Abstract
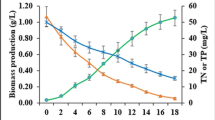
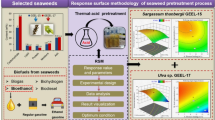
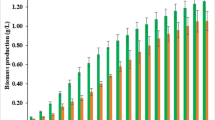
In a previous study, we extracted lipids from raw sewage sludge having a lipid content of 13.1% and used it for biodiesel production. In this study, the residue, lipid-extracted sewage sludge (LESS), was used to obtain sugars for bioethanol production. The LESS was composed of 2.6% lipids, 8.9% carbohydrates, 52.2% proteins, 35.3% ash, and 1.0% moisture. To process the LESS, a conventional dilute acid treatment was used, and this was optimized statistically via central composite design. A sugar yield of 75.5% was obtained under the optimal conditions: 5.9% (v/v) sulfuric acid, 85 min, and 120°C. In addition, commercial dry yeast was used to produce bioethanol from the sugars obtained from the LESS, and 1.8 g/L of bioethanol was obtained from the 5.0 g/L of sugars in the LESS under optimal culture conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korea Ministry of Statistics, National Statistical Office. https://kosis.kr.
Korea Ministry of Environment (2013) 2030: The plan for reducing sewage sludge, and production and utilization of biogas.
Choi, O. K., J. S. Song, D. K. Cha, and J. W. Lee (2014) Biodiesel production from wet municipal sludge: Evaluation of in situ transesterification using xylene as a cosolvent. Bioresour. Technol. 166: 51–56.
Supaporn, P. and S. H. Yeom (2016) Optimization of a two-step biodiesel production process comprised of lipid extraction from blended sewage sludge and subsequent lipid transesterification. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 21: 551–560.
Supaporn, P. and S. H. Yeom (2017) Optimization of a one-step direct process for biodiesel production from blended sewage sludge. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 34: 360–365.
Lenihan, P., A. Orozco, E. Oneill, M. N. M. Ahmad, D. W. Rooney, and G. M. Walker (2010) Dilute acid hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Chem. Eng. J. 156: 395–403.
Deshavath, N. N., M. Mohan, V. D. Veeranki, V. V. Goud, S. R. Pinnamaneni, and T. Benarjee (2017) Dilute acid pretreatment of sorghum biomass to maximize the hemicellulose hydrolysis with minimized levels of fermentative inhibitors for bioethanol production. 3 Biotech. 7: 139.
Teh, Y. Y., K. T. Lee., W. H. Chen, S. C. Lin, H. K. Sheen, and I. S. Tan (2017) Dilute sulfuric acid hydrolysis of red macroalgae Eucheuma denticulatum with microwave-assisted heating for biochar production and sugar recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 246: 20–27.
Greetham, D., J. M. Adams, and C. Du (2020) The utilization of seawater for the hydrolysis of macroalgae and subsequent bioethanol fermentation. Sci. Rep. 10: 9728.
Juarez, G. F. Y., K. B. C. Pabiloña, K. B. L. Manlangit, and A. W. Go (2018) Direct dilute acid hydrolysis of spent coffee grounds: A new approach in sugar and lipid recovery. Waste Biomass Valor. 9: 235–246.
Moutta, R. O., A. K. Chandel, R. C. L. B. Rodrigues, M. B. Silva, G. J. M. Rocha, and S. S. Silva (2012) Statistical optimization of sugarcane leaves hydrolysis into simple sugars by dilute sulfuric acid catalyzed process. Sugar Tech. 14: 53–60.
Choi, J. M., S. Y. Kang, and S. H. Yeom (2011) Pretreatment of wasted corn stalk from Gangwon Province for bioethanol production. J. KORRA. 19: 79–89.
Go, Y. W. and S. H. Yeom (2017) Statistical analysis and optimization of biodiesel production from waste coffee grounds by a two-step process. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 440–449.
Kim, J. Y. and S. H. Yeom (2020) Optimization of biodiesel production from waste coffee grounds by simultaneous lipid extraction and transesterification. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 320–326.
Im, G. H. and S. H. Yeom (2020) Repeated biodiesel production from waste coffee grounds via a one-step direct process with a cartridge containing solid catalysts manufactured from waste eggshells. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 623–632.
Supaporn, P. and S. H. Yeom (2018) Statistical optimization of 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PD) production from crude glycerol by considering four objectives: 1,3-PD concentration, yield, selectivity, and productivity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 186: 644–661.
Bligh, E. G. and W. J. Dyer (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37: 911–917.
Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Rebers, and F. Smith (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 28: 350–356.
Nguyena, Q. A., E. Cho, L. T. P. Trinh, J. S. Jeong, and H. J. Bae (2017) Development of an integrated process to produce Dmannose and bioethanol from coffee residue waste. Bioresour. Technol. 244: 1039–1048.
Lee, O. K., Y. K. Oh, and E. Y. Lee (2015) Bioethanol production from carbohydrate-enriched residual biomass obtained after lipid extraction of Chlorella sp. KR-1. Bioresour. Technol. 196: 22–27.
Meinita, M. D. N., J. Y. Kang, G. T. Jeong, H. M. Koo, S. M. Park, and Y. K. Hong (2012) Bioethanol production from the acid hydrolysate of the carrageenophyte Kappaphycus alvarezii (cottonii). J. Appl. Phycol. 24: 857–862.
Miranda, J. R., P. C. Passarinho, and L. Gouveia (2012) Pretreatment optimization of Scenedesmus obliquus microalga for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 104: 342–348.
Nuanpeng, S., S. Thanonkeo, M. Yamada, and P. Thanonkeo (2016) Ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice at high temperatures using a newly isolated thermotolerant yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae DBKKU Y-53. Energies. 9: 253
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1D1A1B07051113). The authors greatly appreciate this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Supaporn, P., Yeom, S.H. Optimized Sugar Extraction and Bioethanol Production from Lipid-extracted Sewage Sludge. Biotechnol Bioproc E 27, 119–125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0142-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-021-0142-x