Abstract
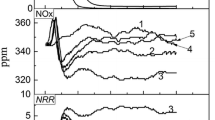
A new process called ‘NO x reduction by coupling combustion with recycling flue gas (RCCRF)’ was proposed to decrease NO x emission during the iron ore sintering process. The simulation test of NO x reduction was performed over sintered ore and in the process of coke combustion. Experimentally, NO x reduction was also carried out by sintering pot test. For sintered ore, the amount of NO x emission is reduced by 15wt%–25wt% at 400–550°C using 2.0vol% H2 or 2.0vol% CO, or reduced by 10wt%–30wt% at 560–720°C using 0.15vol% NH3. NO x reduction is around 10wt% by coupling combustion of pyrolysis gas and coke, or around 16wt% by recycling flue gas into coke combustion. By RCCRF, the maximum NO x reduction ratio is about 23wt% in coke combustion experiment and over 40wt% in sintering pot test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.X. Su, Y.R. Mao, and Z. Xu, Technologies of Controlling NO x Emission during Coal Combustion, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2005, p.11.
M. Fukutome, I. Hanamizu, T. Kodama, and N. TsuboiI, Sintering Method for Decreasing Nitrogen Oxide, Japanese Patent, 55014862(A), 1980-02-01.
M.S. Lee and S.C. Shim, Influence of lime/limestone addition on the SO2 and NO formation during the combustion of coke pellet, ISIJ Int., 44(2004), No.3, p.470.
C.L. Mo, C.S. Teo, I. Hamilton, and J. Morrison, Admixing hydrocarbons in raw mix to reduce NOx emission in iron ore sintering process, ISIJ Int., 37(1997), No.4, p.350.
K. Morioka, S. Inaba, M. Shimizu, K. Ano, and T. Sugiyama, Primary application of the ‘In-bed-deNOx’ process using Ca-Fe oxides in iron ore sintering machines, ISIJ Int., 40(2000), No.3, p.280.
C.G. Jin, H.G. Su, and L.J. Nam, SOx and NOx Reducing Method of Sintering Discharging Gas, Korean Patent, 20020040506(A), 2002-05-30.
J.H. Li, G.W. Xu, L.D. Yang, et al., A Coal Combustion Method of Suppressing NO x Formation and Its Application on Coal Furnace, Chinese Patent, 95102081.1, 1995-10-25.
A.N. Hayhurst and A.D. Lawrence, The reduction of the nitrogen oxides NO and N2O to molecular nitrogen in the presence of iron, its oxides and carbon monoxide in a hot fluidized bed, Combust. Flame, 110(1997), No.3, p.351.
B. Olanders and D. Strömberg, Reduction of nitric oxide over magnesium oxide and dolomite at fluidized bed conditions, Energy Fuels, 9(1995), No.4, p.680.
W. Wittler, K. Schütte, G. Rotzoll, and K. Schügerl, Heterogeneous reduction of nitric oxide by carbon monoxide on quartz surfaces, Fuel, 67(1988), No.3, p.438.
G.J. Zijlma, A.D. Jensen, J.E. Johnsson, and C.M. van den Bleek, NH3 oxidation catalysed by calcined limestone: a kinetic study, Fuel, 81(2002), No.14, p.1871.
T. Furusawa, M. Kyama, and M. Tsujimura, Nitric oxide reduction by carbon monoxide over calcined limestone enhanced by simultaneous sulphur retention, Fuel, 64(1985), No.3, p.413.
J.D. He, W.L. Song, S.Q. Gao, et al., Experimental study of the reduction mechanisms of NO emission in decoupling combustion of coal, Fuel Process. Technol., 87(2006), No.9, p.803.
T. Suzuki, T. Kyotani, and A. Tomita, Study on the carbon-nitric oxide reaction in the presence of oxygen, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 33(1994), No.11, p.2840.
M.J. Illán-Gómez, A. Linares-Solano, C. Salinas-Martínez de Lecea, and J.M. Calo, NO reduction by activated carbons: 1. The role of carbon porosity and surface area, Energy Fuels, 7(1993), No.1, p.146.
M.T. Izquierdo and B. Rubio, Influence of char physicochemical features on the flue gas nitric oxide reduction with chars, Environ. Sci. Technol., 32(1998), No.24, p.4017.
C.K.S. Lai, W.A. Peters, and J.P. Longwell, Reduction of nitric oxide by coke over calcium oxide, Energy Fuels, 2(1988), No.4, p.586.
H. Teng, Y.F. Hsu, and Y.T. Tu, Reduction of NO with NH3 over carbon catalysts: the influence of carbon surface structures and the global kinetics, Appl. Catal. B, 20(1999), No.2, p.145.
Y.Q. Hu, N. Kobayashi, and M. Hasatani, The reduction of recycled-NOx in coal combustion with O2/recycled flue gas under low recycling ratio, Fuel, 80(2001), No.13, p.1851.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50574085).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Yg., Guo, Zc. & Feng, Gs. NO x reduction by coupling combustion with recycling flue gas in iron ore sintering process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 18, 390–396 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-011-0452-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-011-0452-7