Abstract
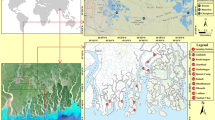
Heavy metal pollution of sediments is a global concern and can be a serious problem in heavily industrialized parts of the world. Pollution by manganese is particularly common due to its ubiquitous natural occurrence, ease of mobilization, and extensive association with industry. In Ningxia, China, manganese pollution of Yellow River alluvial sediments was assessed by comparing manganese concentrations in 35 sediment samples with background values derived from similar sediments obtained at sites considered remote from potential sources of contamination. Natural background values of manganese were found to range from 192 to 323 mg/kg for surface sediments, and from 220 to 325 and 283 to 394 mg/kg for subsurface sediments at depths of 45–50 and 95–100 cm, respectively. In the study area, manganese content ranged from 565 to 1,363 mg/kg, indicating anthropogenic pollution extending to a depth of at least 1 m in the study area. All 35 samples were found to exceed the threshold effect concentration (TEC) of 460 mg/kg, below which adverse effects on sediment-dwelling organisms are not expected to occur, and one sample (T12) was found to exceed the probable effect concentration (PEC) of 1,100 mg/kg. PEC defines the threshold above which adverse effects are likely to be observed. Variogram analysis of the surface sediment manganese data revealed adherence to a Gaussian model, and ordinary kriging was used to generate a manganese distribution map. Analysis of the high nugget effect ratio indicates high, small-scale variations that are consistent with potential emissions from an adjacent electrolytic manganese plant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, B., Ismail, A., Arshad, A., Yap, C. K., & Kamarudin, M. S. (2009). Anthropogenic impacts on heavy metal concentrations in the coastal sediments of Dumai, Indonesia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 148, 291–305. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0159-z.
Band, L. E., Cadenasso, M. L., Grimmond, C. S., Grove, J. M., & Pickett, S. T. A. (2005). Heterogeneity in urban ecosystems patterns and process. In G. M. Lovett, M. G. Turner, C. G. Jones, & K. C. Weathers (Eds.), Ecosystem function in heterogeneous landscapes (pp. 257–278). New York: Springer. doi:10.1007/0-387-24091-8_13.
Batterman, S., Su, F. C., Jia, C. R., Naidoo, R. N., Robins, T., & Naik, I. (2011). Manganese and lead in children’s blood and airborne particulate matter in Durban, South Africa. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 1058–1068. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.12.017.
Baye, A. Y., Razack, M., Ayenew, T., & Zemedagegnehu, E. (2012). Estimating transmissivity using empirical and geostatistical methods in the volcanic aquifers of Upper Awash Basin, central Ethiopia. Environmental Earth Sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2011-6.
Bhuiyan, M. A. H., Parvez, L., Islam, M. A., Dampare, S. B., & Suzuki, S. (2010). Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 384–392. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.085.
Boudissa, S. M., Lambert, J., Müller, C., Kennedy, G., Gareau, L., & Zayed, J. (2006). Manganese concentrations in the soil and air in the vicinity of a closed manganese alloy production plant. Science of the Total Environment, 361, 67–72. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.05.001.
Braimoh, A. K., & Onishi, T. (2007). Geostatistical techniques for incorporating spatial correlation into land use change models. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 9, 438–446. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2007.02.005.
Burton, G. A., Jr. (2002). Sediment quality criteria in use around the world. Limnology, 3, 65–75.
Chaudhary, M. Z., Ahmad, N., Mashiatullah, A., Ahmad, N., & Ghaffar, A. (2013). Geochemical assessment of metal concentrations in sediment core of Korangi Creek along Karachi Coast, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-3056-4.
Chang, T. K., Shyu, G. S., Lin, Y. P., & Chang, N. C. (1999). Geostatistical analysis of soil arsenic content in Taiwan. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 34(7), 1485–1501. doi:10.1080/10934529909376907.
Cheng, B.-Y., Fang, W.-T., Shyu, G.-S., & Chang, T.-K. (2013). Distribution of heavy metals in the sediments of agricultural fields adjacent to urban areas in Central Taiwan. Paddy and Water Environment, 11, 343–351. doi:10.1007/s10333-012-0325-3.
