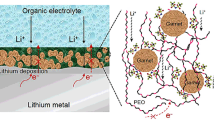
Abstract
The employment of lithium metal anode in rechargeable lithium batteries has been hindered by the safety concerns which are associated with the uncontrolled lithium dendrite growth and the unceasing side reactions with liquid electrolytes. In this work, we report that the use of Ti-containing solid electrolyte-coated separators can greatly enhance the cycle performances of lithium metal anode in cells using liquid electrolytes. The detailed morphologic studies indicate that more uniform lithium deposition is achieved in cells using Ti-containing solid electrolyte-coated separators than that using Al2O3-coated separators, which is likely due to the modified anode and electrolyte interfacial properties induced by the reactive nature of Ti-containing solid electrolytes with metallic lithium. This work demonstrates an effective strategy to enhance the homogeneity of lithium deposition, which leads to the stable cycling of lithium metal anode in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
Graphic abstract
Texture intensity decreases by the increase in the amount of alloying elements








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liang Y, Zhao CZ, Yuan H, Chen Y, Zhang W, Huang JQ, Yu D, Liu Y, Titirici MM, Chueh YL, Yu H, Zhang Q. A review of rechargeable batteries for portable electronic devices. Inf Mater. 2019;1(1):6.
Wu J, Liu P, Hu Y, Li H. Calculation on energy densities of lithium ion batteries and metallic lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Sci and Technol. 2016;5(4):443.
Ma L, Cui J, Yao S, Liu X, Luo Y, Shen X, Kim JK. Dendrite-free lithium metal and sodium metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2020;27:522.
Aurbach D, Zinigard E, Yaron C, Teller H. A short review of failure mechanisms of lithium metal and lithiated graphite anodes in liquid electrolyte solutions. Solid State Ion. 2002;148(3):405.
Wu X, Pan K, Jia M, Ren Y, He H, Zhang L, Zhang S. Electrolyte for lithium protection: from liquid to solid. Green Energy Environ. 2019;4(4):360.
Liang Y, Zhao J, Han Z, Yu H. Application of lithium rare metal in rechargeable batteries. Chin J Rare Met. 2019;43(11):1187.
Li T, Liu H, Shi P, Zhang Q. Recent progress in carbon/lithium metal composite anode for safe lithium metal batteries. Rare Met. 2018;37(6):449.
Liu H, Cheng XB, Jin Z, Zhang R, Wang G, Chen LQ, Liu QB, Huang JQ, Zhang Q. Recent advances in understanding dendrite growth on alkali metal anodes. Energy Chem. 2019;1(1):10003.
Zhang X, Wang A, Liu X, Luo J. Dendrites in lithium metal anodes: suppression, regulation, and elimination. Acc Chem Res. 2019;52(11):3223.
Zhang X-Q, Cheng X-B, Chen X, Yan C, Zhang Q. Fluoroethylene carbonate additives to render uniform Li deposits in lithium metal batteries. Adv Funct Mater. 2017;27(10):1605989.
Ma Y, Zhou Z, Li C, Wang L, Wang Y, Cheng X, Zuo P, Du C, Huo H, Gao Y, Yin G. Enabling reliable lithium metal batteries by a bifunctional anionic electrolyte additive. Energy Storage Mater. 2018;11:197.
Chen D, Tan H, Rui X, Zhang Q, Feng Y, Geng H, Li C, Huang S, Yu Y. Oxyvanite V3O5: a new intercalation-type anode for lithium-ion battery. Informat. 2019;1(2):251.
Lei M, You Z, Ren L, Liu X, Wang J. Construction of copper oxynitride nanoarrays with enhanced lithiophilicity toward stable lithium metal anodes. J Power Sources. 2020;463:228191.
Lei M, Wang J, Ren L, Nan D, Shen C, Xie K, Liu X. Highly lithiophilic cobalt nitride nanobrush as a stable host for high-performance lithium metal anodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(34):30992.
Wang B, Lv R, Lan D. Preparation and electrochemical properties of Sn/C composites. Rare Met. 2019;38(10):996.
