Abstract
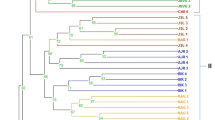
To detect the genetic variation and relationships among different Salvia ecotypes/species, the gene targeted CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP) markers were employed in terms of their efficiency. In this study, 25 CBDP primers amplified a total of 323 different polymorphic fragments that discriminate all 26 Salvia ecotypes/species and produced an informative and differentiated dendrogram and population structure. The CBDP markers were found to be effective in Salvia genetic diversity estimation with regard to the averages polymorphism (100%), polymorphism information content (\(\hbox {PIC}=0.89\)), marker index (\(\hbox {MI}=4.5\)) and the effective multiplex ratio (\(\hbox {EMR}=5.01\)) which were higher than other reported markers on Salvia. The extent of heterozygosity (\(0.034{\le }H{\le }0.223\)) and Shannon index (\(0.042{\le }I{\le }0.278\)) indicated a high level of genetic variation among Salvia species. The species containing the highest basic chromosome number (\(\hbox {X}=12\)) revealed the highest values for the number of different (\(N_{\mathrm{a}}\)) and effective (\(N_{\mathrm{e}}\)) alleles, Shannon index (I), and heterozygosity (H). Additionally, the tetraploid species showed high values of \(N_{\mathrm{a}}\), \(N_{\mathrm{e}}\), I and H compared to the diploid species. Mean of gene differentiation (\(G_{\mathrm{st}}\)) among Salvia species was 0.792, and the estimation of gene flow (\(N_{\mathrm{m}}\)) was 0.13, indicating high genetic differentiation. Remarkably, similar results were obtained from the principal co-ordinate analysis (PCoA) as compared with the cluster analysis, in which all different Salvia species formed individual groups. In conclusion, because the CBDP markers are derived from the gene containing regions of the genome, consequently, the high genetic diversity among studied Salvia species would be more useful for crop improvement programmes, such as hybridization between species and QTL mapping. The potential of CBDPs for analysing the phylogeny and genetic diversity of Salvia species is another key result with practical implications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoist C., Ohare K., Breathnach R. and Chambon P. 1980 The ovalbumin gene sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 127–142.
Bohn M., Utz H. F. and Melchinger A. E. 1999 Genetic similarities among wheat cultivars determined on the basis of RFLPs, AFLPs and SSRs and their use for predicting progeny variance. Crop Sci. 39, 228–237.
Collard B. C. Y. and Mackill D. J. 2009 Start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism: a simple, novel DNA marker technique for generating gene-targeted markers in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 27, 86–93.
Dje Y., Hevretz M., Letebure C. and Vekemans X. 2000 Assessment of genetic diversity within and among germplasm accessions in cultivated sorghum using microsatellite markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 100, 918–925.
Etminan A., Pour-Aboughadareh A. and Nooric A. 2018 Genetic relationships and diversity among wild Salvia accessions revealed by ISSR and SCoT markers. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 32, 610–617
Fan H. Y., Fu F. H., Yang M. Y., Xu H., Zhang A. H. and Liu R. 2010 Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of Salvia nolic acid. Thromb. Res. 126, 17–22.
Gorji A. M., Poczai P. and Polgar Z. 2011 Efficiency of arbitrarily amplified dominant markers (SCoT, ISSR and RAPD) for diagnostic fingerprinting in tetraploid potato. Am. Potato J. 88, 226–237.
Gupta P. K. and Roy J. K. 2002 Molecular markers in crop improvement: present status and future needs in India. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 70, 229–234.
Harley R. M., Atkins S., Budantsev A. L., Cantino P. D., Conn B. J., Grayer R. et al. 2004 Labiatae. In The families and genera of vascular plant (ed. J.W. Kadereit and K. Kubitzki), vol. 7, pp. 167–236. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Heidari P., Etminan A., Azizinezhad R. and Khosroshahli M. 2017 Genomic variation studies in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) using CBDP, SCoT and ISSR markers. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 77, 379–386.
Heikrujam M., Kumar J. and Agrawal V. 2015 Genetic diversity analysis among male and female Jojoba genotypes employing gene targeted molecular markers, start codon targeted (SCoT) polymorphism and CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP) markers. Meta Gene 5, 90–97.
Hosseinzadeh H., Haddakhodaparast M. H. and Arash A. R. 2003 Antinociceptive, antiinflammatory and acute toxicity effects of Salvia leriifolia Benth. seed extract in mice and rats. Phytother. Res. 17, 422–425.
Hu J. and Vick B. A. 2003 Target region amplification polymorphism: a novel marker technique for plant genotyping. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 21, 289–294.
Hubisz M. J., Falush D., Stephens M. and Pritchard J. K. 2009 Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol. Ecol. Res. 9, 1322–1332.
Li G. and Quiros C. F. 2001 Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103, 455–461.
Mayer B., Baggio C. H., Freitas C. S., Santos C., Twardowschy A., Horst H. et al. 2007 Gastro protective constituents of Salvia officinalis L. Fitoterapia 80, 421–426.
Moose S. P. and Mumm R. H. 2008 Molecular plant breeding as the foundation for 21st Century crop improvement. Plant Physiol. 147, 969–977.
Paliwal R., Singh R., Singh A. K., Kumar S., Kumar A. and Majumdar R. S. 2013 Molecular characterization of Giloe (Tinospora cordifolia) accessions using start codon targeted (SCoT) markers. Int. J. Med. Aromat. Plants 3, 413–422.
