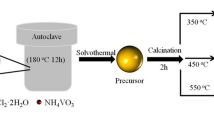
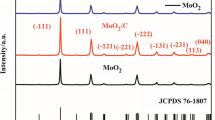
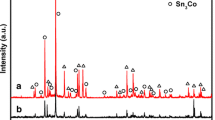
Abstract
Spinel structure Co-doped \(\hbox {ZnMn}_{{2}}\hbox {O}_{{4}}\) nanocrystals were successfully synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The effects of Co-doping concentration on the structure and electrochemical properties of the samples were investigated. The experimental results manifest that all samples exhibit a single-phase with a tetragonal structure, and morphologies are regular hollow microspheres. Cyclic voltammetry curves for all samples are similar to a rectangular shape with symmetric nature and no obvious redox peak. Galvanostatic charge–discharge curves were triangular and symmetric. Impedance spectra revealed that \(\hbox {Zn}_{1-x}\hbox {Co}_{{x}}\hbox {Mn}_{{2}}\hbox {O}_{{4}}\) possess low resistance. Better electrochemical properties of the \(\hbox {ZnMn}_{{2}}\hbox {O}_{{4}}\) electrode could be obtained when the Co-doping ratio is 0.3. \(\hbox {Zn}_{0.7}\hbox {Co}_{0.3}\hbox {Mn}_{{2}}\hbox {O}_{{4}}\) exhibits much higher specific capacitance (\(306\hbox { F g}^{-1}\)) at a scan rate of \(5\hbox { mV s}^{-1}\), and shows excellent cycling stability and retains 98.2% of its initial capacitance after 1000 cycles. The enhanced capacitive performance in this work can be attributed to the incorporation of Co ions doped into the \(\hbox {ZnMn}_{{2}}\hbox {O}_{{4}}\) host lattice.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Kong L-B, Liu M-C, Zhang W B and Kang L 2017 Mater. Lett. 186 289
Wu H, Wu G, Ren Y, Li X and Wang L 2016 Chem. Eur. J. 22 8864
Wei Y, Chen H, Jiang H, Wang B, Liu H, Zhang Y et al 2019 ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7 7823
Wang F, Yang H, Zhang H and Jiang J 2018 J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29 1304
Zheng C, Yang H, Cui Z, Zhang H and Wang X 2017 Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12 608
Huang M, Zhang Y, Li F, Zhang L, Wen Z and Liu Q 2014 J. Power Sources 252 98
Wu H, Wu G, Ren Y, Yang L, Wang L and Li X 2015 J. Mater. Chem. C 3 7677
Zhao L, Li X and Zhao J 2013 Appl. Surf. Sci. 268 274
Bhagwan J, Kumar N, Yadav K L and Sharma Y 2018 Solid State Ionics 321 75
Zou J, Liu B, Liu H, Ding Y, Xin T and Wang Y 2018 Mater. Res. Bull. 107 468
Abdollahifar M, Huang S-S, Lin Y-H, Lin Y C, Shih B Y and Sheu H S 2018 J. Power Sources 378 90
Ameri B, Davarani S S H, Moazami H R and Darjazi H 2017 J. Alloys Compd. 720 408
Wang H, Li Z, Xu J, Zhang Y, Yang L and Qiu W 2015 J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.: Mater. Sci. Ed. 30 1159
Courtel F M, Duncan H, Abu-Lebdeh Y and Davidson I-J 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 10206
Ren N, Jiu H, Jiang L, Zhang Q, Yu S, Gao Y et al 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 740 28
Zhang L-X, Wang Y-L, Jiu H-F, Qiu H and Wang H 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 9655
Zhang T, Gao Y, Yue H, Qiu H, Guo Z, Wei Y et al 2016 Electrochim. Acta 198 84
Zhu X, Wei Z, Zhao W, Zhang X, Zhang L and Wang X 2018 J. Electron. Mater. 47 6428
Liu Q, Zhang Z, Liu B and Xia H 2018 Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 237 855
Gherbi R, Bessekhouad Y and Trari M 2016 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 89 69
Gherbi R, Bessekhouad Y and Trari M 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 655 188
Courtel F M, Abu-Lebdeh Y and Davidson I J 2012 Electrochim. Acta 71 123
Li P, Liu J, Liu Y, Wang Y, Li Z, Wu W et al 2015 Electrochim. Acta 180 164
Lin X X, Zhu Y F and Shen W Z 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 1812
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51261015), the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (No. 1308RJZA238) and the open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Silicate Materials for Architectures (Wuhan University of Technology) (No. SYSJJ2018-20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Wei, Z., Ma, L. et al. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of Co-doped \(\hbox {ZnMn}_{2}\hbox {O}_{4}\) hollow nanospheres. Bull Mater Sci 43, 4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1970-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-019-1970-6