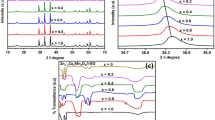
Abstract
A stable, efficient, and economical bifunctional electrolytic catalyst would be incredibly beneficial for the development of hydrogen production by electrocatalytic water splitting. In this study, we synthesized a novel MnS–MnO heterogeneous nanocube@N, S-doped carbon (MnS–MnO@NSC). MnS–MnO nanocubes possess rich heterogeneous interfaces and plentiful catalytic active sites to promote electrochemical reactions, while the N, S-doped carbon shell possesses excellent conductivity and catalytic properties and protects the nanocubes. MnS–MnO@NSC exhibited excellent electrochemical properties as an effective bifunctional electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in KOH solution. In the HER, the overpotential was as low as 124 mV at a current density of 10 mA·cm−2, while in the OER, it was only 340 mV at 100 mA·cm−2 under the same conditions. In addition, a MnS–MnO@NSC||MnS–MnO@NSC electrolyzer exhibited almost comparable activity and higher steadiness than those exhibited by the state-of-the-art Pt/C||RuO2/C system for full water splitting in KOH solution.
Graphical abstract

摘要
稳定、高效、经济的双功能电解催化剂有利于电催化水裂解制氢的发展, 在这项研究中, 我们合成了一种新型的氮硫掺杂碳包覆MnS–MnO异质纳米立方(MnS–MnO@NSC), 合成的MnS–MnO@NSC具有丰富的异质界面和催化活性位点以促进水电解反应, 氮硫掺杂的碳壳不仅具有良好的导电性和催化性能, 同时可以稳定MnS–MnO纳米立方体。MnS–MnO@NSC作为一种高效的双功能水分解电催化剂, 在氢氧化钾溶液中对析氢反应和析氧反应都表现出极好的电化学性能。在析氢反应中, 过电位低至124 mV就能达到电流密度10 mA·cm−2, 在析氧反应中, 过电位仅为340 mV就能实现电流密度为100 mA·cm−2。此外, 氢氧化钾溶液中MnS–MnO@NSC || MnS–MnO@NSC电解槽与最先进的Pt/C || RuO2/C体系进行水电解时表现出几乎相当的催化活性和更高的稳定性。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou YQ, Wolff N, Anaby A, Xie YJ, Milstein D. Ethylene glycol as an efficient and reversible liquid-organic hydrogen carrier. Nat Catal. 2019;2(5):415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0265-z.
Ding WL, Cao YH, Liu H, Wang AX, Zhang CJ, Zheng XR. In situ growth of NiSe@Co0.85Se heterointerface structure with electronic modulation on nickel foam for overall water splitting. Rare Met. 2021;40(6):1373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01541-y.
Liu YL, Luo XH, Zhou CL, Du S, Zhen DS, Chen B, Li J, Wu Q, Iru Y, Chen DC. A modulated electronic state strategy designed to integrate active HER and OER components as hybrid heterostructures for efficient overall water splitting. Appl Catal B. 2020;260:118197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118197.
Cheng Y, Zhou X, Pan Q, Zhang L, Cao Y, Qian T. Bimetallic active site nuclear-shell heterostructure enables efficient dual-functional electrocatalysis in alkaline media. Rare Met. 2023;42(9):3024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02300-5.
Guo D, Wang J, Zhang L, Chen XA, Wan ZX, Xi B. Strategic atomic layer deposition and electrospinning of cobalt sulfide/nitride composite as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Small. 2020;16(35):2002432. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202002432.
Kadam SR, Enyashin AN, Houben L, Bar-Ziv R, Bar-Sadan M. Ni-WSe2 nanostructures as efficient catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in acidic and alkaline media. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8(3):1403. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta10990k.
Zhou J, Wang F, Wang H, Hu S, Zhou W, Liu H. Ferrocene-induced switchable preparation of metal-nonmetal codoped tungsten nitride and carbide nanoarrays for electrocatalytic HER in alkaline and acid media. Nano Res. 2023;16(2):2085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-4901-6.