Çevik, F., Göksu, M. Z. L., Derici, O. B., & Fındık, Ö. (2009). An assessment of metal pollution in surface sediments of Seyhan dam by using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index and statistical analyses. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152, 309–317. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0317-3.
Dao, L., Morrison, L., Kiely, G., & Zhang, C. (2013). Spatial distribution of potentially bioavailable metals in surface soils of a contaminated sports ground in Galway, Ireland. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 227–238. doi:10.1007/s10653-012-9478-7.
De Deckere, E., De Cooman, W., Leloup, V., Meire, P., Schmitt, C., & Von Der Ohe, P. C. (2011). Development of sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11, 504–517. doi:10.1007/s11368-010-0328-x.
Dell’Arciprete, D., Bersezio, R., Felletti, F., Giudici, M., Comunian, A., & Renard, P. (2012). Comparison of three geostatistical methods for hydrofacies simulation: a test on alluvial sediments. Hydrogeology Journal, 20, 299–311. doi:10.1007/s10040-011-0808-0.
Du, J. Z., Mu, H. D., Song, H. Q., Yan, S. P., Gu, Y. J., & Zhang, J. (2008). 100 years of sediment history of heavy metals in Daya Bay, China. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 190, 343–351. doi:10.1007/s11270-007-9593-8.
El Khalil, H., El Hamiani, O., Bitton, G., Ouazzani, N., & Boularbah, A. (2008). Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: monitoring metal content and toxicity of soil runoff and groundwater. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 136, 147–160. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9671-9.
Esen, E., Kucuksezgin, F., & Uluturhan, E. (2010). Assessment of trace metal pollution in surface sediments of Nemrut Bay, Aegean Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 257–266. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0692-9.
Fernández-Caliani, J. C., Barba-Brioso, C., González, I., & Galán, E. (2009). Heavy metal pollution in soils around the abandoned mine sites of the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Southwest Spain). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 200, 211–226. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9905-7.
Fraterrigo, J. M., Turner, M. G., Pearson, S. M., & Dixon, P. (2005). Effects of past land use on spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients in southern Appalachian forests. Ecological Monographs, 75(2), 215–230. doi:10.1890/03-0475.
Fulton, M., Key, P., Wirth, E., Leight, A. K., Daugomah, J., Bearden, D., et al. (2006). An evaluation of contaminated estuarine sites using sediment quality guidelines and ecological assessment methodologies. Ecotoxicology, 15, 573–581. doi:10.1007/s10646-006-0092-2.
Galanopoulou, S., Vgenopoulos, A., & Conispoliatis, N. (2009). Anthropogenic heavy metal pollution in the surficial sediments of the Keratsini Harbor, Saronikos Gulf, Greece. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 202, 121–130. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9962-y.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of PRC (2002). Marine sediment quality, GB18668-2002. (in Chinese)
Ghani, S. A., Zokm, G. E., Shobier, A., Othman, T., & Shreadah, M. (2013). Metal pollution in surface sediments of Abu-Qir Bay and Eastern Harbour of Alexandria, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research. doi:10.1016/j.ejar.2013.03.001.
Guagliardi, I., Cicchella, D., & De Rosa, R. (2012). A geostatistical approach to assess concentration and spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 5983–5998. doi:10.1007/s11270-012-1333-z.
Hahladakis, J., Smaragdaki, E., Vasilaki, G., & Gidarakos, E. (2013). Use of sediment quality guidelines and pollution indicators for the assessment of heavy metal and PAH contamination in Greek surficial sea and lake sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 2843–2853. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2754-2.
Homoncik, S. C., MacDonald, A. M., Heal, K. V., Dochartaigh, B. É. Ó., & Ngwenya, B. T. (2010). Manganese concentrations in Scottish groundwater. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 2467–2473. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.017.
Hübner, R., Astin, K. B., & Herbert, R. J. H. (2009). Comparison of sediment quality guidelines (SQGs) for the assessment of metal contamination in marine and estuarine environments. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 713–722. doi:10.1039/b818593j.
Ingersoll, C. G., MacDonald, D. D., Wang, N., Crane, J. L., Field, L. J., Haverland, P. S., et al. (2001). Predictions of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwater sediment quality guidelines. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 41, 8–21. doi:10.1007/s002440010216.
