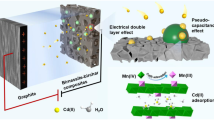
Abstract
Electrolytic manganese residue (EMR) is the waste slag generated from the electrolysis manganese industry. As a promising exploitable adsorbent, EMR has become a hot research topic. However, EMR’s low adsorption capacity has limited its applications as an efficient adsorbent. In this study, the EMR was mixed with serpentine and calcined (at 800 °C for 2 h) to prepare a composite adsorbent (S-EMR) with its specific surface area of 11.998 m2·g−1 (increased compared to the original EMR) and improved adsorption capacities for Cd2+ (98.05 mg·g−1) and Pb2+ (565.81 mg·g−1). Kinetic studies have shown that the pseudo-first-order kinetics (PSO) model could best describe the adsorption kinetics of S-EMR for Cd2+/Pb2+, implying that the chemisorption process is the rate-limiting step. The effects of different interfering ions on S-EMR’s adsorption for Cd2+/Pb2+ may be due to the difference in their electronegativity. Results of response surface methodology tests showed that pH had the highest influence on adsorption, and the removal efficiency of S-EMR reached 99.92% for Cd(II) and 94.00% for Pb(II). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses revealed that chemical precipitation was the predominant mechanism for Cd2+/Pb2+ removal, and the adsorption mechanisms were associated with ion exchange and electrostatic attraction. The results showed that S-EMR could be used as an effective adsorbent for the removal of Cd(II)/Pb(II) from water bodies, rendering dual benefits of pollution control and resource recovery.
Graphical abstract

摘要
电解锰渣是电解锰工业产生的废渣。 EMR作为一种具有开发潜力的吸附剂, 已成为研究的热点。 然而, EMR的低吸附量限制了其作为一种高效吸附剂的应用。 在这项研究中, 将EMR与蛇纹石混合并煅烧 (在800 oC下煅烧2 h), 以制备一种复合吸附剂 (S-EMR), 其比表面积 (SSA) 为11.998 m2·g−1 (与原EMR相比有所增加), 并提高了对Cd2+ (98.05 mg·g−1) 和Pb2+ (565.81 mg·g−1) 的吸收能力。动力学研究表明, 伪一级动力学模型(pseudo-first-order kinetics, PSO)能较好地描述S-EMR对Cd2+/Pb2+的吸附动力学, 表明化学吸附过程是一个限速步骤。 不同干扰离子对S-EMR吸附Cd2+/Pb2+的影响可能是由于它们的电负性不同所致。 响应面法测试结果表明, pH对S-EMR吸附性能影响最大, S-EMR对Cd(II)的去除率达到99.92%, 对Pb(II)的去除率达到94.00%。 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)分析表明, 化学沉淀法是去除Cd2+/Pb2+的主要机制, 吸附机制与离子交换和静电吸引有关。 结果表明, S-EMR可作为水体中Cd(II)/Pb(II)的有效吸附剂, 具有污染控制和资源回收双重效益。









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li J, Du DY, Peng QJ, Wu CJ, Lv KL, Ye HP, Chen SH, Zhan W. Activation of silicon in the electrolytic manganese residue by mechanical grinding-roasting. J Clean Prod. 2018;192:347.
Zhang Y, Liu X, Xu Y, Tang B, Wang Y. Preparation of road base material by utilizing electrolytic manganese residue based on Si-Al structure: mechanical properties and Mn2+ stabilization/solidification characterization. J Hazard Mater. 2020;390:122188.
Zhou C, Du B, Wang N, Chen Z. Preparation and strength property of autoclaved bricks from electrolytic manganese residue. J Clean Prod. 2014;84:701.
Wang J, Peng B, Chai L, Zhang Q, Liu Q. Preparation of electrolytic manganese residue–ground granulated blastfurnace slag cement. Powder Technol. 2013;241:12.
Xin B, Chen B, Duan N, Zhou C. Extraction of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by bioleaching. Biores Technol. 2011;102(2):1683.
Lan J, Sun Y, Chen X, Zhan W, Du Y, Zhang TC, Ye H, Du D, Hou H. Bio-leaching of manganese from electrolytic manganese slag by microbacterium trichothecenolyticum Y1: mechanism and characteristics of microbial metabolites. Biores Technol. 2021;319:124056.
