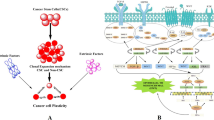
Abstract
PDGF is a growth factor and is extensively involved in multi-dimensional cellular dynamics. It switches on a plethora of molecules other than its classical pathway. It is engaged in various transitions of development; however, if the unleashed potentials lead astray, it brings forth tumourigenesis. Conventionally, it has been assumed that the components of this signalling pathway show fidelity and act with a high degree of autonomy. However, as illustrated by the PDGF signal transduction, reinterpretation of recent data suggests that machinery is often shared between multiple pathways, and other components crosstalk to each other through multiple mechanisms. It is important to note that metastatic cascade is an intricate process that we have only begun to understand in recent years. Many of the early steps of this PDGF cascade are not readily targetable in the clinic. In this review, we will unravel the paradoxes with reference to mitrons and cellular plasticity and discuss how disruption of signalling cascade triggers cellular proliferation phase transition and metastasis. We will also focus on the therapeutic interventions to counteract resultant molecular disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heldin CH, Eriksson U, Ostman A. New members of the platelet-derived growth factor family of mitogens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;398(2):284–90.
Sun PD, Davies DR. The cystine-knot growth-factor superfamily. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1995;24:269–91.
Li X, Eriksson U. Novel PDGF family members: PDGF-C and PDGF-D. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14(2):91–8.
Heldin CH, Westermark B. Signal transduction by the receptors for platelet-derived growth factor. J Cell Sci. 1990;96(Pt 2):193–6.
Bowen-Pope DF, Hart CE, Seifert RA. Sera and conditioned media contain different isoforms of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) which bind to different classes of PDGF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(5):2502–8.
Gronwald RG, Grant FJ, Haldeman BA, Hart CE, O'Hara PJ, Hagen FS, et al. Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor: evidence for more than one receptor class. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85(10):3435–9.
Li X, Pontén A, Aase K, Karlsson L, Abramsson A, Uutela M, et al. PDGF-C is a new protease-activated ligand for the PDGF alpha-receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(5):302–9.
Bergsten E, Uutela M, Li X, Pietras K, Ostman A, Heldin CH, et al. PDGF-D is a specific, protease-activated ligand for the PDGF beta-receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(5):512–6.
Changsirikulchai S, Hudkins KL, Goodpaster TA, Volpone J, Topouzis S, Gilbertson DG, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D expression in developing and mature human kidneys. Kidney Int. 2002;62(6):2043–54.
Cochran BH, Reffel AC, Stiles CD. Molecular cloning of gene sequences regulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983;33(3):939–47.
Linzer DI, Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1983;80(14):4271–5.
Almendral JM, Sommer D, Macdonald-Bravo H, Burckhardt J, Perera J, Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988;8(5):2140–8.
Li L, Blumenthal DK, Terry CM, He Y, Carlson ML, Cheung AK. PDGF-induced proliferation in human arterial and venous smooth muscle cells: molecular basis for differential effects of PDGF isoforms. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:289–98.
Sato S, Sato Y, Hatakeyama K, Marutsuka K, Yamashita A, Takeshima H, et al. Quantitative analysis of vessels with smooth muscle layer in astrocytic tumors: correlation with histological grade and prognostic significance. Histol Histopathol. 2011;26:497–504.
Ishigaki T, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Shimojo N, Matsushima S, Taki W, Yoshida T. Tenascin-C enhances crosstalk signaling of integrin αvβ3/PDGFR-β complex by SRC recruitment promoting PDGF-induced proliferation and migration in smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol. 2011 (in press)
Tsaousi A, Williams H, Lyon CA, Taylor V, Swain A, Johnson JL, et al. Wnt4/β-catenin signaling induces VSMC proliferation and is associated with intimal thickening. Circ Res. 2011;108:427–36.
Sklepkiewicz P, Schermuly RT, Tian X, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N, Sedding D, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta contributes to proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in pulmonary hypertension. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18883.
Keramati AR, Singh R, Lin A, Faramarzi S, Ye ZJ, Mane S, et al. Wild-type LRP6 inhibits, whereas atherosclerosis-linked LRP6R611C increases PDGF-dependent vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:1914–8.
