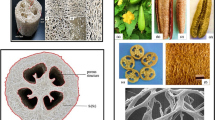
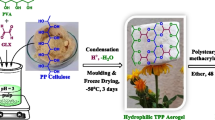
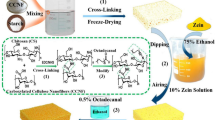
Abstract
The frequent leakage of petroleum and organic solvents has catastrophic and far-reaching implications for the ecological environment, resulting in severe threats to aquatic organisms. Absorbing oil from water with porous material has emerged as an eco-friendly and efficient option. Among these explored sorbents, biomass-based/derived materials are abundant in pores and their multiscale porosity serving as a storage space for the absorption, making them excellent sorbents especially after surface modification. In this review, we summarized several biomass-based/derived porous materials for oil/water separation including biochars (BC), cellulose-based/derived materials, chitosan-based/derived materials, lignin-based/derived materials, biomass waste-based/derived materials and some other common biomass-based/derived materials. The detailed synthesis methodologies and activation/modification mechanism together with their effective participation in the field of oil/water adsorption/absorption were discussed. Moreover, perspectives for future application of the biomass-based/derived porous materials in the area are also provided.
Graphical Abstract



(Copyright 2018 Springer)

(Copyright 2021 Elsevier)

(Copyright 2021 Elsevier)
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Research data available on reasonable request from the corresponding authors.
References
Unur, E.: Functional nanoporous carbons from hydrothermally treated biomass for environmental purification. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 168, 92–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.09.027
Inyang, M., Dickenson, E.: The potential role of biochar in the removal of organic and microbial contaminants from potable and reuse water: a review. Chemosphere 134, 232–240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.072
Gui, X., Zeng, Z., Lin, Z., Gan, Q., Xiang, R., Zhu, Y., Cao, A., Tang, Z.: Magnetic and highly recyclable macroporous carbon nanotubes for spilled oil sorption and separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 5845–5850 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am4015007
Zhang, X., Li, Z., Liu, K., Jiang, L.: Bioinspired multifunctional foam with self-cleaning and oil/water separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 2881–2886 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201202662
Bi, H., Yin, Z., Cao, X., Xie, X., Tan, C., Huang, X., Chen, B., Chen, F., Yang, Q., Bu, X., Lu, X., Sun, L., Zhang, H.: Carbon fiber aerogel made from raw cotton: a novel, efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Adv. Mater. 25, 5916–5921 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302435
Sam, E.K., Sam, D.K., Lv, X., Liu, B., Xiao, X., Gong, S., Yu, W., Chen, J., Liu, J.: Recent development in the fabrication of self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 373, 531–546 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.077
Bhatnagar, A., Sillanpää, M.: Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) and its constituents from water by adsorption—a review. Chemosphere 166, 497–510 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.098
Sabir, S.: Approach of cost-effective adsorbents for oil removal from oily water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 1916–1945 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2014.1001143
Bi, H., Xie, X., Yin, K., Zhou, Y., Wan, S., He, L., Xu, F., Banhart, F., Sun, L., Ruoff, R.S.: Spongy graphene as a highly efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic Solvents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 4421–4425 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201200888
Sakthivel, T., Reid, D.L., Goldstein, I., Hench, L., Seal, S.: Hydrophobic high surface area zeolites derived from fly ash for oil spill remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 5843–5850 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/es3048174
Wang, C.F., Tzeng, F.S., Chen, H.G., Chang, C.J.: Ultraviolet durable superhydrophobic Zinc oxide-coated mesh films for surface and underwater-oil capture and transportation. Langmuir 28, 10015–10019 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/la301839a
Carmody, O., Frost, R., Xi, Y., Kokot, S.: Adsorption of hydrocarbons on organo-clays implications for oil spill remediation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 305, 17–24 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.09.032
Lin, J., Shang, Y., Ding, B., Yang, J., Yu, J., Al-Deyab, S.S.: Nanoporous polystyrene fibers for oil spill cleanup. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 64, 347–352 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.11.002
Doshi, B., Sillanpää, M., Kalliola, S.: A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res. 135, 262–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.034
