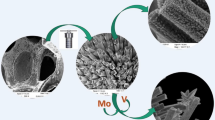
Abstract
The rapid fabrication is described of binary electrocatalyst based on a highly porous metal–organic framework with zirconium metal core (Zr-MOF) decorated over the graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets via facile ultrasonication method. It is used for the robust determination of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine (CLP) from environmental samples. The electrochemical behaviour of 2D Zr-MOF@g-C3N4 was characterized by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) studies. The crystalline and porous nature of the composite was characterized by XRD and SEM analysis. The functional groups and surface characteristics were investigated by FT-IR, Raman and XPS. The major electrochemical properties of the Zr-MOF@g-C3N4 composite towards CLP detection were analyzed by CV, chronocoulometric (CC), chronoamperometric (CA) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) techniques. The composite exhibits a low detection limit (LOD) of 2.45 nM with a linear range of 0.02 to 2.99 µM and attractive sensitivity for CLP. The sensor system shows higher selectivity towards the possible interferences of CLP drug and exhibits better repeatability and stability. Finally, the fabricated sensor system shows a high recovery range varying from 96.2 to 98.9% towards the real samples. The proposed electrochemical probe might be a promising alternative to the prevailing diagnostic tools for the detection of CLP.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd-Kimball D, Gonczy K, Lewis B et al (2019) Classics in chemical neuroscience: chlorpromazine. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00258
Guo S, Cosky E, Li F et al (2021) An inhibitory and beneficial effect of chlorpromazine and promethazine (C + P) on hyperglycolysis through HIF-1α regulation in ischemic stroke. Brain Res 1763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147463
Xu F, Xi H, Liao M et al (2022) Repurposed antipsychotic chlorpromazine inhibits colorectal cancer and pulmonary metastasis by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 89:331–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-021-04386-z
Caponi S (2021) On the so-called psychopharmacological revolution: the discovery of chlorpromazine and the management of madness. Hist Cienc Saude Manguinhos 28:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-59702021000300003
Kesavan G, Gopi PK, Chen SM, Vinothkumar V (2021) Iron vanadate nanoparticles supported on boron nitride nanocomposite: electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. J Electroanal Chem 882:114982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.114982
Dai J, Lin H, Pan Y et al (2023) Determination of chlorpromazine and its metabolites in animal-derived foods using QuEChERS-based extraction, EMR-Lipid cleanup, and UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS analysis. Food Chem 403:134298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134298
Song M, Li C, Wu S, Duan N (2023) Screening of specific aptamers against chlorpromazine and construction of novel ratiometric fluorescent aptasensor based on metal-organic framework. Talanta 252:123850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123850
Riman D, Rozsypal J, Halouzka V et al (2020) The use of micro carbon pencil lead electrode for sensitive HPLC-ED analysis of selected antipsychotic drugs. Microchem J 154:104606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.104606
Nishimura K, Okamura N, Kimachi T, Haginaka J (2019) Evaluation of molecularly imprinted polymers for chlorpromazine and bromopromazine prepared by multi-step swelling and polymerization method—the application for the determination of chlorpromazine and its metabolites in rat plasma by column-switching LC. J Pharm Biomed Anal 174:248–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.05.063
Passos LCM, Saraiva MLMFS (2019) Detection in UV-visible spectrophotometry: detectors, detection systems, and detection strategies. Measurement 135:896–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.12.045
Rajaji U, Chinnapaiyan S, Chen SM, Govindasamy M, Oliveira Filho JID, Khushaim W, Mani V (2021) Design and fabrication of yttrium ferrite garnet-embedded graphitic carbon nitride: a sensitive electrocatalyst for smartphone-enabled point-of-care pesticide (mesotrione) analysis in food samples. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:24865–24876. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c04597
Govindasamy M, Chen SM, Mani V et al (2016) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and uric acid in the presence of high ascorbic acid concentration using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide–polyaniline/activated charcoal composite. RSC advances 6:100605–13. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA18740D
Qian L, Durairaj S, Prins S, Chen A (2021) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the detection of pharmaceutical compounds. Biosens Bioelectron 175:112836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112836
Rajaji U, Chen TW, Chinnapaiyan S, Chen SM et al (2020) Two-dimensional binary nanosheets (Bi2Te3@g-C3N4): application toward the electrochemical detection of food toxic chemical. Anal Chim Acta 1125:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.05.033
Du X, Zhang Z, Zheng X et al (2020) An electrochemical biosensor for the detection of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Commun 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14037-w
