Abstract
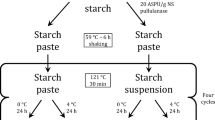
The starch and starch gels from green gram (GG) and foxtail millet (FM) were characterised for their physicochemical, thermal and microstructural characteristics; the features of shape and size were determined by image analysis. Both GG and FM formed well-set gels at 9% concentration of starch. The fracture strain of the gels was between 78 and 80% indicating non-brittle gels. The peak temperatures of the native flour of GG (74.9 °C) and FM (75.7 °C) were significantly higher than their corresponding starch samples (72.2 and 75.0 °C). The conclusion temperatures of the FM native flour (81.2 °C) and starch (79.4 °C) samples were higher than the native GG flour (79.9 °C) and GG starch (77.1 °C) samples. Starches were nearly spherical as the roundness values were between 0.88 and 0.95. Green gram starch was pentagonal having an average diameter of 3.9–9.2 µm while foxtail millet starch was spherical with a diameter of 4.9–10.1 µm. The freeze-dried GG and FM starch gels showed cellular structure containing organised hexagonal pores, bound by thin pore walls; the GG starch gels deviated from the circular shape as they had the highest elongation value of 4.21. The thicker pore walls were observed for GG starch gels (0.88 μm) compared to that of FM samples (0.57 μm). The higher pore wall thickness in the case of GG gel showed the formation of junction zones.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000) Approved method of the American Association of Cereal Chemists. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Adebowale KO, Afolabi TA, Olu-Owolabi BI (2005) Hydrothermal treatments of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) starch. Food Hydrocolloids 19:974–983
Amadou I, Gbadamosi OS, Le GW (2011) Millet-based traditional processed foods and beverages—a review. Cereal Food World 56:115–121
AOAC (2002) Official methods of analysis, 17th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Brown ME (2004) Introduction to thermal analysis, techniques and applications, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York, p 264
Butt MS, Batool R (2010) Nutritional and functional properties of some promising legumes protein isolates. Pak J Nutr 9:373–379
Dharmaraj U, Parameswara P, Somashekar R, Malleshi NG (2014) Effect of processing on the microstructure of finger millet by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. J Food Sci Technol 51:494–502
Fujita S, Fujiyama G (1993) The study of melting temperature and enthalpy of starch from rice, barley, wheat, foxtail- and proso-millets. Starch/Stärke 45:436–441
Fujita N, Kubo A, Suh DS, Wong KS, Jane JL, Ozawa K, Takaiwa F, Inaba Y, Nakamura Y (2003) Antisense inhibition of isoamylase alters the structure of amylopectin and the physicochemical properties of starch in rice endosperm. Plant Cell Physiol 44:607–618
Funami T, Funami M, Yada H, Nakao Y (1999) Rheological and thermal studies on gelling characteristics of curdlan. Food Hydrocolloids 13:317–324
Goñi I, Garcia-Diz L, Mañas E, Saura-Calixto F (1996) Analysis of resistant starch: a method for foods and food products. Food Chem 56:445–449
Hoover R, Sosulski FW (1991) Composition, structure, functionality and chemical modification of legume starches—a review. Can J Physiol Pharm 69:79–92
Kaur M, Sandhu KS, Lim ST (2010) Microstructure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of starches from different Indian lentil (Lens culinaris) cultivars. Carbohydr Polym 79:349–355
Kim SK, Sohn EY, Lee IJ (2009) Starch properties of native foxtail millet, Setaria italica Beauv. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 12:59–62
Liu Q, Charlet G, Yelle S, Arul J (2002) Phase transition in potato starch–water system I. Starch gelatinization at high moisture level. Food Res Int 35:397–407
Madhusudhan B, Tharanathan RN (1995) Legume and cereal starches—Why differences in digestibility? Part I. Isolation and composition of legume (green gram and Bengal gram) starches. Starch/Stärke 47:165–171
Nagaprabha P, Bhattacharya S (2016a) Rheological characterisation of sol–gel phenomenon and stability of green gram and foxtail millet flour gels. LWT Food Sci Technol 65:917–923
Nagaprabha P, Bhattacharya S (2016b) Textural characterization of foxtail millet gels: effect of cations and hydrocolloids. J Food Sci Technol 53:257–268
Pal K, Banthia AK, Majumdar DK (2008) Effect of heat treatment of starch on the properties of the starch hydrogels. Mater Lett 62:215–218
Ratnayake WS, Hoover R, Shahidi F, Perera C, Jane J (2001) Composition, molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from four field pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars. Food Chem 74:189–202
Russ JC (2011) The image processing handbook, 6th edn. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp 597–623
Sandhu KS, Lim ST (2008) Digestibility of legume starches as influenced by their physical and structural properties. Carbohydr Polym 71:245–252
Santha N, Sudha KG, Vijayakumari KP, Nayar VU, Moorthy SN (1990) Raman and infrared spectra of starch samples of sweet potato and cassava. J Chem Sci 102:705–712
Sashikala VB, Sreerama YN, Pratape VM, Narasimha HV (2015) Effect of thermal processing on protein solubility of green gram (Phaseolus aureus) legume cultivars. J Food Sci Technol 52:1552–1560
Sikora M, Kowalski S, Tomasik P, Sady M (2007) Rheological and sensory properties of dessert sauces thickened by starch-xanthan gum combination. J Food Eng 79:1144–1151
Singh V, Ali SZ (2000) Acid degradation of starch. The effect of acid and starch type. Carbohydr Polym 41:191–195
Singh J, Dartois A, Kaur L (2010) Starch digestibility in food matrix: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 21:168–180
Sun Q, Gong M, Li Y, Xiong L (2014) Effect of dry heat treatment on the physicochemical properties and structure of proso millet flour and starch. Carbohydr Polym 110:128–134
Tester RF, Morrison WR (1990) Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. I. Effects of amylopectin, amylose, and lipids. Cereal Chem 67:551–557
Tiwari S, Chakkaravarthi A, Bhattacharya S (2015) Imaging and image analysis of freeze-dried cellular solids of gellan and agar gels. J Food Eng 165:60–65
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi for providing the Senior Research Fellowship to P. Nagaprabha to conduct the Ph.D. programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaprabha, P., Devisetti, R. & Bhattacharya, S. Physicochemical and microstructural characterisation of green gram and foxtail millet starch gels. J Food Sci Technol 55, 782–791 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2991-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2991-z