Abstract
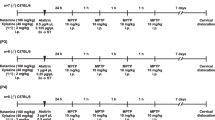
Dopamine oxidation in the pathway leading to neuromelanin formation generates the ortho-quinone aminochrome, which is potentially neurotoxic but normally rapidly converted by DT-diaphorase to nontoxic leukoaminochrome. However, when administered exogenously into rat striatum, aminochrome is able to produce damage to dopaminergic neurons. Because of a recent report that substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) tyrosine hydroxylase (T-OH) levels were unaltered by aminochrome when there was cell shrinkage of dopaminergic neurons along with a reduction in striatal dopamine release, the following study was conducted to more accurately determine the role of DT-diaphorase in aminochrome neurotoxicity. In this study, a low dose of aminochrome (0.8 nmol) with or without the DT-diaphorase inhibitor dicoumarol (0.2 nmol) was injected into the left striatum of rats. Intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA, 32 nmol) was used as a positive neurotoxin control in other rats. Two weeks later, there was significant loss in numbers of T-OH immunoreactive fibers in SNpc, also a loss in cell density in SNpc, and prominent apomorphine (0.5 mg/kg sc)-induced contralateral rotations in rats that had been treated with aminochrome, with aminochrome/dicoumarol, or with 6-OHDA. Findings demonstrate that neurotoxic aminochrome is able to exert neurotoxicity only when DT-diaphorase is suppressed—implying that DT-diaphorase is vital in normally suppressing toxicity of in vivo aminochrome, generated in the pathway towards neuromelanin formation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre P, Urrutia P, Tapia V, Villa M, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J, Núñez MT (2012) The dopamine metabolite aminochrome inhibits mitochondrial complex I and modifies the expression of iron transporters DMT1 and FPN1. Biometals 25:795–803
Arriagada C, Paris I, Sanchez de las Matas MJ, Martinez-Alvarado P, Cardenas S, Castañeda P, Graumann R, Perez-Pastene C, Olea-Azar C, Couve E, Herrero MT, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2004) On the neurotoxicity mechanism of leukoaminochrome o-semiquinone radical derived from dopamine oxidation: mitochondria damage, necrosis, and hydroxyl radical formation. Neurobiol Dis 16:468–477
Athauda D, Foltynie T (2015) The ongoing pursuit of neuroprotective therapies in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 11:25–40
Faunes M, Fernandez S, Gutierrez-Ibanez C, Iwaniuk AN, Wylie DR, Mpodozis J, Karten HJ, Marin G (2013) Laminar segregation of GABAergic neurons in the avian nucleus isthmi pars magnocellularis: a retrograde tracer and comparative study. J Comp Neurol 521:1727–1742
Faunes M, Oñate-Ponce A, Fernández-Collemann S, Henny P (2015) Excitatory and inhibitory innervation of the mouse orofacial motor nuclei: a stereological study. J Comp Neuro l524:738–758
Fuentes P, Paris I, Nassif M, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2007) Inhibition of VMAT-2 and DT-diaphorase induce cell death in a substantia nigra-derived cell line—an experimental cell model for dopamine toxicity studies. Chem Res Toxicol 20:776–783
Gutiérrez-Ibánez C, Iwaniuk AN, Lisney TJ, Faunes M, Marin GJ, Wylie DR (2012) Functional implications of species differences in the size and morphology of the isthmo optic nucleus (ION) in birds. PLoS One 7:e37816
Henny P, Brown MT, Northrop A, Faunes M, Ungless MA, Magill PJ, Bolam JP (2012) Structural correlates of heterogeneous in vivo activity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Nat Neurosci 15:613–619
Herrera A, Muñoz P, Paris I, Díaz-Veliz G, Mora S, Inzunza J, Hultenby K, Cardenas C, Jaña F, Raisman-Vozari R, Gysling K, Abarca J, Steinbusch HW, Segura-Aguilar J (2016) Aminochrome induces dopaminergic neuronal dysfunction: a new animal model for Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3583–3597
Herrera A, Muñoz P, Steinbusch HW, Segura-Aguilar J. (2017) Are Dopamine Oxidation Metabolites Involved in the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Nigrostriatal System in Parkinson's Disease? ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017 Mar 3. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00034
Huenchuguala S, Muñoz P, Zavala P, Villa M, Cuevas C, Ahumada U, Graumann R, Nore BF, Couve E, Mannervik B, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2014) Glutathione transferase mu 2 protects glioblastoma cells against aminochrome toxicity by preventing autophagy and lysosome dysfunction. Autophagy 10:618–630
Huenchuguala S, Muñoz P, Graumann R, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2016) DT-diaphorase protects astrocytes from aminochrome-induced toxicity. Neurotoxicology 55:10–12
Lindholm D, Mäkelä J, Di Liberto V, Mudò G, Belluardo N, Eriksson O, Saarma M (2015) Current disease modifying approaches to treat Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:1365–1379
Lozano J, Muñoz P, Nore BF, Ledoux S, Segura-Aguilar J (2010) Stable expression of short interfering RNA for DT-diaphorase induces neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1492–1496