Li R, Qi H, Ma Y et al (2020) A flexible and physically transient electrochemical sensor for real-time wireless nitric oxide monitoring. Nat Commun 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-17008-8
Daniel M, Mathew G, Anpo M, Neppolian B (2022) MOF based electrochemical sensors for the detection of physiologically relevant biomolecules: an overview. Coord Chem Rev 468:214627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214627
Rong S, Zou L, Meng L et al (2022) Dual function metal-organic frameworks based ratiometric electrochemical sensor for detection of doxorubicin. Anal Chim Acta 1196:339545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339545
Tajik S, Beitollahi H, Garkani Nejad F et al (2021) Performance of metal-organic frameworks in the electrochemical sensing of environmental pollutants. J Mater Chem A 9:8195–8220. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta08344e
Gao L, Gao E (2021) Metal-organic frameworks for electrochemical sensors of neurotransmitters. Coord Chem Rev 434:213784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2021.213784
Deng D, Wang Y, Wen S et al (2023) Metal-organic framework composite Mn/Fe-MOF@Pd with peroxidase-like activities for sensitive colorimetric detection of hydroquinone. Anal Chim Acta 1279:341797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341797
Wang X, Zhang Y, Shi Z et al (2021) Multifunctional Zr-MOF based on bisimidazole tetracarboxylic acid for pH sensing and photoreduction of Cr(VI). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c18130
Jia C, He T, Wang G (2023) Zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks for fluorescent sensing. Coord Chem Rev 476:214930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214930
Zhou T, Liang Q, Zhou X, et al (2021) Enhanced removal of toxic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by magnetic Zr-MOF @ polypyrrole : performance and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut Res 13084–13096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12341-x
Thomas A, Fischer A, Goettmann F et al (2008) Graphitic carbon nitride materials: variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts. J Mater Chem 18:4893–4908. https://doi.org/10.1039/b800274f
Liu SG, Han L, Li N et al (2019) A ratiometric fluorescent strategy for alkaline phosphatase activity assay based on g-C3N4/CoOOH nanohybrid via target-triggered competitive redox reaction. Sens Actuators B Chem 283:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.052
Gu W, Hu L, Li J, Wang E (2016) Hybrid of g-C3N4 assisted metal-organic frameworks and their derived high-efficiency oxygen reduction electrocatalyst in the whole pH range. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:35281–35288. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12031
Singh AK, Jaiswal N, Gautam RK, Tiwari I (2021) Development of g-C3N4/Cu-DTO MOF nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor towards sensitive determination of an endocrine disruptor BPSIP. J Electroanal Chem 887:115170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115170
Pandiaraj S, Aiyappa HB, Banerjee R, Kurungot S (2014) Post modification of mof derived carbon via g-c3n4 entrapment for an efficient metal-free oxygen reduction reaction. Chem Commun 50:3363–3366. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc47620k
Wang Y, Guo L, Zeng Y et al (2019) Amino-assisted NH2-UiO-66 anchored on porous g-C3N4 for enhanced visible-light-driven CO2 reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:30673–30681. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b04302
Ge L (2011) Synthesis and photocatalytic performance of novel metal-free g-C 3N4 photocatalysts. Mater Lett 65:2652–2654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.05.069
Fang X, Chen X, Liu Y et al (2019) Nanocomposites of Zr ( IV )-based metal−organic frameworks and reduced graphene oxide for electrochemically sensing cipro fl oxacin in Water. 2–11. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00243
Yu J, Li X, Wu Q et al (2021) Effective low-temperature methanol aqueous phase reforming with metal-free carbon dots/C3N4 composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c03140
Chang C, Xue Q, Wang R et al (2023) Development of a novel sensor based on Bi2O3 and carbonized UIO-66-NH2 nanocomposite for efficient detection of Pb(II) ion in water environment. Appl Surf Sci 616:156510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156510
Das I, Noori MT, Shaikh M et al (2020) Synthesis and application of zirconium metal-organic framework in microbial fuel cells as a cost-effective oxygen reduction catalyst with competitive performance. ACS Appl Energy Mater 3:3512–3520. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.0c00054
Fang X, Wu S, Wu Y, et al (2020) High-efficiency adsorption of norfloxacin using octahedral UIO-66-NH2 nanomaterials: dynamics, thermodynamics, and mechanisms. Appl Surf Sci 518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146226
Fan J, Ning P, Song Z et al (2018) Mechanistic aspects of NH3-SCR reaction over CeO2/TiO2-ZrO2-SO42−catalyst: in situ DRIFTS investigation. Chem Eng J 334:855–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.011
Lu J, Li R, Cui Y et al (2023) Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of zirconium nitride nanofibers by electrospinning combined with carbon thermal reduction nitriding method. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 34:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11004-6
