Abstract
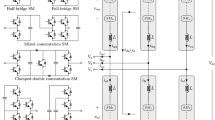
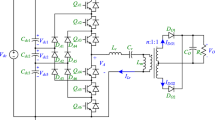
Modern industrial applications deal with power conversion system with lesser harmonic content for variable voltage and variable frequency application. In this paper, a generalized multilevel inverter has been proposed with nearest level modulation technique. A nine-level asymmetrical inverter of 5 kW has been developed as laboratory prototype and tested with three-phase isolated winding induction motor of rating 1 HP, 200 V, 50 Hz. Unlike any other control technique, the output voltage levels remain fixed at different modulation indexes using nearest level modulation technique, thereby reducing the harmonic content, switching losses and total harmonic distortion. In this paper, a DC–DC converter stage is used to control the DC link voltage of inverter for variable speed application. AC link system (a multiwinding transformer–rectifier) and a closed-loop voltage control technique are used to obtain multiple variable DC voltage sources. A single DC source is used for constant V/f control and frequency control of induction motor, i.e. isolated or open-end winding at above base speed as well as below base speeds. Simulation results of phase voltage of stator terminal, phase current of stator terminal, speed and torque are shown at different speeds. The experimental results of output voltages at different speeds for constant V/f control and frequency control are recorded as well. The experiment is carried out at different stator voltages (or stator frequencies) below and above the rated speed, and a few experimental results are presented. The numbers of inverter voltage levels are always same, and hence, their total harmonic distortion also remains nearly constant at different speeds of operation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-rub H, Holtz J, Rodriguez J, Baoming G (2010) Medium-voltage multilevel converters—State of the art, challenges, and requirements in industrial applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(8):2581–2596
Al-Othman AK, Abdelhamid TH (2009) Elimination of harmonics in multilevel inverters with non-equal dc sources using PSO. Energy Convers Manag 50(3):756–764
Babaei E, Moeinian MS (2010) Asymmetric cascaded multilevel inverter with charge balance control of a low resolution symmetric subsystem. Energy Convers Manag 51(11):2272–2278
Banaei MR, Salary E (2011) New multilevel inverter with reduction of switches and gate driver. Energy Convers Manag 52(2):1129–1136
Bhuvaneswari G, Nagaraju (2005) Multi-level inverters—a comparative study. IETE J Res 51(2):141–153. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2005.11416389
Boby M, Pramanick S, Kaarthik RS, Rahul SA, Gopakumar K, Umanand L (2016) Multilevel dodecagonal voltage space vector structure generation for open-end winding IM using a single DC source. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(5):2757–2765
Cheng Y, Qian C, Crow ML, Pekarek S, Atcitty S (2006) A comparison of diode-clamped and cascaded multilevel converters for a STATCOM with energy storage. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 53(5):1512–1521
Chowdhury S, Wheeler P, Patel C, Gerada C (2016) A multi-level converter with a floating bridge for open-ended winding motor drive applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(9):5366–5375
Colak I, Kabalci E, Bayindir R (2011) Review of multilevel voltage source inverter topologies and control schemes. Energy Convers Manag 52(2):1114–1128
Dahidah MSA, Konstantinou G, Agelidis VG (2015) A review of multilevel selective harmonic elimination PWM: formulations, solving algorithms, implementation and applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(8):4091–4106
Deng Y, Harley RG (2015) Space-vector versus nearest-level pulse width modulation for multilevel converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(6):2962–2974
Dixon J, Morán L (2005) A clean four-quadrant sinusoidal power rectifier using multistage converters for subway applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 52(2):653–661
Dixon J, Pereda J, Castillo C, Bosch S (2010) Asymmetrical multilevel inverter for traction drives using only one DC supply. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 59(8):3736–3743
Edpuganti A, Rathore AK (2015) New optimal pulsewidth modulation for single DC-link dual inverter fed open-end stator winding induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 30(8):4386–4393
Franquelo LG, Rodriguez J, Leon JI, Kouro S, Portillo R, Prats MAM (2008) The age of multilevel converters arrives. IEEE Ind Electron Mag 2(2):28–39
Hosseinzadeh MA, Farhadi KM, Babaei E (2013) Asymmetrical multilevel converter topology with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron 6(6):1188–1196
Hu P, Jiang D (2015) A level-increased nearest level modulation method for modular multilevel converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(4):1836–1842
Jana KC, Biswas SK (2015) Generalised switching scheme for a space vector pulse-width modulation-based N-level inverter with reduced switching frequency and harmonics. IET Power Electron 8(12):2377–2385
