantly improving inverter cost and performance. With some newly developed topologies, a wide range of comparisons are made in order to prove the performance of the proposed MLI. Besides, the total standing voltage and the level-to-switch ratio are estimated to show the effectiveness of the proposed inverter further, and the parameters are compared with the newly developed MLI topologies. A multicarrier pulse width method, as well as a low-frequency modulation technique, is adopted to generate the desired gate pulses of the IGBT switches using the DSPACE-1103-based controller. A laboratory prototype of the proposed seven-level, 11-level, 13-level, and 15-level inverters is developed, and the experimental results of the MLIs at different loading or voltage conditions are presented. Further, the inverter losses, efficiency, and the %THD are also analyzed and compared with the other topologies.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiltie, O.: New type of D-C TO A-C vibrator inverter. Trans. Am. Inst. Electr. Eng. 59(4), 245–248 (1940). https://doi.org/10.1109/T-AIEE.1940.5058125
Franquelo, L.G.; Rodriguez, J.; Leon, J.I.; Kouro, S.; Portillo, R.; Prats, M.A.M.: The age of multilevel converters arrives. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2(2), 28–39 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/MIE.2008.923519
Mahato, B.; Jana, K.C.; Thakura, P.R.: Constant V / f control and frequency control of isolated winding induction motor using nine-level three-phase inverter. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 6(1), 1–13 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0064-6
Jha, K.K.; Mahato, B.; Prakash, P.; Jana, K.C.: Hardware implementation of single phase power factor correction system using micro-controller. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 7(3), 790–799 (2016). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v7.i3.pp790-799
Mahato, B.; Raushan, R.; Jana, K.C.: Modulation and control of multilevel inverter for an open-end winding induction motor with constant voltage levels and harmonics. IET Power Electron. 10(1), 71–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2016.0105
Mukherjee, A.; Mahato, B.; Sinha, A.; Jana, K.C.: Comparative performance analysis of PV based grid-tied single phase asymmetrical multilevel inverter using different PWM techniques. J. Electr. Eng. 17(1), 132–141 (2017)
Kumar, N.; Saha, T.K.; Dey, J.: Multilevel inverter (MLI)-based stand-alone photovoltaic system: modeling, analysis, and control. IEEE Syst. J. 1, 1–7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2019.2900485
Lai, J.S.; Peng, F.Z.: Multilevel converters - a new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 32(3), 509–517 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1109/28.502161
Malinowski, M.; Gopakumar, K.; Rodriguez, J.; Pérez, M.A.: A survey on cascaded multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(7), 2197–2206 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2009.2030767
Jing, H.; Corzine, K.A.: Extended operation of flying capacitor multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 21(1), 140–147 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2005.861108
Nabae, A.; Takahashi, I.; Akagi, H.: A new neutral-point-clamped PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. (1981). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.1981.4503992
Reza Ahrabi, R.; Farakhor, A.; Najafi Ravadanegh, S.; Ardi, H.: Symmetric and asymmetric transformer based cascaded multilevel inverter with minimum number of components. IET Power Electron. 8(6), 1052–1060 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2014.0378
Rodríguez, J.; Lai, J.S.; Peng, F.Z.: Multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 49(4), 724–738 (2002)
Saeedian, M.; Adabi, J.; Hosseini, S.M.: Cascaded multilevel inverter based on symmetric–asymmetric DC sources with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron. 10(12), 1468–1478 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2017.0039
Agrawal, R.; Jain, S.: Multilevel inverter for interfacing renewable energy sources with low/medium- and high-voltage grids. IET Renew. Power Gener. 11(14), 1822–1831 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2016.1034
Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M.: Optimal design of new cascaded Switch-Ladder multilevel inverter structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(3), 2072–2080 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2627019
Samadaei, E.; Gholamian, S.A.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Adabi, J.: An envelope type (E-Type) module: asymmetric multilevel inverters with reduced components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(11), 7148–7156 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2520913
Gautam, S.P.; Gupta, S.; Sahu, L.K.: Reduction in number of devices for symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverters. IET Power Electron. 9(4), 698–709 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2015.0176
Babaei, E.; Farhadi Kangarlu, M.; Sabahi, M.: “Extended multilevel converters: an attempt to reduce the number of independent DC voltage sources in cascaded multilevel converters. IET Power Electron. 7(1), 157–166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2013.0057
Farhadi Kangarlu, M.; Babaei, E.: Cross-switched multilevel inverter: an innovative topology. IET Power Electron. 6(4), 642–651 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2012.0265
Babei, E.; Hosseini, S.H.: New cascaded multilevel inverter topology with minimum number of switches. Energy Convers. Manag. 50(11), 2761–2767 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TENCON.2010.5686368
Ounejjar, Y.; Al-haddad, K.; Grégoire, L.: Packed U cells multilevel converter topology: theoretical study and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(4), 1294–1306 (2011)
Babaei, E.; Gowgani, S.S.: Hybrid multilevel inverter using switched capacitor units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(9), 4614–4621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2290769
Gupta, K.K.; Jain, S.: A novel multilevel inverter based on switched DC sources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(7), 3269–3278 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2282606
Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Alilu, S.: Cascaded multilevel inverter with series connection of novel H-bridge basic units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(12), 6664–6671 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2014.2316264
Boora, K.; Kumar, J.: General topology for asymmetrical multilevel inverter with reduced number of switches. IET Power Electron. 10(15), 2034–2041 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2016.1011
Babaei, E.; Alilu, S.; Laali, S.: A new general topology for cascaded multilevel inverters with reduced number of components based on developed H-bridge. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. 61(8), 3932–3939 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2286561