Chai, W., Liu, X., Zou, J., Zhang, X., Li, B., Yin, T.: Pomelo peel modified with acetic anhydride and styrene as new sorbents for removal of oil pollution. Carbohydr. Polym. 132, 245–251 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.060
Wu, C., Huang, X.Y., Wu, X.F., Qian, R., Jiang, P.K.: Mechanically flexible and multifunctional polymer-based graphene foams for elastic conductors and oil/water separators. Adv. Mater. 25, 5658–5662 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302406
Sun, H.Y., Xu, Z., Gao, C.: Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels. Adv. Mater. 25, 2554–2560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201204576
Kang, W.W., Cui, Y., Qin, L., Yang, Y.Z., Zhao, Z.B., Wang, X.Z., Liu, X.G.: A novel robust adsorbent for efficient oil/water separation: magnetic carbon nanospheres/graphene composite aerogel. J. Hazard. Mater. 392, 122499 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122499
Zhu, Q., Chu, Y., Wang, Z.K., Chen, N., Lin, L., Liu, F.T., Pan, Q.M.: Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5386–5393 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA00125C
Ge, D.D., Zhang, Y., Cui, Z.S., Wang, G.L., Liu, J., Lv, X.M.: Constructing robust and magnetic PU sponges modified with Fe3O4/GO nanohybrids for efficient oil/water separation. J. Coat. Technol. Res. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-022-00699-7
Zhang, L., Wu, J.J., Wang, Y.X., Long, Y.H., Zhao, N., Xu, J.: Combination of bioinspiration: a general route to superhydrophobic particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 9879–9881 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja303037j
Zhou, X.Y., Zhang, Z.Z., Xu, X.H., Guo, F., Zhu, X.T., Men, X.H., Ge, B.: Robust and durable superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 7208–7214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/am4015346
Tang, X.M., Si, Y., Ge, J.L., Ding, B., Liu, L.F., Zheng, G., Luo, W.J., Yu, J.Y.: In-situ polymerized superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for gravity driven oil/water separation. Nanoscale 5, 11657–11664 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NR03937D
Zhang, J.P., Seeger, S.: Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 4699–4704 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201101090
Wang, Z.J., Wang, Y., Liu, G.J.: Rapid and efficient separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions using a janus cotton fabric. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 1291–1294 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201507451
Wang, Y.F., Lai, C.L., Wang, X.W., Liu, Y., Hu, H.W., Guo, Y.J., Ma, K.K., Fei, B., Xin, J.H.: Beads-on-string structured nanofibers for smart and reversible oil/water separation with outstanding antifouling property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 25612–25620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b08747
Niu, Z.Q., Liu, L., Zhang, L., Chen, X.: Porous graphene materials for water remediation. Small 10, 3434–3441 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201400128
Sankaranarayanan, S., Lakshmi, D.S., Vivekanandhan, S., Ngamcharussrivichai, C.: Biocarbons as emerging and sustainable hydrophobic/oleophilic sorbent materials for oil/water separation, Sustainable. Mater. Technol. 28, 2214–9937 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00268
Yang, W.J., Yuen, A.C.Y., Li, A., Lin, B., Chen, T.B.Y., Yang, W., Lu, H.D., Yeoh, G.H.: Recent progress in bio-based aerogel absorbents for oil/water separation. Cellulose 26, 6449–6476 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02559-x
Spiridon, I., Darie-Nit, R.N., Hitruc, G.E., Ludwiczak, J., Spiridon, I.A.C., Niculaua, M.: New opportunities to valorize biomass wastes into green materials. J. Cleaner Prod. 133, 235–242 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.143
Tao, Y.S., Kanoh, H., Abrams, L., Kaneko, K.: Mesopore modified zeolites: preparation, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev. 106, 896–910 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040204o
Tan, I.A.W., Hameed, B.H., Ahmad, A.L.: Equilibrium, kinetic studies on basic dye adsorption by oil palm fibre activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 127, 111–119 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040204o
Mahari, W.A.W., Waiho, K., Azwar, E., Fazhan, H., Peng, W.X.: A state-of-the-art review on producing engineered biochar from shellfish waste and its application in aquaculture wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 288, 132559 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132559
Guleria, A., Kumari, G., Lima, E.C., Ashish, D.K., Thakur, V., Singh, K.: Removal of inorganic toxic contaminants from wastewater using sustainable biomass: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 823, 153689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153689
Sam, E.K., Liu, J., Lv, X.M.: Surface Engineering materials of superhydrophobic sponges for oil/water separation: a review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60, 2353–2364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05906