Mendelson K, Swendeman S, Saftig P, Blobel CP. Stimulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRbeta) activates ADAM17 and promotes metalloproteinase-dependent cross-talk between the PDGFRbeta and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:25024–32.
Chen PY, Simons M, Friesel R. FRS2 via fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is required for platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta-mediated regulation of vascular smooth muscle marker gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(23):15980–92.
Pellet-Many C, Frankel P, Evans IM, Herzog B, Jünemann-Ramírez M, Zachary IC. Neuropilin-1 mediates PDGF stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cell migration and signalling via p130Cas. Biochem J. 2011;435:609–18.
Miraoui H, Ringe J, Häupl T, Marie PJ. Increased EFG- and PDGFalpha-receptor signaling by mutant FGF-receptor 2 contributes to osteoblast dysfunction in Apert craniosynostosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19:1678–89.
Sápi Z, Füle T, Hajdu M, Matolcsy A, Moskovszky L, Márk A, et al. The activated targets of mTOR signaling pathway are characteristic for PDGFRA mutant and wild-type rather than KIT mutant GISTs. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2011;20:22–33.
Pérez J, Torres RA, Rocic P, Cismowski MJ, Weber DS, Darley-Usmar VM, et al. PYK2 signaling is required for PDGF-dependent vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;301:C242–51.
Zhao Y, Biswas SK, McNulty PH, Kozak M, Jun JY, Segar L. PDGF-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation is associated with dysregulation of insulin receptor substrates. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011;300:C1375–85.
Ning Y, Sun Q, Dong Y, Xu W, Zhang W, Huang H, et al. Slit2-N inhibits PDGF-induced migration in rat airway smooth muscle cells: WASP and Arp2/3 involved. Toxicology. 2011;283:32–40.
Ucuzian AA, Brewster LP, East AT, Pang Y, Gassman AA, Greisler HP. Characterization of the chemotactic and mitogenic response of SMCs to PDGF-BB and FGF-2 in fibrin hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94:988–96.
Martino MM, Hubbell JA. The 12th-14th type III repeats of fibronectin function as a highly promiscuous growth factor-binding domain. FASEB J. 2010;24:4711–21.
Foehr ED, Tatavos A, Tanabe E, Raffioni S, Goetz S, Dimarco E, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) signaling in PC12 cells: activation of juxtamembrane domains in PDGFR/DDR/TrkA chimeric receptors. FASEB J. 2000;14:973–81.
Toffalini F, Kallin A, Vandenberghe P, Pierre P, Michaux L, Cools J, et al. The fusion proteins TEL-PDGFRbeta and FIP1L1-PDGFRalpha escape ubiquitination and degradation. Haematologica. 2009;94:1085–93.
Gueller S, Hehn S, Nowak V, Gery S, Serve H, Brandts CH, et al. Adaptor protein Lnk binds to PDGF receptor and inhibits PDGF-dependent signaling. Exp Hematol. 2011;39:591–600.
Medves S, Noel LA, Montano-Almendras CP, Albu RI, Schoemans H, Constantinescu SN, Demoulin JB. Multiple oligomerization domains of KANK1-PDGFRB are required for JAK2-independent hematopoietic cell proliferation and signaling via STAT5 and ERK. Haematologica. 2011 (in press) AOP 32
Cao Y, Cao R, Hedlund EM. R Regulation of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by FGF and PDGF signaling pathways. J Mol Med. 2008;86(7):785–9.
Cao R, Björndahl MA, Religa P, Clasper S, Garvin S, Galter D, et al. PDGF-BB induces intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2004;6(4):333–45.
Jechlinger M, Sommer A, Moriggl R, Seither P, Kraut N, Capodiecci P, et al. Autocrine PDGFR signaling promotes mammary cancer metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(6):1561–70.
Cimpean AM, Ceauşu R, Encică S, Gaje PN, Ribatti D, Raica M. Platelet-derived growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor-α expression in the normal human thymus and thymoma. Int J Exp Pathol. 2011 (in press) AOP
Suzuki S, Dobashi Y, Hatakeyama Y, Tajiri R, Fujimura T, Heldin CH, et al. Clinicopathological significance of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-B and vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression, PDGF receptor-β phosphorylation, and microvessel density in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:659.
