Abstract
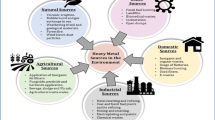
A study was conducted on 16 sites in four Ramsar designated wetlands soils regarding soil properties and pollution indices in the Sylhet basin of Bangladesh. The wetlands sites’ soil quality remained favorable for agricultural sustainability. Arsenic and cadmium contents were found at minimum detection levels. Rubidium and zirconium were found below critical levels. Pollution indices revealed that zinc and titanium content is slightly higher than the other elements. It was observed that Fe, Ti, Zr, and Mn originate from natural sources or sediments. In contrast, Zn and Cu originate from the artificial fertilizer sources used in and around agricultural lands of the wetland bodies. Moreover, the wetlands are used only for Boro rice crop, and for most of the year, they remain fallow. As a result, grazing activities are predominant. It is assumed that Cu and Zn are often used as additives for animal feed and enter animal wastes through incomplete absorption, and thus, the application of animal wastes in agriculture causes pollution with Zn and Cu. Pollution load index revealed that 42% of the study sites were polluted and 58% remained unpolluted. Principal component analysis and enrichment factors show that anthropogenic activities are responsible for the current pollution, where Zn and Cu predominate. The wetland sites are being polluted at a minor level. The main reasons for the higher level of metal pollution in Balai wetland might be its geomorphic nature and even anthropogenic activities. This wetland is located at the junction point of the Surma-Kushiyara River in Bangladesh, where an international river, Barak, intersects there, which originated from the upper territory. It is urgent to formulate an integrated action plan to prevent the source points of pollution.


(This map was adopted from Worm et al. (1998) showing the Dupi Tila (youngest deposits of the Tertiary) deposits)







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
It can be delivered upon the corresponding reviewers’ request.
References
Atieh MA, Ji Y, Kochkodan V (2017) Metals in the environment: toxic metals removal. Bioinorg Chem Appl. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4309198
Barbieri M (2016) The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J Geol Geophys 5(1):1000237. https://doi.org/10.4172/2381-8719.1000237
BARC (2018) Fertilizer recommendation guide. Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council, Dhaka, p 274
Bartolomeo DA, Poletti L, Sanchini G, Sebastiani B, Morozzi G (2004) Relationship among parameters of lake polluted sediments evaluated by multivariate statistical analysis. Chemosphere 55(10):1323e1329
Bhuiyan MAH, Parvez L, Islam MA, Dampare SB, Suzuki S (2010) Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 173(1–3):384–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.085
Black CA (1965) Methods of soil analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS (1982) Total nitrogen. In: Page AL, RH Miller, DR Keeney (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, USA. pp 595–622. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c31
Cassidy ES, West PC, Gerber JS, Foley JA (2013) Redefining agricultural yields: from tonnes to people nourished per hectare. Environ Res Lett 8:034015. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/3/034015
Donahue RL, Miller RW, Shickluna JC (1977) An introduction to soils and plant growth. Prentice hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs, p 626
Drobner U, Tyler G (1998) Conditions controlling relative uptake of potassium and rubidium by plants from soils. Plant Soil 201(2):285–293. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004319803952
Fan TT, Wang YJ, Li CB, He JZ, Gao J, Zhou DM, Friedman SP, Sparks DL (2016) Effect of organic matter on sorption of Zn on soil: elucidation by Wien effect measurements and EXAFS spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol 50(6):2931–2937. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05281
FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP, WHO (2018) The state of food security and nutrition in the world. Building climate resilience for food security and nutrition. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Ferligoj A, Batagelj V (1982) Clustering with relational constraint. Psychometrika 47(4):413–426
Greany KM (2005) An assessment of heavy metal contamination in the marine sediments of Las Perlas Archipelago, Gulf of Panama. Thesis: Master of Science Department of Life Sciences Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland. http://www.sciepub.com/reference/29645