Yang, J., Xu, P., Xia, Y.F., Chen, B.B.: Multifunctional carbon aerogels from typha orientalis for oil/water separation and simultaneous removal of oil-soluble pollutants. Cellulose 25, 5863–5875 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1994-x
Foong, S.Y., Chan, Y.H., Chin, B.L.F., Lock, S.S.M., Yee, C.Y.: Production of biochar from rice straw and its application for wastewater remediation—an overview. Bioresour. Technol. 360, 127588 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127588
Xiang, W., Zhang, X., Chen, J., Zou, W., He, F., Hu, X., Tsang, D.C.W., Ok, Y.S., Gao, B.: Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: a critical review. Chemosphere 252, 126539 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126539
Foong, S.Y., Chan, Y.H., Lock, S.S.M., Chin, B.L.F.: Microwave processing of oil palm wastes for bioenergy production and circular economy: recent advancements, challenges, and future prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 369, 128478 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128478
Nguyen, H.N., Pignatello, J.J.: Laboratory tests of biochars as absorbents for use in recovery or containment of marine crude oil spills. Environ. Eng. Sci. 30, 374–380 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2012.0411
Sohaimi, K.S.A., Ngadi, N., Mat, H., Inuwa, I.M., Wong, S.: Synthesis, characterization and application of textile sludge biochars for oil removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 1415–1422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.02.002
Alameri, K., Giwa, A., Yousef, L., Alraeesi, A., Taher, H.: Sorption and removal of crude oil spills from seawater using peat-derived biochar: an optimization study. J. Environ. Manag. 250, 109465 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109465
Gheriany, I.A.E., El Saqa, F.A., Amer, A.A., El, R., Hussein, M.: Oil spill sorption capacity of raw and thermally modified orange peel waste. Alexandr. Eng. J. 59, 925–932 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.03.024
Devi, N.S., Hariram, M., Vivekanandhan, S.: Modification techniques to improve the capacitive performance of biocarbon materials. J. Energy Storage 33, 101870 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101870
Guo, S., Peng, J., Li, W., Yang, K., Zhang, L., Zhang, S., Xia, H.: Effects of CO2 activation on porous structures of coconut shell-based activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8443–8449 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.05.150
Rajapaksha, A.U., Vithanage, M., Ahmad, M., Seo, D.C., Cho, J.S., Lee, S.E., Lee, S.S., Ok, Y.S.: Enhanced sulfamethazine removal by steam-activated invasive plant-derived biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 290, 43–50 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.02.046
Rajak, V.K., Kumar, S., Thombre, N.V., Mandal, A.: Synthesis of activated charcoal from saw-dust and characterization for adsorptive separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsion. Chem. Eng. Commun. 205, 897–913 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2017.1423288
Gao, S., Li, X., Li, L., Wei, X.: A versatile biomass derived carbon material for oxygen reduction reaction, supercapacitors and oil/water separation. Nano Energy 33, 334–342 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.01.045
Yang, I., Jung, M., Kim, M.S., Choi, D., Jung, J.C.: Physical and chemical activation mechanisms of carbon materials based on the microdomain model. J. Mater. Chem. A 9, 9815–9825 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta00765c
Canales-Flores, R.A., Prieto-García, F.: Activation methods of carbonaceous materials obtained from agricultural waste. Chem. Biodivers. 13, 261–268 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201500039
MohamadNor, N., Lau, L.C., Lee, K.T., Mohamed, A.R.: Synthesis of activated carbon from lignocellulosic biomass and its applications in air pollution control—a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1, 658 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.09.017
Gwenzi, W., Chaukura, N., Noubactep, C., Mukome, F.N.D.: Biochar-based water treatment systems as a potential low-cost and sustainable technology for clean water provision. J. Environ. Manag. 197, 732–749 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.03.087
Sam, D.K., Sam, E.K., Durairaj, A., Lv, X.M., Zhou, Z.J., Liu, J.: Synthesis of biomass-based carbon aerogels in energy and sustainability. Carbohydr. Res. 491, 107986 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2020.107986
A. C. Pierre, A. Rigacci, Adv. Sol–Gel Deriv. Materials Technol, in: Aerogels Handbook, 2011, pp. 21–46, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7589-8_2
Joshi, P., Sharma, O.P., Ganguly, S.K., Srivastava, M., Khatri, O.P.: Fruit waste-derived cellulose and graphene-based aerogels: plausible adsorption pathways for fast and efficient removal of organic dyes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 608, 2870–2883 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.016