Shu J, Liu R, Wu H, Liu Z, Sun X, Tao C. Adsorption of methylene blue on modified electrolytic manganese residue: kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2018;82:351.
Lan JR, Sun Y, Guo L, Du YG, Du DY, Zhang TC, Li J, Ye HP. Highly efficient removal of As(V) with modified electrolytic manganese residues (M-EMRs) as a novel adsorbent. J Alloy Compd. 2019;811:151973.
Li C, Zhong H, Wang S, Xue J, Zhang Z. Removal of basic dye (methylene blue) from aqueous solution using zeolite synthesized from electrolytic manganese residue. J Ind Eng Chem. 2015;23:344.
Ma M, Du Y, Bao S, Li J, Wei H, Lv Y, Song X, Zhang T, Du D. Removal of cadmium and lead from aqueous solutions by thermal activated electrolytic manganese residues. Sci Total Environ. 2020;748:141490.
Lan J, Sun Y, Huang P, Du Y, Zhan W, Zhang TC, Du D. Using electrolytic manganese residue to prepare novel nanocomposite catalysts for efficient degradation of Azo Dyes in Fenton-like processes. Chemosphere. 2020;252:126487.
Sun Z, Zheng L, Zheng S, Frost RL. Preparation and characterization of TiO2/acid leached serpentinite tailings composites and their photocatalytic reduction of Chromium(VI). J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;404:102.
Li Z, Huang P, Hu H, Zhang Q, Chen M. Efficient separation of Zn(II) from Cd(II) in sulfate solution by mechanochemically activated serpentine. Chemosphere. 2020;258:127275.
Cao CY, Liang CH, Yin Y, Du LY. Thermal activation of serpentine for adsorption of cadmium. J Hazard Mater. 2017;329:222.
Qin Q, Wang Q, Fu D, Ma J. An efficient approach for Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal using manganese dioxide formed in situ. Chem Eng J. 2011;172(1):68.
Yang T, Wang Y, Sheng L, He C, Sun W, He Q. Enhancing Cd(II) sorption by red mud with heat treatment: performance and mechanisms of sorption. J Environ Manag. 2020;255:109866.
Zhao DL, Chen SH, Yang SB, Yang X, Yang ST. Investigation of the sorption behavior of Cd(II) on GMZ bentonite as affected by solution chemistry. Chem Eng J. 2011;166(3):1010.
Zhang L, Tang S, He F, Liu Y, Mao W, Guan Y. Highly efficient and selective capture of heavy metals by poly(acrylic acid) grafted chitosan and biochar composite for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J. 2019;378:122215.
Feng HF, Yu YX, Jiang SQ, Shang J, Cheng Y, Wang L, Hao WC, Wang TM. Synthesis of magnetic core–shell iron nanochains for potential applications in Cr(VI) ion pollution treatment. Rare Met. 2021;40(1):1.
Hu QL, Wang LS, Yu NN, Zhang ZF, Zheng X, Hu XM. Preparation of Fe3O4@C@TiO2 and its application for oxytetracycline hydrochloride adsorption. Rare Met. 2020;39(11):1333.
Chen G, Shah KJ, Shi L, Chiang PC. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by synthetic mineral adsorbent: performance and mechanisms. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;409:296.
Aljerf L. High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite: kinetics and equilibrium study. J Environ Manage. 2018;225:120.
Weber W, Morris JC. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div. 1963;1:1.
Ye C, Ruan Q, Huang S, Li L. Study on the adsorption statics and kinetics of sisomicin on marcoporous weakly basic acid resins—LDF model and determination of effective diffusion coefficient. Front Sep Sci Technol. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812702623_0096.
Tan P, Sun J, Hu Y, Fang Z, Bi Q, Chen Y, Cheng J. Adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous single metal solutions on graphene oxide membranes. J Hazard Mater. 2015;297:251.
Ghorbani F, Kamari S. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of methyl orange adsorption by Fe-grafting sugar beet bagasse. Adsorpt Sci Technol. 2016;35(3–4):317.
Kamari S, Ghorbani F. Synthesis of magMCM-41 with rice husk silica as cadmium sorbent from aqueous solutions: parameters’ optimization by response surface methodology. Environ Technol. 2016;38(12):1562.
