Abstract
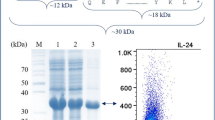
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is one of the important alarmins of the immune system and possesses dual functions as an anti- or pro-inflammatory molecule. The production of this cytokine in E. coli is hampered by the insoluble expression in the cytoplasm, resulting in inclusion body formation. In this study, the expression of IL-33 was optimized by fusing the N-terminus of IL-33 with several solubilizing tags that act as chaperones for proper protein folding: maltose binding protein (MBP), b´a´ domain of protein disulfide isomerase (PDIb´a´) and glutathione Stransferase (GST). The expression of the fusion proteins was stimulated by 0.5 mM IPTG at different temperatures, 37, 30, 25, and 18°C. As a result, IL-33 was expressed highly and in soluble form in the cytoplasm of E. coli when fused with MBP or PDIb´a´ tags in the presence of 0.5 mM IPTG at 25 or 30°C. We describe a simple purification procedure of IL-33 from the PDIb´a´-IL-33 construct using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMACs) with supplementary of tobacco etch virus (TEV) protease for tag removal. The high bioactivity of purified IL-33 on the proliferation and activation of macrophages was confirmed by MTT and nitrite releasing assays using RAW 264.7 These data show an improved method for producing high grade and yield IL-33.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moussion, C., N. Ortega, and J. P. Girard (2008) The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PloS one 3: e3331.
Lefrancais, E., S. Roga, V. Gautier, A. Gonzalez-de-Peredo, B. Monsarrat, J. P. Girard, and C. Cayrol (2012) IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 109: 1673–1678.
Liu, X., M. Hammel, Y. He, J. A. Tainer, U. S. Jeng, L. Zhang, S. Wang, and X. Wang (2013) Structural insights into the interaction of IL-33 with its receptors. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 110: 14918–14923.
Schmitz, J., A. Owyang, E. Oldham, Y. Song, E. Murphy, T. K. McClanahan, G. Zurawski, M. Moshrefi, J. Qin, X. Li, D. M. Gorman, J. F. Bazan, and R. A. Kastelein (2005) IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 23: 479–490.
Saluja, R., M. Khan, M. K. Church, and M. Maurer (2015) The role of IL-33 and mast cells in allergy and inflammation. Clinic. Translation. Aller. 5: 33.
Schiering, C., T. Krausgruber, A. Chomka, A. Frohlich, K. Adelmann, E. A. Wohlfert, J. Pott, T. Griseri, J. Bollrath, A. N. Hegazy, O. J. Harrison, B. M. Owens, M. Lohning, Y. Belkaid, P. G. Fallon, and F. Powrie (2014) The alarmin IL-33 promotes regulatory T-cell function in the intestine. Nature 513: 564–568.
Hung, L. Y., I. P. Lewkowich, L. A. Dawson, J. Downey, Y. Yang, D. E. Smith, and D. R. Herbert (2013) IL-33 drives biphasic IL-13 production for noncanonical Type 2 immunity against hookworms. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 110: 282–287.
Yasuoka, S., J. Kawanokuchi, B. Parajuli, S. Jin, Y. Doi, M. Noda, Y. Sonobe, H. Takeuchi, T. Mizuno, and A. Suzumura (2011) Production and functions of IL-33 in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1385: 8–17.
Fu, A. K., K. W. Hung, M. Y. Yuen, X. Zhou, D. S. Mak, I. C. Chan, T. H. Cheung, B. Zhang, W. Y. Fu, F. Y. Liew, and N. Y. Ip (2016) IL-33 ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 113: 2705–2713.
Miller, A. M., D. L. Asquith, A. J. Hueber, L. A. Anderson, W. M. Holmes, A. N. McKenzie, D. Xu, N. Sattar, I. B. McInnes, and F. Y. Liew (2010) Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circulation Res. 107: 650–658.
Demain, A. L. and P. Vaishnav (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 27: 297–306.
Lingel, A., T. M. Weiss, M. Niebuhr, B. Pan, B. A. Appleton, C. Wiesmann, J. F. Bazan, and W. J. Fairbrother (2009) Structure of IL-33 and its interaction with the ST2 and IL-1RAcP receptors—insight into heterotrimeric IL-1 signaling complexes. Structure 17: 1398–1410.
Nguyen, M. T., B. K. Koo, T. T. Thi Vu, J. A. Song, S. H. Chong, B. Jeong, H. B. Ryu, S. H. Moh, and H. Choe (2014) Prokaryotic soluble overexpression and purification of bioactive human growth hormone by fusion to thioredoxin, maltose binding protein, and protein disulfide isomerase. PloS one 9: e89038.
Stewart, E. J., F. Aslund, and J. Beckwith (1998) Disulfide bond formation in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm: An in vivo role reversal for the thioredoxins. The EMBO J. 17: 5543–5550.
Singh, S. M. and A. K. Panda (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 99: 303–310.
Do, B. H., H. B. Ryu, P. Hoang, B. K. Koo, and H. Choe (2014) Soluble prokaryotic overexpression and purification of bioactive human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor by maltose binding protein and protein disulfide isomerase. PloS one 9: e89906.
Vu, T. T., B. Jeong, M. Krupa, U. Kwon, J. A. Song, B. H. Do, M. T. Nguyen, T. Seo, A. N. Nguyen, C. H. Joo, and H. Choe (2016) Soluble prokaryotic expression and purification of human interferon Alpha-2b using a maltose-binding protein tag. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26: 359–368.
Nguyen, M. T., M. Krupa, B. K. Koo, J. A. Song, T. T. Vu, B. H. Do, A. N. Nguyen, T. Seo, J. Yoo, B. Jeong, J. Jin, K. J. Lee, H. B. Oh, and H. Choe (2016) Prokaryotic soluble overexpression and purification of human VEGF165 by fusion to a maltose binding protein tag. PloS one 11: e0156296.
Song, J. A., B. K. Koo, S. H. Chong, J. Kwak, H. B. Ryu, M. T. Nguyen, T. T. Vu, B. Jeong, S. W. Kim, and H. Choe (2013) Expression and purification of biologically active human FGF2 containing the b'a' domains of human PDI in Escherichia coli. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 170: 67–80.
Appenzeller-Herzog, C. and L. Ellgaard (2008) In vivo reductionoxidation state of protein disulfide isomerase: The two active sites independently occur in the reduced and oxidized forms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 10: 55–64.
Vera, A., N. Gonzalez-Montalban, A. Aris, and A. Villaverde (2007) The conformational quality of insoluble recombinant proteins is enhanced at low growth temperatures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 96: 1101–1106.
Schellman, J. A. (1997) Temperature, stability, and the hydrophobic interaction. Biophysic. J. 73: 2960–2964.
Verri, W. A., Jr., F. O. Souto, S. M. Vieira, S. C. Almeida, S. Y. Fukada, D. Xu, J. C. Alves-Filho, T. M. Cunha, A. T. Guerrero, R. B. Mattos-Guimaraes, F. R. Oliveira, M. M. Teixeira, J. S. Silva, I. B. McInnes, S. H. Ferreira, P. Louzada-Junior, F. Y. Liew, and F. Q. Cunha (2010) IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann. Rheumat. Diseas. 69: 1697–1703.
Valledor, A. F., M. Comalada, J. Xaus, and A. Celada (2000) The differential time-course of extracellular-regulated kinase activity correlates with the macrophage response toward proliferation or activation. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 7403–7409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, B.H., Park, S., Kwon, G.G. et al. Soluble expression and purification of bioactive interleukin 33 in E. coli. Biotechnol Bioproc E 22, 256–264 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0060-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-017-0060-0