Wang, S., Peng, X., Zhong, L., Tan, J., Jing, S., Cao, X., Chen, W., Liu, C., Sun, R.: An ultralight, elastic, cost-effective, and highly recyclable superabsorbent from microfibrillated cellulose fibers for oil spillage cleanup. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 8772–8781 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA07057G
Li, Y.Q., Samad, Y.A., Polychronopoulou, K., Alhassan, S.M., Liao, K.: Carbon aerogel from winter melon for highly efficient and recyclable oils and organic solvents absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2, 1492–1497 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500161b
Wang, Y., Zhu, L., Zhu, F., You, L., Shen, X., Li, S.: Removal of organic solvents/oils using carbon aerogels derived from waste durian shell. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 78, 351–358 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.06.037
Yuan, W., Zhang, X., Zhao, J., Li, Q., Ao, C., Xia, T., Zhang, W., Lu, C.: Ultra-lightweight and highly porous carbon aerogels from bamboo pulp fibers as an effective sorbent for water treatment. Results Phys. 7, 2919–2924 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.08.011
Liu, Y., Zhang, K., Yao, W.G., Zhang, C.C., Han, Z.W., Ren, L.Q.: A facile electrodeposition process for the fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic copper mesh for efficient oil/water separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 2704–2712 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03503
Sun, F., Liu, W., Dong, Z., Deng, Y.: Underwater superoleophobicity cellulose nanofibril aerogel through regioselective sulfonation for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 15, 774–782 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.142
Zhang, H., Li, Y.Q., Shi, R.H., Chen, L.H., Fan, M.Z.: A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic chitosan/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel for highly efficient oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 200, 611–615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.071
Meng, G., Peng, H., Wu, J., Wang, Y., Wang, H.: Fabrication of superhydrophobic cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for oil/water separation. Fibers Polym. 18, 706–712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-1099-4
Li, Y.Z., Zhu, L.Q., Grishkewich, N., Tam, K.C., Yuan, J.Y., Mao, Z.P., Sui, X.F.: CO2-responsive cellulose nanofibers aerogels for switchable oil−water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 9367–9373 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b22159
Zhao, L., Li, L., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Meng, G., Liu, Z., Guo, X.: Preparation and characterization of thermo- and pH dual-responsive 3D cellulose-based aerogel for oil/water separation. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 124, 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1358-7
Li, Z.X., Lei, S.J., Xi, J.C., Ye, D.L., Hu, W.Z., Song, L., Hu, Y., Cai, W., Gui, Z.: Bio-based multifunctional carbon aerogels from sugarcane residue for organic solvents adsorption and solar-thermal-driven oil removal. Chem. Eng. J. 426, 129580 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129580
Wang, G., He, Y., Wang, H., Zhang, L., Yu, Q.Y., Peng, S.S., Wu, X.D., Ren, T.H., Zeng, Z.X., Xue, Q.J.: Robust superhydrophilicity and under-water superoleophobicity cellulose sponge for highly effective oil/water separation. Green Chem. 17, 3093–3099 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5GC00025D
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, C., Xu, M., Wang, G., Zeng, Z., Wang, L., Xue, Q.: Cellulose sponge with superhydrophilicity and high oleophobicity both in air and under water for efficient oil/water emulsion separation. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 302, 1700086 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/mame.201700086
Meng, X., Dong, Y.Y., Zhao, Y.J., Liang, L.P.: Preparation and modification of cellulose sponge and application of oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 10, 41713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA07910C
Qin, Y., Li, S., Li, Y., Pan, F., Han, L., Chen, Z., Yin, X., Wang, L., Wang, H.: Mechanically robust polybenzoxazine/reduced graphene oxide wrapped-cellulose sponge towards highly efficient oil/water separation, and solar-driven for cleaning up crude oil. Compos. Sci. Technol. 197, 54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108254
Wei, M., Gao, Y., Li, X., Serpe, M.J.: Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 8, 127–143 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PY01585A
Li, L., Rong, L., Xu, Z., Wang, B., Feng, X., Mao, Z., Xu, H., Yuan, J., Liu, S., Sui, X.: Cellulosic sponges with pH responsive wettability for efficient oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 237, 116133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116133
