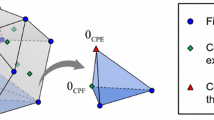
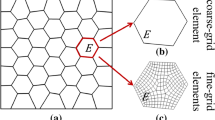
Abstract
Thermoelastic analysis by means of three-dimensional polyhedral elements based on the Smoothed Finite elements method (S-FEM), for example nodal Cell-based S-FEM (CS-FEM), Node-based S-FEM (NS-FEM), and Edge-based S-FEM (ES-FEM), was studied. S-FEM allows implicit shape functions, making it possible to construct shape functions of S-FEM based polyhedral elements in a straightforward manner. The performance of S-FEM based polyhedral elements was compared with one another and with the conventional finite elements including hexahedral and tetrahedral element. Numerical examples show that the polyhedral elements by means of CS-FEM and ES-FEM provide better accuracy and convergence rate than conventional hexahedral finite elements, while the polyhedral elements by means of NS-FEM leads to spurious mode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. M. Rashid and M. Selimotic, A three-dimensional finite element method with arbitrary polyhedral elements, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 67 (2) (2006) 226–252.
M. Wicke, M. Botsch and M. Gross, A finite element method on convex polyhedra, Computer Graphics Forum, 26 (3) (2007) 355–364.
P. Milbradt and T. Pick, Polytope finite elements, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 73 (12) (2008) 1811–1835.
J. E. Bishop, A displacement-based finite element formulation for general polyhedra using harmonic shape functions, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 97 (1) (2014) 1–31.
S. Martin, P. Kaufmann, M. Botsch, M. Wicke and M. Gross, Polyhedral finite elements using harmonic basis functions, Computer Graphics Forum, 27 (5) (2008) 1521–1529.
S. E. Mousavi and N. Sukumar, Numerical integration of polynomials and discontinuous functions on irregular convex polygons and polyhedrons, Computational Mechanics, 47 (5) (2011) 535–554.
M. S. Floater, G. Kos and M. Reimers, Mean value coordinates in 3d, Computer Aided Geometric Design, 22 (7) (2005) 623–631.
G. Manzini, A. Russo and N. Sukumar, New perspectives on polygonal and polyhedral finite element methods, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 24 (8) (2014) 1665–1699.
C. Talischi and G. H. Paulino, Addressing integration error for polygonal finite elements through polynomial projections: A patch test connection, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 24 (8) (2014) 1701–1727.
L. B. da Veiga, F. Brezzi, A. Cangiani, G. Manzini, L. D. Marini and A. Russo, Basic principles of virtual element methods, Mathematical Models & Methods in Applied Sciences, 23 (1) (2013) 199–214.
C. R. Dohrmann, S. W. Key and M. W. Heinstein, Methods for connecting dissimilar three-dimensional finite element meshes, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 47 (5) (2000) 1057–1080.
D. Sohn and S. Jin, Polyhedral elements with strain smoothing for coupling hexahedral meshes at arbitrary nonmatching interfaces, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 293 (2015) 92–113.
S. Ghosh and S. Moorthy, Elastic-plastic analysis of arbitrary heterogeneous materials with the voronoi-cell finite-element method, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 121 (1–4) (1995) 373–409.
H. Chi, C. Talischi, O. Lopez-Pamies and G. H. Paulino, Polygonal finite elements for finite elasticity, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 101 (4) (2015) 305–328.
D. W. Spring and G. H. Paulino, Computational homogenization of the debonding of particle reinforced composites: The role of interphases in interfaces, Computational Materials Science, 109 (2015) 209–224.
B. El Said, D. Ivanov, A. C. Long and S. R. Hallett, Multiscale modelling of strongly heterogeneous 3d composite structures using spatial voronoi tessellation, J. of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 88 (2016) 50–71.
D. W. Spring, S. E. Leon and G. H. Paulino, Unstructured polygonal meshes with adaptive refinement for the numerical simulation of dynamic cohesive fracture, International J. of Fracture, 189 (1) (2014) 33–57.
A. Khoei, R. Yasbolaghi and S. Biabanaki, A polygonal finite element method for modeling crack propagation with minimum remeshing, International J. of Fracture, 194 (2) (2015) 123–148.
C. Talischi, G. H. Paulino and C. H. Le, Honeycomb wachspress finite elements for structural topology optimization, Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 37 (6) (2009) 569–583.
