Abstract
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive, uncurable neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degradation of motor neurons leading to muscle impairment, failure, and death. Senataxin, encoded by the SETX gene, is a human helicase protein whose mutations have been linked with ALS onset, particularly in its juvenile ALS4 form. Using senataxin’s yeast homolog Sen1 as a model for study, it is suggested that senataxin’s N-terminus interacts with RNA polymerase II, whilst its C-terminus engages in helicase activity. Senataxin is heavily involved in transcription regulation, termination, and R-loop resolution, enabled by recruitment and interactions with enzymes such as ubiquitin protein ligase SAN1 and ribonuclease H (RNase H). Senataxin also engages in DNA damage response (DDR), primarily interacting with the exosome subunit Rrp45. The Sen1 mutation E1597K, alongside the L389S and R2136H gain-of-function mutations to senataxin, is shown to cause negative structural and thus functional effects to the protein, thus contributing to a disruption in WT functions, motor neuron (MN) degeneration, and the manifestation of ALS clinical symptoms. This review corroborates and summarizes published papers concerning the structure and function of senataxin as well as the effects of their mutations in ALS pathology in order to compile current knowledge and provide a reference for future research. The findings compiled in this review are indicative of the experimental and therapeutic potential of senataxin and its mutations as a target in future ALS treatment/cure discovery, with some potential therapeutic routes also being discussed in the review.

(Reproduced from the open source, Masrori and Van Damme (2020))


(Reproduced from the open source, Bennett and La Spada (2021))

(Reproduced from the open source, Rivosecchi et al. (2019))

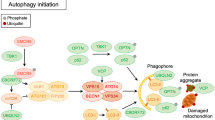
(Reproduced from the open source, Uruci et al. (2021))

(Reproduced from the open source, Richard and Manley (2014))

(Reproduced from the open source, Cohen et al. (2018))

(Reproduced from the open source, Chen et al. (2014))

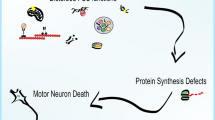
(Reproduced from the open source, Grunseich et al. (2018))

