Abstract
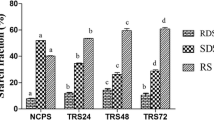
The most widely employed methodologies for type III (retrograded) resistant starch formation is a cyclic heating-cooling treatment or its combination with a previous enzymatic debranching step. In this work, two retrogradation temperatures, 0 and 4 °C, were evaluated for obtaining type III resistant starch from non-debranched and pullulanase-debranched wheat starch. The starches were characterized by their thermal and pasting behavior. Also, microstructural and crystalline aspects were related to the production process and the nutritional properties of the products. The most influencing factor for resistant starch formation was the application of the pullulanase-debranching step previous to the cyclic treatment. This led to a higher starch retrogradation and a more compact microstructure, which decreased the thickening capacity and the digestibility of the starches. Then, even though all the obtained starches exhibited lower digestibility, the pullulanase-debranched ones presented the lowest estimated glycemic index (ca. 34%), showing the highest yield of resistant starch formation. Finally, this work presents a concise protocol for obtaining type III resistant starch enriched powder with low digestibility that could be used in the formulation of different healthy foods such as dairy products, cereal bars, and even drinks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC International. (2009). Method 76-21.01 - general pasting method for wheat or rye flour of starch using the rapid visco analyser. In AACC international approved methods (pp. 7–10). AACC International. https://doi.org/10.1094/AACCIntMethod-76-21.01.
Arp, C. G., Correa, M. J., & Ferrero, C. (2018). High-amylose resistant starch as a functional ingredient in breads: a technological and microstructural approach. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 11(12), 2182–2193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-018-2168-4.
Ashwar, B. A., Gani, A., Shah, A., Wani, I. A., & Masoodi, F. A. (2016). Preparation, health benefits and applications of resistant starch - a review. Starch/Staerke, 68(3–4), 287–301. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201500064.
Bello-Perez, L. A., & Hoyos-Leyva, J. D. (2018). Development of foods high in slowly digestible and resistant starch. In M. Sjöö & L. Nilsson (Eds.), Starch in food (2nd ed., pp. 827–854). Cambridge: Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100868-3.00022-6.
Bertoft, E. (2013). On the building block and backbone concepts of amylopectin structure. Cereal Chemistry, 90(4), 294–311. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-01-13-0004-FI.
Brumovsky, L. A., Brumovsky, J. O., Fretes, M. R., & Peralta, J. M. (2009). Quantification of resistant starch in several starch sources treated thermally. International Journal of Food Properties, 12(3), 451–460. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942910701867673.
Cai, L., & Shi, Y. C. (2014). Preparation, structure, and digestibility of crystalline A- and B-type aggregates from debranched waxy starches. Carbohydrate Polymers, 105(1), 341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.075.
Champ, M. (2004). Resistant starch. In A.-C. Eliasson (Ed.), Starch in food (Vol. 38, 1st ed., pp. 560–574). Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Limited. https://doi.org/10.1533/9781855739093.4.560.
Chang, R., Tian, Y., Lu, H., Sun, C., & Jin, Z. (2020). Effects of fractionation and heat-moisture treatment on structural changes and digestibility of debranched waxy maize starch. Food Hydrocolloids, 101(October 2019), 105488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105488.
Chávez-Murillo, C. E., Veyna-Torres, J. I., Cavazos-Tamez, L. M., de la Rosa-Millán, J., & Serna-Saldívar, S. O. (2018). Physicochemical characteristics, ATR-FTIR molecular interactions and in vitro starch and protein digestion of thermally-treated whole pulse flours. Food Research International, 105(December 2016), 371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2017.11.029.
Cordoba, L. d. P., da Silva, R. G., Gomes, D. d. S., Schnitzler, E., & Waszczynskyj, N. (2018). Brazilian green banana - a thermal, structural and rheological investigation of resistant starch from different cultivars. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 134(3), 2065–2073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7374-9.
Dong, H., & Vasanthan, T. (2020). Amylase resistance of corn, faba bean, and field pea starches as influenced by three different phosphorylation (cross-linking) techniques. Food Hydrocolloids, 101(November 2019), 105506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105506.
Dundar, A. N., & Gocmen, D. (2013). Effects of autoclaving temperature and storing time on resistant starch formation and its functional and physicochemical properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 97(2), 764–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.083.
Gelders, G. G., Duyck, J. P., Goesaert, H., & Delcour, J. A. (2005). Enzyme and acid resistance of amylose-lipid complexes differing in amylose chain length, lipid and complexation temperature. Carbohydrate Polymers, 60(3), 379–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.02.008.