Juan, P., Mateu, J., Jordan, M. M., Mataix-Solera, J., Meléndez-Pastor, I., & Navarro-Pedreño, J. (2011). Geostatistical methods to identify and map spatial variations of soil salinity. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 108, 62–72. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.10.003.
Léopold, E. N., Jung, M. C., Auguste, O., Ngatcha, N., Georges, E., & Lape, M. (2008). Metals pollution in freshly deposited sediments from river Mingoa, main tributary to the Municipal lake of Yaounde, Cameroon. Geosciences Journal, 12(4), 337–347. doi:10.1007/s12303-008-0034-5.
Li, P. Y., & Qian, H. (2010). Spatial variability of fluoride in drinking groundwater and its relationship with geologic environment in Pengyang County. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 21(2), 33–38 (in Chinese).
Lin, Y. P. (2002). Multivariate geostatistical methods to identify and map spatial variations of soil heavy metals. Environmental Geology, 42, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s00254-002-0523-1.
Lin, Y. P., Tan, Y. C., & Rouhani, S. (2001). Identifying spatial characteristics of transmissivity using simulated annealing and kriging methods. Environmental Geology, 41, 200–208. doi:10.1007/s002540100383.
Lin, C., He, M., Zhou, Y., Guo, W., & Yang, Z. (2008). Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in sediment of the Second Songhua River, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137, 329–342. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9768-1.
Lin, Y. P., Cheng, B. Y., Shyu, G. S., & Chang, T. K. (2010). Combining a finite mixture distribution model with indicator kriging to delineate and map the spatial patterns of soil heavy metal pollution in Chunghua County, central Taiwan. Environmental Pollution, 158, 235–244. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.07.015.
Lin, Y. P., Chu, H. J., Huang, Y. L., Cheng, B. Y., & Chang, T. K. (2011). Modeling spatial uncertainty of heavy metal content in soil by conditional Latin hypercube sampling and geostatistical simulation. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62, 299–311. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0523-5.
Liu, J. S., Wang, R. Q., Dai, J. L., Zhang, Y. L., & Wang, Q. (2008). Soil environmental background concentrations in old course of the Yellow River in Shandong Province. Environmental Science, 29(6), 1699–1704 (in Chinese).
Lu, Z., Cai, M., Wang, J., Yin, Z., & Yang, H. (2013). Levels and distribution of trace metals in surface sediments from Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Norwegian Arctic. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 257–269. doi:10.1007/s10653-012-9481-z.
Lu, X., Wang, L., Lei, K., Huang, J., & Zhai, Y. (2009). Contamination assessment of copper, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2–3), 1058–1062. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04.052.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31. doi:10.1007/s002440010075.
Morton-Bermea, O., Hernández-Álvarez, E., González-Hernándeza, G., Romero, F., Lozano, R., & Beramendi-Orosco, L. E. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban topsoils from the metropolitan area of Mexico City. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 101, 218–224. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.07.002.
National Bureau of Environmental Protection. (1995). Environmental quality standard for soils, GB15618-1995. (in Chinese)
National Environmental Monitoring Centre of China. (1990). Background values of Chinese Soils (p. 501). Beijing: China Environmental Science Press (in Chinese).
Ningxia Institute of Environmental Monitoring. (2011). Report of environmental quality monitoring in Nigxia Tianyuan Manganese Company Limited. Yinchuan: Ningxia Institute of Environmental Monitoring (in Chinese).
Ong, G. H., Yap, C. K., Maziah, M., Suhaimi, H., & Tan, S. G. (2013). An investigation of arsenic contamination in Peninsular Malaysia based on Centella asiatica and soil samples. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 3243–3254. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2787-6.
Paschke, M. W., Valdecantos, A., & Redente, E. F. (2005). Manganese toxicity thresholds for restoration grass species. Environmental Pollution, 135, 313–322. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.08.006.
Qian, H., Zhang, Y. L., Li, P. Y., et al. (2013). Report of investigation on regional environmental conditions and assessment of heavy metal pollution in Shikong Industrial Area, China (p. 157 pp). Yinchuan: Ningxia Institute of Environmental Monitoring (in Chinese).