Chaoran Z, Zhirong L, Gezhi X. Combination of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor/platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibition markedly improves the antiangiogenic efficacy for advanced stage mouse corneal neovascularization. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2011. (in press) AOP
Ahmad A, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali R, Ali S, Banerjee S, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D contributes to aggressiveness of breast cancer cells by up-regulating Notch and NF-κB signaling pathways. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126(1):15–25.
Wang Z, Kong D, Banerjee S, Li Y, Adsay NV, Abbruzzese J, et al. Down-regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-D inhibits cell growth and angiogenesis through inactivation of Notch-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res. 2007;67(23):11377–85.
Kang DW, Min do S. Platelet derived growth factor increases phospholipase D1 but not phospholipase D2 expression via NFkappaB signaling pathway and enhances invasion of breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;294(1):125–33.
Rykala J, Przybylowska K, Majsterek I, Pasz-Walczak G, Sygut A, Dziki A, Kruk-Jeromin J. Angiogenesis markers quantification in breast cancer and their correlation with clinicopathological prognostic variables. Pathol Oncol Res. 2011 (in press).
Liu J, Liao S, Huang Y, Samuel R, Shi T, Naxerova K, et al. PDGF-D improves drug delivery and efficacy via vascular normalization, but promotes lymphatic metastasis by activating CXCR4 in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3638–48.
Gehmert S, Gehmert S, Prantl L, Vykoukal J, Alt E, Song YH. Breast cancer cells attract the migration of adipose tissue-derived stem cells via the PDGF-BB/PDGFR-beta signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;398:601–5.
Maurer B, Stanczyk J, Jüngel A, Akhmetshina A, Trenkmann M, Brock M, et al. MicroRNA-29, a key regulator of collagen expression in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:1733–43.
Quintavalle M, Elia L, Condorelli G, Courtneidge SA. MicroRNA control of podosome formation in vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 2010;189:13–22.
Dugas JC, Cuellar TL, Scholze A, Ason B, Ibrahim A, Emery B, et al. Dicer1 and miR-219 are required for normal oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. Neuron. 2010;65:597–611.
Zhang J, Chintalgattu V, Shih T, Ai D, Xia Y, Khakoo AY. MicroRNA-9 is an activation-induced regulator of PDGFR-beta expression in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 (in press) AOP.
Würdinger T, Tannous BA, Saydam O, Skog J, Grau S, Soutschek J, et al. miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:382–93.
Eberhart JK, He X, Swartz ME, Yan YL, Song H, Boling TC, et al. MicroRNA Mirn140 modulates Pdgf signaling during palatogenesis. Nat Genet. 2008;40:290–8.
Goff LA, Boucher S, Ricupero CL, Fenstermacher S, Swerdel M, Chase LG, et al. Differentiating human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells regulate microRNAs: prediction of microRNA regulation by PDGF during osteogenesis. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(10):1354–69.
Chan MC, Hilyard AC, Wu C, Davis BN, Hill NS, Lal A, et al. Molecular basis for antagonism between PDGF and the TGFbeta family of signalling pathways by control of miR-24 expression. EMBO J. 2010;29(3):559–73.
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Kim HR, et al. miR-200 regulates PDGF-D-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion, and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1712–21.
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Nguyen PH, Lagna G, Hata A. Induction of microRNA-221 by platelet-derived growth factor signaling is critical for modulation of vascular smooth muscle phenotype. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(6):3728–38.
Muhl L, Nykjaer A, Wygrecka M, Monard D, Preissner KT, Kanse SM. Inhibition of PDGF-BB by Factor VII-activating protease (FSAP) is neutralized by protease nexin-1, and the FSAP-inhibitor complexes are internalized via LRP. Biochem J. 2007;404(2):191–6.
Takayama Y, May P, Anderson RG, Herz J. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) controls endocytosis and c-CBL-mediated ubiquitination of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFR beta). J Biol Chem. 2005;280(18):18504–10.
Zhou L, Takayama Y, Boucher P, Tallquist MD, Herz J. LRP1 regulates architecture of the vascular wall by controlling PDGFRbeta-dependent phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. PLoS One. 2009;4(9):e6922.
