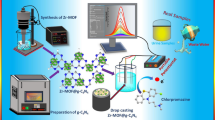
Abstract
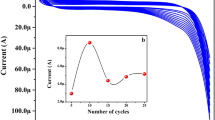
In this work, an accurate, high sensitive and economy electrochemical sensor based on a carbon paste electrode provided by copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NP/CPE) was constructed. CuO-NP were obtained from the recycling of copper waste wires and analyzed using SEM and XRD measurements. The handmade electrode was used in actual pharmaceutical formulations for the determination of theophylline (TP). Using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) methods, the output accuracy of the sensor against TP was explored. Different experimental conditions have been studied, such as different supporting electrolytes, pH, and scan rate. The results showed that while only one peak of oxidation was observed at 1.16 V, no reduction peaks were observed. The improved CuO-NP/CPE sensor showed supreme analytical rendering towards TP, with an anodic peak current rising by 4 μA compared to the unimproved CPE. The peak of oxidation current was linearly proportional to the concentration of TP from 4.0 to 70.0 nM, and the detection limit was determined to be 1.2 nM, which, relative to previous research using the same technology, was considered the lowest value ever. In addition, handmade CuO-NP/CPE showed high selectivity, stability, and good reproducibility in the presence of any interference. Therefore, it has been successfully used in actual pharmaceutical samples to assess TP. The data showed that the adjusted sensor significantly improved the detection of TP as well as accelerated the process of charge transfer on its surface with efficient reusability for eight successive measurements at 4 × 10−4 M of TP.
Graphic Abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Spina, C.P. Page, Xanthines and phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. Asthma COPD 63–91 (2016)
H.R. Ha, J. Chen, A.U. Freiburghaus, F. Follath, Metabolism of theophylline by cDNA-expressed human cytochromes P-450. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 39(3), 321–326 (1995)
H. Sereshti, M. Khosraviani, S. Samadia, M.S. Amini-Fazl, Simultaneous determination of theophylline, theobromine and caffeine in different tea beverages by graphene-oxide based ultrasonic-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction combined with HPLC-UV. RSC Adv. 4(87), 47114–47120 (2014)
M. Charehsaz, A. Gürbay, A. Aydin, G. Şahin, Simple, fast and reliable liquid chromatographic and spectrophotometric methods for the determination of theophylline in urine, saliva and plasma samples. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 13(2), 431–439 (2014)
Y. Liu, W. Shen, J. Shen, Z. Song, Y. Xia, Determination of theophylline and doxofylline in human plasma by HPLC. Chinese J Pharmaceut 2, 25 (2010)
Y. Wang, K. Zheng, Content determination of theophylline in aminophylline injection by HPLC. China Med. Herald 19, (2010)
M.S. Bispo, M.C. Veloso, H.L. Pinheiro, R.F.S. De Oliveira, J.O.N. Reis, J.B. De Andrade, Simultaneous determination of caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 40(1), 45–48 (2002)
C. Oellig, J. Schunck, W. Schwack, Determination of caffeine, theobromine and theophylline in Mate beer and Mate soft drinks by high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1533, 208–212 (2018)
K. Ma, H. Wang, M. Zhao, J. Xing, Purity determination and uncertainty evaluation of theophylline by mass balance method, high performance liquid chromatography and differential scanning calorimetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 650(2), 227–233 (2009)
A.G. Mwalupindi, I.M. Warner, Determination of theophylline by liquid chromatography with sensitized lanthanide luminescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 306(1), 49–56 (1995)
F. Susanto, S. Humfeld, C.M. Niederau, H. Reinauer, A method for the determination of theophylline in serum by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 344(12), 549–553 (1992)
M.J. Culzoni, M.M. De Zan, J.C. Robles, V.E. Mantovani, H.C. Goicoechea, Chemometrics-assisted UV-spectroscopic strategies for the determination of theophylline in syrups. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 39(5), 1068–1074 (2005)
A.M. Amado, M.M. Nolasco, P.J. Ribeiro-Claro, Probing pseudopolymorphic transitions in pharmaceutical solids using Raman spectroscopy: hydration and dehydration of theophylline. J. Pharm. Sci. 96(5), 1366–1379 (2007)
T. Gan, A. Zhao, Z. Wang, P. Liu, J. Sun, Y. Liu, An electrochemical sensor based on SiO2@ TiO2-embedded molecularly imprinted polymers for selective and sensitive determination of theophylline. J. Solid State Electrochem. 21(12), 3683–3691 (2017)
J.C. Kilele, R. Chokkareddy, N. Rono, G.G. Redhi, A novel electrochemical sensor for selective determination of theophylline in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 111, 228–238 (2020)
S.A. Rezvani, A. Soleymanpour, Application of a sensitive electrochemical sensor modified with WO3 nanoparticles for the trace determination of theophylline. Microchem. J. 149, 104005 (2019)
X. Kan, T. Liu, H. Zhou, C. Li, B. Fang, Molecular imprinting polymer electrosensor based on gold nanoparticles for theophylline recognition and determination. Microchim. Acta 171(3–4), 423–429 (2010)
Y.J. Yang, W. Li, High sensitive determination of theophylline based on manganese oxide nanoparticles/multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite modified electrode. Ionics 21(4), 1121–1128 (2015)