Qian, H., Li, P. Y., Howard, K. W. F., Yang, C., & Zhang, X. D. (2012). Assessment of groundwater vulnerability in the Yinchuan Plain, Northwest China using OREADIC. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(6), 3613–3628. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2211-7.
Qi, W., Liu, H., Han, H., Chai, W., & Qu, J. (2013). A study of metal contamination in sediments in Beisan River System. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 33(1), 117–124 (in Chinese).
Raju, K. V., Somashekar, R. K., & Prakash, K. L. (2012). Heavy metal status of sediment in river Cauvery, Karnataka. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 361–373. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1973-2.
Rama Rao, K. V., Reddy, P. V. B., Hazell, A. S., & Norenberg, M. D. (2007). Manganese induces cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. NeuroToxicology, 28, 807–812. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.03.001.
Reimann, C., & Garrett, R. G. (2005). Geochemical background concept and reality. Science of the Total Environment, 350, 12–27. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.047.
Reimann, C., Filzmoser, P., & Garrett, R. G. (2005). Background and threshold: critical comparison of methods of determination. Science of the Total Environment, 346(1–3), 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.11.023.
Rékási, M., & Filep, T. (2012). Fractions and background concentrations of potentially toxic elements in Hungarian surface soils. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 7461–7471. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2513-9.
Rizo, O. D., Castillo, F. E., López, J. O. A., & Merlo, M. H. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban soils of Havana City, Cuba. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 87, 414–419. doi:10.1007/s00128-011-0378-9.
Robertson, G. P. (2008). GS + : geostatistics for the environmental sciences. Plainwell: Gamma Design Software.
Rodríguez-Barroso, M. R., Benhamou, Y., El Moumni, B., El Hatimi, I., & García-Morales, J. L. (2009). Evaluation of metal contamination in sediments from north of Morocco: geochemical and statistical approaches. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159, 169–181. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0620-z.
Shah, M. H., Iqbal, J., Shaheen, N., Khan, N., Choudhary, M. A., & Akhter, G. (2012). Assessment of background levels of trace metals in water and soil from a remote region of Himalaya. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1243–1252. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2036-4.
Sheykhi, V., & Moore, F. (2013). Evaluation of potentially toxic metals pollution in the sediments of the Kor river, southwest Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 3219–3232. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2785-8.
SPSS, Inc. (2004) SPSS Base 13.0 User’s guide. SPSS, Inc., New York.
Turekian, K.K., & Wedepohl, K.H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Bulletin of Geological Society of America, 72(2), 175–192, doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1961)72[175:DOTEIS]2.0.CO;2
Thuong, N. T., Yoneda, M., Ikegami, M., & Takakura, M. (2013). Source discrimination of heavy metals in sediment and water of To Lich River in Hanoi City using multivariate statistical approaches. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3155-x.
Ünlü, S., Topçuoğlu, S., Alpar, B., Kırbaşoğlu, Ç., & Yılmaz, Y. Z. (2008). Heavy metal pollution in surface sediment and mussel samples in the Gulf of Gemlik. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 144, 169–178. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9986-6.
Wu, B., Song, J. M., Li, X. G., Yuan, H. M., & Li, N. (2011). Consensus based sediment quality guidelines (CBSQGs) and its application in coastal sediment quality assessment. Environmental Chemistry, 30(11), 1949–1956 (in Chinese).
Yap, C. K., & Pang, B. H. (2011). Assessment of Cu, Pb and Zn contamination in sediment of north western Peninsular Malaysia by using sediment quality values and different geochemical indices. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 183(1–4), 23–39. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1903-3.
Zhou, J., Ma, D., Pan, J., Nie, W., & Wu, K. (2008). Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediment and waters: a case study in Yangzhong, China. Environmental Geology, 54, 373–380. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0824-5.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Doctor Postgraduate Technical Project of Chang’an University (2013G5290002 and CHD2011ZY022), the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (CHD2011ZY020 and CHD2012TD003), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41172212). Two anonymous reviewers are sincerely acknowledged for their valuable comments on the original version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Qian, H., Howard, K.W.F. et al. Anthropogenic pollution and variability of manganese in alluvial sediments of the Yellow River, Ningxia, northwest China. Environ Monit Assess 186, 1385–1398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3461-3