Abstract
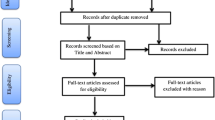
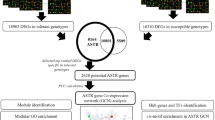
Wheat (Triticum aestivum) is one of the major crops worldwide and a primary source of calories for human food. Biotic stresses such as fungi, bacteria, and diseases limit wheat production. Although plant breeding and genetic engineering for biotic stress resistance have been suggested as promising solutions to handle losses caused by biotic stress factors, a comprehensive understanding of molecular mechanisms and identifying key genes is a critical step to obtaining success. Here, a network-based meta-analysis approach based on two main statistical methods was used to identify key genes and molecular mechanisms of the wheat response to biotic stress. A total of 163 samples (21,792 genes) from 10 datasets were analyzed. Fisher Z test based on the p-value and REM method based on effect size resulted in 533 differentially expressed genes (p < 0.001 and FDR < 0.001). WGCNA analysis using a dynamic tree-cutting algorithm was used to construct a co-expression network and three significant modules were detected. The modules were significantly enriched by 16 BP terms and 4 KEGG pathways (Benjamini–Hochberg FDR < 0.001). A total of nine hub genes (a top 1.5% of genes with the highest degree) were identified from the constructed network. The identification of DE genes, gene–gene co-expressing network, and hub genes may contribute to uncovering the molecular mechanisms of the wheat response to biotic stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Figueroa, M., Hammond-Kosack, K. E., & Solomon, P. S. (2018). A review of wheat diseases-a field perspective. Molecular Plant Pathology, 19, 1523–1536.
Bhalla, P. L. (2006). Genetic engineering of wheat–current challenges and opportunities. TRENDS in Biotechnology, 24, 305–311.
Coram, T. E., Huang, X., Zhan, G., Settles, M. L., & Chen, X. (2010). Meta-analysis of transcripts associated with race-specific resistance to stripe rust in wheat demonstrates common induction of blue copper-binding protein, heat-stress transcription factor, pathogen-induced WIR1A protein, and ent-kaurene synthase transcripts. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 10, 383–392.
Wang, L., Xiang, L., Hong, J., Xie, Z., & Li, B. (2019). Genome-wide analysis of bHLH transcription factor family reveals their involvement in biotic and abiotic stress responses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). 3 Biotech, 9, 1–12.
Perochon, A., Vary, Z., Malla, K. B., Halford, N. G., Paul, M. J., & Doohan, F. M. (2019). The wheat SnRK1alpha family and its contribution to Fusarium toxin tolerance. Plant Science, 288, 110217.
Lv, S., Guo, H., Zhang, M., Wang, Q., Zhang, H., & Ji, W. (2020). Large-scale cloning and comparative analysis of TaNAC genes in response to stripe rust and powdery mildew in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genes (Basel), 11, 1073.
Bhatta, M., Morgounov, A., Belamkar, V., Wegulo, S. N., Dababat, A. A., Erginbas-Orakci, G., Bouhssini, M. E., Gautam, P., Poland, J., Akci, N., Demir, L., Wanyera, R., & Baenziger, P. S. (2019). Genome-wide association study for multiple biotic stress resistance in synthetic hexaploid wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 3667.
Golkari, S., Gilbert, J., Ban, T., & Procunier, J. D. (2009). QTL-specific microarray gene expression analysis of wheat resistance to Fusarium head blight in Sumai-3 and two susceptible NILs. Genome, 52, 409–418.
Bozkurt, T. O., McGrann, G. R., MacCormack, R., Boyd, L. A., & Akkaya, M. S. (2010). Cellular and transcriptional responses of wheat during compatible and incompatible race-specific interactions with Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Molecular Plant Pathology, 11, 625–640.
Bolton, M. D., Kolmer, J. A., Xu, W. W., & Garvin, D. F. (2008). Lr34-mediated leaf rust resistance in wheat: Transcript profiling reveals a high energetic demand supported by transient recruitment of multiple metabolic pathways. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 21, 1515–1527.