Gelencsér, T., Juhász, R., Hódsági, M., Gergely, S., & Salgó, A. (2008). Comparative study of native and resistant starches. Acta Alimentaria, 37(2), 255–270. https://doi.org/10.1556/AAlim.37.2008.2.11.
Goñi, I., Garcia-Alonso, A., & Saura-Calixto, F. (1997). A starch hydrolysis procedure to estimate glycemic index. Nutrition Research, 17(3), 427–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0271-5317(97)00010-9.
Gopalsamy, G., Mortimer, E., Greenfield, P., Bird, A. R., Young, G. P., & Christophersen, C. T. (2019). Resistant starch is actively fermented by infant faecal microbiota and increases microbial diversity. Nutrients, 11(6), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11061345.
Hódsági, M., Gelencsér, T., Gergely, S., & Salgó, A. (2012). In vitro digestibility of native and resistant starches: correlation to the change of its rheological properties. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(3), 1038–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0391-8.
Hoover, R. (1995). Starch retrogradation. Food Reviews International, 11(2), 331–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/87559129509541044.
Jiang, F., Du, C., Jiang, W., Wang, L., & Du, S. (2020). The preparation, formation, fermentability, and applications of resistant starch. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 150, 1155–1161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.124.
Khan, A., Rahman, U. U., Siddiqui, S., Irfan, M., Shah, A. A., Badshah, M., Hasan, F., & Khan, S. (2019). Preparation and characterization of resistant starch type III from enzymatically hydrolyzed maize flour. Molecular Biology Reports, 46(4), 4565–4580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04913-5.
Kovrlija, R., & Rondeau-Mouro, C. (2017). Hydrothermal changes of starch monitored by combined NMR and DSC methods. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 10(3), 445–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1832-9.
Li, T., Chen, L., Xiao, J., An, F., Wan, C., & Song, H. (2018). Prebiotic effects of resistant starch from purple yam (Dioscorea alata L.) on the tolerance and proliferation ability of Bifidobacterium adolescentis in vitro. Food & Function, 9(4), 2416–2425. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7FO01919J.
Liu, H., Liang, R., Antoniou, J., Liu, F., Shoemaker, C. F., Li, Y., & Zhong, F. (2014). The effect of high moisture heat-acid treatment on the structure and digestion property of normal maize starch. Food Chemistry, 159, 222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.162.
Liu, G., Gu, Z., Hong, Y., Cheng, L., & Li, C. (2017). Structure, functionality and applications of debranched starch: a review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 63, 70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.03.004.
Montonen, J., Knekt, P., Järvinen, R., Aromaa, A., & Reunanen, A. (2003). Whole-grain and fiber intake and the incidence of type 2 diabetes. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 77(3), 622–629. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/77.3.622.
Okumus, B. N., Tacer-Caba, Z., Kahraman, K., & Nilufer-Erdil, D. (2018). Resistant starch type V formation in brown lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) starch with different lipids/fatty acids. Food Chemistry, 240(April 2017), 550–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.157.
Öztürk, S., & Köksel, H. (2014). Production and characterisation of resistant starch and its utilisation as food ingredient: a review. Quality Assurance & Safety of Crops and Food, 6(3), 335–346. https://doi.org/10.3920/QAS2013.0367.
Planchot, V., Colonna, P., & Buleon, A. (1997). Enzymatic hydrolysis of α-glucan crystallites. Carbohydrate Research, 298(4), 319–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(96)00317-5.
Polesi, L. F., & Sarmento, S. B. S. (2011). Structural and physicochemical characterization of RS prepared using hydrolysis and heat treatments of chickpea starch. Starch - Stärke, 63(4), 226–235. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201000114.
Pratiwi, W. S. W., Anal, A. K., & Putra, S. R. (2015). Production by lintnerization-autoclaving and physicochemical characterization of resistant starch III from sago palm (Metroxylon sagu Rottb). Indonesian Journal of Chemistry, 15(3), 295–304. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.21199.
Pratiwi, M., Faridah, D. N., & Lioe, H. N. (2018). Structural changes to starch after acid hydrolysis, debranching, autoclaving-cooling cycles, and heat moisture treatment (HMT): a review. Starch - Stärke, 70(1–2), 1700028. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201700028.
Remya, R., Jyothi, A. N., & Sreekumar, J. (2018). Effect of chemical modification with citric acid on the physicochemical properties and resistant starch formation in different starches. Carbohydrate Polymers, 202(August), 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.128.
