Abstract
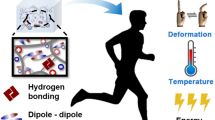
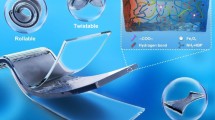
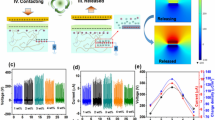
A flexible and stable power supply is essential to the rapid development of wearable electronic devices. In this work, a transparent, flexible, temperature-stable and ionogel electrode-based self-healing triboelectric nanogenerator (IS-TENG) was developed. The ionogel with excellent stretchability (1,012%), high ionic conductivity (0.3 S·m−1) and high-temperature stability (temperature range of −77 to 250 °C) was used as the electrode of the IS-TENG. The IS-TENG exhibited excellent transparency (92.1%) and stability. The output performance did not decrease when placed in a 60 °C oven for 48 h. In addition, the IS-TENG behaved like a stable output in the range of −20 to 60 °C. More importantly, the IS-TENG could also achieve self-healing of electrical performance at temperatures between −20 and 60 °C and its output can be restored to its original state after healing. When the single-electrode IS-TENG with an area of 3 cm × 3 cm was conducted under the working frequency of 1.5 Hz, the output values for open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, short-circuit transferred charge, and maximum peak power density were 189 V, 6.2 µA, 57 nC, and 2.17 W·m−2, respectively. The IS-TENG enables to harvest biomechanical energy, and drive electronic devices. Furthermore, the application of IS-TENGs as self-driven sensors for detecting human behavior was also demonstrated, showing good application prospects in the field of wearable power technology and self-driven sensing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, T.; Liu, M. M.; Dou, S.; Sun, J. M.; Cong, Z. F.; Jiang, C. Y.; Du, C. H.; Pu, X.; Hu, W. G.; Wang, Z. L. Triboelectric-nanogenerator-based soft energy-harvesting skin enabled by toughly bonded elastomer/hydrogel hybrids. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2818–2826.
Fan, F. R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4283–4305.
Li, H. B.; Lv, S. Y.; Fang, Y. Bio-inspired micro/nanostructures for flexible and stretchable electronics. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1244–1252.
Tee, B. C. K.; Wang, C.; Allen, R.; Bao, Z. N. An electrically and mechanically self-healing composite with pressure-and flexion-sensitive properties for electronic skin applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 825–832.
Wehner, M.; Truby, R. L.; Fitzgerald, D. J.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G. M.; Lewis, J. A.; Wood, R. J. An integrated design and fabrication strategy for entirely soft, autonomous robots. Nature 2016, 536, 451–455.
Jao, Y. T.; Yang, P. K.; Chiu, C. M.; Lin, Y. J.; Chen, S. W.; Choi, D.; Lin, Z. H. A textile-based triboelectric nanogenerator with humidity-resistant output characteristic and its applications in self-powered healthcare sensors. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 513–520.
Wen, Z.; Yeh, M. H.; Guo, H. Y.; Wang, J.; Zi, Y. L.; Xu, W. D.; Deng, J. N.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, C. G. et al. Self-powered textile for wearable electronics by hybridizing fiber-shaped nanogenerators, solar cells, and supercapacitors. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600097.
Xie, L. J.; Chen, X. P.; Wen, Z.; Yang, Y. Q.; Shi, J. H.; Chen, C.; Peng, M. F.; Liu, Y. N.; Sun, X. H. Spiral steel wire based fiber-shaped stretchable and tailorable triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable power source and active gesture sensor. Nano—Micro Lett. 2019, 11, 39.
Shi, Q. F.; He, T. Y. Y.; Lee, C. More than energy harvesting-combining triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible electronics technology for enabling novel micro-/nano-systems. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 851–871.
Fan, F. R.; Tian, Z. Q.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334.
Zhou, C. J.; Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, P.; Xie, X. K.; Shao, H. Y.; Shen, Q. Q.; Chen, X. P.; Liu, Y. N. et al. Flexible self-charging power units for portable electronics based on folded carbon paper. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4313–4322.
Li, X. J.; Jiang, C. M.; Zhao, F. N.; Lan, L. Y.; Yao, Y.; Yu, Y. H.; Ping, J. F.; Ying, Y. B. Fully stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting and self-powered sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 78–85.
Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zheng, H. C.; Shao, H. Y.; Xia, Y. J.; Chen, C.; Lan, H. W.; Xie, X. K. et al. Liquid-metal-based super-stretchable and structure-designable triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable electronics. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2027–2034.
Lv, P. L.; Shi, L.; Fan, C. Y.; Gao, Y. Y.; Yang, A. J.; Wang, X. H.; Ding, S. J.; Rong, M. Z. Hydrophobic ionic liquid gel-based triboelectric nanogenerator: Next generation of ultrastable, flexible, and transparent power sources for sustainable electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15012–15022.
Zi, Y. L.; Guo, H. Y.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M. H.; Hu, C. G.; Wang, Z. L. Harvesting low-frequency (< 5 Hz) irregular mechanical energy: A possible killer application of triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4797–4805.
