Abstract
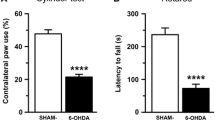
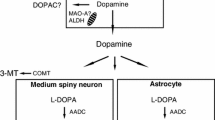
The object of the current study was to determine the effect of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA) on the in vivo striatal microdialysate levels of the respective dopamine and serotonin metabolites 3,4-dihydroxyphenlalanine (DOPAC) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) and hydroxyl radical level (HO•; 2,3- and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3- and 2,5-DHBA) in adult rats made parkinsonian by treatment at 3 days after birth with the neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA; 66.7 μg, base form, on each side; desipramine pretreatment, 1 h). Using HPLC/ED we found that in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats the basal striatal extraneuronal level of DOPAC was dramatically reduced and constituted only ~4.5% of referenced value (intact rats). Conversely, the striatal microdialysate level of 5-HIAA was elevated 2-fold in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Acute l-DOPA (60 mg/kg i.p.; S-carbidopa pretreatment, 12.5 mg/kg i.p., 30 min) produced a rapid rise in the extraneuronal DOPAC in both tested groups but to a much greater extent in intact rats (P < 0.05). Levels of HO• (spin-trap products of salicylate, 2,3- and 2,5-DHBA) were elevated 2-fold in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. However, l-DOPA did not enhance HO• production; acute 6-OHDOPA treatment (60 mg/kg i.p.) also did not alter HO• production. In summary, l-DOPA, an effective drug in ameliorating PD symptoms, did not acutely pose a risk for HO• generation in parkinsonian rats. We conclude that l-DOPA is not likely to generate reactive oxygen species in humans nor is l-DOPA likely to accelerate PD in humans.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger TW, Kaul S, Stricker EM, Zigmond MJ (1985) Hyperinnervation of the striatum by dorsal raphe afferents after dopamine-depleting brain lesions in neonatal rats. Brain Res 366:354–358
Chen JJ, Swope DM (2007) Pharmacotherapy for Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacotherapy 27:161S–173S
Ferger B, Teismann P, Mierau J (2000) The dopamine agonist pramipexole scavenges hydroxyl free radicals induced by striatal application of 6-hydroxydopamine in rats: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 883:216–223
Huang NK, Wan FJ, Tseng CJ, Tung CS (1997) Amphetamine induces hydroxyl radical formation in the striatum of rats. Life Sci 61:2219–2229
Ishida Y, Hashiguchi H, Todaka K, Ishizuka Y, Mitsuyama Y (2000) Repeated administration of high dose levodopa enhances hydroxyl radical production in the rat striatum denervated with 6-hydroxydopamine. Neurosci Lett 290:33–36
Kannari K, Tanaka H, Maeda T, Tomiyami M, Suda T, Matsunaga M (2000) Reserpine pretreatment prevents increases in extracellular striatal dopamine following L-DOPA administration in rats with nigrostriatal denervation. J Neurochem 74:263–269
Kostrzewa RM (1998) 6-Hydroxydopa, a catecholamine neurotoxin and endogenous excitotoxin at non-NMDA receptors. In: Kostrzewa RM (ed) Highly selective neurotoxins: basic, clinical applications. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 109–129
Kostrzewa RM, Gong L (1991) Supersensitized D1 receptors mediate enhanced oral activity after neonatal 6-OHDA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:677–682
Kostrzewa RM, Reader TA, Descarries L (1998) Serotonin neural adaptations to ontogenetic loss of dopamine neurons in rat brain. J Neurochem 70:889–898
Kostrzewa RM, Kostrzewa JP, Brus R (2000) Dopaminergic denervation enhances susceptibility to hydroxyl radicals in rat neostriatum. Amino Acids 19:183–199
Kostrzewa RM, Kostrzewa JP, Brus R (2002) Neuroprotective and neurotoxic roles of levodopa (L-DOPA) in neurodegenerative disorders relating to Parkinson’s disease. Amino Acids 23:57–63
Kostrzewa RM, Nowak P, Kostrzewa JP, Kostrzewa RA, Brus R (2005) Peculiarities of L-DOPA treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Amino Acids 28:157–164
Lew M (2007) Overview of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacotherapy 27:155S–160S
Miele M, Fillenz M (1996) In vivo determination of extracellular brain ascorbate. J Neurosci Methods 70:15–19
Müller T, Hefter H, Hueber R, Jost WH, Leenders KL, Odin P, Schwarz J (2004) Is levodopa toxic? J Neurol 251(Suppl 6):VI/44–46
Murer MG, Dziewczapolski G, Menalled LB, García MC, Agid Y, Gershanik O, Raisman-Vozari R (1998) Chronic levodopa is not toxic for remaining dopamine neurons, but instead promotes their recovery, in rats with moderate nigrostriatal lesions. Ann Neurol 43:561–575
Nowak P, Bortel A, Dabrowska J, Oswiecimska J, Drosik M, Kwiecinski A, Opara J, Kostrzewa RM, Brus R (2007) Amphetamine and mCPP effects on dopamine and serotonin striatal in vivo microdialysates in an animal model of hyperactivity. Neurotox Res 11:131–144
Nowak P, Bortel A, Dąbrowska J, Biedka I, Słomian G, Roczniak W, Kostrzewa RM, Brus R (2008) Histamine H3 receptor ligands modulate L-dopa-evoked behavioral responses and L-dopa-derived extracellular dopamine in dopamine-denervated rat striatum. Neurotox Res 13:231–240
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Pinheiro-Carrera M, Tomaz C, Huston JP, Dai H, Carey RJ (1994) L-dopa induced increases in brain uric acid in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease: a relationship to behavioral activation. Life Sci 55:991–997
Rocchitta G, Migheli R, Esposito G, Marchetti B, Desole MS, Miele E, Serra PA (2006) Endogenous melatonin protects L-DOPA from autoxidation in the striatal extracellular compartment of the freely moving rat: potential implication for long-term L-DOPA therapy in Parkinson’s disease. J Pineal Res 40:204–213
Snyder AM, Zigmond MJ, Lund RD (1986) Sprouting of serotonergic afferents into striatum after dopamine depleting lesions in intact rats. A retrograde transport and immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 245:274–281
Tanaka K, Ogawa N (2005) Dopamine agonist cabergoline inhibits levodopa-induced caspase activation in 6-OHDA-lesioned mice. Neurosci Res 51:9–13
Yamamoto BK, Zhu W (1998) The effects of methamphetamine on the production of free radicals and oxidative stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:107–114
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by NS 39272 to RM Kostrzewa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowak, P., Kostrzewa, R.A., Skaba, D. et al. Acute l-DOPA Effect on Hydroxyl Radical- and DOPAC-Levels in Striatal Microdialysates of Parkinsonian Rats. Neurotox Res 17, 299–304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9105-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9105-2