Alishah, R.S.; Nazarpour, D.; Hosseini, S.H.; Sabahi, M.: Reduction of power electronic elements in multilevel converters using a new cascade structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(1), 256–269 (2015)
Mokhberdoran, A.; Ajami, A.: Symmetric and asymmetric design and implementation of new cascaded multilevel inverter topology. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 29(12), 6712–6724 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2014.2302873
Gupta, K.K.; Jain, S.: Multilevel inverter topology based on series connected switched sources. IET Power Electron. 6(1), 164–174 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2012.0209
Arun, N.; Noel, M.M.: Crisscross switched multilevel inverter using cascaded semi-half-bridge cells. IET Power Electron. 11(1), 23–32 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2016.0644
Samadaei, E.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Gholamian, S.A.; Adabi, J.: A square T-type (ST-Type) module for asymmetrical multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(2), 987–996 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2017.2675381
Lee, S.S.; Sidorov, M.; Lim, C.S.; Idris, N.R.N.; Heng, Y.E.: Hybrid cascaded Multilevel inverter (HCMLI) with improved symmetrical 4-level submodule. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(2), 932–935 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2017.2726087
Lee, S.S.: Single-stage switched-capacitor module (S3CM) topology for cascaded multilevel inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33(10), 8204–8207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2018.2805685
Lee, S.S.; Sidorov, M.; Idris, N.R.N.; Heng, Y.E.: A symmetrical cascaded compact-module multilevel inverter (CCM-MLI) with pulsewidth modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(6), 4631–4639 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2772209
Gautam, S.P.; Kumar, L.; Gupta, S.: Single-phase multilevel inverter topologies with self-voltage balancing capabilities. IET Power Electron. 11(5), 844–855 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2017.0401
Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M.: A new general multilevel converter topology based on cascaded connection of submultilevel units with reduced switching components, DC sources, and blocked voltage by switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(11), 7157–7164 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2016.2592460
Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Vatsyayan, S.; Jana, K.C.: A new and generalized structure of MLI topology with half-bridge cell with minimum number of power electronic devices. IETE Tech. Rev. 4602, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2020.1726215
Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, K.C.: A new and generalized structure of single-phase and three-phase cascaded multilevel inverter with reduced power components. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 30(2), 1–23 (2019)
Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Chandra Jana, K.: Single-phase modified T-type–based multilevel inverter with reduced number of power electronic devices. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 29(11), 1–16 (2019)
Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M.; Sarwar, A.; Iqbal, A.; Memon, M.A.: A new multilevel inverter topology with reduce switch count. IEEE Access 7, 58584–58594 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2914430
Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M.; Memon, M.A.: Optimal design of a new cascaded multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count. IEEE Access 7, 24498–24510 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2890872
Siddique, M.D., et al.: Low switching frequency based asymmetrical multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count. IEEE Access 7, 86374–86383 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2925277
Siddique, M.D.; Iqbal, A.; Memon, M.A.; Mekhilef, S.: A new configurable topology for multilevel inverter with reduced switching components. IEEE Access 8, 188726–188741 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2020.3030951
Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Rawa, M.; Wahyudie, A.; Chokaev, B.; Salamov, I.: Extended multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count and voltage stress. IEEE Access 8, 201835–201846 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3026616
Rawa, M., et al.: Dual input switched-capacitor-based singlephase hybrid boost multilevel inverter topology with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron. 13(4), 881–891 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2019.0826
Suresh, Y.; Venkataramanaiah, J.; Panda, A.K.; Dhanamjayulu, C.; Venugopal, P.: Investigation on cascade multilevel inverter with symmetric, asymmetric, hybrid and multi-cell configurations. Ain Shams Eng. J. 8(2), 263–276 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2016.09.006
Anand, V.; Singh, V.: Compact symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverter with reduced switches. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 5, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12458
Dahidah, M.S.A.; Konstantinou, G.: A review of multilevel selective harmonic elimination PWM: formulations, solving algorithms, implementation and applications. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 30, 4091–4106 (2015)
Majumdar, S.; Mahato, B.; Jana, K.C.: Implementation of an optimum reduced components multi-cell multilevel (MC-MLI) inverter for lower standing voltage. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/tie.2019.2913812
Deng, Y.; Harley, R.G.: Space-vector versus nearest-level pulse width modulation for multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30, 2962–2974 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2014.2331687
Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, K.C.: Carrier-based PWM techniques for multi-level inverters: a comprehensive performance study. J. Sci. Part A Eng. Innov. 5, 101–111 (2018)
Mahato, B.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, C.K.: Reduction of power electronic devices in a single-phase generalized multilevel. J. Circuits. Syst Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126620500930
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Table
6 shows the circuit parameters in simulation and experimental tests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahato, B., Majumdar, S., Jana, K.C. et al. A Generalized Series-Connected Multilevel Inverter (MLI) Based on Reduced Power Electronic Devices for Symmetrical/Asymmetrical Sources. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 5907–5924 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07066-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07066-z