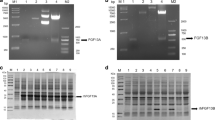
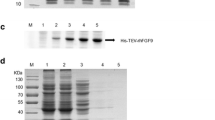
Abstract
Among the members of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family that affect the growth, differentiation, migration, and survival of many cell types, FGF2 is the most abundant in the central nervous system. Because of its wound healing effects, FGF2 has potential as a therapeutic agent. The protein is also added to the culture media to maintain stem cells. Expression and purification procedures for FGF2 that are highly efficient and low cost have been intensively investigated for the past two decades. Our current study focuses on the purification of FGF2 fused with b′a′ domains of human protein disulfide isomerase to elevate overexpression, solubility, and stability with a simplified experimental procedure using only ion exchange chromatography, as well as on the confirmation of the biological activity of FGF2 on fibroblast Balb/c 3T3 cells and hippocampal neural cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alibolandi, M., & Mirzahoseini, H. (2011). Purification and refolding of overexpressed human basic fibroblast growth factor in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Res Int, 2011, 973741.
Amit, M., Carpenter, M. K., Inokuma, M. S., Chiu, C. P., Harris, C. P., Waknitz, M. A., et al. (2000). Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Developmental Biology, 227, 271–278.
Andrades, J. A., Wu, L. T., Hall, F. L., Nimni, M. E., & Becerra, J. (2001). Engineering, expression, and renaturation of a collagen-targeted human bFGF fusion protein. Growth Factors, 18, 261–275.
Arakawa, T., Hsu, Y. R., Schiffer, S. G., Tsai, L. B., Curless, C., & Fox, G. M. (1989). Characterization of a cysteine-free analog of recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 161, 335–341.
Belluardo, N., Wu, G., Mudo, G., Hansson, A. C., Pettersson, R., & Fuxe, K. (1997). Comparative localization of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1, -2, and -3 mRNAs in the rat brain: in situ hybridization analysis. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 379, 226–246.
Bikfalvi, A., Klein, S., Pintucci, G., & Rifkin, D. B. (1997). Biological roles of fibroblast growth factor-2. Endocrine Reviews, 18, 26–45.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Busso, D., Delagoutte-Busso, B., & Moras, D. (2005). Construction of a set Gateway-based destination vectors for high-throughput cloning and expression screening in Escherichia coli. Analytical Biochemistry, 343, 313–321.
Chen, X. J., Sun, F. Y., Xie, Q. L., Liao, M. D., Zhang, L., Li, Z. Y., et al. (2002). Cloning and high level nonfusion expression of recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor in Escherichia coli. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 23, 782–786.
Clark, E. D. (2001). Protein refolding for industrial processes. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 12, 202–207.
Denisov, A. Y., Maattanen, P., Dabrowski, C., Kozlov, G., Thomas, D. Y., & Gehring, K. (2009). Solution structure of the bb' domains of human protein disulfide isomerase. FEBS Journal, 276, 1440–1449.
Ferrer, M., Chernikova, T. N., Timmis, K. N., & Golyshin, P. N. (2004). Expression of a temperature-sensitive esterase in a novel chaperone-based Escherichia coli strain. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 4499–4504.
Fox, G. M., Schiffer, S. G., Rohde, M. F., Tsai, L. B., Banks, A. R., & Arakawa, T. (1988). Production, biological activity, and structure of recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor and an analog with cysteine replaced by serine. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 263, 18452–18458.
Gage, F. H., Coates, P. W., Palmer, T. D., Kuhn, H. G., Fisher, L. J., Suhonen, J. O., et al. (1995). Survival and differentiation of adult neuronal progenitor cells transplanted to the adult brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 11879–11883.
Garke, G., Deckwer, W. D., & Anspach, F. B. (2000). Preparative two-step purification of recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor from high-cell-density cultivation of Escherichia coli. Journal of Chromatography B: Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 737, 25–38.
Gasparian, M. E., Elistratov, P. A., Drize, N. I., Nifontova, I. N., Dolgikh, D. A., & Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2009). Overexpression in Escherichia coli and purification of human fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Biochemistry (Mosc), 74, 221–225.
Gospodarowicz, D., Ferrara, N., Schweigerer, L., & Neufeld, G. (1987). Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocrine Reviews, 8, 95–114.
Gritti, A., Parati, E. A., Cova, L., Frolichsthal, P., Galli, R., Wanke, E., et al. (1996). Multipotential stem cells from the adult mouse brain proliferate and self-renew in response to basic fibroblast growth factor. Journal of Neuroscience, 16, 1091–1100.
Grothe, C., & Wewetzer, K. (1996). Fibroblast growth factor and its implications for developing and regenerating neurons. International Journal of Developmental Biology, 40, 403–410.
Hartley, J. L., Temple, G. F., & Brasch, M. A. (2000). DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination. Genome Research, 10, 1788–1795.
Ke, Y., Wilkinson, M. C., Fernig, D. G., Smith, J. A., Rudland, P. S., & Barraclough, R. (1992). A rapid procedure for production of human basic fibroblast growth factor in Escherichia coli cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1131, 307–310.
Klappa, P., Ruddock, L. W., Darby, N. J., & Freedman, R. B. (1998). The b' domain provides the principal peptide-binding site of protein disulfide isomerase but all domains contribute to binding of misfolded proteins. EMBO Journal, 17, 927–935.
