Abstract
The distribution of soil moisture in loess-paleosol sequences is a critical factor that impacts the regional environment in the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP). In this study, samples were collected from the Xiushidu (XSD) profile at the southern edge of the Jinghe River in Guanzhong Basin; specifically, the Holocene-Middle Pleistocene Lishi strata loess. They were then dry weighed, and moisture content and grain size distribution were determined using the grain size testing method. The impacts of different soil textures, sedimentary environments and other factors on the XSD profile moisture distribution in the study area were examined. The results showed that: (1) During the sequence change process from top to bottom, the soil moisture content of the loess-paleosol sequence increased and the overall average moisture content of the XSD profile was ranked in a descending order as: the middle layer of Middle Pleistocene Lishi loess > the upper layer of Middle Pleistocene Lishi loess > the Holocene > the Late Pleistocene; (2) When film water was predominant, the correlation coefficients for soil moisture content and clay, fine-silty sand, coarse silt sand and microsand content were 0.389, 0.394, − 0.419 and − 0.451, respectively; (3) In adjacent loess and paleosol layers, the soil moisture content of the overlying loess layer was always greater than the underlying paleosol layer. (4) In the same loess layer, minimum moisture content values were subject to the East Asia winter monsoon; as such, they often appeared in the middle layer of this glacial period. In the same paleosol layer, the opposite trend was observed.

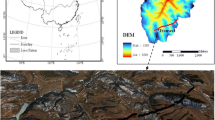
modified from Ge et al. 2013). b Guanzhong Basin is in the Chinese Loess Plateau c The study section at Xiushidu (XSD) is in Guanzhong Basin, south of the Chinese Loess Plateau and north of the Qinling Mountains







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Chandra R (2013) Geochemistry of loess-paleosol sediments of Kashmir valley, India: provenance and weathering. J Asian Earth Sci 66:73–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.029
An Z, Wu G, Li J, Sun Y, Lu Y, Zhou W, Cai Y, Duan A, Li L, Mao J, Cheng H, Shi Z, Tan L, Yan H, Ao H, Chang H, Feng J (2015) Global monsoon dynamics and climate change. J Earth Environ 43:29–77. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054623
Bates SL, Siddall M, Waelbroeck C (2014) Hydrographic variations in deep ocean temperature over the mid-Pleistocene transition. Quatern Sci Rev 88:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.01.020
Berndtsson R, Nodomi K, Yasuda H (1996) Soil water and temperature patterns in an arid desert dune sand. J Hydrol 185(1–4):221–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)02987-7
Breshears D, Barnes F (1999) Interrelationships between plant functional types and soil moisture heterogeneity for semiarid landscapes within the grassland/forest continuum: a unified conceptual model. Landscape Ecol 14(5):465–478. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008040327508
Brocca L, Melone F, Moramarco T, Morbidelli R (2009) Soil moisture temporal stability over experimental areas in Central Italy. Geoderma 148:364–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.11.004
Buggle B, Hambach U, Muller K, Zoller L, Markovic SB, Glaser B (2014) Iron mineralogical proxies and Quaternary climate change in SE-European loess-paleosol sequences. CATENA 117:4–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.06.012
Cai Y, Tan L, Cheng H, An Z, Edwards R, Kelly M, Kong X, Wang X (2010) The variation of summer monsoon precipitation in central China since the last deglaciation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 291:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.12.039
Canton Y, Sole-Benet A, Domingo F (2004) Temporal and spatial patterns of soil moisture in semiarid badlands of SE Spain. J Hydrol 285:199–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.08.018
Chen Y, Qian H (2019) variation in runoff series regimes and the impacts of human activities in the upper yellow river basin. Polish J Environ Stud 3:1071–1082. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/86218
Chen Y, Wang K, Lin Y, Shi W, Song Y, He X (2015) Balancing green and grain trade. Nat Geosci 8:739–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2544
Chen Y, Huo WX, Qian H, Li BC (2020) Research on holocene loess erosion associated to climate evolution in china. Polish J Environ Stud 1:409–417. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/99936
Clift PD, Wan S, Blusztajn J (2014) Reconstructing chemical weathering, physical erosion and monsoon intensity since 25 Ma in the northern South China Sea: a review of competing proxies. Earth Sci Rev 130:86–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.01.002
Ding Z, Sun J, Yang S, Liu T (2001) Geochemistry of the Pliocene red clay formation in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for its origin, source provenance and paleoclimate change. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:901–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00571-8
Fu BJ, Chen LD, Ma KM, Zhou HF, Wang J (2000) The relationships between land use and soil conditions in the hilly area of the loess plateau in northern Shaanxi, China. CATENA 39:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0341-8162(99)00084-3
Fu CF, Zhao JB, Mei FM, Shao TJ (2015) Vertical distribution of soil moisture and surface sandy soil wind erosion for different types of sand dune on the southeastern margin of the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Sci Cold Arid Reg 7:675–686. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.226.2015.00675
