Abstract
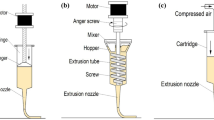
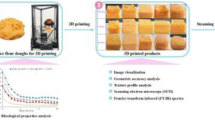
3D printing is an innovative technology for food industry, which provides tremendous opportunities for the designing of customized and personalized nutrition for fruit and vegetable based food products. Various researchers have worked on the development of printable ink, stability of printed products and quality parameters. The aim of this review is to cover the most recent advancements on 3D food printing for fruits and vegetables and explore the prospect. Extrusion-based 3D printing is the most extensively used technique due to their several advantages. The review examines the three groups of extrusion printing such as room temperature extrusion, fused deposition manufacturing and gel forming extrusion. The development in last few years in the area of 3D food products of fruits and vegetables powder has been assembled in this review article. Based on these results, it can conclude that fruit and vegetable has been successfully used to fabricate 3D and even 4D food products. Future studies are required for improvement in pre and post-processing technique. Functional food can also be developed by using 3D printing but more research is required in this area.


Source: Reproduced with the permission from Feng et al. 2020. Copyright © 2020, Elsevier)

Source: Reproduced with the permission from Liu et al. 2018a, b, c. Copyright © 2018, Elsevier)

Source: Reproduced with the permission from Azam et al. (2018). Copyright © Springer Science + Business Media2018)

Source: Reproduced with the permission from Liu et al. 2019. Copyright © 2019, Elsevier)

Source: Reproduced with the permission from Yang et al. 2017. Copyright © 2017, Elsevier)