Román, L., Dura, Á., Martínez, M. M., Rosell, C. M., & Gómez, M. (2016). Combination of extrusion and cyclodextrin glucanotransferase treatment to modify wheat flours functionality. Food Chemistry, 199, 287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.12.040.
Shi, J., Sweedman, M. C., & Shi, Y.-C. (2018). Structural changes and digestibility of waxy maize starch debranched by different levels of pullulanase. Carbohydrate Polymers, 194(January), 350–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.053.
Silverio, J., Fredriksson, H., Andersson, R., Eliasson, A.-C., & Åman, P. (2000). The effect of temperature cycling on the amylopectin retrogradation of starches with different amylopectin unit-chain length distribution. Carbohydrate Polymers, 42(2), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(99)00140-X.
Surendra Babu, A., & Parimalavalli, R. (2018). Effect of pullulanase debranching and storage temperatures on structural characteristics and digestibility of sweet potato starch. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 17(2), 208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2016.04.005.
Vamadevan, V., & Bertoft, E. (2014). Structure-function relationships of starch components. Starch - Stärke, 66(1-2), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201400188.
Vamadevan, V., & Bertoft, E. (2018). Impact of different structural types of amylopectin on retrogradation. Food Hydrocolloids, 80, 88–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.01.029.
Van Hung, P., Lan Phi, N. T., & Vy Vy, T. T. (2012). Effect of debranching and storage condition on crystallinity and functional properties of cassava and potato starches. Starch - Stärke, 64(12), 964–971. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201200039.
Van Hung, P., Binh, V. T., Nhi, P. H. Y., & Phi, N. T. L. (2020). Effect of heat-moisture treatment of unpolished red rice on its starch properties and in vitro and in vivo digestibility. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 154, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.071.
Wandee, Y., Puttanlek, C., Rungsardthong, V., Puncha-arnon, S., & Uttapap, D. (2012). Effects of gelatinization and gel storage conditions on the formation of canna resistant starch. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 5(7), 2665–2673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-011-0629-0.
Willett, W., Manson, J., & Liu, S. (2002). Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of type 2 diabetes. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 76(1), 274S–280S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/76.1.274S.
Williamson, G., Belshaw, N. J., Self, D. J., Noel, T. R., Ring, S. G., Cairns, P., et al. (1992). Hydrolysis of A- and B-type crystalline polymorphs of starch by α-amylase, β-amylase and glucoamylase 1. Carbohydrate Polymers, 18(3), 179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-8617(92)90062-U.
Wong, T. H. T., & Louie, J. C. Y. (2017). The relationship between resistant starch and glycemic control: a review on current evidence and possible mechanisms. Starch - Stärke, 69(7–8), 1600205. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201600205.
Wongprayoon, S., Tran, T., Gibert, O., Dubreucq, E., Piyachomkwan, K., & Sriroth, K. (2018). Pullulanase debranching of various starches upgrades the crystalline structure and thermostability of starch-lauric acid complexes. Starch/Staerke, 70(7-8), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201700351.
Yadav, B. S., Sharma, A., & Yadav, R. B. (2010). Effect of storage on resistant starch content and in vitro starch digestibility of some pressure-cooked cereals and legumes commonly used in India. International Journal of Food Science and Technology, 45(12), 2449–2455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2010.02214.x.
Yu, Z., Wang, Y. S., Chen, H. H., Li, Q. Q., & Wang, Q. (2018). The gelatinization and retrogradation properties of wheat starch with the addition of stearic acid and sodium alginate. Food Hydrocolloids, 81, 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.02.041.
Zhang, H., & Jin, Z. (2011). Preparation of resistant starch by hydrolysis of maize starch with pullulanase. Carbohydrate Polymers, 83(2), 865–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.066.
Zhao, X., Andersson, M., & Andersson, R. (2018). Resistant starch and other dietary fiber components in tubers from a high-amylose potato. Food Chemistry, 251(September 2017), 58–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.028.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Javier Lecot and Verónica Ferraresi-Curotto for their kind collaboration in the DSC and X-ray diffraction assays, respectively.
Funding
The authors received financial support from Universidad Nacional de La Plata (UNLP, project X661 and project X771), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT, PICT 2014-3421, PICT 2015-0007 and PICT 2016-3047), and Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Arp, C. G.: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, visualization; Correa, M. J.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition; Ferrero, C.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arp, C.G., Correa, M.J. & Ferrero, C. Production and Characterization of Type III Resistant Starch from Native Wheat Starch Using Thermal and Enzymatic Modifications. Food Bioprocess Technol 13, 1181–1192 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02470-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02470-5