S. Duczek and U. Gabbert, The finite cell method for polygonal meshes: Poly-fcm, Computational Mechanics, 58 (4) (2016) 587–618.
G. R. Liu, K. Y. Dai and T. T. Nguyen, A smoothed finite element method for mechanics problems, Computational Mechanics, 39 (6) (2007) 859–877.
J. S. Chen, C. T. Wu, S. Yoon and Y. You, A stabilized conforming nodal integration for galerkin mesh-free methods, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 50 (2) (2001) 435–466.
G. R. Liu, A generalized gradient smoothing technique and the smoothed bilinear form for galerkin formulation of a wide class of computational methods, International J. of Computational Methods, 5 (2) (2008) 199–236.
H. Nguyen-Xuan, H. V. Nguyen, S. Bordas, T. Rabczuk and M. Duflot, A cell-based smoothed finite element method for three dimensional solid structures, KSCE J. Civ. Eng., 16 (7) (2012) 1230–1242.
G. R. Liu, T. Nguyen-Thoi, H. Nguyen-Xuan and K. Y. Lam, A node-based smoothed finite element method (nsfem) for upper bound solutions to solid mechanics problems, Computers & Structures, 87 (1–2) (2009) 14–26.
T. Nguyen-Thoi, G. R. Liu and H. Nguyen-Xuan, Additional properties of the node-based smoothed finite element method (ns-fem) for solid mechanics problems, International J. of Computational Methods, 6 (4) (2009) 633–666.
G. R. Liu, T. Nguyen-Thoi and K. Y. Lam, An edge-based smoothed finite element method (es-fem) for static, free and forced vibration analyses of solids, J. of Sound and Vibration, 320 (4–5) (2009) 1100–1130.
Z. C. He, G. Y. Li, Z. H. Zhong, A. G. Cheng, G. Y. Zhang, G. R. Liu, E. Li and Z. Zhou, An edge-based smoothed tetrahedron finite element method (es-t-fem) for 3d static and dynamic problems, Computational Mechanics, 52 (1) (2013) 221–236.
T. Nguyen-Thoi, G. R. Liu, K. Y. Lam and G. Y. Zhang, A face-based smoothed finite element method (fs-fem) for 3d linear and geometrically non-linear solid mechanics problems using 4-node tetrahedral elements, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 78 (3) (2009) 324–353.
K. Y. Dai, G. R. Liu and T. T. Nguyen, An n-sided polygonal smoothed finite element method (nsfem) for solid mechanics, Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 43 (11–12) (2007) 847–860.
T. Nguyen-Thoi, G. R. Liu and H. Nguyen-Xuan, An nsided polygonal edge-based smoothed finite element method (nes-fem) for solid mechanics, International J. for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering, 27 (9) (2011) 1446–1472.
D. Sohn, J. Han, Y. S. Cho and S. Im, A finite element scheme with the aid of a new carving technique combined with smoothed integration, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 254 (2013) 42–60.
K. Lee, Y. Son and S. Im, Three-dimensional variable-node elements based upon cs-fem for elastic-plastic analysis, Computers & Structures, 158 (2015) 308–332.
S. Jin, D. Sohn and S. Im, Node-to-node scheme for three-dimensional contact mechanics using polyhedral type variable-node elements, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 304 (2016) 217–242.
J. Kim and S. Im, Polygonal type variable-node elements by means of the smoothed finite element method for analysis of two-dimensional fluid-solid interaction problems in viscous incompressible flows, Computers & Structures, 182 (2017) 475–490.
C. Lee, H. Kim and S. Im, Polyhedral elements by means of node/edge-based smoothed finite element method, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 110 (11) (2017) 1069–1100.
S. Wu, G. Liu, H. Zhang and G. Zhang, A node-based smoothed point interpolation method (ns-pim) for threedimensional thermoelastic problems, Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 54 (12) (2008) 1121–1147.
S. C. Wu, G. R. Li, H. O. Zhang and G. Y. Zhang, A nodebased smoothed point interpolation method (ns-pim) for thermoelastic problems with solution bounds, International J. of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52 (5–6) (2009) 1464–1471.
