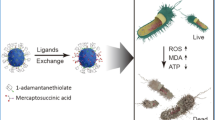
Abstract
Metallic silver (Ag) and its ability to combat infection have been known since ancient history. In the wake of nanotechnology advancement, silver’s efficacy to fight broad spectrum bacterial infections is further improved in the form of Ag nanoparticles (NPs). Recent studies have ascribed the broad spectrum antimicrobial properties of Ag NPs to dissociation of Ag+ ions from the NPs, which may not be entirely applicable when the size of Ag NPs decreases to the sub-2 nm range [denoted Ag nanoclusters (NCs)]. In this paper we report that ultrasmall glutathione (GSH)-protected Ag+-rich NCs (Ag+-R NCs for short, with a predominance of Ag+ species in the NCs) have much higher antimicrobial activities towards both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria than the reference NC, GSH-Ag0-R NCs. They have the same size and surface ligand, but with different oxidation states of the core silver. This interesting finding suggests that the undissociated Ag+-R NCs armed with abundant Ag+ ions on the surface are highly active in bacterial killing, which was not observed in the system of their larger counterpart, Ag NPs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J. W. History of the medical use of silver. Surg. Infect. 2009, 10, 289–292.
Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: Ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653.
Melaiye, A.; Youngs, W. J. Silver and its application as an antimicrobial agent. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2005, 15, 125–130.
Silver, S.; Phung, L.; Silver, G. Silver as biocides in burn and wound dressings and bacterial resistance to silver compounds. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 627–634.
Baker, C.; Pradhan, A.; Pakstis, L.; Pochan, D. J.; Shah, S. I. Synthesis and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 244–249.
Morones, J. R.; Elechiguerra, J. L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J. B.; Ramírez, J. T.; Yacaman, M. J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353.
Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y. Y.; Liu, S. The potent antimicrobial properties of cell penetrating peptide-conjugated silver nanoparticles with excellent selectivity for Gram-positive bacteria over erythrocytes. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3834–3840.
Chen, Y.; Gao, N.; Jiang, J. Surface matters: Enhanced bactericidal property of core-shell Ag-Fe2O3 nanostructures to their heteromer counterparts from one-pot synthesis. Small 2013, 9, 3242–3246.
Pratsinis, A.; Hervella, P.; Leroux, J.-C.; Pratsinis, S. E.; Sotiriou, G. A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages. Small 2013, 9, 2576–2584.
Setyawati, M. I.; Fang, W.; Chia, S. L.; Leong, D. T. Nanotoxicology of common metal oxide based nanomaterials: Their ROS-y and non-ROS-y consequences. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 8, 205–217.
Xiu, Z. M.; Zhang, Q. B.; Puppala, H. L.; Colvin, V. L.; Alvarez, P. J. J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275.
Kim, J. S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K. N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S. J.; Lee, H. J.; Kim, S. H.; Park, Y. K.; Park, Y. H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101.
Cheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Ji, Y.; Meng, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, H. Revealing silver cytotoxicity using Au nanorods/Ag shell nanostructures: Disrupting cell membrane and causing apoptosis through oxidative damage. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2296–2305.
Banerjee, M.; Sharma, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S. S. Enhanced antibacterial activity of bimetallic gold-silver core-shell nanoparticles at low silver concentration. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 5120–5125.
Bakr, O. M.; Amendola, V.; Aikens, C. M.; Wenseleers, W.; Li, R.; Dal Negro, L.; Schatz, G. C.; Stellacci, F. Silver nanoparticles with broad multiband linear optical absorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5921–5926.
Negishi, Y.; Arai, R.; Niihori, Y.; Tsukuda, T. Isolation and structural characterization of magic silver clusters protected by 4-(tert-butyl)benzyl mercaptan. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5693–5695.
Desireddy, A.; Conn, B. E.; Guo, J.; Yoon, B.; Barnett, R. N.; Monahan, B. M.; Kirschbaum, K.; Griffith, W. P.; Whetten, R. L.; Landman, U.; et al. Ultrastable silver nanoparticles. Nature 2013, 501, 399–402.
Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Gell, L.; Lehtovaara, L.; Malola, S.; Häkkinen, H.; Zheng, N. All-thiol-stabilized Ag44 and Au12Ag32 nanoparticles with single-crystal structures. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2422.
Lu, Y.; Chen, W. Sub-nanometre sized metal clusters: From synthetic challenges to the unique property discoveries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3594–3623.