Periyasamy, T., Asrafali, S.P., Haldhar, R., Madhappan, S., Vanaraj, R., Raorane, C.J., Kim, S.C.: Modified cotton sponge with bio-based polybenzoxazine for plasticizer absorption and oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 4, 950–959 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.1c01408
Yi, L.F., Yang, J.Y., Fang, X., Xia, Y., Zhao, L.J., Wu, H., Guo, S.Y.: Facile fabrication of wood-inspired aerogel from chitosan for efficient removal of oil from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 385, 121507 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121507
Yin, Z.C., Sun, X.J., Bao, M.M., Li, Y.: Construction of a hydrophobic magnetic aerogel based on chitosan for oil/water separation applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 1869–1880 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.068
Su, C., Yang, H., Zhao, H., Liu, Y., Chen, R.: Recyclable and biodegradable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic chitosan sponge for the effective removal of oily pollutants from water. Chem. Eng. J. 330, 423–432 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.157
Li, Z.Y., Shao, L., Hu, W.B., Zheng, T.T., Lu, L.B., Cao, Y., Chen, Y.J.: Excellent reusable chitosan/cellulose aerogel as an oil and organic solvent absorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 191, 183–190 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.027
Wang, C., He, G., Cao, J., Fan, L., Cai, W., Yin, Y.: Underwater superoleophobic and salt tolerant sodium alginate/N-Succinyl chitosan composite aerogel for highly efficient oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2, 1124–1133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.9b00908
Liang, F.Y., Hou, T.T., Li, S.D., Liao, L.S., Li, P.W., Li, C.P.: Elastic, super-hydrophobic and biodegradable chitosan sponges fabricated for oil/water separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 106027 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.106027
Yu, M.D., Mishra, D., Cui, Z.Y., Wang, X., Lu, Q.Y.: Recycling papermill waste lignin into recyclable and flowerlike composites for effective oil/water separation. Compos. Part B 216, 108884 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108884
Oribayo, O., Feng, X.S., Rempel, G.L., Pan, Q.M.: Synthesis of lignin-based polyurethane/graphene oxide foam and its application as an absorbent for oil spill clean-ups and recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 323, 191–202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.054
Bertella, S., Luterbacher, J.S.: Lignin functionalization for the production of novel materials. Trends Chem. 5, 440–453 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trechm.2020.03.001
Zhang, N., Li, Z., Xiao, Y., Pan, Z., Jia, P., Feng, G., Bao, C., Zhou, Y., Hua, L.: Lignin-based phenolic resin modified with whisker silicon and its application. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 5, 67–77 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2020.03.008
Xia, Z., Li, J., Zhang, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, J.: Processing and valorization of cellulose, lignin and lignocellulose using ionic liquids. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 5, 79–95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2020.04.001
Zhou, W., Chen, F., Zhang, H., Wang, J.: Preparation of a polyhydric aminated lignin and its use in the preparation of polyurethane film. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 37, 323–333 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/02773813.2017.1299185
Chen, S., Shen, S., Yan, X., Mi, J., Wang, G., Zhang, J., Zhou, Y.: Synthesis of surfactants from alkali lignin for enhanced oil recovery. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 37, 1574–1580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2015.1118703
Chio, C.L., Sain, M., Qin, W.S.: Lignin utilization: a review of lignin depolymerization from various aspects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 107, 232–249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.03.008
Kazzaz, A.E., Feizia, Z.H., Fatehi, P.: Grafting strategies for hydroxy groups of lignin for producing materials. Green Chem. 21, 5714–5752 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC02598G
Huang, D., Li, R., Xu, P., Li, T., Deng, R., Chen, S., Zhang, Q.: The cornerstone of realizing lignin value-addition: Exploiting the native structure and properties of lignin by extraction methods. Chem. Eng. J. 402, 126237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126237
Chen, C.Z., Li, F.F., Zhang, Y.R., Wang, B.X., Fan, Y.M., Wang, X.L., Sun, R.K.: Compressive, ultralight and fire-resistant lignin-modified graphene aerogels as recyclable absorbents for oil and organic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 350, 173–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.189
Meng, Y., Liu, T., Yu, S., Cheng, Y., Lu, J., Wang, H.: A lignin-based carbon aerogel enhanced by graphene oxide and application in oil/water separation. Fuel 15, 118376 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118376