S. C. Wu, G. R. Liu, X. Y. Cui, T. T. Nguyen and G. Y. Zhang, An edge-based smoothed point interpolation method (es-pim) for heat transfer analysis of rapid manufacturing system, International J. of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53 (9–10) (2010) 1938–1950.
G. Wu, J. Zhang, Y. L. Li, L. R. Yin and Z. Q. Liu, Analysis of transient thermo-elastic problems using a cellbased smoothed radial point interpolation method, International J. of Computational Methods, 13 (5) (2016).
S. Z. Feng, X. Y. Cui and G. Y. Li, Analysis of transient thermo-elastic problems using edge-based smoothed finite element method, International J. of Thermal Sciences, 65 (2013) 127–135.
S. Z. Feng, X. Y. Cui and G. Y. Li, Transient thermal mechanical analyses using a face-based smoothed finite element method (fs-fem), International J. of Thermal Sciences, 74 (2013) 95–103.
S. Z. Feng, X. Y. Cui, G. Y. Li, H. Feng and F. X. Xu, Thermo-mechanical analysis of functionally graded cylindrical vessels using edge-based smoothed finite element method, International J. of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 111 (2013) 302–309.
S. Feng, X. Cui and G. Li, Thermo-mechanical analyses of composite structures using face-based smoothed finite element method, International J. of Applied Mechanics, 6 (2) (2014) 1450020.
S. Feng, X. Cui and G. Li, Thermo-mechanical analysis of composite pressure vessels using edge-based smoothed finite element method, International J. of Computational Methods, 11 (6) (2014) 1350089.
S. Z. Feng, X. Y. Cui, A. M. Li and G. Z. Xie, A face-based smoothed point interpolation method (fs-pim) for analysis of nonlinear heat conduction in multi-material bodies, International J. of Thermal Sciences, 100 (2016) 430–437.
X. Y. Cui, Z. C. Li, H. Feng and S. Z. Feng, Steady and transient heat transfer analysis using a stable node-based smoothed finite element method, International J. of Thermal Sciences, 110 (2016) 12–25.
G.-R. Liu and T. T. Nguyen, Smoothed finite element methods, CRC Press, Boca Raton (2010).
O. C. Zienkiewicz, R. L. Taylor and J. Z. Zhu, The finite element method: Its basis and fundamentals, 7th Ed., Elsevier: Butterworth-Heinemann (2013).
J. L. Nowinski, Theory of thermoelasticity with applications, Sijthoff & Noordhoff International Publishers (1978).
M. A. Puso, J. S. Chen, E. Zywicz and W. Elmer, Meshfree and finite element nodal integration methods, International J. for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 74 (3) (2008) 416–446.
Z. Q. Zhang and G. R. Liu, Solution bound and nearly exact solution to nonlinear solid mechanics problems based on the smoothed fem concept, Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 42 (2014) 99–114.
C. Lee, H. Kim, J. Kim and S. Im, Polyhedral elements using an edge-based smoothed finite element method for nonlinear elastic deformations of compressible and nearly incompressible materials, Computational Mechanics (2017) Online available.
S. Beissel and T. Belytschko, Nodal integration of the element-free Galerkin method, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 139 (1–4) (1996) 49–74.
Z. Q. Zhang and G. R. Liu, Temporal stabilization of the node-based smoothed finite element method and solution bound of linear elastostatics and vibration problems, Computational Mechanics, 46 (2) (2010) 229–246.
H. Feng, X. Y. Cui, G. Y. Li and S. Z. Feng, A temporal stable node-based smoothed finite element method for threedimensional elasticity problems, Computational Mechanics, 53 (5) (2014) 859–876.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Chang-Wan Kim
Hobeom Kim received his B.S. (2013) in Mechanical Engineering from Inha University, Korea. His M.S. (2014) is from KAIST, Korea. He is a Ph.D. candidate in Mechanical Engineering at KAIST. His current interests are computational methods for thermomechanical contact analysis.
Seyoung Im received the B.S. (1976) in Mechanical Engineering from Seoul National University, Korea and Ph.D. (1985) in Theoretical and Applied Mechanics from University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA. He is currently a Professor at the Department of Mechanical Engineering in Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). His current interests are computational solid mechanics and multiphysics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Im, S. Polyhedral smoothed finite element method for thermoelastic analysis. J Mech Sci Technol 31, 5937–5949 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-1138-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-1138-5