Fu CF, Bian ZH, Xi JJ, Zhao JB (2018) Spatial distribution characteristics of soil moisture in different types of sand dune in the Mu Us Sandy Land, adjacent to north of Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7307-8
Gao X, Wu P, Zhao X, Shi Y, Wang J, Zhang B (2011) Soil moisture variability along transects over a well-developed gully in the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 87:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.07.004
Ge J, Dai Y, Zhang Z, Zhao D, Li Q, Zhang Y, Yi L, Wu H, Oldfield F, Guo Z (2013) Major changes in East Asian climate in the mid-Pliocene: triggered by the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau or global cooling? J Asian Earth Sci 69:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.10.009
Geiss CE, Egli R, Zanner CW (2008) Direct estimates of pedogenic magnetite as a tool to reconstruct past climates from buried soils. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 113(B11):B11102. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB005669
Guan H, Zhu C, Zhu T, Wu L, Li Y (2016) Grain size, magnetic susceptibility and geochemical characteristics of the loess in the Chaohu lake basin: Implications for the origin, palaeoclimatic change and provenance. J Asian Earth Sci 117:170–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.013
He S, Wu J (2019a) Relationships of groundwater quality and associated health risks with land use/land cover patterns: a case study in a loess area, northwest China. Hum Ecolog Risk Assessm 25(1–2):354–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1570463
He S, Wu J (2019b) Hydrogeochemical characteristics, groundwater quality and health risks from hexavalent chromium and nitrate in groundwater of Huanhe Formation in Wuqi County, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0289-7
He X, Wu J, He S (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Hum Ecolog Risk Assessm 25(1–2):32–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
Li XA, Li LC (2017) Quantification of the pore structures of Malan loess and the effects on loess permeability and environmental significance, Shaanxi Province, China: an experimental study. Environ Earth Sci 76(15):523
Li P, Qian H (2018a) Water in Loess. In: Encyclopedia of Sustainability Science and Technology. In: Meyers RA (ed) Springer, New York, pp. 1–17. Doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2493-6-968-1.
Li PY, Qian H (2018b) Water resource development and protection in loess areas of the world: a summary to the thematic issue of water in loess. Environ Earth Sci 77(24):796. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7984-3
Li MX, Ma ZG, Niu GY (2011) Modeling spatial and temporal variations in soil moisture in China. Chin Sci Bull 2011(17):67–78
Li PY, Qian H, Wu JH, Zhang YQ, Zhang HB (2013a) Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Mine Water Environ 32:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H (2013b) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydro geochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County. China Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li PY, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu JH, Lyu XS (2014a) Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 186:1385–1398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3
Li PY, Qian H, Wu JH (2014b) Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 510(7503):29–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/510029a
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H, Lyu XS, Liu HW (2014c) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36:693–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H (2016) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County. China Arabian J Geosci 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2018a) Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1443059
Li PY, He S, Yang NN, Xiang G (2018b) Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City, northwest China: implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 77(23):775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-2018-7968-3
Li P, He S, He X, Tian R (2018c) Seasonal hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality delineation based on matter element extension analysis in a paper wastewater irrigation area, northwest China. Expo Health 10(4):241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-17-0258-6
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018d) Geochemistry, Hydraulic Connectivity and Quality Appraisal of Multilayered Groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Li P, He X, Guo W (2019a) Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: a case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):11–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1553612
Li P, Xe H, Li Y, Xiang G (2019b) Occurrence and Health Implication of Fluoride in Groundwater of Loess Aquifer in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study of Tongchuan. Northwest China Expo Health 11(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Li X, Lu YD, Zhang XZ (2019c) Influencing factors of the Spatial-Temporal Variation of Layered Soils and Sediments Moistures and Infiltration Characteristics under Irrigation in a Desert Oasis by Deterministic Spatial Interpolation Methods. Water 11(7):1483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071483
Liu X, He YH, Zhang TH, Zhao XY, Li YQ, Zhang LM, Wei SL, Yun JY, Yue XF (2015) The response of infiltration depth, evaporation, and soil water replenishment to rainfall in mobile dunes in the Horqin Sandy Land, Northern China. Environ Earth Sci 73:8699–8708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4125-0