Xin, M., Wang, X., Peng, H., Yao, Y., Xie, C., Han, Y., Ni, Z., & Sun, Q. (2012). Transcriptome comparison of susceptible and resistant wheat in response to powdery mildew infection. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 10, 94–106.
Erayman, M., Turktas, M., Akdogan, G., Gurkok, T., Inal, B., Ishakoglu, E., Ilhan, E., & Unver, T. (2015). Transcriptome analysis of wheat inoculated with Fusarium graminearum. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 867.
Gurevitch, J., Koricheva, J., Nakagawa, S., & Stewart, G. (2018). Meta-analysis and the science of research synthesis. Nature, 555, 175–182.
Adie, B. A., Pérez-Pérez, J., Pérez-Pérez, M. M., Godoy, M., Sánchez-Serrano, J.-J., Schmelz, E. A., & Solano, R. J. T. P. C. (2007). ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 19, 1665–1681.
Ehlting, J., Chowrira, S. G., Mattheus, N., Aeschliman, D. S., Arimura, G., & Bohlmann, J. (2008). Comparative transcriptome analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana infested by diamond back moth (Plutella xylostella) larvae reveals signatures of stress response, secondary metabolism, and signalling. BMC Genomics, 9, 154.
Ransbotyn, V., Yeger-Lotem, E., Basha, O., Acuna, T., Verduyn, C., Gordon, M., Chalifa-Caspi, V., Hannah, M. A., & Barak, S. (2015). A combination of gene expression ranking and co-expression network analysis increases discovery rate in large-scale mutant screens for novel Arabidopsis thaliana abiotic stress genes. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 13, 501–513.
Shaik, R., & Ramakrishna, W. (2014). Machine learning approaches distinguish multiple stress conditions using stress-responsive genes and identify candidate genes for broad resistance in rice. Plant Physiology, 164, 481–495.
Sirohi, P., Yadav, B. S., Afzal, S., Mani, A., & Singh, N. K. (2020). Identification of drought stress-responsive genes in rice (Oryza sativa) by meta-analysis of microarray data. Journal of Genetics, 99, 1–10.
Tahmasebi, A., Ashrafi-Dehkordi, E., Shahriari, A. G., Mazloomi, S. M., & Ebrahimie, E. (2019). Integrative meta-analysis of transcriptomic responses to abiotic stress in cotton. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 146, 112–122.
Shen, P. C., Hour, A. L., & Liu, L. D. (2017). Microarray meta-analysis to explore abiotic stress-specific gene expression patterns in Arabidopsis. Botanical Studies, 58, 22.
de Abreu Neto, J. B., & Frei, M. (2015). Microarray meta-analysis focused on the response of genes involved in redox homeostasis to diverse abiotic stresses in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 1260.
Zinati, Z., Sazegari, S., Tahmasebi, A., & Delavari, A. (2020). A comprehensive meta-analysis to identify transcriptional signatures of abiotic stress responses in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Cereal Research Communications, 49, 1–7.
Cohen, S. P., & Leach, J. E. (2019). Abiotic and biotic stresses induce a core transcriptome response in rice. Science and Reports, 9, 6273.
Balan, B., Marra, F. P., Caruso, T., & Martinelli, F. (2018). Transcriptomic responses to biotic stresses in Malus x domestica: A meta-analysis study. Science and Reports, 8, 1970.
Ashrafi-Dehkordi, E., Alemzadeh, A., Tanaka, N., & Razi, H. (2018). Meta-analysis of transcriptomic responses to biotic and abiotic stress in tomato. PeerJ, 6, e4631.
Bilgin, D. D., Zavala, J. A., Zhu, J., Clough, S. J., Ort, D. R., & DeLucia, E. H. (2010). Biotic stress globally downregulates photosynthesis genes. Plant, Cell and Environment, 33, 1597–1613.
Osmani, Z., Sabet, M. S., Shams-Bakhsh, M., Moieni, A., & Vahabi, K. (2019). Virus-specific and common transcriptomic responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum) against PVY, PVA and PLRV using microarray meta-analysis. Plant Breeding, 138, 216–228.