Sun, H.D., Liu, Z.M., Liu, K.Y., Gibril, M.E., Kong, F.G., Wang, S.J.: Lignin-based superhydrophobic melamine resin sponges and their application in oil/water separation. Ind. Crops Prod. 170, 113798 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113798
Yue, Y.Y., Wang, Y., Li, J.Y., Cheng, W.L., Han, G.P., Lu, T., Huang, C.B., Wu, Q.L., Jiang, J.C.: High strength and ultralight lignin-mediated fire-resistant aerogel for repeated oil/water separation. Carbon 193, 285–297 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2022.03.015
Vannarath, A., Thalla, A.K.: Synthesis and characterisation of an ultra-light, hydrophobic and flame-retardant robust lignin-carbon foam for oil/water separation. J. Cleaner Prod. 325, 129263 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129263
Zhang, S.G., Yang, M.C., Meng, S.Y., Yang, Y.C., Li, Y.C., Tong, Z.H.: Biowaste-derived, nanohybrid-reinforced double-function slow-release fertilizer with metal-adsorptive function. Chem. Eng. J. 450, 138084 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.138084
Matveeva, V.G., Bronstein, L.M.: From renewable biomass to nanomaterials: does biomass origin matter? Prog. Mater. Sci. 130, 100999 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2022.100999
Li, L., Li, B., Zhang, J.: Dopamine-mediated fabrication of ultralight graphene aerogels with low volume shrinkage. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 512–518 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA08829A
Liu, Y., Peng, Y., Zhang, T., Qiu, F., Yuan, D.: Superhydrophobic, ultralight and flexible biomass carbon aerogels derived from sisal fibers for highly efficient oil/water separation. Cellulose 25, 3067–3078 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1774-7
Lv, Y., Gan, L., Liu, M., Xiong, W., Xu, Z., Zhu, D.: A self-template synthesis of hierarchical porous carbon foams based on banana peel for supercapacitor electrodes. J. Power Sources 209, 152–157 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.089
Ma, Q., Yu, Y., Sindoro, M., Fane, A.G., Wang, R., Zhang, H.: Carbon-based functional materials derived from waste for water remediation and energy storage. Adv. Mater. 29, 1605361 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201605361
Nguyen, S.T., Feng, J., Le, N.T., Le, A.T.T., Hoang, N., Tan, V.B.C., Duong, H.M.: Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 18386–18391 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4032567
Akhlamadi, G., Goharshadi, E.K.: Sustainable and superhydrophobic cellulose nanocrystal-based aerogel derived from waste tissue paper as a sorbent for efficient oil/water separation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 154, 155–167 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2021.08.009
Li, L., Li, B., Sun, H., Zhang, J.: Compressible and conductive carbon aerogels from waste paper with exceptional performance for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 14858–14864 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA03511J
Bi, H.C., Huang, X., Wu, X., Cao, X.H., Tan, C.L., Yin, Z.Y., Lu, X.H., Sun, L.T., Zhang, H.: Carbon microbelt aerogel prepared by waste paper: an efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents. Small 10, 3544–3550 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201303413
Han, S.J., Sun, Q.F., Zheng, H.H., Li, J.P., Jin, C.D.: Green and facile fabrication of carbon aerogels from cellulose-based waste newspaper for solving organic pollution. Carbohydr. Polym. 136, 95–100 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.02
Li, N., Yue, Q.Y., Gao, B.Y., Xu, X., Su, R.D., Yu, B.J.: One-step synthesis of peanut hull/graphene aerogel for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Cleaner Prod. 207, 764–771 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.038
Jing, F., Ding, J.C., Zhang, T., Yang, D.Y., Qiu, F.X., Chen, Q.Y., Xu, J.C.: Flexible, versatility and superhydrophobic biomass carbon aerogels derived from corn bracts for efficient oil/water separation. Food Bioprod. Process. 115, 134–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2019.03.010
Huang, J.W., Li, D.D., Huang, L.H., Tan, S.A., Liu, T.: Bio-based aerogel based on bamboo, waste paper, and reduced graphene oxide for oil/water separation. Langmuir 38, 3064–3075 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02821
Baig, N., Alghunaimi, F.I., Saleh, T.A.: Hydrophobic and oleophilic carbon nanofiber impregnated styrofoam for oil and water separation: a green technology. Chem. Eng. J. 360, 1613–1622 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.042
Zhang, Z.T., Dai, G.C., Liu, Y., Fan, W.W., Yang, K.F., Li, Z.J.: A reusable, biomass-derived, and pH-responsive collagen fiber-based oil absorbent material for effective separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A 633, 127906 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127906