Source: Reproduced with the permission from He et al. 2020. Copyright © 2019, Elsevier)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam SM, Zhang M, Mujumdar AS, Yang C (2017) Study on 3D printing of orange concentrate and material. J Food Process Eng 41:e12689. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12689
Azam RS, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Yang C (2018) Effect of different gums on features of 3D printed object based on vitamin-D enriched orange concentrate. Food Biophys 13:250–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9531-x
Brown A, Beer DD, Conradie P (2014) Development of a stereolithography (stl) input and computer numerical control (cnc) output algorithm for an entry-level 3-d printer. S Afr J Ind Eng. https://doi.org/10.7166/25-2-675
Chang H, Min Z, Zhongxiang F (2020) 3D printing of food: pretreatment and posttreatment of materials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60:2379–2392. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1641065
Chen H, Xie F, Chen L, Zheng B (2019) Effect of rheological properties of potato, rice and corn starches on their hot-extrusion 3D printing behaviours. J Food Eng 244:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.09.011
Choi J, Kwon OC, Jo W, Lee HJ, Moon M (2015) 4D printing technology: a review. 3D Print Addit Manuf 2:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1089/3dp.2015.0039
Dankar I, Haddarah A, Omar FE, Sepulcre F, Pujola M (2018a) 3D printing technology: the new era for food customization and elaboration. Trends Food Sci Technol 75:231–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.018
Dankar I, Pujolà M, Omar FE, Sepulcre F, Haddarah A (2018b) Impact of mechanical and microstructural properties of potato puree-food additive complexes on extrusion-based 3D printing. Food Bioprocess Technol 11:2021–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2159-5
Dick A, Bhandari B, Prakash S (2019) 3D printing of meat. Meat Sci 153:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.03.005
Feng C, Zhanga M, Bhandari B (2019) Materials properties of printable edible inks and printing parameters optimization during 3D printing: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59(19):3074–3081. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1481823
Feng C, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Ye Y (2020) Use of potato processing by-product: effects on the 3D printing characteristics of the yam and the texture of air-fried yam snacks. LWT 125:109265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109265
Godoi FC, Prakash S, Bhandari BR (2016) 3d printing technologies applied for food design: status and prospects. J Food Eng 179:44–54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.01.025
Guo C, Zhang M, Bhandari B (2019) Model building and slicing in food 3D printing processes: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 18:1052–1069. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12443
He C, Zhang M, Fang Z (2019) 3D printing of food: pretreatment and posttreatment of materials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60:2379–2392. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1641065
He C, Zhang M, Guoa C (2020) 4D printing of mashed potato/purple sweet potato puree with spontaneous color change. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 59:102250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102250
Imeson A, (1992) Thickening and Gelling agents for food. Springer. ISBN 978–1–4613–5921–0
Keerthana K, Anukiruthika T, Moses J, Anandharamakrishnan C (2020) Development of fiber-enriched 3D printed snacks from alternative foods: a study on button mushroom. J Food Eng 287:110116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110116
Khoo Z, Joanne EMT, Liu Y, Chua CK, Yang S, An J, Leong KF, Yeong WY (2015) 3D printing of smart materials: a review on recent progresses in 4D printing. Virtual Phys Prototyp 10:103–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2015.1097054
Kim HW, Lee JH, Park SM, Lee MH, Lee IW, Doh HS, Park HJ (2018) Effect of hydrocolloids on rheological properties and printability of vegetable inks for 3D food printing. J Food Sci 83:2923–2932. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14391
Le-Bail A, Maniglia BC, Le-Bail P (2020) Recent advances and future perspective in additive manufacturing of foods based on 3D printing. Curr Opin Food Sci 35:54–64
Lee JH, Won DJ, Kim HW, Park HJ (2019) Effect of particle size on 3D printing performance of the food-ink system with cellular food materials. J Food Eng 256:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.03.014
Lille M, Nurmela A, Nordlund E, Metsa-Kortelainen S, Sozer N (2018) Applicability of protein and fiber-rich food materials in extrusion-based 3D printing. J Food Eng 220:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.04.034
Lipson H, Kurman M (2013) Structure, Processing and Properties of 3D printable metallic materials. In J. Wiley, Fabricated: the new world of 3D printing. ISBN: 978–1–118–35063–8
Liu Z, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Wang Y (2017) 3D printing: Printing precision and application in food sector. Trends Food Sci Technol 69:83–94
Liu Z, Bhandari B, Prakash S, Zhang M (2018a) Creation of internal structure of mashed potato construct by 3D printing and its textural properties. Food Res Int 111:534–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.075
Liu Z, Zhang M, Yang C-h (2018b) Dual extrusion 3D printing of mashed potatoes/strawberry juice gel. LWT 96:589–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.06.014
Liu Z, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Yang C (2018c) Impact of rheological properties of mashed potatoes on 3D printing. J Food Eng 220:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.04.017
Liu Y, Liang X, Saeed A, Lan W, Qin W (2019) Properties of 3D printed dough and optimization of printing parameters. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 54:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.03.008
Liu Z, Bhandari B, Zhang M (2020) Incorporation of probiotics (Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis) into 3D printed mashed potatoes: Effects of variables on the viability. Food Res Int 128:108795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108795
Long J, Gholizadeh H, Lu J, Bunt C, Seyfoddin A (2017) Application of fused deposition modelling (FDM) method of 3D printing in drug delivery. Curr Pharm Des 23:433–439. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666161026162707
Martínez-Monzó J, Cárdenas J, García-Segovia P (2018) Effect of temperature on 3D printing of commercial potato puree. Food Biophys 14:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-019-09576-0
Momeni F, Hassani NS, Liu X, Ni J (2017) A review of 4D printing. Mater Des 122:42–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.02.068
Pei E (2014) 4D printing: Dawn of an emerging technology cycle. Assem Autom 34:310–314. https://doi.org/10.1108/AA-07-2014-062
Periard D, Schaal N, Schaal M, Malone E, Lipson H (2007) Printing food. In: 18th solid freeform fabrication symposium. 564–574.
Pitayachaval P, Sanklong N, Thongrak A (2018) A review of 3D food printing technology. MATEC web of conferences. EDP sciences. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201821301012
Ricci I, Derossi A, Severini C (2019) 3D printed food from fruits and vegetables. In fundamentals of 3D Food printing and applications, 117–149. ISBN: 9780128145654
Severini C, Derossi A, Ricci I, Caporizzi R, Fiore A (2018) Printing a blend of fruit and vegetables. new advances on critical variables and shelf life of 3D edible objects. J Food Eng 220:89–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.08.025
Sun J, Peng Z, Zhou W, Fuh YHJ, Hong GS, Chiu A (2015a) A review on 3D printing for customized food fabrication. Procedia Manuf 1:308–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2015.09.057
Sun J, Zhou W, Huang D, Fuh JY, Hong GS (2015b) An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Food Fabrication. Food Bioproc Tech 8:1605–1615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1528-6
Sun J, Zhou W, Yan L, Huang D, Lin L (2018) Extrusion-based food printing for digitalized food design and nutrition control. J Food Eng 220:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.02.028
Voon SL, An J, Wong G, Zhang Y, Chua CK (2019) 3D food printing: a categorised review of inks and their development. Virtual Phys Prototyp 14:203–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/17452759.2019.1603508
Yang F, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Liu Y (2018) Investigation on lemon juice gel as food material for 3D printing and optimization of printing parameters. LWT 87:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.08.054
Yang F, Zhang M, Liu Y (2019b) Effect of post-treatment microwave vacuum drying on the quality of 3D-printed mango juice gel. Dry Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2018.1536884
Yang F, Guo C, Zhang M, Bhandaric B, Liud Y (2019a) Improving 3D printing process of lemon juice gel based on fluid flow numerical simulation. LWT 102: 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.12.031
Zhenbin L, Zhang M, Ye Y (2020) Indirect prediction of 3D printability of mashed potatoes based on LF-NMR measurements. J Food Eng 287:110137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110137
Zhua S, Stiegerb MA, Goota AJ, Schutysera MA (2019) Extrusion-based 3D printing of food pastes: correlating rheological properties with printing behaviour. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 58:102214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102214
Acknowledgements
Author declares no acknowledgements.
Funding
This work did not receive any grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing—review and editing. DS: Writing —review and editing. SK: Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author declares no any conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waghmare, R., Suryawanshi, D. & Karadbhajne, S. Designing 3D printable food based on fruit and vegetable products—opportunities and challenges. J Food Sci Technol 60, 1447–1460 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05386-4
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05386-4