Rodrigo, G., Carrera, J., Ruiz-Ferrer, V., del Toro, F. J., Llave, C., Voinnet, O., & Elena, S. F. (2012). A meta-analysis reveals the commonalities and differences in Arabidopsis thaliana response to different viral pathogens. PLoS ONE, 7, e40526.
Ostlund, G., & Sonnhammer, E. L. (2014). Avoiding pitfalls in gene (co)expression meta-analysis. Genomics, 103, 21–30.
Tseng, G. C., Ghosh, D., & Feingold, E. (2012). Comprehensive literature review and statistical considerations for microarray meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 40, 3785–3799.
Chang, L. C., Lin, H. M., Sibille, E., & Tseng, G. C. (2013). Meta-analysis methods for combining multiple expression profiles: Comparisons, statistical characterization and an application guideline. BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 368.
Christie, N., Myburg, A. A., Joubert, F., Murray, S. L., Carstens, M., Lin, Y. C., Meyer, J., Crampton, B. G., Christensen, S. A., Ntuli, J. F., Wighard, S. S., Van de Peer, Y., & Berger, D. K. (2017). Systems genetics reveals a transcriptional network associated with susceptibility in the maize-grey leaf spot pathosystem. The Plant Journal, 89, 746–763.
Sircar, S., & Parekh, N. (2015). Functional characterization of drought-responsive modules and genes in Oryza sativa: A network-based approach. Frontiers in Genetics, 6, 256.
Sircar, S., & Parekh, N. (2019). Meta-analysis of drought-tolerant genotypes in Oryza sativa: A network-based approach. PLoS ONE, 14, e0216068.
Zhang, B., & Horvath, S. (2005). A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.2202/1544-6115.1128
Langfelder, P., & Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 559.
Irizarry, R. A., Hobbs, B., Collin, F., Beazer-Barclay, Y. D., Antonellis, K. J., Scherf, U., & Speed, T. P. (2003). Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics, 4, 249–264.
Gautier, L., Cope, L., Bolstad, B. M., & Irizarry, R. A. (2004). affy—Analysis of affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics, 20, 307–315.
Kauffmann, A., Gentleman, R., & Huber, W. (2009). arrayQualityMetrics—A bioconductor package for quality assessment of microarray data. Bioinformatics, 25, 415–416.
Johnson, W. E., Li, C., & Rabinovic, A. (2007). Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics, 8, 118–127.
Xia, J., Gill, E. E., & Hancock, R. E. (2015). NetworkAnalyst for statistical, visual and network-based meta-analysis of gene expression data. Nature Protocols, 10, 823–844.
Piras, I. S., Manchia, M., Huentelman, M. J., Pinna, F., Zai, C. C., Kennedy, J. L., & Carpiniello, B. (2019). Peripheral biomarkers in Schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of microarray gene expression datasets. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 22, 186–193.
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Yao, Y., Wang, R., Duan, B., & Fan, S. (2019). Comprehensive meta-analysis and co-expression network analysis identify candidate genes for salt stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Biosystems, 153, 367–377.
Wang, X., Kang, D. D., Shen, K., Song, C., Lu, S., Chang, L. C., Liao, S. G., Huo, Z., Tang, S., Ding, Y., Kaminski, N., Sibille, E., Lin, Y., Li, J., & Tseng, G. C. (2012). An R package suite for microarray meta-analysis in quality control, differentially expressed gene analysis and pathway enrichment detection. Bioinformatics, 28, 2534–2536.
Zaykin, D. V. (2011). Optimally weighted Z-test is a powerful method for combining probabilities in meta-analysis. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 24, 1836–1841.
Choi, J. K., Yu, U., Kim, S., & Yoo, O. J. (2003). Combining multiple microarray studies and modeling interstudy variation. Bioinformatics, 19(Suppl 1), i84-90.
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., Valentin, F., Wallace, I. M., Wilm, A., & Lopez, R. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23, 2947–2948.
Guindon, S., Lethiec, F., Duroux, P., & Gascuel, O. (2005). PHYML online—A web server for fast maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic inference. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, W557–W559.