Zhai, Z.Z., Zheng, Y.X., Du, T.M., Tian, Z.S., Ren, B., Xu, Y.L., Wang, S.S., Zhang, L.H., Liu, Z.F.: Green and sustainable carbon aerogels from starch for supercapacitors and oil/water separation. Ceram. Int. 47, 22080–22087 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.229
Kuang, Y.D., Chen, C.J., Chen, G., Pei, Y., Pastel, G., Jia, C., Song, J.W., Mi, R.Y., Yang, B., Das, S., Hu, L.B.: Bioinspired solar-heated carbon absorbent for efficient cleanup of highly viscous crude oil. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1900162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201900162
Mahari, W.A.W., Waiho, K., Fazhan, H., Necibi, M.C.: Progress in valorisation of agriculture, aquaculture and shellfish biomass into biochemicals and biomaterials towards sustainable bioeconomy. Chemosphere 291, 133036 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133036
Yong, J.L., Huo, J.L., Chen, F., Yang, Q.: Oil/water separation based on the natural materials with super-wettability: recent advances. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 25140–25163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cp04009e
Wang, N., Deng, Z.W.: Synthesis of magnetic, durable and superhydrophobic carbon sponges for oil/water separation. Mater. Res. Bull. 115, 19–26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.03.007
Nematian, M., Keske, C., Ng’ombe, J.N.: A techno-economic analysis of biochar production and the bioeconomy for orchard biomass. Waste Manag. 135, 467–477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.09.014
Harsono, S.S., Grundman, P., Lau, L.H., Hansen, A., Salleh, M.A.M.: Energy balances, greenhouse gas emissions and economics of biochar production from palm oil empty fruit bunches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 77, 108–115 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2013.04.005
Osman, A.I.: Mass spectrometry study of lignocellulosic biomass combustion and pyrolysis with NOx removal. Renew. Energy 146, 484–496 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.155
Zhang, H., Zhao, T., Chen, Y., Hu, X., Xu, Y.: A sustainable nanocellulose-based superabsorbent from kapok fiber with advanced oil absorption and recyclability. Carbohydr. Polym. 278, 118948 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118948
Thinkohkaew, K., Rodthongkum, N., Ummartyotin, S.: Coconut husk (Cocos nucifera) cellulose reinforced poly vinyl alcohol-based hydrogel composite with control-release behavior of methylene blue. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 6602–6611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.04.051
Tian, F., Yang, Y., Wang, X.L., An, W.L., Zhao, X., Xu, S.M., Wang, Y.Z.: From waste epoxy resins to efficient oil/water separation materials via a microwave assisted pore-forming strategy. Mater. Horiz. 6, 1733–1739 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MH00541B
Kazaka, O., Eker, Y.R., Bingol, H., Tora, A.: Novel preparation of activated carbon by cold oxygen plasma treatment combined with pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 325, 564–575 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.05.107
Roy, P., Dias, G.: Prospects for pyrolysis technologies in the bioenergy sector: a review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 77, 59–69 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.136
Wang, T.T., Li, G.L., Yang, K.Q., Zhang, X.Y., Wang, K., Cai, J.J., Zheng, J.Y.: Enhanced ammonium removal on biochar from a new forestry waste by ultrasonic activation: characteristics, mechanisms and evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 778, 146295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146295
Xu, Y.H., Zhang, Z.D., Geng, X.F., Jin, J., Iqbal, M., Han, A., Ding, B., Liu, J.F.: Smart carbon foams with switchable wettability for fast oil recovery. Carbon 149, 242–247 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2019.04.039
Acknowledgements
The research work is funded by the Zhenjiang Key Research and Development Program (GY2021004), the Opening Project of Henan Province Key Laboratory of Water Pollution Control and Rehabilitation Technology (CJSP202205), Innovation and Practice fund of Jiangsu University Industrial Center (ZXJG202208), Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Water Treatment Technology and Materials.
Funding
Zhenjiang Key Research and Development Program, GY2021004, Xiaomeng Lv, Opening Project of Henan Province Key Laboratory of Water Pollution Control and Rehabilitation Technology, CJSP202205, Jun Liu, Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Water Treatment Technology and Materials, Innovation and Practice fund of Jiangsu University Industrial Center, ZXJG202208, Yun Zhang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Sam, E.K., Liu, J. et al. Biomass-Based/Derived Value-Added Porous Absorbents for Oil/Water Separation. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 3147–3168 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02112-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-023-02112-9