Chang CJ, Zhu YP, Wang JL, Chen HC, Tung CW, Chu YC, Chen HM. In situ X-ray diffraction and X-ray absorption spectroscopy of electrocatalysts for energy conversion reactions. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8(37):19079. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta06656g.
Deng BL, Guo LP, Lu Y, Rong HB, Cheng DC. Sulfur–nitrogen co-doped graphene supported cobalt–nickel sulfide rGO@SN-CoNi2S4 as highly efficient bifunctional catalysts for hydrogen/oxygen evolution reactions. Rare Met. 2022;41(3):911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-021-01828-8.
Li M, Zhu HY, Yuan Q, Li TY, Wang M, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Qin D, Guo W, Liu B, Yang X, Liu Y, Pan Y. Proximity electronic effect of Ni/Co diatomic sites for synergistic promotion of electrocatalytic oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33(4):2210867. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210867.
Chen H, Xu H, Song Z, Liu Y, Cui H, Gao J. Pressure-induced bimetallic carbon nanotubes from metal-organic frameworks as optimized bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting. Rare Met. 2023;42(1):155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02121-y.
Wang XQ, Huang G, Pan Z, Kang S, Ma S, Shen PK, Zhu JL. One-pot synthesis of Mn2P-Mn2O3 heterogeneous nanoparticles in a P, N -doped three-dimensional porous carbon framework as a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem Eng J. 2022;428:131190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131190.
Fu W, Lin Y, Wang M, Si S, Wei L, Zhao X, Wei Y. Sepaktakraw-like catalyst Mn-doped CoP enabling ultrastable electrocatalytic oxygen evolution at 100 mA cm in alkali media. Rare Met. 2022;41(9):3069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02006-0.
Jiang EJ, Li JQ, Li XL, Ali A, Wang GF, Ma SJ, Shen PK, Zhu JL. MoP-Mo2C quantum dot heterostructures uniformly hosted on a heteroatom-doped 3D porous carbon sheet network as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem Eng J. 2022;431:133719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133719.
Wang MQ, Ye C, Liu H, Xu M, Bao SJ. Nanosized metal phosphides embedded in nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanofibers for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2018;57(7):1963. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201710150.
Yan L, Zhang B, Zhu J, Liu Z, Zhang H, Li Y. Callistemon-like Zn and S codoped CoP nanorod clusters as highly efficient electrocatalysts for neutral-pH overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7(39):22453. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta08812a.
Duan H, Wang C, Li G, Tan H, Hu W, Cai L, Liu W, Li N, Ji Q, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yan W, Hu F, Zhang W, Sun Z, Qi Z, Song L, Wei S. Single-atom-layer catalysis in a MoS2 monolayer activated by long-range ferromagnetism for the hydrogen evolution reaction: beyond single-atom catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;133(13):7251. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202014968.
Hinnemann B, Moses PG, Bonde J, Jorgensen KP, Nielsen JH, Horch S, Chorkendorff I, Norskov JK. Biornimetic hydrogen evolution: MoS2 nanoparticles as catalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(15):5308. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.200525015.
Lu T, Li T, Shi D, Sun J, Pang H, Xu L, Yang J, Tang Y. In situ establishment of Co/MoS2 heterostructures onto inverse opal-structured N, S-doped carbon hollow nanospheres: interfacial and architectural dual engineering for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. SmartMat. 2021;2:591. https://doi.org/10.1002/smm2.1063.
Zhang SL, Guan BY, Lu XF, Xi SB, Du YH, Lou XW. Metal atom-doped Co3O4 hierarchical nanoplates for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Adv Mater. 2020;32(31):2002235. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202002235.
Liu Z, Xiao Z, Luo G, Chen R, Dong CL, Chen X, Cen J, Yang H, Wang Y, Su D, Li Y, Wang S. Defects-induced in-plane heterophase in cobalt oxide nanosheets for oxygen evolution reaction. Small. 2019;15(20):1904903. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201904903.
Liao C, Yang B, Zhang N, Liu M, Chen G, Jiang X, Chen G, Yang J, Liu X, Chan T, Lu Y, Ma R, Zhou W. Constructing conductive interfaces between nickel oxide nanocrystals and polymer carbon nitride for efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(40):1904020. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201904020.