Li J, Sun P, Li J, Lv Y, Ye H, Shao L, Du D. Synthesis of electrolytic manganese residue-fly ash based geopolymers with high compressive strength. Constr Build Mater. 2020;248:118489.
Sirviö JA, Visanko M. Lignin-rich sulfated wood nanofibers as high-performing adsorbents for the removal of lead and copper from water. J Hazard Mater. 2020;383:121174.1.
Yang H, Lu M, Chen D, Chen R, Li L, Han W. Efficient and rapid removal of Pb2+ from water by magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2 core-shell nanoflower attached to carbon microtube: adsorption behavior and process study. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;563:218.
Zhao J, Liu J, Li N, Wang W, Nan J, Zhao Z, Cui F. Highly efficient removal of bivalent heavy metals from aqueous systems by magnetic porous Fe3O4-MnO2: adsorption behavior and process study. Chem Eng J. 2016;304:304737.
Zhou Y, Liu X, Xiang Y, Wang P, Zhang J, Zhang F, Wei J, Luo L, Lei M, Tang L. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: adsorption mechanism and modelling. Biores Technol. 2017;245:266.
Ho YS, McKay G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999;34(5):451.
Miretzky P, Muñoz C. Enhanced metal removal from aqueous solution by Fenton activated macrophyte biomass. Desalination. 2011;271(1):20.
Albadarin AB, Mangwandi C, Al-Muhtaseb AAH, Walker GM, Allen SJ, Ahmad MNM. Kinetic and thermodynamics of chromium ions adsorption onto low-cost dolomite adsorbent. Chem Eng J. 2012;179:193.
Gan M, Sun S, Zheng Z, Tang H, Sheng J, Zhu J, Liu X. Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) by AlPO4 modified biosynthetic Schwertmannite. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;356:986.
Smiljanić S, Smičiklas I, Perić-Grujić A, Šljivić M, Đukić B, Lončar B. Study of factors affecting Ni2+ immobilization efficiency by temperature activated red mud. Chem Eng J. 2011;168(2):610.
Zheng SA, Zheng X, Chen C. Leaching behavior of heavy metals and transformation of their speciation in polluted soil receiving simulated acid rain. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(11):e49664.
Zhou G, Luo J, Liu C, Chu L, Crittenden J. Efficient heavy metal removal from industrial melting effluent using fixed-bed process based on porous hydrogel adsorbents. Water Res. 2018;131:246.
Hadi P, Barford J, McKay G. Toxic heavy metal capture using a novel electronic waste-based material - mechanism, modeling and comparison. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(15):8248.
Yang GX, Jiang H. Amino modification of biochar for enhanced adsorption of copper ions from synthetic wastewater. Water Res. 2014;48:396.
Zhang F, Wang X, Yin D, Peng B, Tan C, Liu Y, Tan X, Wu S. Efficiency and mechanisms of Cd removal from aqueous solution by biochar derived from water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes). J Environ Manag. 2015;153:68.
Wang T, Liu W, Xiong L, Xu N, Ni J. Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes. Chem Eng J. 2013;215:366.
Peng ZD, Lin XM, Zhang YL, Hu Z, Yang XJ, Chen CY, Chen HY, Li YT, Wang JJ. Removal of cadmium from wastewater by magnetic zeolite synthesized from natural, low-grade molybdenum. Sci Total Environ. 2021;772(1):145355.
Sahu MK, Mandal S, Yadav LS, Dash SS, Patel RK. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of Cd(II) ion adsorption from aqueous solution by activated red mud. Desalin Water Treat. 2016;57(30):14251.
Yu S, Zhai L, Wang Y, Liu X, Xu L, Cheng L. Synthesis of magnetic chrysotile nanotubes for adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solution. J Environ Chem Eng. 2015;3(2):752.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Open-Up and Innovation Funds of Hubei Three Gorges Laboratory (No. SK211004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, MY., Ke, X., Liu, YC. et al. A novel electrolytic-manganese-residues-and-serpentine-based composite (S-EMR) for enhanced Cd(II) and Pb(II) adsorption in aquatic environment. Rare Met. 42, 346–358 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02042-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02042-w