Abstract
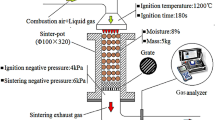
Reducing NOx emission of iron ore sintering process in a cost effective manner is a challenge for the iron and steel industry at present. Effects of the proportion of mill scale and coke breeze on the NOx emission, strength of sinter, and sinter indexes were studied by combustion and sinter pot tests. Results showed that the peak value of NO concentration, total of NO emission, and fuel-N conversion rate gradually decreased as the proportions of the mill scale increased because NO was reduced to N2 by Fe3O4, FeO, and Fe in the mill scale. The strength of sinter reached the highest value at 8.0wt% mill scale due to the formation of minerals with low melting point. The fuel-N conversion rate slightly fluctuated and total NOx emission significantly decreased with the decreased proportions of coke breeze because CO formation and content of N element in the sintered mixture decreased. However, the sinter strength also decreased due to the decrease in the amount of the melting minerals. Furthermore, results of the sinter pot tests indicated that NOx emission decreased. The sinter indexes performed well when the proportions of mill scale and coke breeze were 8.0wt% and 3.70wt% respectively in the sintered mixture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Qie, C.X. Zhang, H.F. Wang, X.P. Li, and X.Y. Shi, Analysis of emission situation and emission reduction technology of typical sintering flue gas pollutants, Sintering Pelletizing, 41(2016), No. 6, p. 59.
Y.D. Su, X.W. Li, and X.H. Fan, Research progress of NOx reduction technology in sintering process, Sintering Pelletizing, 38(2013), No. 6, p. 41.
S.L. Wu, Z.G. Que, B. Su, and Y.Z. Zhang, Research progress of the “in-bed-de NOx” technology in iron ore sintering, J. Eng. Stud., 9(2017), No. 1, p. 61.
B.J. Yan, Y. Xing, P. Lu, W. Su, B. Jiang, and X.X. Cui, A critical review on the research progress of multi-pollutant collaborative control technologies of sintering flue gas in the iron and steel industry, Chin. J. Eng., 40(2018), No. 7, p. 767.
X.M. Yan, Y.R. Li, T.Y. Zhu, and F. Qi, Review of emission and simultaneous control of multiple pollutants from iron-steel sintering flue gas, J. Environ. Eng. Technol., 5(2015), No. 2, p. 85.
H.L. Zhang, Q. Shi, H.M. Long, J.X. Li, T.J. Chun, and Z.F. Gao, Analysis of NOx removal process in sintering flue gas, Iron Steel, 52(2017), No. 5, p. 100.
G. Suzuki, R. Ando, H. Yoshikoshi, Y. Yamaoka, and S. Nagaoka, A study of the reduction of NOx in the waste gas from sinter plant, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 61(1975), No. 13, p. 2775.
H. Hu, H. Huang, Z.W. Zeng, J.L. Zhang, S. Annanurov, and Q.Z. Zhao, The formation of NOx during sintering, Eneggy Sources A, 39(2017), No. 12, p. 1228.
C.B. Xu, S.L Wu, and D.Q. Cang, Numerical modeling of NO formation during packed-bed combustion of coke granules, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing, 7(2000), No. 4, p. 261.
Y. Hida, M. Sasaki, T. Enokido, Y. Umezu, T. Iida, and S. Uno, Effect of the existing state of coke breeze in quasi-particles of raw mix on coke combustion in the sintering process, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 68(1982), No. 3, p. 400.
E. Kasai and Y. Omori, Combustion rate of coke at different existing states prepared by fine alumina, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 72(1986), No. 10, p. 1537.
P.L. Hou, S.M. Choi, W. Yang, E.S. Choi, and H.J. Kang, Application of intra-particle combustion model for iron ore sintering bed, Mater. Sci. Appl., 2(2011), No. 5, p. 370.
K.I. Ohno, K. Noda, K. Nishioka, T. Maeda, and M. Shimizu, Combustion rate of coke in quasi-particle at iron ore sintering process, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 101(2015), No. 3, p. 184.
P.N. Ma, M. Cheng, M.X. Zhou, Y.W. Li, and H. Zhou, Combustion characteristics of different types of quasi-particles in iron ore sintering process, Chin. J. Eng., 41(2019), No. 3, p. 316.
J. Pan, Theoretical and Process Studies of the Abatement of Flue Gasemissions during Iron Ore Sintering [Dissertation], Central South University of Technology, Changsha, 2007.
Z.G. Que, J.S. Wang, X.B. Ai, and S.L. Wu, Reduction of NOx emission in sintering process based on optimization of solid fuels particle size, China Metall., 29(2019), No. 6, p. 8.
S.L. Wu, Y.Z. Zhang, B. Su, X.M. Wang, and L. Zhang, Analysis of main factors affecting NOx emissions in sintering process, Chin. J. Eng., 39(2017), No. 5, p. 693.
Z.G. Que, S.L. Wu, G.L. Zhang, B. Su, and Y.Z. Zhang, Effect of mill scale adding methods on NOx emission of coke combustion during iron ore sintering, [in] AISTech and ICSTI 2015, Cleveland, 2015, p. 1406.