Muratoglu SC, Mikhailenko I, Newton C, Migliorini M, Strickland DK. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) forms a signaling complex with platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta in endosomes and regulates activation of the MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(19):14308–17.
Boucher P, Li WP, Matz RL, Takayama Y, Auwerx J, Anderson RG, et al. LRP1 functions as an atheroprotective integrator of TGFbeta and PDFG signals in the vascular wall: implications for Marfan syndrome. PLoS One. 2007;2(5):e448.
Hellberg C, Schmees C, Karlsson S, Ahgren A, Heldin CH. Activation of protein kinase C alpha is necessary for sorting the PDGF beta-receptor to Rab4a-dependent recycling. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20(12):2856–63.
Chiarugi P, Cirri P, Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Buricchi F, et al. Insight into the role of low molecular weight phosphotyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTP) on platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGF-r) signaling. LMW-PTP controls PDGF-r kinase activity through TYR-857 dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(40):37331–8.
Kappert K, Paulsson J, Sparwel J, Leppänen O, Hellberg C, Ostman A, et al. Dynamic changes in the expression of DEP-1 and other PDGF receptor-antagonizing PTPs during onset and termination of neointima formation. FASEB J. 2007;21:523–34.
Karlsson S, Kowanetz K, Sandin A, Persson C, Ostman A, Heldin CH, et al. Loss of T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase induces recycling of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) beta-receptor but not the PDGF alpha-receptor. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:4846–55.
Kanda M, Ihara Y, Murata H, Urata Y, Kono T, Yodoi J, et al. Glutaredoxin modulates platelet-derived growth factor-dependent cell signaling by regulating the redox status of low molecular weight protein-tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:28518–28.
Freyhaus H, Dagnell M, Leuchs M, Vantler M, Berghausen EM, Caglayan E, et al. Hypoxia enhances platelet-derived growth factor signaling in the pulmonary vasculature by down-regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:1092–102.
Conrad M, Sandin A, Förster H, Seiler A, Frijhoff J, Dagnell M, et al. Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Aspenström P, Böhmer F, Ostman A. 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived lipid peroxides control receptor tyrosine kinase signaling through oxidation of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:15774–9.
Boivin B, Tonks NK. Analysis of the redox regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase superfamily members utilizing a cysteinyl-labeling assay. Methods Enzymol. 2010;474:35–50.
Sandin A, Dagnell M, Gonon A, Pernow J, Stangl V, Aspenström P, et al. Hypoxia followed by re-oxygenation induces oxidation of tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Signal. 2011;23:820–6.
Juarez JC, Manuia M, Burnett ME, Betancourt O, Boivin B, Shaw DE, et al. Superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) is essential for H2O2-mediated oxidation and inactivation of phosphatases in growth factor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7147–52.
Cortesio CL, Perrin BJ, Bennin DA, Huttenlocher A. Actin-binding protein-1 interacts with WASp-interacting protein to regulate growth factor-induced dorsal ruffle formation. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(1):186–97.
Abella JV, Vaillancourt R, Frigault MM, Ponzo MG, Zuo D, Sangwan V, et al. The Gab1 scaffold regulates RTK-dependent dorsal ruffle formation through the adaptor Nck. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:1306–19.
Campa F, Machuy N, Klein A, Rudel T. A new interaction between Abi-1 and betaPIX involved in PDGF-activated actin cytoskeleton reorganisation. Cell Res. 2006;16:759–70.
Veracini L, Franco M, Boureux A, Simon V, Roche S, Benistant C. Two distinct pools of Src family tyrosine kinases regulate PDGF-induced DNA synthesis and actin dorsal ruffles. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:2921–34.
Goicoechea S, Arneman D, Disanza A, Garcia-Mata R, Scita G, Otey CA. Palladin binds to Eps8 and enhances the formation of dorsal ruffles and podosomes in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:3316–24.
Toguchi M, Richnau N, Ruusala A, Aspenström P. Members of the CIP4 family of proteins participate in the regulation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta-dependent actin reorganization and migration. Biol Cell. 2010;102(4):215–30.