Komi-Kuramochi, A., Kawano, M., Oda, Y., Asada, M., Suzuki, M., Oki, J., et al. (2005). Expression of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors during full-thickness skin wound healing in young and aged mice. Journal of Endocrinology, 186, 273–289.
Kroiher, M., Raffioni, S., & Steele, R. E. (1995). Single step purification of biologically active recombinant rat basic fibroblast growth factor by immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1250, 29–34.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685.
LaVallie, E. R., DiBlasio, E. A., Kovacic, S., Grant, K. L., Schendel, P. F., & McCoy, J. M. (1993). A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Biotechnology (N. Y), 11, 187–193.
Lee, J. W., & Helmann, J. D. (2006). The PerR transcription factor senses H2O2 by metal-catalysed histidine oxidation. Nature, 440, 363–367.
Lemaitre, G., Laaroubi, K., Soulet, L., Barritault, D., & Miskulin, M. (1995). Production and purification of active FGF2 via recombinant fusion protein. Biochimie, 77, 162–6.
Liao, S., Bodmer, J., Pietras, D., Azhar, M., Doetschman, T., & Schultz Jel, J. (2009). Biological functions of the low and high molecular weight protein isoforms of fibroblast growth factor-2 in cardiovascular development and disease. Developmental Dynamics, 238, 249–264.
Mosmann, T. (1983). Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. Journal of Immunological Methods, 65, 55–63.
Murakami, S. (2011). Periodontal tissue regeneration by signaling molecule(s): what role does basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) have in periodontal therapy? Periodontology 2000, 2000(56), 188–208.
Nallamsetty, S., & Waugh, D. S. (2006). Solubility-enhancing proteins MBP and NusA play a passive role in the folding of their fusion partners. Protein Expression and Purification, 45, 175–182.
Nygren, P. A., Stahl, S., & Uhlen, M. (1994). Engineering proteins to facilitate bioprocessing. Trends in Biotechnology, 12, 184–188.
Palmer, T. D., Takahashi, J., & Gage, F. H. (1997). The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 8, 389–404.
Pryor, K. D., & Leiting, B. (1997). High-level expression of soluble protein in Escherichia coli using a His6-tag and maltose-binding-protein double-affinity fusion system. Protein Expression and Purification, 10, 309–319.
Schultz, G. S., & Wysocki, A. (2009). Interactions between extracellular matrix and growth factors in wound healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 17, 153–162.
Schwartz, S. M., & Liaw, L. (1993). Growth control and morphogenesis in the development and pathology of arteries. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 21(Suppl 1), S31–49.
Seeger, A., & Rinas, U. (1996). Two-step chromatographic procedure for purification of basic fibroblast growth factor from recombinant Escherichia coli and characterization of the equilibrium parameters of adsorption. Journal of Chromatography. A, 746, 17–24.
Seno, M., Sasada, R., Iwane, M., Sudo, K., Kurokawa, T., Ito, K., et al. (1988). Stabilizing basic fibroblast growth factor using protein engineering. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 151, 701–708.
Sheng, Z., Chang, S. B., & Chirico, W. J. (2003). Expression and purification of a biologically active basic fibroblast growth factor fusion protein. Protein Expression and Purification, 27, 267–271.
Squires, C. H., Childs, J., Eisenberg, S. P., Polverini, P. J., & Sommer, A. (1988). Production and characterization of human basic fibroblast growth factor from Escherichia coli. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 263, 16297–16302.
Thompson, S. A. (1992). The disulfide structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 2269–2273.
Thompson, S. A., Protter, A. A., Bitting, L., Fiddes, J. C., & Abraham, J. A. (1991). Cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization of basic fibroblast growth factor. Methods in Enzymology, 198, 96–116.
Vera, A., Gonzalez-Montalban, N., Aris, A., & Villaverde, A. (2007). The conformational quality of insoluble recombinant proteins is enhanced at low growth temperatures. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 96, 1101–1106.
Wu, X., Liu, X., Xiao, Y., Huang, Z., Xiao, J., Lin, S., et al. (2007). Purification and modification by polyethylene glycol of a new human basic fibroblast growth factor mutant-hbFGF(Ser25,87,92). Journal of Chromatography. A, 1161, 51–55.
Yu, S. W., Baek, S. H., Brennan, R. T., Bradley, C. J., Park, S. K., Lee, Y. S., et al. (2008). Autophagic death of adult hippocampal neural stem cells following insulin withdrawal. Stem Cells, 26, 2602–2610.
Zechel, S., Werner, S., Unsicker, K., Von Bohlen, & Halbach, O. (2010). Expression and functions of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) in hippocampal formation. The Neuroscientist, 16, 357–373.
Zhang, Y., Olsen, D. R., Nguyen, K. B., Olson, P. S., Rhodes, E. T., & Mascarenhas, D. (1998). Expression of eukaryotic proteins in soluble form in Escherichia coli. Protein Expression and Purification, 12, 159–165.
Zhu, X., Komiya, H., Chirino, A., Faham, S., Fox, G. M., Arakawa, T., et al. (1991). Three-dimensional structures of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Science, 251, 90–93.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation (2010-0029522 and 2010-0029521), the Brain Research Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program (2012K001122) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J.-A. Song and B.-K. Koo contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 818 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, JA., Koo, BK., Chong, S.H. et al. Expression and Purification of Biologically Active Human FGF2 Containing the b′a′ Domains of Human PDI in Escherichia coli . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170, 67–80 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0140-3