E. Kasai, S.L. Wu, T. Sugiyama, S. Inaba, and Y. Omori, Combustion rate and NO emission during combustion of coke granules in packed beds, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 78(1992), No. 7, p. 1005.
Z.G. Que, S.L. Wu, and X.B. Ai, To reduce NOx ermssion based on optimizing the existing states of coarse coke breeze during iron ore sintering process, Chin. J. Eng., 42(2020), No. 2, p. 163.
M.S. Lee and S.C. Shim, Influence of lime/limestone addition on the SO2 and NO formation during the combustion of coke pellet, ISIJ Int., 44(2004), No. 3, p. 470.
K. Katayama and S. Kasama, Influence of lime coating coke on NOx concentration in sintering process, ISIJ Int., 56(2016), No. 9, p. 1563.
M.Y. Gan, Z.N. Wei, C.G. Shi, H. Liu, M.F. Zhu, and T.J. Chun, Influences of fuel modified using burnt lime on NOx emission in burning and sintering process, J. Iron Steel Res., 31(2019), No. 9, p. 816.
Y.G. Chen, Z.C. Guo, Z. Wang, and G.S. Feng, NOx reduction in the sintering process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 16(2009), No. 2, p. 143.
Y.G. Chen, Z.C. Guo, and G.S. Feng, NOx reduction by coupling combustion with recycling flue gas in iron ore sintering process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 18(2011), No. 4, p. 390.
M. Gan, X.H. Fan, W. Lv, X.L. Chen, Z.Y. Ji, T. Jiang, Z.Y. Yu, and Y. Zhou, Fuel pre-granulation for reducing NOx emissions from the iron ore sintering process, Powder Technol., 301(2016), p. 478.
W. Lv, X.H. Fan, X.B. Min, M. Gan, X.L. Chen, and Z.Y. Ji, Formation of nitrogen mono oxide (NO) during iron ore sintering process, ISIJ Int., 58(2018), No. 2, p. 236.
Z.Y. Yu, X.H. Fan, M. Gan, and X.L. Chen, Effect of Ca-Fe oxides additives on NOx reduction in iron ore sintering, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 24(2017), No. 12, p. 1184.
K. Morioka S. Inaba, M. Shimizu, K. Ano, and T. Sugiyama, Primary application of the “in-bed-deNOx” process using Ca-Fe oxides in iron ore sintering machines, ISIJ Int., 40(2000), No. 3, p. 280.
W. Xiong, J.Y. Liao, X.G. Bi, and G.F. Zhou, Experiment study of the de-NOx in sintering waste gas, Sintering Pelletizing, 32(2007), No. 1, p. 12.
S.L. Wu, T. Sugiyama, K. Morioka, E. Kasai, and Y. Omori, Elimination reaction of NO gas generated from coke combustion in iron ore sinter bed, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 80(1994), No. 4, p. 276.
B.V. Reddy and S.N. Khanna, Self-stimulated NO reduction and CO oxidation by iron oxide clusters, Phys. Rev. Lett., 93(2004), No. 6, art. No. 068301.
E. Kasai, T. Sugiyama, and Y. Omori, Reduction of the amount of nitrogen oxides formed during sintering by using coke prepared from the mixture of coal and iron ore, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 80(1994), No. 4, p. 282.
M. Nakano, T. Yamakawa, N. Hayakawa, and M. Nagabuchi, Effects of metallic iron bearing resources on iron ore sintering, ISIJ Int., 38(1998), No. 1, p. 16.
S.L. Wu, G.L. Zhang, S.G. Chen, and B. Su, Influencing factors and effects of assimilation characteristic of iron ores in sintering process, ISIJ Int., 54(2014), No. 3, p. 582.
G.L. Zhang, S.L. Wu, B. Su, Z.G. Que, C.G. Hou, and Y. Jiang, Influencing factor of sinter body strength and its effects on iron ore sintering indexes, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 22(2015), No. 6, p. 553.
C.C. Yang, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, and Y. Shi, Some basic properties of granules from ore blends consisting of ultrafine magnetite and hematite ores, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 26(2019), No. 8, p. 953.
F. Zhang, D.Q. Zhu, J. Pan, Y.P. Mo, and Z.Q. Guo, Improving the sintering performance of blends containing Canadian specularite concentrate by modifying the binding medium, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 25(2018), No. 6, p. 598.
S.L. Wu, B. Su, Y.H. Qi, Y. Li, and B.B. Du, Major melt formation characteristic factor analysis of iron ore liquid phase fluidity during the sintering process, Chin. J. Eng., 40(2018), No. 3, p. 321.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904127), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (No. 20192BAB216018), and the research and development Project (No. 2018-YYB-05) and collaborative innovation Project (No. 2018-XTPH1-05) of Jiangxi Academy of Sciences, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Que, Zg., Ai, Xb. & Wu, Sl. Reduction of NOx emission based on optimized proportions of mill scale and coke breeze in sintering process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 28, 1453–1461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2103-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2103-3