Jana KC, Biswas S, Chowdhury SK (2016) Dual reference phase shifted PWM technique for a N-level inverter based grid connected solar photovoltaic system. IET Renew Power Gener 10(7):928–935
Krug D, Bernet S, Fazel SS, Jalili K, Malinowski M (2007) Comparison of 2.3-kV medium-voltage multilevel converters for industrial medium-voltage drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(6):2979–2992
Lai JS, Peng FZ (1996) Multilevel converters—a new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32(3):509–517
Lezana P, Ortiz G (2009) Extended operation of cascade multicell converters under fault condition. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(7):2697–2703
Li W, He X, Hu J et al (2016) Common-mode voltage injection-based nearest level modulation with loss reduction for modular multilevel converters. IET Renew Power Gener 10(6):798–806
Lu S, Mariéthoz S, Corzine KA (2010) Asymmetrical cascade multilevel converters with noninteger or dynamically changing DC voltage ratios: concepts and modulation techniques. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(7):2411–2418
Luo H, Wang Q, Deng X, Wan S (2006) A novel V/f scalar controlled induction motor drives with compensation based on decoupled stator current. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on industrial technology, pp 1989–1994
Mahato B, Thakura PR, Jana KC (2014) Hardware design and implementation of unity power factor rectifiers using microcontrollers. In: IEEE 6th India international conference on power electronics, India, pp 1–5
McGrath BP, Holmes DG (2002) Multicarrier PWM strategies for multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49(4):858–867
Malekjamshidi Z, Jafari M, Islam R, Zhu J, Member, S (2014) A comparative study on characteristics of major topologies of voltage source multilevel inverters. In: Innovative smart grid technologies—Asia (ISGT Asia), pp 612–617
Meshram PM, Borghate VB (2015) A simplified nearest level control (NLC) voltage balancing method for modular multilevel converter (MMC). IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(1):450–462
Naderi R, Rahmati A (2008) Phase-shifted carrier PWM technique for general cascaded inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(3):1257–1269
Perez M, Rodriguez J, Pontt J, Kouro S (2007) Power distribution in hybrid multi-cell converter with nearest level modulation. In: IEEE international symposium industrial electronics, pp 736–741
Pramanick S, Azeez NA, Kaarthik RS, Gopakumar K, Cecati C (2015) Low-order harmonic suppression for open-end winding IM with dodecagonal space vector using a single DC-link supply. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(9):5340–5347
Rathore A, Edpuganti A (2015) Optimal low switching frequency pulsewidth modulation of nine-level cascade inverter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(1):482–495
Rech C, Pinheiro JR (2007) Hybrid multilevel converters: unified analysis and design considerations. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(2):1092–1104
Rodríguez J, Lai JS, Peng FZ (2002) Multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 49(4):724–738
Rodríguez J, Bernet S, Wu B, Pontt JO, Kouro S (2007) Multilevel voltage-source-converter topologies for industrial medium-voltage drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(6):2930–2945
Rodríguez J, Franquelo LG, Kouro S, Leon JI, Portillo RC, Prats MAM, Perez MA (2009) Multilevel Converters: an enabling technology for high-power applications. Proc IEEE 97(11):1786–1817
Ruiz-Caballero D, Martinez L, Ramos AR, Mussa SA (2009) New asymmetrical hybrid multilevel voltage inverter. In: Brazilian power electron conference, pp 354–361
Son GT, Lee HJ, Nam TS et al (2012) Design and control of a modular multilevel HVDC converter with redundant power modules for noninterruptible energy transfer. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 27(3):1611–1619
Sudharshan KR, Gopakumar K, Mathew J, Undeland T (2015) Medium-voltage drive for induction machine with multileveldodecagonal voltage space vectors with symmetric triangles. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(1):79–87
Sudheer P, Prasad KRS (2014) H-bridge multi level under different loads. Int J Sci Res Publ 4(5):1–5
Vazquez S, Leon JI, Franquelo LG, Padilla JJ, Carrasco JM (2009) DC-voltage-ratio control strategy for multilevel cascaded converters fed with a single DC source. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(7):2513–2521
Wang C-C, Fang C-H (2003) Sensorless scalar-controlled induction motor drives with modified flux observer. IEEE Trans EnergyConvers 18(2):181–186
Wen J, Smedley KM (2008) Synthesis of multilevel converters based on single- and/or three-phase converter building blocks. IEEE Trans Power Electron 23(3):1247–1256
Xiong C-L, Feng X-Y, Diao F, Wu X-J (2016) Improved nearest level modulation for cascaded H-bridge converter. Electron Lett 52(8):648–650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahato, B., Jana, K.C. & Thakura, P.R. Constant V/f Control and Frequency Control of Isolated Winding Induction Motor Using Nine-Level Three-Phase Inverter. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Electr Eng 43, 123–135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0064-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-018-0064-6