Ye, C.; Xu, Q. F.; Ren, J.; Ling, S. J. Violin string inspired core-sheath silk/steel yarns for wearable triboelectric nanogenerator applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2020, 2, 24–33.
Das, P. S.; Chhetry, A.; Maharjan, P.; Rasel, M. S.; Park, J. Y. A laser ablated graphene-based flexible self-powered pressure sensor for human gestures and finger pulse monitoring. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 1789–1795.
Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Zuo, H.; Qian, S. H.; Guo, Y. F.; Sun, L. J.; Lei, D.; Wu, Q. L.; Zhu, B.; He, C. L. et al. A single integrated 3D-printing process customizes elastic and sustainable triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805108.
Wen, Z.; Yang, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Li, G. F.; Liu, Y. N.; Chen, C.; Shi, J. H.; Xie, L. J.; Jiang, H. X.; Bao, D. Q. et al. A wrinkled PEDOT: PSS film based stretchable and transparent triboelectric nanogenerator for wearable energy harvesters and active motion sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803684.
Pu, X.; Liu, M. M.; Chen, X. Y.; Sun, J. M.; Du, C. H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J. Y.; Hu, W. G.; Wang, Z. L. Ultrastretchable, transparent triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700015.
Parida, K.; Kumar, V.; Wang, J. X.; Bhavanasi, V.; Bendi, R.; Lee, P. S. Highly transparent, stretchable, and self-healing ionic-skin triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and touch applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702181.
Sun, L. J.; Huang, H. F.; Ding, Q. Y.; Guo, Y. F.; Sun, W.; Wu, Z. C.; Qin, M. L.; Guan, Q. B.; You, Z. W. Highly transparent, stretchable, and self-healable ionogel for multifunctional sensors, triboelectric nanogenerator, and wearable fibrous electronics. Adv. Fiber Mate., in press, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-021-00086-8.
Zhang, Y. J.; He, P.; Luo, M.; Xu, X. W.; Dai, G. Z.; Yang, J. L. Highly stretchable polymer/silver nanowires composite sensor for human health monitoring. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 919–926.
Chen, H. T.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X. L.; Zhang, H. X. Self-powered electronic skin based on the triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 252–268.
Deng, J. N.; Kuang, X.; Liu, R. Y.; Ding, W. B.; Wang, A. C.; Lai, Y. C.; Dong, K.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y. X.; Wang, L. L. et al. Vitrimer elastomer-based jigsaw puzzle-like healable triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705918.
Wu, C. S.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Guo, H. Y.; Wang, Z. L. Paper-based triboelectric nanogenerators made of stretchable interlocking kirigami patterns. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4652–4659.
Dong, K.; Wu, Z. Y.; Deng, J. N.; Wang, A. C.; Zou, H. Y.; Chen, C. Y.; Hu, D. M.; Gu, B. H.; Sun, B. Z.; Wang, Z. L. A stretchable yarn embedded triboelectric nanogenerator as electronic skin for biomechanical energy harvesting and multifunctional pressure sensing. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804944.
Lim, G. H.; Kwak, S. S.; Kwon, N.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. M.; Kim, S. W.; Lim, B. Fully stretchable and highly durable triboelectric nanogenerators based on gold-nanosheet electrodes for self-powered human-motion detection. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 300–306.
Yi, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. F.; Niu, S. M.; Li, S. M.; Liao, Q. L.; Xu, Y. L.; You, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Stretchable and waterproof self-charging power system for harvesting energy from diverse deformation and powering wearable electronics. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6519–6525.
Lai, Y. C.; Deng, J. N.; Niu, S. M.; Peng, W. B.; Wu, C. S.; Liu, R. Y.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Z. L. Electric eel-skin-inspired mechanically durable and super-stretchable nanogenerator for deformable power source and fully autonomous conformable electronic-skin applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10024–10032.
Chen, Y. H.; Pu, X.; Liu, M. M.; Kuang, S. Y.; Zhang, P. P.; Hua, Q. L.; Cong, Z. F.; Guo, W. B.; Hu, W. G.; Wang, Z. L. Shape-adaptive, self-healable triboelectric nanogenerator with enhanced performances by soft solid-solid contact electrification. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8936–8945.
Guan, Q. B.; Lin, G. H.; Gong, Y. Z.; Wang, J. F.; Tan, W. Y.; Bao, D. Q.; Liu, Y. N.; You, Z. W.; Sun, X. H.; Wen, Z. et al. Highly efficient self-healable and dual responsive hydrogel-based deformable triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13948–13955.
Bao, D. Q.; Wen, Z.; Shi, J. H.; Xie, L. J.; Jiang, H. X.; Jiang, J. X.; Yang, Y. Q.; Liao, W. Q.; Sun, X. H. An anti-freezing hydrogel based stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy harvesting at sub-zero temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 13787–13794.