Xu X, Liang H, Tang G, Hong Y, Xie Y, Qi Z, Xu B, Wang Z. Accelerating the water splitting kinetics of CoP microcubes anchored on a graphene electrocatalyst by Mn incorporation. Nanoscale Adv. 2019;1(1):177. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8na00261d.
Li Q, Xing Z, Wang D, Sun X, Yang X. In situ electrochemically activated CoMn-S@NiO/CC nanosheets array for enhanced hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 2016;6(5):2797. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b00014.
Kuo CH, Mosa IM, Poyraz AS, Biswas S, El-Sawy AM, Song WQ, Luo Z, Chen S, Rusling JF, He J, Suib SL. Robust mesoporous manganese oxide catalysts for water oxidation. ACS Catal. 2015;5(3):1693. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs501739e.
Li D, Baydoun H, Verani CN, Brock SL. Efficient water oxidation using CoMnP nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(12):4006. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b01543.
Swathi S, Yuvakkumar R, Kumar PS, Ravi G, Velauthapillai D. Hydrothermally synthesized alpha-MnS nanostructures for electrochemical water oxidation and photocatalytic hydrogen production. Fuel. 2021;303:121293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121293.
Rehman KU, Airam S, Song L, Gao J, Guo Q, Xiao Y, Zhang Z. MnS-nanoparticles-decorated three-dimensional graphene hybrid as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reaction. Catalysts. 2020;10(10):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10101141.
Zhang Y, Fu J, Zhao H, Jiang R, Tian F, Zhang R. Tremella-like Ni3S2/MnS with ultrathin nanosheets and abundant oxygen vacancies directly used for high speed overall water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ. 2019;257:117899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117899.
Zhu J, Sun M, Liu S, Liu X, Hu K, Wang L. Study of active sites on Se-MnS/NiS heterojunctions as highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7(47):26975. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta10860b.
Liu Y, Li L, Zhu J, Meng T, Ma L, Zhang H, Xu M, Jiang J, Li C. One-dimensional integrated MnS @ carbon nanoreactors hybrid: an alternative anode for full-cell Li-ion and Na-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(33):27911. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b05688.
Miao M, Hou R, Liang Z, Qi R, He T, Yan Y, Qi K, Liu H, Feng G, Xia B. Chainmail catalyst of ultrathin P- doped carbon shell- encapsulated nickel phosphides on graphene towards robust and efficient hydrogen generation. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(47):24107. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta09629e.
Yan H, Xie Y, Wu A, Cai Z, Wang L, Tian C, Zhang X, Fu H. Anion-modulated HER and OER activities of 3D Ni-V-based interstitial compound heterojunctions for high-efficiency and stable overall water splitting. Adv Mater. 2019;31(23):1901174. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201901174.
Qian G, Yu G, Lu J, Luo L, Wang T, Zhang C, Ku R, Yin S, Chen W, Mu S. Ultra-thin N-doped-graphene encapsulated Ni nanoparticles coupled with MoO2 nanosheets for highly efficient water splitting at large current density. J Mater Chem A. 2020;8(29):14545. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ta04388e.
Wang Y, Wu H, Huang L, Zhao H, Liu Z, Chen X, Liu H, Zhang Y. Hierarchically porous N, S-codoped carbon-embedded dual phase MnO/MnS nanoparticles for efficient lithium ion storage. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(13):7993. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b01156.
Liu B, Liu Z, Li D, Guo P, Liu D, Shang X, Lv M, He D. Nanoscale α-MnS crystallites grown on N-S Co-doped rGO as a long-life and high-capacity anode material of Li-ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;416:858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.230.
Camacho RAP, Wu AM, Jin XZ, Dong XF, Li XN, Huang H. Effective carbon constraint of MnS nanoparticles as high-performance anode of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2019;437:226931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.226931.
Chen Q, Cheng Y, Liu H, Zhang Q, Petrova V, Chen H, Liu P, Peng D, Liu M, Wang M. Hierarchical design of Mn2P nanoparticles embedded in N, P-codoped porous carbon nanosheets enables highly durable lithium storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(32):36247. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c11678.