Liu X, Sun Y, Vandenberghe J et al (2018) Palaeoenvironmental implication of grain-size compositions of terrace deposits on the western Chinese Loess Plateau. Aeol Res 32:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2018.03.008
Marticorena B, Bergametti G (1995) Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle: 1 design of a soil derived dust emission scheme. J Geophys Res Atmos 100(D8):16415–16430. https://doi.org/10.1029/95JD00690
Nehme C, Verheyden S, Breitenbach SF (2018) Climate dynamics during the penultimate glacial period recorded in a speleothem from Kanaan Cave, Lebanon (central Levant). Quatern Res 90(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1017/qua.2018.18
Pan Y, Zhang H, Li X, Xie Y (2016) Effects of sedimentation on soil physical and chemical properties and vegetation characteristics in sand dunes at the Southern Dongting Lake region. China Sci Rep 6:36300. https://doi.org/10.1061/41139(387)92
Qian H, Li PY (2011) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in Yinchuan plain and their control factors. Asian J Chem 23(7):2927–2938
Shi ZH, Fang NF, Wu FZ, Wang L, Yue BJ, Wu GL (2012) Soil erosion processes and sediment sorting associated with transport mechanisms on steep slopes. J Hydrol 454:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.06.004
Sun JZ (2005) Loessology. Hong Kong Archaeological Society, Hong Kong
Sun Y, Kutzbach J, An Z, Clemens S, Liu Z, Liu W, Liu X, Shi Z, Zheng W, Liang L, Yan Y, Li Y (2015) Astronomical and glacial forcing of East Asian summer monsoon variability. Quatern Sci Rev 115:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.03.009
Sveditchnyi AA, Plotnitskiy SV, Stepovaya OY (2003) Spatial distribution of soil moisture content within catchments and its modelling on the basis of topographic data. J Hydrol 277:50–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(03)00083-0
Tian R, Wu J (2019) Groundwater quality appraisal by improved set pair analysis with game theory weightage and health risk estimation of contaminants for Xuecha drinking water source in a loess area in Northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):132–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1573035
Wang T (2014) Modeling the impacts of soil hydraulic properties on temporal stability of soil moisture under a semi-arid climate. J Hydrol 519:1214–1224
Wang Q, Song Y, Zhao Z, Li J (2016) Color characteristics of Chinese loess and its paleoclimatic significance during the last glacial-interglacial cycle. J Asian Earth Sci 116:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.013
Wang W, Wang Y, Sun Q, Zhang M, Qiang Y, Liu M (2018a) Spatial variation of saturated hydraulic conductivity of a loess slope in the South Jingyang Plateau, China. Eng Geol 236:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.002
Wang X, Wang B, Xu X, Liu T, Duan Y, Zhao Y (2018b) Spatial and temporal variations in surface soil moisture and vegetation cover in the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2015. Ecol Ind 95:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.07.058
Wu H, Qian H (2017) Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int J Climatol 37(5):2582–2592. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4866
Wu J, Li P, Wang D, Ren X, Wei M (2019a) Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1594156
Wu J, Zhou H, He S (2019b) Zhang Y (2019b) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu X, Tian Y, Yue L, Gao Q (2010) The response of soil moisture content to rainfall events in semi-arid area of Inner Mongolia. Procedia Environ Sci 2:1970–1978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.211
Zhang H, Lu H, Jiang S, Vandenberghe J, Wang S, Cosgrove R (2012) Provenance of loess deposits in the Eastern Qinling Mountains (central China) and their implications for the paleoenvironment. Quatern Sci Rev 43:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.04.010
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77(7):273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zhao JB, Long TW, Wang CY, Zhang Y (2012) How the Quaternary climatic change affects present hydrogeological system on the Chinese Loess Plateau: A case study into vertical variation of permeability of the loess-palaeosol sequence. CATENA 92:179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.12.009
Zhao JB, Ma YD, Cao JJ, Wei JP, Shao TJ (2015) Effect of Quaternary climatic change on modern hydrological systems in the southern Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 73:1161–1167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3469-1
Zhao JB, Ma YD, Luo XQ, Yue DP, Shao TJ, Dong ZB (2017) The discovery of surface runoff in the mega dunes of Badain Jaran Desert, China, and its significance. Sci China Earth Sci 60:707–719
Zhou J, Fu B, Gao G, Nan L, Lu Y, Wang S (2015) Temporal stability of surface soil moisture of different vegetation types in the Loess Plateau of China. CATENA 128:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.01.015
Acknowledgements
We thank Lin Tao and Qu Wengang for their assistance in the field and laboratory. The comments of 3 anonymous reviewers and Editor Dr. Peiyue Li greatly improved the paper, and we are grateful to them. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 41931285, 41572236 and 41790441).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Water in Large Basins” guest edited by Peiyue Li and Jianhua Wu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Qian, H., Hou, K. et al. Vertical distribution characteristics of soil moisture with different strata in deep profile in Guanzhong Basin, China. Environ Earth Sci 79, 103 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8836-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8836-5