Ramirez-Gonzalez, R. H., Borrill, P., Lang, D., Harrington, S. A., Brinton, J., Venturini, L., Davey, M., Jacobs, J., van Ex, F., Pasha, A., Khedikar, Y., Robinson, S. J., Cory, A. T., Florio, T., Concia, L., Juery, C., Schoonbeek, H., Steuernagel, B., Xiang, D., … International Wheat Genome Sequencing C. (2018). The transcriptional landscape of polyploid wheat. Science, 361, 6403.
Borrill, P., Ramirez-Gonzalez, R., & Uauy, C. (2016). expVIP: A customizable RNA-seq data analysis and visualization platform. Plant Physiology, 170, 2172–2186.
Yang, F., Li, W., & Jorgensen, H. J. (2013). Transcriptional reprogramming of wheat and the hemibiotrophic pathogen Septoria tritici during two phases of the compatible interaction. PLoS ONE, 8, e81606.
Cantu, D., Segovia, V., MacLean, D., Bayles, R., Chen, X., Kamoun, S., Dubcovsky, J., Saunders, D. G., & Uauy, C. (2013). Genome analyses of the wheat yellow (stripe) rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici reveal polymorphic and haustorial expressed secreted proteins as candidate effectors. BMC Genomics, 14, 1–18.
Kugler, K. G., Siegwart, G., Nussbaumer, T., Ametz, C., Spannagl, M., Steiner, B., Lemmens, M., Mayer, K. F., Buerstmayr, H., & Schweiger, W. (2013). Quantitative trait loci-dependent analysis of a gene co-expression network associated with Fusarium head blight resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genomics, 14, 1–15.
Zhang, H., Yang, Y., Wang, C., Liu, M., Li, H., Fu, Y., Wang, Y., Nie, Y., Liu, X., & Ji, W. (2014). Large-scale transcriptome comparison reveals distinct gene activations in wheat responding to stripe rust and powdery mildew. BMC Genomics, 15, 898.
Powell, J. J., Carere, J., Fitzgerald, T. L., Stiller, J., Covarelli, L., Xu, Q., Gubler, F., Colgrave, M. L., Gardiner, D. M., Manners, J. M., Henry, R. J., & Kazan, K. (2017). The Fusarium crown rot pathogen Fusarium pseudograminearum triggers a suite of transcriptional and metabolic changes in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Annals of Botany, 119, 853–867.
Gou, L., Hattori, J., Fedak, G., Balcerzak, M., Sharpe, A., Visendi, P., Edwards, D., Tinker, N., Wei, Y. M., & Chen, G. Y. (2016). Development and validation of Thinopyrum elongatum—expressed molecular markers specific for the long arm of chromosome 7E. Crop Science, 56, 354–364.
Ma, J., Stiller, J., Zhao, Q., Feng, Q., Cavanagh, C., Wang, P., Gardiner, D., Choulet, F., Feuillet, C., Zheng, Y. L., Wei, Y., Yan, G., Han, B., Manners, J. M., & Liu, C. (2014). Transcriptome and allele specificity associated with a 3BL locus for Fusarium crown rot resistance in bread wheat. PLoS ONE, 9, e113309.
Raudvere, U., Kolberg, L., Kuzmin, I., Arak, T., Adler, P., Peterson, H., & Vilo, J. (2019). g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Research, 47, W191–W198.
Hong, F., & Breitling, R. (2008). A comparison of meta-analysis methods for detecting differentially expressed genes in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics, 24, 374–382.
de Abreu Neto, J. B., & Frei, M. (2016). Microarray meta-analysis focused on the response of genes involved in redox homeostasis to diverse abiotic stresses in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 1260.
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z., Zhang, X., Yao, Y., Wang, R., Duan, B., & Fan, S. (2019). Comprehensive meta-analysis and co-expression network analysis identify candidate genes for salt stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Biosystems—An International Journal Dealing with all Aspects of Plant Biology, 153, 367–377.
Zhu, L., Liu, X., Wang, H., Khajuria, C., Reese, J. C., Whitworth, R. J., Welti, R., & Chen, M. S. (2012). Rapid mobilization of membrane lipids in wheat leaf sheaths during incompatible interactions with Hessian fly. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 25, 920–930.