Berrou E, Bryckaert M. Recruitment of protein phosphatase 2A to dorsal ruffles by platelet-derived growth factor in smooth muscle cells: dephosphorylation of Hsp27. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:836–48.
Nagano K, Bornhauser BC, Warnasuriya G, Entwistle A, Cramer R, Lindholm D, et al. PDGF regulates the actin cytoskeleton through hnRNP-K-mediated activation of the ubiquitin E3-ligase MIR. EMBO J. 2006;25(9):1871–82.
Uribe DJ, Guo K, Shin YJ, Sun D. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K and nucleolin as transcriptional activators of the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter through interaction with secondary DNA structures. Biochemistry. 2011;50:3796–806.
Mikula M, Bomsztyk K. Direct recruitment of ERK cascade components to inducible genes is regulated by heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) K. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:9763–75.
Chen K, Albano A, Ho A, Keaney Jr JF. Activation of p53 by oxidative stress involves platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor-mediated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:39527–33.
Kim TS, Kawaguchi M, Suzuki M, Jung CG, Asai K, Shibamoto Y, et al. The ZFHX3 (ATBF1) transcription factor induces PDGFRB, which activates ATM in the cytoplasm to protect cerebellar neurons from oxidative stress. Dis Model Mech. 2010;3:752–62.
Ikushima H, Komuro A, Isogaya K, Shinozaki M, Hellman U, Miyazawa K, et al. An Id-like molecule, HHM, is a synexpression group-restricted regulator of TGF-beta signalling. EMBO J. 2008;27(22):2955–65.
Patel P, West-Mays J, Kolb M, Rodrigues JC, Hoff CM, Margetts PJ. Platelet derived growth factor B and epithelial mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial cells. Matrix Biol. 2010;29(2):97–106.
Cheng X, Yang G, Schmeler KM, Coleman RL, Tu X, Liu J, et al. Recurrence patterns and prognosis of endometrial stromal sarcoma and the potential of tyrosine kinase-inhibiting therapy. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;121:323–7.
Pitter KL, Galbán CJ, Galbán S, Tehrani OS, Li F, Charles N, et al. Perifosine and CCI 779 co-operate to induce cell death and decrease proliferation in PTEN-intact and PTEN-deficient PDGF-driven murine glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2011;6:e14545. AOP.
Dong Y, Jia L, Wang X, Tan X, Xu J, Deng Z, et al. Selective inhibition of PDGFR by imatinib elicits the sustained activation of ERK and downstream receptor signaling in malignant glioma cells. Int J Oncol. 2011;38:555–69.
Xu XL, Huang YJ, Wang YQ, Chen XF, Zhang W. 2,3,4′,5-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating the cell cycle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011;38:307–13.
Kim TJ, Yun YP. Antiproliferative activity of NQ304, a synthetic 1,4-naphthoquinone, is mediated via the suppressions of the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in PDGF-BB-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007;46:43–51.
Kim TJ, Han HJ, Kim YJ, Jung JC, Yu JY, Lee JJ, et al. Inhibitory effects of BST406, a newly synthesized benzylideneacetophenone derivative, on abnormal vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33:900–4.
Schultz JD, Rotunno S, Riedel F, Anders C, Erben P, Hofheinz RD, et al. Synergistic effects of imatinib and carboplatin on VEGF, PDGF and PDGF-Rα/ß expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck in vitro. Int J Oncol. 2011;38:1001–12.
Kłosowska-Wardęga A, Hasumi Y, Ahgren A, Heldin CH, Hellberg C. Combination therapy using imatinib and vatalanib improves the therapeutic efficiency of paclitaxel towards a mouse melanoma tumor. Melanoma Res. 2011 (in press) AOP.
Park ES, Yoo JM, Lim Y, Tudev M, Yoo HS, Hong JT, et al. Inhibitory effects of docetaxel on platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through blocking PDGF-receptor β phosphorylation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;116:204–13.
Mathew P, Thall PF, Wen S, Bucana C, Jones D, Horne E, et al. Dynamic change in phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor receptor in peripheral blood leukocytes following docetaxel therapy predicts progression-free and overall survival in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1426–32.