Yang Y, Zhao Y, Hu H et al (2023) Synthesis and characterization of g-C3N4@ZrO2 composites through calcination method for enhanced photocatalytic activities. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 34:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10422-w
Subramanian N, Priya KM, Valappil MO et al (2019) Electrochemically exfoliated porous WS 2 nanosheets: a potential electrochemical sensing platform for chlorpromazine detection. J Electrochem Soc 166:B749–B755. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1301908jes
Rajaji U, Selvi SV, Chen SM et al (2020) A nanocomposite consisting of cuprous oxide supported on graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine. Microchim Acta 187:459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04416-2
Randles JEB (1948) A cathode ray polarograph.The current-voltage curves. Trans Faraday Soc 44:327–338
Sabatani E, Rubinstein I, Maoz R, Sagiv J (1987) Organized self-assembling monolayers on electrodes. Part I. Octadecyl derivatives on gold. J Electroanal Chem 219:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(87)85054-4
Anson FC (1966) Innovations in the study of adsorbed reactants by chronocoulometry. Anal Chem 38:54–57. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60233a014
Gupta VK, Sadeghi R, Karimi F (2013) A novel electrochemical sensor based on ZnO nanoparticle and ionic liquid binder for square wave voltammetric determination of droxidopa in pharmaceutical and urine samples. Sens Actuators B Chem 186:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.06.048
Laviron E (1979) The use of linear potential sweep voltammetry and of a.c. voltammetry for the study of the surface electrochemical reaction of strongly adsorbed systems and of redox modified electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 100:263–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(79)80167-9
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2022) Electrochemical methods : fundamentals and applications. John Wiley & Sons Inc
Vinothkumar V, Sakthivel R, Chen SM et al (2021) Facile synthesis of alpha-phase strontium pyrophosphate incorporated with polypyrrole composite for the electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. J Alloy Compd 888:161537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161537
Kokulnathan T, Kumar JV, Chen SM et al (2018) One-step sonochemical synthesis of 1D β-stannous tungstate nanorods: an efficient and excellent electrocatalyst for the selective electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. Ultrason Sonochem 44:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.02.025
Koventhan C, Pandiyan R, Chen SM, Lo AY (2023) Nickel molybdate/cobalt molybdate nanoflakes by one-pot synthesis approach for electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine in biological and environmental samples. J Environ Chem Eng 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110121
Martinez-Rojas F, Espinosa-Bustos C, Ramirez G, Armijo F (2023) Electrochemical oxidation of chlorpromazine, characterisation of products by mass spectroscopy and determination in pharmaceutical samples. Electrochim Acta 443:141873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2023.141873
Sebastian N, Yu WC, Hu YC et al (2019) Sonochemical synthesis of iron-graphene oxide/honeycomb-like ZnO ternary nanohybrids for sensitive electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. Ultrason Sonochem 59:104696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.104696
Palanisamy S, Thirumalraj B, Chen SM et al (2016) A facile electrochemical preparation of reduced graphene oxide@polydopamine composite: a novel electrochemical sensing platform for amperometric detection of chlorpromazine. Sci Rep 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33599
Liu Y, Hu X, Xia Y et al (2022) A novel ratiometric electrochemical sensor based on dual-monomer molecularly imprinted polymer and Pt/Co3O4 for sensitive detection of chlorpromazine hydrochloride. Anal Chim Acta 1190:339245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339245
Kumar JV, Karthik R, Chen SM et al (2018) Highly selective electrochemical detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine in drug and human urine samples based on peas-like strontium molybdate as an electrocatalyst. Inorg Chem Front 5:643–655. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7qi00743d
Balamurugan K, Karthik R, Chen SM et al (2022) Heterostructures of mixed metal oxides (ZnMnO3/ZnO) synthesized by a wet-chemical approach and their application for the electrochemical detection of the drug chlorpromazine. Compos B Eng 236:109822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109822
Shanmugam R, Ganesamurthi J, Chen T et al (2022) Preparation and fabrication of porous-Fe 2 O 3 / carbon black nanocomposite : a portable electrochemical sensor for psychotropic drug detection in environmental samples. Mater Today Chem 25:100982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.100982
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project Number (RSP2023R429) at King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. This work was supported by the TEEP, Ministry of Education, National Taipei University of Technology and Ming Chi University of Technology, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ashkar, M.A., Kutti Rani, S., Vasimalai, N. et al. Design of sonochemical assisted synthesis of Zr-MOF/g-C3N4-modified electrode for ultrasensitive detection of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine from biological samples. Microchim Acta 191, 182 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06253-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06253-z