Abstract
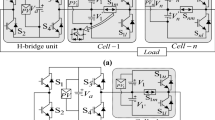
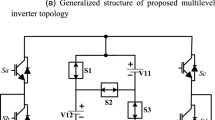
Multilevel inverter (MLI) has grown rapidly to achieve higher voltage levels, lesser voltage stress of the power devices, and lesser harmonic distortion of the inverter voltage. This paper presents the analysis of a reduced component hybrid nine-level inverter designed with only three DC sources. The proposed work emphasizes developing a hybrid multilevel inverter using symmetrical and asymmetrical DC sources at the input. The merit of the proposed MLI can efficiently reduce the power of electronic devices to produce the output voltage and generate nine-level using nine IGBTs only. Proposed MLI can be reducing complexity, size, and thus significantly improve inverter cost and performance. Also, a multicarrier-based, level-shifted PWM (LSPWM) method is adopted to generate the desired gate pulses of the IGBT switches using the DSPACE-1103-based controller. A laboratory prototype of the proposed seven-level and nine-level inverters is developed, and the experimental results of the MLIs at RL loading or voltage conditions are present. Further, the inverter losses, efficiency, and the %THD are also analyzed and compared with the other topologies.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kiltie O (1940) New type of D-C to A-C vibrator inverter. Trans Am 59(4):245–248
Sinha A et al (2018) An inclusive review on different multi-level inverter topologies, their modulation and control strategies for a grid connected photo-voltaic system. J Solar Energy 170:633–657
Panda KP et al (2019) Reduced switch cascaded multilevel inverter with new selective harmonic elimination control for standalone. Renew Energy Syst 55(6):7561–7574
Das MK et al (2016) A new half-cascaded multilevel inverter topology to improve systems performance parameters. J Mines Metals Fuels 64:267–270
Panda KP, Panda G (2018) Application of swarm optimisation-based modified algorithm for selective harmonic elimination in reduced switch count multilevel inverter. IET Power Electron 11(8):1–11
Das MK, Chauhan SS, Buduma P, Mishra S, Jana KC (2021) A hybrid novel cascaded asymmetrical 21-level inverter with reduced switches. In: 3rd IEEE international conference on energy, power and environment (ICEPE)
Kumar N, Saha TK, Dey J (2019) Multilevel inverter (MLI)-based stand-alone photovoltaic system: modelling, analysis, and control. IEEE Syst 1:1–7
Lai JS, Peng FZ (1996) Multilevel converters—a new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32(3):509–517
Malinowski M, Gopakumar K, Rodriguez J, Pérez M (2010) A survey on cascaded multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(7):2197–2206
Jing H, Corzine KA (2006) Extended operation of flying capacitor multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 21(1):140–147
Das MK, Sinha A, Jana KC (2019) A novel asymmetrical reduced switch nine-level inverter. J Circuit Syst Comput (World Sci) 29(8)
Ahrabi RR, Farakhor A, Ravadanegh SN, Ardi H (2015) Symmetric and asymmetric transformer based cascaded multilevel inverter with minimum number of components. IET Power Electron 8(6):1052–1060
Rodríguez J, Lai JS, Peng FZ (2002) Multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49(4):724–738
Saeedian M, Adabi J, Hosseini SM (2017) Cascaded multilevel inverter based on symmetric–asymmetric DC sources with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron 10(12):1468–1478
Das MK, Jana KC, Sinha A (2018) Performance evaluation of an asymmetrical reduced switched multi-level inverter for a grid-connected PV system. IET Renew Power Gener 12(2):252–263
Siddique MD et al (2019) Low switching frequency based asymmetrical multilevel inverter topology with reduced switch count. IEEE Access 7:86374–86383
Siddique MD, Iqbal A, Memon MA, Mekhilef S (2020) A new configurable topology for multilevel inverter with reduced switching components. IEEE Access 8:188726–188741
Das MK, Buduma P, Mishra S (2021) An asymmetrical reduced switch multilevel inverter based grid-connected PV system. In: 3rd IEEE international conference on energy, power and environment (ICEPE)
Rawa M et al (2020) Dual input switched-capacitor-based singlephase hybrid boost multilevel inverter topology with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron 13(4):881–891
Das MK, Sinha A, Jana KC (2018) A generalized hybrid multilevel inverter with reduced number of switches. In: IEEE 4th international conference on recent advances in information technology (RAIT)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Das, M.K., Buduma, P., Alam, P., Mishra, S. (2022). Generalized Hybrid Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced Number of Switches. In: Panda, G., Naayagi, R.T., Mishra, S. (eds) Sustainable Energy and Technological Advancements. Advances in Sustainability Science and Technology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9033-4_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9033-4_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9032-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9033-4
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)