Lu C, Shahzad MM, Moreno-Smith M, Lin YG, Jennings NB, Allen JK, et al. Targeting pericytes with a PDGF-B aptamer in human ovarian carcinoma models. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;9:176–82.
Prakash J, de Jong E, Post E, Gouw AS, Beljaars L, Poelstra K. A novel approach to deliver anticancer drugs to key cell types in tumors using a PDGF receptor-binding cyclic peptide containing carrier. J Control Release. 2010;145:91–101.
Tailor TD, Hanna G, Yarmolenko PS, Dreher MR, Betof AS, Nixon AB, et al. Effect of pazopanib on tumor microenvironment and liposome delivery. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:1798–808.
Hutson TE, Davis ID, Machiels JP, De Souza PL, Rottey S, Hong BF, et al. Efficacy and safety of pazopanib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:475–80.
Dong LH, Wen JK, Miao SB, Jia Z, Hu HJ, Sun RH, et al. Baicalin inhibits PDGF-BB-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through suppressing PDGFRβ-ERK signaling and increase in p27 accumulation and prevents injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia. Cell Res. 2010;20:1252–62.
Brave SR, Ratcliffe K, Wilson Z, James NH, Ashton S, Wainwright A, et al. Assessing the activity of cediranib, a VEGFR-2/3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, against VEGFR-1 and members of the structurally related PDGFR family. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:861–73.
Lindborg M, Cortez E, Höidén-Guthenberg I, Gunneriusson E, von Hage E, Syud F, et al. Engineered high-affinity affibody molecules targeting platelet-derived growth factor receptor β in vivo. J Mol Biol. 2011;407:298–315.
Mabry R, Gilbertson DG, Frank A, Vu T, Ardourel D, Ostrander C, et al. A dual-targeting PDGFRbeta/VEGF-A molecule assembled from stable antibody fragments demonstrates anti-angiogenic activity in vitro and in vivo. MAbs. 2010;2:20–34.
Lin J, Chen A. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by curcumin blocks the signaling pathways for PDGF and EGF in hepatic stellate cells. Lab Invest. 2008;88:529–40.
Zhao ZD, Huang ZS. Study on effects of curcumin on expressions of PDGF-BB, PDGFRbeta and ERK1 of HSC. Zhong Yao Cai. 2009;32:732–5.
Oak MH, Bedoui JE, Madeira SV, Chalupsky K, Schini-Kerth VB. Delphinidin and cyanidin inhibit PDGF(AB)-induced VEGF release in vascular smooth muscle cells by preventing activation of p38 MAPK and JNK. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149:283–90.
Venkatesan B, Ghosh-Choudhury N, Das F, Mahimainathan L, Kamat A, Kasinath BS, et al. Resveratrol inhibits PDGF receptor mitogenic signaling in mesangial cells: role of PTP1B. FASEB J. 2008;22:3469–82.
Choi KH, Kim JE, Song NR, Son JE, Hwang MK, Byun S, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is a novel target of piceatannol for inhibiting PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;85:836–44.
Park ES, Lim Y, Hong JT, Yoo HS, Lee CK, Pyo MY, et al. Pterostilbene, a natural dimethylated analog of resveratrol, inhibits rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by blocking Akt-dependent pathway. Vascul Pharmacol. 2010;53:61–7.
Chen CP, Hung CF, Lee SC, Lo HM, Wu PH, Wu WB. Lycopene binding compromised PDGF-AA/-AB signaling and migration in smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts: prediction of the possible lycopene binding site within PDGF. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2010;381:401–14.
Chan CM, Fang JY, Lin HH, Yang CY, Hung CF. Lycopene inhibits PDGF-BB-induced retinal pigment epithelial cell migration by suppression of PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;388:172–6.
Chiang HS, Wu WB, Fang JY, Chen DF, Chen BH, Huang CC, et al. Lycopene inhibits PDGF-BB-induced signaling and migration in human dermal fibroblasts through interaction with PDGF-BB. Life Sci. 2007;81:1509–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooqi, A.A., Waseem, S., Riaz, A.M. et al. PDGF: the nuts and bolts of signalling toolbox. Tumor Biol. 32, 1057–1070 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0212-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0212-3