Gupta N, Yadav KK, Kumar V, Krishnan S, Kumar S, Nejad ZD, Khan MAM, Alam J (2021) Evaluating heavy metals contamination in soil and vegetables in the region of North India: levels, transfer and potential human health risk analysis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 82:103563
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hossain MF, Kamal ASM, Eva MA, Ahmed SM, Parveen Z (2020) Soil organic carbon pool and its storage in Arial Beel wetland soils of Bangladesh. Am J Environ Sci 16(3):55–67. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2020.55.67
Hu J, Lin B, Yuan M, Lao Z, Wu K, Zeng Y, Liang Z, Li H, Li Y, Zhu D, Liu J, Fan H (2018) Trace metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in agricultural soil in Dexing Pb/Zn mining area China. Environ Geochem Health 41(2):967–980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0193-x
Huizing HGJ (1971) A reconnaissance study of the mineralogy of sand fractions from East Pakistan sediments and soils. Geoderma 6(2):109–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7061(71)90029-2
Huq SMI, Shoaib JUM (2013) Soil properties. In: The soils of Bangladesh. World soils book series, vol 1. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1128-0_1
Islam MS (2008) Soil fertility history, present status and future scenario in Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Agric Environ 4:129–151
Islam MD, Rahman MM, Kabir MH, Rahman GKMM, Hossain MS (2017) Status and spatial variability of trace elements in the Low Ganges river floodplain soils of Bangladesh. J Environ Sci Nat Resour 9(2):71–78. https://doi.org/10.3329/jesnr.v9i2.32160
Jansson JK, Hofmockel KS (2020) Soil microbiomes and climate change. Nat Rev Microbiol 18(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0265-7
Jolliffe IT (2002) Principal component analysis, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Jolliffe IT, Cadima J (2016) Principal component analysis: a review and recent developments. Philos Trans R Soc A 374:20150202. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2015.0202
Jolly YN, Islam A, Akbar S (2013) Transfer of metals from soil to vegetables and possible health risk assessment. Springerplus 2:385. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-2-385
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 47–52
Khan R, Parvez MS, Jolly YN, Haydar MA, Alam MF, Khatun MA, Sarker MMR, Habib MA, Tamim U, Das S (2019) Elemental abundances, natural radioactivity and physicochemical records of a southern part of Bangladesh: implication for assessing the environmental geochemistry. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 12:100225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100225
Kopittke PM, Menzies NW, Wang P, McKenna BA, Lombi E (2019) Soil and the intensification of agriculture for global food security. Environ Int 132:105078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105078
Le Quéré C et al (2018) Global carbon budget. Earth Syst Sci Data 10:2141–2194. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-10-2141-201
Lee CL, Fang MD, Hsieh MT (1998) Characterization and distribution of metals in surficial sediments in Southwestern Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 36(6):464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(98)00006-X
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhou W (2016) Distribution, enrichment and sources of trace metals in the topsoil in the vicinity of a steel wire plant along the Silk Road economic belt, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):909–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5719-x
Loska K, Wiechuła D, Korus I (2004) Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ Int 30(2):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00157-0
Morgan JP, McIntire WG (1959) Quaternary geology of the Bengal basin, East Pakistan and India. Bull Geol Soc Am 70(3):329–342. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1959)70[319:QGOTBB]2.0.CO;2
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Nelson DW, Sommers LW (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, RH Miller, DR Keeney (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2, 2nd edn. American Soc. Agron., Soil Sci Soc Am, Madison, USA, pp 539–577
Ouyang Y, Evans S, Friesen ML, Tiemann LK (2018) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis of field studies. Soil Biol Biochem 127:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.024
Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (1982) Methods of soil analysis. Part 2, 2nd edn. Chemical and microbiological properties. ASA/SSSA Inc., Madison, WI, USA, pp 199–200
