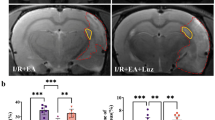
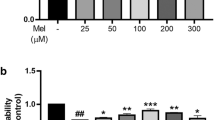
Abstract
Cerebral ischemic stroke is one of the main causes of death and long-term disability worldwide. However, the mechanism is unclear, and treatments are limited. In this study, we aimed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of agomelatine in a permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) model. Forty-eight male Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham, pMCAO + vehicle, pMCAO + agomelatine (40 mg/kg, i.p.), and pMCAO + melatonin (10 mg/kg, i.p.) groups. On day 1 after permanent cerebral ischemia, the animals were sacrificed, and brain tissues were collected for western blot analysis, and immunohistochemistry. Agomelatine treatment ameliorated inflammatory responses by decreasing the protein levels of trigger Toll-like receptor (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) pathway components together with nucleotide-binding domain, leucine-rich-containing family, pyrin domain–containing-3 (NLRP3) inflammasome components. In addition, agomelatine suppressed microglial activation and pyroptotic cell death after cerebral ischemic injury. These results suggest that agomelatine exerts an anti-inflammatory effect and attenuates brain damage by inhibiting microglial activation through the TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballester P, Martínez MJ, Inda MD, Javaloyes A, Richdale AL et al (2019) Evaluation of agomelatine for the treatment of sleep problems in adults with autism spectrum disorder and co-morbid intellectual disability. J Psychopharmacol 33:1395–1406. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881119864968
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR et al (2017) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135:e146–e603. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485
Braeuninger S, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B, Stoll G (2012) Focal cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol Biol 788:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-307-3_3
Bu J, Shi S, Wang HQ, Niu XS, Zhao ZF et al (2019) Acacetin protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via the NLRP3 signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res 14:605–612
Buoli M, Grassi S, Serati M, Altamura AC (2017) Agomelatine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. Expert Opin Pharmacother 18:1373–1379. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2017.1359257
Cai W, Zhang K, Li P, Zhu L, Xu J et al (2017) Dysfunction of the neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke and neurodegenerative diseases: an aging effect. Ageing Res Rev 34:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.006
Chumboatong W, Khamchai S, Tocharus C, Govitrapong P, Tocharus J (2020) Agomelatine protects against permanent cerebral ischaemia via the Nrf2-HO-1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 874:173028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173028
Chumboatong W, Thummayot S, Govitrapong P, Tocharus C, Jittiwat J, Tocharus J (2017) Neuroprotection of agomelatine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through an antiapoptotic pathway in rat. Neurochem Int 102:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.011
Fann DY, Lim YA, Cheng YL, Lok KZ, Chunduri P et al (2018) Evidence that NF-κB and MAPK signaling promotes NLRP inflammasome activation in neurons following ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol 55:1082–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0394-9
Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Parmar P, Norrving B, Mensah GA et al (2015) Update on the Global Burden of Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in 1990–2013: The GBD 2013 Study. Neuroepidemiology 45:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000441085
Freiesleben SD, Furczyk K (2015) A systematic review of agomelatine-induced liver injury. J Mol Psychiatry 3:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40303-015-0011-7
Gong Z, Pan J, Shen Q, Li M, Peng Y (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Neuroinflammation 15:242. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1282-6
Guaiana G, Gupta S, Chiodo D, Davies SJ, Haederle K et al (2013) Agomelatine versus other antidepressive agents for major depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:Cd008851. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008851.pub2
Hardeland R (2018) Melatonin and inflammation-story of a double-edged blade. J Pineal Res 65:e12525. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12525
Hong P, Gu RN, Li FX, Xiong XX, Liang WB et al (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome as a potential treatment in ischemic stroke concomitant with diabetes. J Neuroinflammation 16:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1498-0
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farzaneh M, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF (2017) Pathogenic mechanisms following ischemic stroke. Neurol Sci 38:1167–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2938-1
Li SJ, Zhang YF, Ma SH, Yi Y, Yu HY et al (2018) The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in stroke and central poststroke pain. Medicine (baltimore) 97:e11861. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011861
Li X, Shi MQ, Chen C, Du JR (2020) Phthalide derivative CD21 ameliorates ischemic brain injury in a mouse model of global cerebral ischemia: involvement of inhibition of NLRP3. Int Immunopharmacol 86:106714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106714
Ma C, Wang X, Xu T, Yu X, Zhang S et al (2019) Qingkailing injection ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and modulates the AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome signalling pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med 19:320. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2703-5
Mo Z, Tang C, Li H, Lei J, Zhu L et al (2020) Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents inflammation induced by acute cerebral infarction through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Life Sci 242:117133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117133
Plasencia-García BO, Romero-Guillena SL, Quirós-López A, Ruiz-Doblado S (2015) Agomelatine and migraine management: a successfully treated case series. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 5:243–245. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125315584869
Platnich JM, Muruve DA (2019) NOD-like receptors and inflammasomes: a review of their canonical and non-canonical signaling pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys 670:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.008
Savran M, Aslankoc R, Ozmen O, Erzurumlu Y, Savas HB et al (2020) Agomelatine could prevent brain and cerebellum injury against LPS-induced neuroinflammation in rats. Cytokine 127:154957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154957
Tsuchiya K (2020) Inflammasome-associated cell death: pyroptosis, apoptosis, and physiological implications. Microbiol Immunol 64:252–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/1348-0421.12771
Wang S, Yuan YH, Chen NH, Wang HB (2019) The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in Parkinson’s disease. Int Immunopharmacol 67:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.12.019
Xu L, He D, Bai Y (2016) Microglia-mediated inflammation and neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol 53:6709–6715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9593-4
Xu Y, Zhang J, Ma L, Zhao S, Li S et al (2018) The pathogenesis of necroptosis-dependent signaling pathway in cerebral ischemic disease. Behav Neurol 2018:6814393. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6814393
Ye Y, Jin T, Zhang X, Zeng Z, Ye B et al (2019) Meisoindigo protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and regulating microglia/macrophage polarization via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Cell Neurosci 13:553. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00553
Zhao C, Zhao W (2020) NLRP3 Inflammasome-a key player in antiviral responses. Front Immunol 11:211. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00211
Zhao H, Chen Z, Xie LJ, Liu GF (2018) Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol 55:4311–4319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0552-0
Funding
This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (grant number RSA6080025 to JT) and the Royal Golden Jubilee (PHD/0018/2559 WC; PHD/0011/2558 SK). This work was partially supported by Center for Research and Development of Natural Products for Health, Chiang Mai University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: WC JT. Data curation: WC SK JT. Funding acquisition: JT. Investigation: WC SK CT. Methodology: WC SK CT JT. Project administration: JT. Resources: PG JT. Visualization: WC JT. Writing—original draft: WC PG JT.
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chumboatong, W., Khamchai, S., Tocharus, C. et al. Agomelatine Exerts an Anti-inflammatory Effect by Inhibiting Microglial Activation Through TLR4/NLRP3 Pathway in pMCAO Rats. Neurotox Res 40, 259–266 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00447-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-021-00447-6