Muñoz P, Segura-Aguilar J (2016) Commentary: a humanized clinically calibrated quantitative systems pharmacology model for hypokinetic motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Front Pharmacol 27:179
Muñoz P, Segura-Aguilar J. (2017) Why we cannot translate successful results to new therapies in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Pharmacol Transl Med. 1
Muñoz P, Huenchuguala S, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2012a) Dopamine oxidation and autophagy. Parkinsons Dis 920953
Muñoz P, Paris I, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Segura-Aguilar J (2012b) Overexpression of VMAT-2 and DT-diaphorase protects substantia nigra-derived cells against aminochrome neurotoxicity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1125–1136
Muñoz P, Cardenas S, Huenchuguala S, Briceño A, Couve E, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2015) DT-diaphorase prevents aminochrome-induced alpha-synuclein oligomer formation and neurotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 145:37–47
Muñoz P, Paris I, Segura-Aguilar J (2016) Commentary: evaluation of models of Parkinson's disease. Front Neurosci 19:10–161
Olanow W, Bartus RT, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Kordower JH (2015) Trophic factors for Parkinson's disease: to live or let die. Mov Disord 30:1715–1724
Paris I, Perez-Pastene C, Cardenas S, Iturriaga-Vasquez P, Muñoz P, Couve E, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2010) Aminochrome induces disruption of actin, alpha-, and beta-tubulin cytoskeleton networks in substantia-nigra-derived cell line. Neurotox Res 18:82–92
Paris I, Muñoz P, Huenchuguala S, Couve E, Sanders LH, Greenamyre JT, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2011) Autophagy protects against aminochrome-induced cell death in substantia nigra-derived cell line. Toxicol Sci 121:376–388
Park A, Stacy M (2015) Modifying drugs in Parkinson's disease. Drugs 75:2065–2071
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, CA
Segura-Aguilar J (2016d) New preclinical model are required to discover neuroprotective compound in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Res pii S1043-6618(16):31198–31197
Segura-Aguilar J, Kostrzewa RM (2015) Neurotoxin mechanisms and processes relevant to Parkinson's disease: an update. Neurotox Res 27:328–354
Segura-Aguilar J, Metodiewa D, Welch CJ. (1998) Metabolic activation of dopamine o-quinones to osemiquinones by NADPH cytochrome P450 reductase may play an important role in oxidative stress and apoptotic effects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1381:1-6
Segura-Aguilar J, Lind C (1989) On the mechanism of the Mn3(+)-induced neurotoxicity of dopamine: prevention of quinone-derived oxygen toxicity by DT-diaphorase and superoxide dismutase. Chem Biol Interact 72:309–324
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P, Ferrari E, Zecca L, Zucca FA (2014) Protective and toxic roles of dopamine in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 129:898–915
Segura-Aguilar J, Muñoz P, Paris I (2016a) Aminochrome as new preclinical model to find new pharmacological treatment that stop the development of Parkinson's disease. Curr Med Chem 23:346–359
Segura-Aguilar J, Paris I, Muñoz P (2016b) The need of a new and more physiological preclinical model for Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:1381–1382
Segura-Aguilar J (2016c) New preclinical model are required to discover neuroprotective compound in Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Res pii S1043-6618(16):31198–31197
West MJ, Slomianka L, Gundersen HJG (1991) Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat Rec 231:482–497
Williams A (1986) MPTP toxicity: clinical features. J Neural Transm Suppl 20:5–9
Xiong R, Siegel D, Ross D (2014) Quinone-induced protein handling changes: implications for major protein handling systems in quinone-mediated toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:285–295
Zafar KS, Siegel D, Ross D (2006) A potential role for cyclized quinones derived from dopamine, DOPA, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in proteasomal inhibition. MolPharmacol 70:1079–1086
Zecca L, Fariello R, Riederer P, Sulzer D, Gatti A, Tampellini D (2002) The absolute concentration of nigral neuromelanin, assayed by a new sensitive method, increases throughout the life and is dramatically decreased in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett 510:216–220
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Ali Jahanshahi (Postdoctoral Fellow at Maastricht University), João Oliveira (PhD student at Maastricht University) and Denise Hermes, and Hellen Steinbusch for all the technical support and guidance.
This work was supported by FONDECYT no. 1100165 (JSA), University of Chile ENL014/14 (JSA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera-Soto, A., Díaz-Veliz, G., Mora, S. et al. On the Role of DT-Diaphorase Inhibition in Aminochrome-Induced Neurotoxicity In Vivo. Neurotox Res 32, 134–140 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9719-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-017-9719-8