Pang M., Percy R. G., Ed H. and Zhang J. 2009 Promoter anchored amplified polymorphism based on random amplified polymorphic DNA (PAAP-RAPD) in cotton. Euphytica 167, 281–291.
Poczai P., Varga I. and Laos M. 2013 Advances in plant gene-targeted and functional markers: a review. Plant Methods 9, 6–37.
Pour-Aboughadareh A., Ahmadi J., Mehrabi A., Etminan A. and Moghaddam M. 2017 Assessment of genetic diversity among Iranian Triticum germplasm using agro-morphological traits and start codon targeted (SCoT) markers. Cereal Res. Commun. 45, 574–586.
Pour-Aboughadareh A., Ahmadi J., Mehrabi A., Etminan A. and Moghaddam M. 2018 Insight into the genetic variability analysis and relationships among some Aegilops and Triticum species, as genome progenitors of bread wheat, using SCoT markers. Plant Biosys. For. 152, 694–703.
Powell W., Morgante M., Doyle J. J., McNicol J. W., Tingey S. V. and Rafalski A. J. 1996 Gene pool variation in genus Glycine subgenus Soja revealed by polymorphic nuclear and chloroplast microsatellites. Genetics 144, 793–803.
Que Y., Pan Y., Lu Y., Yang C., Yang Y., Huang N. et al. 2014 Genetic analysis of diversity within a Chinese local sugarcane germplasm based on start codon targeted polymorphism. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 1–10.
Rajesh M. K., Sabana A. A. and Rachana K. E. 2015 Genetic relationship and diversity among coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) accessions revealed through SCoT analysis. 3 Bitech 5, 999–1006.
Randi E. and Lucchini V. 2002 Detecting rare introgression of domestic dog genes into wild wolf (Canis lupus) populations by Bayesian admixture analyses of microsatellite variation. Conserv. Genetics 3, 29–43.
Rohlf F. 2000 NTSYS-PC numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, ver 2.11L. Applied Biostatistics, New York.
Safaei M., Sheidai M., Alijanpoor B. and Noormohammadi Z. 2016 Species delimitation and genetic diversity analysis in Salvia with the use of ISSR molecular markers. Acta Bot. Croa. 75, 42–52.
Javan Z. S., Rahmani F. and Heidari R. 2012 Assessment of genetic variation of genus Salvia by RAPD and ISSR markers. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 6, 1068–1073.
Shahmuradov I. A., Gammerman A. J., Hancock J. M., Bramley P. M. and Solovyev V. V. 2003 Plant Prom: a database of plant promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 114–117.
Singh A. K., Rana M. K., Singh S., Kumar S., Kumar R. and Singh R. 2014 CAAT box-derived polymorphism (CBDP): a novel promoter-targeted molecular marker for plants. J. Plant Biochem. Biotech. 23, 175–183.
Sivaprakash K. R., Prasanth S. R., Mohanty B. P. and Parida A. 2004 Genetic diversity of black gram landraces as evaluated by AFLP markers. Curr. Sci. 86, 1411–1415.
Song Z., Li X., Wang H. and Wang J. 2010 Genetic diversity and population structure of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge in China revealed by ISSR and SRAP. Genetica 138, 241–249.
Souframanien J. and Gopalakrishna T. 2004 A comparative analysis of genetic diversity in blackgram genotypes using RAPD and ISSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 109, 1687–1693.
Tams S. H., Melchinger A. E. and Bauer E. 2005 Genetic similarity among European winter triticale elite germplasms assessed with AFLP and comparisons with SSR and pedigree data. Plant Breed. 124, 154–160.
Tiwari G., Singh R., Singh N., Choudhury D., Paliwal R., Kumar A. et al. 2016 Study of arbitrarily amplified (RAPD and ISSR) and gene targeted (SCoT and CBDP) markers for genetic diversity and population structure in Kalmegh (Andrographis paniculata Nees). Ind. Crops Prod. 86, 1–11.
Ude G., Pillay M. and Ogundiwin E. 2003 Genetic diversity in an African plantain core collection using AFLP and RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 107, 248–255.
Walker J. B., Sytsma K. J., Treutlelin J. and Wink M. 2004 Salvia (Lamiaceae) is not monophyletic: implication for the systematics, radiation, and ecological specialization of Salvia and Tribe Mentheae. Am. J. Bot. 91, 1115–1125.
Wang B., Zhang Y., Chen C. B., Li X. L., Chen R. Y. and Chen L. 2007 Analysis on genetic diversity of different Salvia miltiorrhiza geographical populations in China. Chin. Med. J. 32, 1988–1991.
Wang O., Zhang B. and Lu L. 2009 Conserved region amplification polymorphism (CoRAP), a novel marker technique for plant genotyping in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 27, 139–143.
Yeh F. C., Yang R. C. and Boyle T. 1999 POPGENE 32-version 1.31. Population Genetics Software. http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/fyeh/.
Yousefiazar-Khanian M., Asghari A. and Ahmadi J. 2016 Genetic diversity of Salvia species assessed by ISSR and RAPD markers. Not. Bot. Horti. Agrobo. 44, 431–436.
Acknowledgements
Authors thank the Genetics and Genomics Laboratory at Imam Khomeini International University for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding Editor: Manoj Prasad
Experimental design, S. Fabriki-Ourang; laboratory work, H. Karimi; statistical data analysis, H. Karimi; interpretation of results, writing the manuscript and critical revision: S. Fabriki-Ourang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabriki-Ourang, S., Karimi, H. Assessment of genetic diversity and relationships among Salvia species using gene targeted CAAT box-derived polymorphism markers. J Genet 98, 75 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1121-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1121-2