M. Hamidi, K. Zarei, Electrochemical determination of theophylline on a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide-sodium dodecyl sulfate-Nafion composite film. Russ. Chem. Bull. 69(11), 2107–2112 (2020)
Z. Zhang, X. Zhao, J. Liu, J. Yin, X. Cao, Highly sensitive sandwich electrochemical sensor based on DNA-scaffolded bivalent split aptamer signal probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 311, 127920 (2020)
A.A. Janaj, N.P. Shetti, S.J. Malode, S.D. Bukkitgar, R.M. Kulkarni, TiO2 nanoparticles modified sensor for theophylline drug. Mater. Today Proc. 18, 606–612 (2019)
G.T. Gnahore, T. Velasco-Torrijos, J. Colleran, The selective electrochemical detection of dopamine using a sulfated β-cyclodextrin carbon paste electrode. Electrocatalysis 8(5), 459–471 (2017)
T. Tamiji, A. Nezamzadeh, Electrocatalytic determination of Hg (II) by the modified carbon paste electrode with Sn (IV)-clinoptilolite nanoparticles. Electrocatalysis 10(5), 466–476 (2019)
O.C. Ozoemena, L.J. Shai, T. Maphumulo, K.I. Ozoemena, Electrochemical sensing of dopamine using onion-like carbons and their carbon nanofiber composites. Electrocatalysis 10(4), 381–391 (2019)
H.F. Assaf, H. Salah, N. Hashem, M. Khodari, A. Toghan, Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on copper waste wire recycling and its application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 331, 112962 (2021)
B. Zargar, H. Parham, A. Hatamie, Electrochemical investigation and stripping voltammetric determination of captopril at CuO nanoparticles/multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite electrode in tablet and urine samples. Anal. Methods 7(3), 1026–1035 (2015)
H. Karimi-Maleh, M. Sheikhshoaie, I. Sheikhshoaie, M. Ranjbar, J. Alizadeh, N.W. Maxakato, A. Abbaspourrad, A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and an-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode. New J. Chem. 43(5), 2362–2367 (2019)
R.A. Al-Haidari, N.A. Abdallah, M.M. Al-Oqail, E.S. Al-Sheddi, S.M. Al-Massarani, N.N. Farshori, Nanoparticles based solid contact potentiometric sensor for the determination of theophylline in different types of tea extract. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 119, 108080 (2020)
K.S. Siddegowda, B. Mahesh, Fabrication of copper oxide nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode and its application in simultaneous electroanalysis of guanine, adenine and thymine. Sens. Actuators, A 280, 277–286 (2018)
I. Chiarottoo, L. Mattiello, F. Pandolfi, D. Rocco, M. Feroci, R. Petrucc, Electrochemical oxidation of theophylline in organic solvents: HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS analysis of the oxidation products. ChemElectroChem 6, 4511–4521 (2019)
E.A. Zeid, A.M. Nassar, M.A. Hussein, M.M. Alam, A.M. Asiri, H.H. Hegazy, M.M. Rahman, Mixed oxides CuO-NiO fabricated for selective detection of 2-Aminophenol by electrochemical approach. J. Market. Res. 9(2), 1457–1467 (2020)
A.M. Nassar, A.M. Elseman, I.H. Alsohaimi, N.F. Alotaibi, A. Khan, Diaqua oxalato strontium (II) complex as a precursor for facile fabrication of Ag-NPs@ SrCO3, characterization, optical properties, morphological studies and adsorption efficiency. J. Coord. Chem. 72(5–7), 771–785 (2019)
S.J. Malode, N.P. Shetti, S.T. Nandibewoor, Voltammetric behavior of theophylline and its determination at multi-wall carbon nanotube paste electrode. Colloids Surf. B 97, 1–6 (2012)
Y. Li, S. Wu, P. Luo, J. Liu, G. Song, K. Zhang, B. Ye, Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of theophylline at a glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene/nafion. Anal. Sci. 28(5), 497–502 (2012)
J.M. Zen, T.Y. Yu, Y. Shih, Determination of theophylline in tea and drug formulation using a Nafion/lead–ruthenium oxide pyrochlore chemically modified electrode. Talanta 50(3), 635–640 (1999)
N. Spãtaru, B.V. Sarada, D.A. Tryk, A. Fujishima, Anodic voltammetry of xanthine, theophylline, theobromine and caffeine at conductive diamond electrodes and its analytical application. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted to Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 14(11), 721–728 (2002)
R.N. Hegde, R.R. Hosamani, S.T. Nandibewoor, Electrochemical oxidation and determination of theophylline at a carbon paste electrode using cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide as enhancing agent. Anal. Lett. 42(16), 2665–2682 (2009)
E.M. Rabie, H.F. Assaf, A.A. Shamrouk, M. Khodari, Fabrication of a new electrochemical sensor based on carbon paste electrode modified by silica gel/ MWCNTs for the voltammetric determination of salicylic acid in tomato. Egypt. J.f Chem. 62, 165–175 (2019)
A.A. Abdelwahab, A.M. Elseman, N.F. Alotaibi, A.M. Nassar, Simultaneous voltammetric determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, acetaminophen and tryptophan based on hybrid trimetallic nanoparticles-capped electropretreated graphene. Microchem. J. 156, 104927 (2020)
M. Amare, S. Admassie, Differential pulse voltammetric determination of theophylline at poly (4-amino-3-hydroxyl naphthalene sulfonic acid) modified glassy carbon electrode. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 26(1), 73–84 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassar, A.M., Salah, H., Hashem, N. et al. Electrochemical Sensor Based on CuO Nanoparticles Fabricated From Copper Wire Recycling-loaded Carbon Paste Electrode for Excellent Detection of Theophylline in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Electrocatalysis 13, 154–164 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00698-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-021-00698-z