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Sayed A, Khadka S, Idris AM (2021) Potential toxic metals (PTMs) contamination in agricultural soils and foodstuffs with associated source identification and model uncertainty. Sci Total Environ 789:147962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147962
Quispe N, Zanabria D, Chavez E, Cuadros F, Carling G, Paredes B (2021) Health risk assessment of heavy metals (Hg, Pb, Cd, Cr and As) via consumption of vegetables cultured in agricultural site in Arequipa, Peru. Chem Data Collect 33:100723
Rahman A, Farzana F, Islam MS, Jahanara I, Mohiuddin ASM, Akter M, Uddin MJ (2020) Distribution and geospatial maps based on spatial availability of soil physicochemical characteristics at a cyclone-affected area in southwestern Bangladesh. J Geogr Environ Earth Sci Int 24(6):86–102. https://doi.org/10.9734/jgeesi/2020/v24i630238
Rahman A, Uddin MJ, Sikder MR, Murshed HB, Faysal JA, Ahmad M, Mohiuddin ASM (2021) Soil properties and carbon stock along the toposequence of Lalmai hill ecosystem of Bangladesh. Dhaka Univ J Biol Sci 30(2):331–343. https://doi.org/10.3329/dujbs.v30i2.54658
Ravindran B, Mupambwa AH, Silwan S, Mnkeni PS (2017) Assessment of nutrient quality, heavy metals and phytotoxic properties of chicken manure on selected commercial vegetable crops. Heliyon 3(12):e00493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00493
Reimann C, Garrett RG (2005) Geochemical background - concept and reality. Sci Total Environ 350(1–3):12–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.047
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2014) Composition of the continental crust. Treatise on geochemistry, 2nd edn. Vol 4, pp 1–51. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00301-6
Shen F, Liao R, Ali A, Mahar A, Guo D, Li R, Sun X, Awasthi MK, Wang Q, Zhang Z (2017) Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil near a Pb/Zn smelter in Feng County, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.01.044
SRDI (2010) Land and soil statistical appraisal book of Bangladesh. Soil resource Development Institute, Ministry of Agriculture, Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp 1–24
Tamim U, Khan R, Jolly YN, Fatema K, Das S, Naher K, Islam MA, Islam SMA, Hossain SM (2016) Elemental distribution of metals in urban river sediments near an industrial effluent source. Chemosphere 155:509518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.04.099
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metal level in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Meeresunters 33:566–575
Uddin MJ, Mohiuddin ASM, Kamal ATMM, Hossain MA (2012) The agricultural potentiality of some wetland soils under Sylhet basin of Bangladesh. Dhaka Univ J Biol Sci 21(1):39–46. https://doi.org/10.3329/dujbs.v21i1.9743
Uddin MJ, Mohiuddin ASM, Hossain ST (2013) Eco-environmental changes of Hail Haor wetland resources under Sylhet basin of Bangladesh due to sedimentation: a GIS approach. J Asiat Soc Bangladesh Sci 39(1):125–128
Uddin MJ, Rahman A, Ali AHMZ, Rahman MK (2020) Estimation of carbon stock in the Sylhet basin soils of Bangladesh. J Asiat Soc Bangladesh Sci 46(1):49–60
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
WHO (1996) Possible limits of heavy metals in soils and plants. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland
Worm HU, Ahmed AMM, Ahmed NU, Islam HO, Huq MM, Hambach U, Lietz J (1998) Large sedimentation rate in the Bengal delta: magnetostratigraphic dating of Cenozoic sediments from northeastern Bangladesh. Geology 26(6):487–490. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026%3c0487:LSRITB%3e2.3
Wuana RA, Okieimen FE (2011) Heavy metals in contaminated soils: a review of sources, chemistry, risks and best available strategies for remediation. ISRN Ecol 2011:1–20. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/402647
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54(6):1051–1070. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2001.0879
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR: conceived and designed the study, performed analysis, and wrote the paper. YNJ: conceived and designed the study. IJ: performed statistical analysis and wrote the paper. MJU: conducted sample collection, contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript, and carried out expenses. ASMM and MKR: contributed to reviewing and editing the manuscript. JK, SA, and KMM: performed sample analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial and non-financial conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, A., Jahanara, I., Jolly, Y.N. et al. Soil properties and pollution indices in four designated wetlands in the Sylhet basin of Bangladesh. Environ Earth Sci 81, 62 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10187-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10187-1