Hou Z, Zhang J, Wang W, Chen Q, Li B, Li C. Towards high-performance lithium metal anodes via the modification of solid electrolyte interphases. J Energy Chem. 2020;45:7.
Zhao CZ, Zhao BC, Yan C, Zhang XQ, Huang JQ, Mo Y, Xu X, Li H, Zhang Q. Liquid phase therapy to solid electrolyte–electrode interface in solid-state Li metal batteries: a review. Energy Storage Mater. 2020;24:75.
Wang P, Qu W, Song WL, Chen H, Chen R, Fang D. Electro-chemo-mechanical issues at the interfaces in solid-state lithium metal batteries. Adv Func Mater. 2019;29(27):1900950.
Shen Y, Zhang Y, Han S, Wang J, Peng Z, Chen L. Unlocking the energy capabilities of lithium metal electrode with solid-state electrolytes. Joule. 2018;2(9):1674.
Liu Y, Liu Q, Xin L, Liu Y, Yang F, Stach E, Xie J. Making Li-metal electrodes rechargeable by controlling the dendrite growth direction. Nat Energy. 2017;2:17083.
Na W, Lee AS, Lee JH, Hwang SS, Kim E, Hong SM, Koo CM. Lithium dendrite suppression with UV-curable polysilsesquioxane separator binders. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(20):12852.
Zhang F, Shen F, Fan Z, Ji X, Zhao B, Sun Z, Xuan Y, Han X. Ultrathin Al2O3-coated reduced graphene oxide membrane for stable lithium metal anode. Rare Metals. 2018;37(6):510.
Qiu J, Yang L, Sun G, Yu X, Li H, Chen L. A stabilized PEO-based solid electrolyte via a facile interfacial engineering method for a high voltage solid-state lithium metal battery. Chem Commun. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC01829E.
Liu Q, Yu Q, Li S, Wang S, Zhang L, Cai B, Zhou D, Li B. Safe LAGP-based all solid-state Li metal batteries with plastic super-conductive interlayer enabled by in situ solidification. Energy Storage Mater. 2020;25:613.
Zhao CZ, Chen PY, Zhang R, Chen X, Li BQ, Zhang XQ, Cheng XB, Zhang Q. An ion redistributor for dendrite-free lithium metal anodes. Sci Adv. 2018;4(11):3446.
Shi J, Xia Y, Han S, Fang L, Pan M, Xu X, Liu Z. Lithium ion conductive Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 based inorganic-organic composite separator with enhanced thermal stability and excellent electrochemical performances in 5 V lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources. 2015;273:389.
Liang T, Cao JH, Liang WH, Li Q, He L, Wu DY. Asymmetrically coated LAGP/PP/PVDF-HFP composite separator film and its effect on the improvement of NCM battery performance. R Soc Chem Adv. 2019;9(70):41151.
Zhu Y, He X, Mo Y. First principles study on electrochemical and chemical stability of solid electrolyte–electrode interfaces in all-solid-state Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4(9):3253.
Wenzel S, Leichtweiss T, Krüger D, Sann J, Janek J. Interphase formation on lithium solid electrolytes—an in situ approach to study interfacial reactions by photoelectron spectroscopy. Solid State Ion. 2015;278:98.
Chen R, Li Q, Yu X, Chen L, Li H. Approaching practically accessible solid-state batteries: stability issues related to solid electrolytes and interfaces. Chem Rev. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00268.
Wu J, Ling S, Yang Q, Li H, Xu X, Chen L. Forming solid electrolyte interphase in situ in an ionic conducting Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3-polypropylene (PP) based separator for Li-ion batteries. Chin Phys B. 2016;25(7):078204.
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFB0102004) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51822211, U1932220, U1964205, and Y5JC011E21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Z., Pan, HY., Wang, JY. et al. Enhancing cycle stability of Li metal anode by using polymer separators coated with Ti-containing solid electrolytes. Rare Met. 40, 1357–1365 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01494-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01494-2