Evangelou, E., & Ioannidis, J. (2013). Meta-analysis methods for genome-wide association studies and beyond. Nature Reviews Genetics, 14, 379–389.
Chang, L.-C., Lin, H.-M., Sibille, E., & Tseng, G. C. (2013). Meta-analysis methods for combining multiple expression profiles: Comparisons, statistical characterization and an application guideline. BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 1–15.
Hahn, A., Vonck, J., Mills, D. J., Meier, T., & Kuhlbrandt, W. (2018). Structure, mechanism, and regulation of the chloroplast ATP synthase. Science, 360, 6389.
Gong, C., Cheng, M. Z., Li, J. F., Chen, H. Y., Zhang, Z. Z., Qi, H. N., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Chen, X. L., & Wang, A. X. (2021). The alpha-subunit of the chloroplast ATP synthase of tomato reinforces resistance to gray mold and broad-spectrum resistance in transgenic tobacco. Phytopathology, 111, 485–495.
Schmelz, E. A., LeClere, S., Carroll, M. J., Alborn, H. T., & Teal, P. E. (2007). Cowpea chloroplastic ATP synthase is the source of multiple plant defense elicitors during insect herbivory. Plant physiology, 144, 793–805.
Farahani, A. S., & Taghavi, S. (2015). Expression profiling of malate dehydrogenase, superoxide dismutase and polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein in common bean in response to host and non-host pathogens. Journal of Plant Pathology, 97, 491.
Guo, Y., Song, Y., Zheng, H., Zhang, Y., Guo, J., & Sui, N. (2018). NADP-malate dehydrogenase of sweet sorghum improves salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 66, 5992–6002.
Kandoi, D., Mohanty, S., & Tripathy, B. C. (2018). Overexpression of plastidic maize NADP-malate dehydrogenase (ZmNADP-MDH) in Arabidopsis thaliana confers tolerance to salt stress. Protoplasma, 255, 547–563.
Ahn, H. K., Yoon, J. T., Choi, I., Kim, S., Lee, H. S., & Pai, H. S. (2019). Functional characterization of chaperonin containing T-complex polypeptide-1 and its conserved and novel substrates in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 70, 2741–2757.
Srivastava, D., Shamim, M., Kumar, M., Mishra, A., Maurya, R., Sharma, D., Pandey, P., & Singh, K. (2019). Role of circadian rhythm in plant system: An update from development to stress response. Environmental Experimental Botany, 162, 256–271.
Tiwari, S., Rahul, S. N., Sehrawat, A., & Rawat, B. (2020). Circadian redox rhythms play an important role in plant-pathogen interaction. Plant microbiome paradigm (pp. 147–162). Springer.
Grundy, J., Stoker, C., & Carre, I. A. (2015). Circadian regulation of abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6, 648.
Bhattacharya, A., Khanale, V., & Char, B. (2017). Plant circadian rhythm in stress signaling. Indian Journal of Plant Physiology, 22, 147–155.
Hildebrandt, T., Knuesting, J., Berndt, C., Morgan, B., & Scheibe, R. (2015). Cytosolic thiol switches regulating basic cellular functions: GAPDH as an information hub? Biological Chemistry, 396, 523–537.
Kim, S. C., Guo, L., & Wang, X. (2020). Nuclear moonlighting of cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase regulates Arabidopsis response to heat stress. Nature Communications, 11, 3439.
Zeng, L., Deng, R., Guo, Z., Yang, S., & Deng, X. (2016). Genome-wide identification and characterization of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes family in wheat (Triticum aestivum). BMC Genomics, 17, 240.
Li, X., Wei, W., Li, F., Zhang, L., Deng, X., Liu, Y., & Yang, S. (2019). The plastidial glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is critical for abiotic stress response in wheat. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, 1104.
Hashimoto, M., Neriya, Y., Yamaji, Y., & Namba, S. (2016). Recessive resistance to plant viruses: Potential resistance genes beyond translation initiation factors. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, 1695.
Moin, M., Bakshi, A., Saha, A., Dutta, M., Madhav, S. M., & Kirti, P. (2016). Rice ribosomal protein large subunit genes and their spatio-temporal and stress regulation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1284.
