Abstract
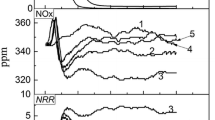
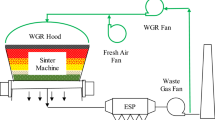
The pressure to reduce the emissions of the flue gas pollutants from iron ore sintering is enlarging increasingly. Based on the accumulation heat effect of sinter bed, the reasonable distribution of fuel in sinter bed was identified through the calculation of material balance and heat balance of raw materials. The sinter bed with a height of 300 mm was divided into three units, and the average available accumulation heat rate was about 38%. The reasonable coke powder addition ratio of each unit was 6.6%, 5.7%, and 5.2%, respectively, from the top to the bottom of sinter pot. The sinter-pot test results showed that the fuel consumption and the emissions of SO2, NOx, CO, and CO2 was reduced by 7.5 kg/t, 57.7%, 18.4%, 72.5%, and 31.7%, respectively, when compared with the conventional method in which the coke powder addition ratio of raw materials was 6.6%. Meanwhile, the sinter quality was improved.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu C Q, and Zhang C X, J Chin Rare Earth Soc 22 (2004) 588 (in Chinese).
Xu B, Ph D Thesis (2011) (in Chinese).
Pan J, Zhu D Q, Xue Z X, Chun T J, and Ruan Z Y, Environ Chem 32 (2013) 1660 (in Chinese).
Jin Y L, Sinter Pellet 29 (2004) 6 (in Chinese).
Zhao C L, Wu T, Bo X, and Su Y, Environ Eng 32 (2014) 76 (in Chinese).
Zhao R Z, and Liang B R, The Desulphurization and Denitrification Technological Status of Sintering Flue Gases, in Proc of 2013 national sintering flue gas pollutants integrated treatment technology forum, The Chinese Society for Metals, Datong (2013) (in Chinese).
Liu H Q, Fu J X, Liu S Y, Xie X Y, and Yang X Y, Iron Steel 51 (2016) 74 (in Chinese).
Jiang T, Sintering and Pelletizing Productive and Technical Manual, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing (2014), p 92 (in Chinese).
Zhang J H, Xu N P, and Xie A G, Energy Metall Ind 21 (2002) 25 (in Chinese).
Song G L, Fu Z H, and Zhang Q, J Iron Steel Res 12 (2000) 61 (in Chinese).
Kpchko A K, Cmaib 1 (1979) 245 (in Russian).
Huang Z C, Jiang Y, Mao X M, Xu B, Guo Y F, and Jiang T, J Cenral South Univ (Sci Technol) 37 (2006) 884 (in Chinese).
Bai C G, Xie X, Qiu G B, Lv X W, Xu G, and Pu X D, J Chongqing Univ 31 (2008) 1002 (in Chinese).
Masaaki N, Kanji T, and Yoshiyuki M, ISIJ Int 55 (2015) 7.
Li F S, Zhang X J, Zhang J Y, and Tian W Y, J Central South Univ (Sci Technol) 46 (2015) 386 (in Chinese).
Zhang B, Zhou J M, and Li M, J CIESC 68 (2017) 1811 (in Chinese).
Huang X X, Fan X H, Chen X L, Zhao X Z, and Gan M, Ironmak Steelmak 2 (2018) 1.
Fu J Y, Jiang T, and Zhu D Q, Sintering and Pelletizing, Central South University of Technology Press, Changsha (1996), p 105 (in Chinese).
Miyer K, The Research of Iron Ore Spheric Agglomeration, Metallurgical Technology Press, Beijing (1980), p 112 (in Chinese).
Kasai E, Wu S, Sugiyama T, Inaba S, and Omori Y, Testo-to-Hagané 78 (1992) 51 (in Japanese).
Wu S, Sugiyama T, Morioka K, Kasai E, and Omori Y, Testo-to-Hagané 80 (1994) 276 (in Japanese).
Kasai E, and Saito F, Kagaku Kogaku Ronbunshu 20 (1994) 857 (in Japanese).
Umadevi T, Karthik P, Mahapatra P C, Prabhu M, and Ranjan M, Ironmak Steelmak 39 (2013) 180.
Mochόn J, Cores A, Ruizbustinza Í, Verdeja L F, Robla J I, and Garciacarcedo F, Dyna 81 (2014) 168.
Xu H F, Sinter Production, Chemical Industry Press, Beijng (2013), p 242 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant No. 2017YFB0304001; National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant No. 2017YFB0304301; National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51234003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qie, J.M., Zhang, C.X., Guo, Y.H. et al. Reducing the Sintering Flue Gas Pollutants Emissions Based on the Accumulation Heat Effect in Iron Ore Sintering Process. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 581–589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1456-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1456-z