Kaneti YV, Guo Y, Septiani NLW, Iqbal M, Jiang X, Takei T, Yuliarto B, Alothman ZA, Golberg D, Yamauchi Y. Self-templated fabrication of hierarchical hollow manganese-cobalt phosphide yolk-shell spheres for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Chem Eng J. 2021;405:126580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126580.
Chen W, Qin Z, McElhenny B, Zhang F, Chen S, Bao J, Wang Z, Song H, Ren Z. The effect of carbon quantum dots on the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction of manganese-nickel phosphide nanosheets. J Mate Chem A. 2019;7(37):21488. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ta06944e.
Gao Y, Lang Z, Yu F, Tan H, Yan G, Wang Y, Ma Y, Li Y. A Co2P/WC nano-heterojunction covered with N-doped carbon as highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chemsuschem. 2018;11(6):1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201702328.
Zhang J, Qu L, Shi G, Liu J, Chen J, Dai L. N, P-codoped carbon networks as efficient metal-free bifunctional catalysts for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;55(6):2270. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201510495.
Peng Z, Yu Y, Jiang D, Wu Y, Xia BY, Dong Z. N-doped carbon shell coated CoP nanocrystals encapsulated in porous N-doped carbon substrate as efficient electrocatalyst of water splitting. Carbon. 2019;144:464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.12.085.
Huang G, Hu M, Xu X, Alothman AA, Mushab MSS, Ma S, Shen PK, Zhu J, Yamauchi Y. Optimizing heterointerface of Co2P–CoxOy nanoparticles within a porous carbon network for deciphering superior water splitting. Small Struct. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/sstr.202200235.
Pan Y, Sun K, Liu S, Cao X, Wu K, Cheong WC, Chen Z, Wang Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Wang D, Peng Q, Chen C, Li Y. Core-shell ZIF-8@ZIF-67-derived CoP nanoparticle-embedded N-doped carbon nanotube hollow polyhedron for efficient overall water splitting. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(7):2610. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b12420.
Li PK, Zhu JG, Handoko AD, Zhang RF, Wang HT, Legut D, Wen X, Fu Z, Seh ZW, Zhang Q. High-throughput theoretical optimization of the hydrogen evolution reaction on MXenes by transition metal modification. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(10):4271. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta00173a.
Li M, Qian Y, Du J, Wu H, Zhang L, Li G, Li K, Wang W, Kang D. CuS nanosheets decorated with CoS2 nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(16):14016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssusche-meng.9b02519.
Zhang LC, Liang J, Yue L, Dong K, Li J, Zhao D, Li Z, Sun S, Luo Y, Liu Q, Cui G, Ali Alshehri A, Guo X, Sun X. Benzoate anions-intercalated NiFe-layered double hydroxide nanosheet array with enhanced stability for electrochemical seawater oxidation. Nano Res Energy. 2022. https://doi.org/10.26599/NRE.2022.9120028.
Dong X, Liu X, Shen PK, Zhu J. Phase Evolution of VC-VO heterogeneous particles to facilitate sulfur species conversion in Li−S batteries. Adv Funct Mater. 2023;33(3):2210987. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202210987.
Li W, Jiang Y, Li Y, Gao Q, Shen W, Jiang Y, He R, Li M. Electronic modulation of CoP nanoarrays by Cr-doping for efficient overall water splitting. Chem Eng J. 2021;425:130651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130651.
Zhang X, Zheng R, Jin M, Shi R, Ai Z, Amini A, Lian Q, Cheng C, Song S. NiCoSx@cobalt car bonate hydroxide obtained by surface sulfurization for efficient and stable hydrogen evolution at large current densities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(30):35647. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c07504.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51962002) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (No. 2022GXNSFAA035463).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XQ., Ma, XY., Wu, WZ. et al. MnS–MnO heterogeneous nanocube@N, S-doped carbon as a highly efficient bifunctional water splitting electrocatalyst. Rare Met. 43, 1977–1988 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02547-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02547-y