Cheng, Z., Dong, K., Ge, P., Bian, Y., Dong, L., Deng, X., Li, X., & Yan, Y. (2015). Identification of leaf proteins differentially accumulated between wheat cultivars distinct in their levels of drought tolerance. PLoS ONE, 10, e0125302.
Gietler, M., Nykiel, M., Orzechowski, S., Fettke, J., & Zagdanska, B. (2016). Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylated and S-glutathionylated proteins in wheat seedlings with different dehydration tolerances. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 108, 507–518.
Zang, X., & Komatsu, S. (2007). A proteomics approach for identifying osmotic-stress-related proteins in rice. Phytochemistry, 68, 426–437.
Begum, Y., & Mondal, S. K. (2020). Comprehensive study of the genes involved in chlorophyll synthesis and degradation pathways in some monocot and dicot plant species. Journal of Biomolecular Structure Dynamics, 39, 1–28.
Komatsu, S., Kamal, A. H., & Hossain, Z. (2014). Wheat proteomics: Proteome modulation and abiotic stress acclimation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5, 684.
Li, X.-W., Zhu, Y.-L., Chen, C.-Y., Geng, Z.-J., Li, X.-Y., Ye, T.-T., Mao, X.-N., & Du, F. (2020). Cloning and characterization of two chlorophyll A/B binding protein genes and analysis of their gene family in Camellia sinensis. Scientific Reports, 10, 1–9.
Gao, J., Liu, Z., Zhao, B., Liu, P., & Zhang, J.-W. (2020). Physiological and comparative proteomic analysis provides new insights into the effects of shade stress in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biology, 20, 60.
Xu, Y. H., Liu, R., Yan, L., Liu, Z. Q., Jiang, S. C., Shen, Y. Y., Wang, X. F., & Zhang, D. P. (2012). Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins are required for stomatal response to abscisic acid in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 63, 1095–1106.
Liu, R., Xu, Y.-H., Jiang, S.-C., Lu, K., Lu, Y.-F., Feng, X.-J., Wu, Z., Liang, S., Yu, Y.-T., & Wang, X.-F. (2013). Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins, positively involved in abscisic acid signalling, require a transcription repressor, WRKY40, to balance their function. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64, 5443–5456.
Li, P., Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Xing, J., Li, J., Feng, J., Su, X., & Zhao, J. (2019). Fungal canker pathogens trigger carbon starvation by inhibiting carbon metabolism in poplar stems. Science and Reports, 9, 10111.
Ye, C., Zhou, Q., Wu, X., Ji, G., & Li, Q. Q. (2019). Genome-wide alternative polyadenylation dynamics in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in rice. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 183, 109485.
Pitino, M., Armstrong, C. M., & Duan, Y. (2017). Molecular mechanisms behind the accumulation of ATP and H2O2 in citrus plants in response to ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ infection. Horticulture Research. https://doi.org/10.1038/hortres.2017.40
Casassola, A., Brammer, S. P., Chaves, M. S., Martinelli, J. A., Stefanato, F., & Boyd, L. A. (2015). Changes in gene expression profiles as they relate to the adult plant leaf rust resistance in the wheat cv. Toropi. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 89, 49–54.
Laxalt, A. M., Cassia, R. O., Sanllorenti, P. M., Madrid, E. A., Andreu, A. B., Daleo, G. R., Conde, R. D., & Lamattina, L. (1996). Accumulation of cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA under biological stress conditions and elicitor treatments in potato. Plant Molecular Biology, 30, 961–972.
Berger, S., Sinha, A. K., & Roitsch, T. (2007). Plant physiology meets phytopathology: Plant primary metabolism and plant–pathogen interactions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 58, 4019–4026.
Jones, J. D., & Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature, 444, 323–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nemati, M., Zare, N., Hedayat-Evrigh, N. et al. Identification of Key Gene Network Modules and Hub Genes Associated with Wheat Response to Biotic Stress Using Combined Microarray Meta-analysis and WGCN Analysis. Mol Biotechnol 65, 453–465 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00541-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00541-w