Lai, Y. C.; Wu, H. M.; Lin, H. C.; Chang, C. L.; Chou, H. H.; Hsiao, Y. C.; Wu, Y. C. Entirely, intrinsically, and autonomously self-healable, highly transparent, and superstretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for personal power sources and self-powered electronic skins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904626.
Wang, L. Y.; Daoud, W. A. Hybrid conductive hydrogels for washable human motion energy harvester and self-powered temperature-stress dual sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104080.
Shuai, L. Y. Z.; Guo, Z. H.; Zhang, P. P.; Wan, J. M.; Pu, X.; Wang, Z. L. Stretchable, self-healing, conductive hydrogel fibers for strain sensing and triboelectric energy-harvesting smart textiles. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105389.
Chen, B. D.; Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, L. P.; Chen, X. Y.; He, C.; Xu, L.; Guo, H. Y.; Lin, P.; Li, D. et al. Three-dimensional ultraflexible triboelectric nanogenerator made by 3D printing. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 380–389.
Zhang, P. P.; Chen, Y. H.; Guo, Z. H.; Guo, W. B.; Pu, X.; Wang, Z. L. Stretchable, transparent, and thermally stable triboelectric nanogenerators based on solvent-free ion-conducting elastomer electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909252.
Mo, F. N.; Liang, G. J.; Meng, Q. Q.; Liu, Z. X.; Li, H. F.; Fan, J.; Zhi, C. Y. A flexible rechargeable aqueous zinc manganese-dioxide battery working at −20°C. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 706–715.
Armand, M.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Ohno, H.; Scrosati, B. Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 621–629.
Sun, L. J.; Chen, S.; Guo, Y. F.; Song, J. C.; Zhang, L. Z.; Xiao, L. J.; Guan, Q. B.; You, Z. W. Ionogel-based, highly stretchable, transparent, durable triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and motion sensing over a wide temperature range. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103847.
Ge, G.; Lu, Y.; Qu, X. Y.; Zhao, W.; Ren, Y. F.; Wang, W. J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. C. Muscle-inspired self-healing hydrogels for strain and temperature sensor. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 218–228.
Bai, Y. K.; Zhang, J. W.; Wen, D. D.; Yuan, B.; Gong, P. W.; Liu, J. M.; Chen, X. Fabrication of remote controllable devices with multistage responsiveness based on a NIR light-induced shape memory ionomer containing various bridge ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20723–20732.
Zhang, L. M.; He, Y.; Cheng, S. B.; Sheng, H.; Dai, K. R.; Zheng, W. J.; Wang, M. X.; Chen, Z. S.; Chen, Y. M.; Suo, Z. G. Self-healing, adhesive, and highly stretchable ionogel as a strain sensor for extremely large deformation. Small 2019, 15, 1804651.
Cao, Y.; Morrissey, T. G.; Acome, E.; Allec, S. I.; Wong, B. M.; Keplinger, C.; Wang, C. A transparent, self-healing, highly stretchable ionic conductor. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605099.
Tiwari, N.; Ho, F.; Ankit; Mathews, N. A rapid low temperature self-healable polymeric composite for flexible electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21428–21434.
Liu, Y. Q.; Sun, N.; Liu, J. W.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X. H.; Lee, S. T.; Sun, B. Q. Integrating a silicon solar cell with a triboelectric nanogenerator via a mutual electrode for harvesting energy from sunlight and raindrops. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2893–2899.
Wen, X. N.; Su, Y. J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. L.; Wang, Z. L. Applicability of triboelectric generator over a wide range of temperature. Nano Energy 2014, 4, 150–156.
Guan, Q. B.; Dai, Y. H.; Yang, Y. Q.; Bi, X. Y.; Wen, Z.; Pan, Y. Near-infrared irradiation induced remote and efficient self-healable triboelectric nanogenerator for potential implantable electronics. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 333–339.
Zhao, G. R.; Zhang, Y. W.; Shi, N.; Liu, Z. R.; Zhang, X. D.; Wu, M. Q.; Pan, C. F.; Liu, H. L.; Li, L. L.; Wang, Z. L. Transparent and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 302–310.
Hu, J.; Pu, X. J.; Yang, H. M.; Zeng, Q. X.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, D. Z.; Hu, C. G.; Xi, Y. A flutter-effect-based triboelectric nanogenerator for breeze energy collection from arbitrary directions and self-powered wind speed sensor. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 3018–3023.
Guo, Y. F.; Chen, S.; Sun, L. J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L. Z.; Lou, J. M.; You, Z. W. Degradable and fully recyclable dynamic thermoset elastomer for 3D-printed wearable electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009799.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51605109 and 61804103), the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2018GXNSFBA281052 and 2018GXNSFAA281296) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Nos. 2017M610346 and 2021T140494). The authors also acknowledge the support from the Collaborative Innovation Center of Suzhou Nano Science & Technology, the 111 Project and Joint International Research Laboratory of Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2021_3797_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Transparent, stretchable, temperature-stable and self-healing ionogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy collection
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, W., Liu, X., Li, Y. et al. Transparent, stretchable, temperature-stable and self-healing ionogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy collection. Nano Res. 15, 2060–2068 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3797-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3797-x