Qian, H.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Z.; Jin, R. Quantum sized gold nanoclusters with atomic precision. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1470–1479.
Maity, P.; Xie, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Tsukuda, T. Stabilized gold clusters: From isolation toward controlled synthesis. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4027–4037.
Jiang, D. E.; Overbury, S. H.; Dai, S. Structure of Au15(SR)13 and its implication for the origin of the nucleus in thiolated gold nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8786–8789.
Dass, A. Faradaurate nanomolecules: A superstable plasmonic 76.3 kDa cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19259–19261.
Yao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yu, Y.; Xie, J.; Lee, J. Y. Two-phase synthesis of small thiolate-protected Au15 and Au18 nanoclusters. Small 2013, 9, 2696–2701.
Luo, Z.; Yuan, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Leong, D. T.; Lee, J. Y.; Xie, J. From aggregation-induced emission of Au(I)-thiolate complexes to ultrabright Au(0)@Au(I)-thiolate core-shell nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16662–16670.
Zheng, J.; Zhou, C.; Yu, M.; Liu, J. Different sized luminescent gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4073–4083.
Udaya Bhaskara Rao, T.; Pradeep, T. Luminescent Ag7 and Ag8 clusters by interfacial synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3925–3929.
Tang, Z.; Ahuja, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, G. Near infrared luminescence of gold nanoclusters affected by the bonding of 1,4-dithiolate durene and monothiolate phenylethanethiolate. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4119–4124.
Yuan, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, J. Y.; Xie, J. Synthesis of highly fluorescent metal (Ag, Au, Pt, and Cu) nanoclusters by electrostatically induced reversible phase transfer. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8800–8808.
Yu, M.; Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; Hankins, J. D.; Zheng, J. Luminescent gold nanoparticles with pH-dependent membrane adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11014–11017.
Choi, S.; Dickson, R. M.; Yu, J. Developing luminescent silver nanodots for biological applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1867–1891.
Shang, L.; Dong, S.; Nienhaus, G. U. Ultra-small fluorescent metal nanoclusters: Synthesis and biological applications. Nano Today 2011, 6, 401–418.
Chevrier, D. M.; Chatt, A.; Zhang, P. Properties and applications of protein-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters: Short review. J. Nanophoton. 2012, 6, 064504.
Yuan, X.; Luo, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Xie, J. Luminescent noble metal nanoclusters as an emerging optical probe for sensor development. Chem.-Asian J. 2013, 8, 858–871.
Yuan, X.; Tay, Y.; Dou, X.; Luo, Z.; Leong, D. T.; Xie, J. Glutathione-protected silver nanoclusters as cysteine-selective fluorometric and colorimetric probe. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1913–1919.
Yuan, X.; Setyawati, M. I.; Tan, A. S.; Ong, C. N.; Leong, D. T.; Xie, J. Highly luminescent silver nanoclusters with tunable emissions: Cyclic reduction-decomposition synthesis and antimicrobial properties. NPG Asia Mater. 2013, 5, e39.
Kumar, S.; Bolan, M. D.; Bigioni, T. P. Glutathione-stabilized magic-number silver cluster compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13141–13143.
Negishi, Y.; Nobusada, K.; Tsukuda, T. Glutathione-protected gold clusters revisited: Bridging the gap between gold(I)-thiolate complexes and thiolate-protected gold nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5261–5270.
Anand, U.; Ghosh, S.; Mukherjee, S. Toggling between blue- and red-emitting fluorescent silver nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3605–3609.
Beveridge, T. J. Biotechnology for the Mining, Metal-refining, and Fossil Fuel Processing Industries: Proceedings of a Workshop; Wiley Interscience: New York, 1986.
Feng, Q. L.; Wu, J.; Chen, G. Q.; Cui, F. Z.; Kim, T. N.; Kim, J. O. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 662–668.
McLean, R. J. C.; Beveridge, T. J. Microbial mineral recovery. McGraw-Hill: New York, 1990.
Chwalibog, A.; Sawosz, E.; Hotowy, A.; Szeliga, J.; Mitura, S.; Mitura, K.; Grodzik, M.; Orlowski, P.; Sokolowska, A. Visualization of interaction between inorganic nanoparticles and bacteria or fungi. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5 1085–1094.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
X. Yuan and M. I. Setyawati contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, X., Setyawati, M.I., Leong, D.T. et al. Ultrasmall Ag+-rich nanoclusters as highly efficient nanoreservoirs for bacterial killing. Nano Res. 7, 301–307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0395-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-013-0395-6