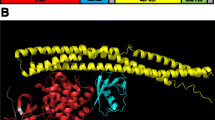
(Reproduced from the open source, Hasanova et al. (2023))
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data used in this article are included in the publication. There is no additional data.
References
Allison DF, Wang GG (2019) R-loops: formation, function, and relevance to cell stress. Cell Stress 3(2):38–46. https://doi.org/10.15698/cst2019.02.175
Andrews AM, McCartney HJ, Errington TM, D’Andrea AD, Macara IG (2018) A senataxin-associated exonuclease SAN1 is required for resistance to DNA interstrand cross-links. Nat Commun 9(1):2592. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05008-8
Asadi MR, Sadat Moslehian M, Sabaie H, Jalaiei A, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M, Rezazadeh M (2021) Stress granules and neurodegenerative disorders: a scoping review. Front Aging Neurosci 13:650740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.650740
Becherel OJ, Yeo AJ, Stellati A, Heng EY, Luff J, Suraweera AM, Woods R, Fleming J, Carrie D, McKinney K, Xu X, Deng C, Lavin MF (2013) Senataxin plays an essential role with DNA damage response proteins in meiotic recombination and gene silencing. PLoS Genet 9(4):e1003435. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003435
Bennett CL, Chen Y, Vignali M, Lo RS, Mason AG, Unal A, Huq Saifee NP, Fields S, La Spada AR (2013) Protein interaction analysis of senataxin and the ALS4 L389S mutant yields insights into senataxin post-translational modification and uncovers mutant-specific binding with a brain cytoplasmic RNA-encoded peptide. PLoS ONE 8(11):e78837. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078837
Bennett CL, Dastidar SG, Ling SC, Malik B, Ashe T, Wadhwa M, Miller DB, Lee C, Mitchell MB, van Es MA, Grunseich C, Chen Y, Sopher BL, Greensmith L, Cleveland DW, La Spada AR (2018) Senataxin mutations elicit motor neuron degeneration phenotypes and yield TDP-43 mislocalization in ALS4 mice and human patients. Acta Neuropathol 136(3):425–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1852-9
Bennett CL, La Spada AR (2015) Unwinding the role of senataxin in neurodegeneration. Discov Med 19(103):127–136
Bennett CL, La Spada AR (2018) Senataxin, a novel helicase at the interface of RNA transcriptome regulation and neurobiology: from normal function to pathological roles in motor neuron disease and cerebellar degeneration. Adv Neurobiol 20:265–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-89689-2_10
Bennett CL, La Spada AR (2021) SUMOylated senataxin functions in genome stability, RNA degradation, and stress granule disassembly, and is linked with inherited ataxia and motor neuron disease. Mol Gen Genomic Med 9(12):e1745. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.1745
Bunton-Stasyshyn RK, Saccon RA, Fratta P, Fisher EM (2015) SOD1 function and its implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology: new and renascent themes. Neuroscientist 21(5):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858414561795
Casey AE, Liu W, Hein LK, Sargeant TJ, Pederson SM, Mäkinen VP (2022) Transcriptional targets of senataxin and E2 promoter binding factors are associated with neuro-degenerative pathways during increased autophagic flux. Sci Rep 12(1):17665. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21617-2
Chen X, Müller U, Sundling KE, Brow DA (2014) Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sen1 as a model for the study of mutations in human senataxin that elicit cerebellar ataxia. Genet 198(2):577–590. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.114.167585
Chen YC, Backus KM, Merkulova M, Yang C, Brown D, Cravatt BF, Zhang C (2017) Covalent modulators of the vacuolar ATPase. J Am Chem Soc 139(2):639–642. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b12511
Chen YZ, Bennett CL, Huynh HM, Blair IP, Puls I, Irobi J, Dierick I, Abel A, Kennerson ML, Rabin BA, Nicholson GA, Auer-Grumbach M, Wagner K, De Jonghe P, Griffin JW, Fischbeck KH, Timmerman V, Cornblath DR, Chance PF (2004) DNA/RNA helicase gene mutations in a form of juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS4). American J Hum Genet 74(6):1128–1135. https://doi.org/10.1086/421054
Cohen S, Puget N, Lin YL, Clouaire T, Aguirrebengoa M, Rocher V, Pasero P, Canitrot Y, Legube G (2018) Senataxin resolves RNA:DNA hybrids forming at DNA double-strand breaks to prevent translocations. Nat Commun 9(1):533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-02894-w
Connolly O, Le Gall L, McCluskey G, Donaghy CG, Duddy WJ, Duguez S (2020) A systematic review of genotype-phenotype correlation across cohorts having causal mutations of different genes in ALS. J Pers Med 10(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030058
Coyne AN, Zaepfel BL, Zarnescu DC (2017) Failure to deliver and translate-new insights into RNA dysregulation in ALS. Front Cell Neurosci 11:243. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00243
Fang MY, Markmiller S, Vu AQ, Javaherian A, Dowdle WE, Jolivet P, Bushway PJ, Castello NA, Baral A, Chan MY, Linsley JW, Linsley D, Mercola M, Finkbeiner S, Lecuyer E, Lewcock JW, Yeo GW (2019) Small-molecule modulation of TDP-43 recruitment to stress granules prevents persistent TDP-43 accumulation in ALS/FTD. Neuron 103(5):802-819.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.048
Gatti V, De Domenico S, Melino G, Peschiaroli A (2023) Senataxin and R-loops homeostasis: multifaced implications in carcinogenesis. Cell Death Discov 9(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-023-01441-x
Grunseich C, Wang IX, Watts JA, Burdick JT, Guber RD, Zhu Z, Bruzel A, Lanman T, Chen K, Schindler AB, Edwards N, Ray-Chaudhury A, Yao J, Lehky T, Piszczek G, Crain B, Fischbeck KH, Cheung VG (2018) Senataxin mutation reveals how R-loops promote transcription by blocking DNA methylation at gene promoters. Mol Cell 69(3):426-437.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.030
Hasanova Z, Klapstova V, Porrua O, Stefl R, Sebesta M (2023) Human senataxin is a bona fide R-loop resolving enzyme and transcription termination factor. Nucleic Acids Res 51(6):2818–2837. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad092
Jo M, Lee S, Jeon YM, Kim S, Kwon Y, Kim HJ (2020) The role of TDP-43 propagation in neurodegenerative diseases: integrating insights from clinical and experimental studies. Exp Mol Med 52(10):1652–1662. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-00513-7
Kamelgarn M, Chen J, Kuang L, Jin H, Kasarskis EJ, Zhu H (2018) ALS mutations of FUS suppress protein translation and disrupt the regulation of nonsense-mediated decay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(51):E11904–E11913. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810413115
Kenna KP, McLaughlin RL, Byrne S, Elamin M, Heverin M, Kenny EM, Cormican P, Morris DW, Donaghy CG, Bradley DG, Hardiman O (2013) Delineating the genetic heterogeneity of ALS using targeted high-throughput sequencing. J Med Genet 50(11):776–783. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101795
Kremers CJP (2022) Characterising a novel mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a study of senataxin pathology in ALS4. Dissertation, University College London
Laverde EE, Lai Y, Leng F, Balakrishnan L, Freudenreich CH, Liu Y (2020) R-loops promote trinucleotide repeat deletion through DNA base excision repair enzymatic activities. J Biol Chem 295(40):13902–13913. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.014161
Laverde EE, Polyzos AA, Tsegay PP, Shaver M, Hutcheson JD, Balakrishnan L, McMurray CT, Liu Y (2022) Flap endonuclease 1 endonucleolytically processes RNA to resolve R-Loops through DNA base excision repair. Genes 14(1):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010098
Lee J, Hyeon SJ, Im H, Ryu H, Kim Y, Ryu H (2016) Astrocytes and microglia as non-cell autonomous players in the pathogenesis of ALS. Exp Neurobiol 25(5):233–240. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2016.25.5.233
Leonaitė B, Han Z, Basquin J, Bonneau F, Libri D, Porrua O, Conti E (2017) Sen1 has unique structural features grafted on the architecture of the Upf1-like helicase family. EMBO J 36(11):1590–1604. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696174
Li W, Li S (2017) Facilitators and repressors of transcription-coupled DNA repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Photochem Photobiol 93(1):259–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12655
Li W, Selvam K, Rahman SA, Li S (2016) Sen1, the yeast homolog of human senataxin, plays a more direct role than Rad26 in transcription coupled DNA repair. Nucleic aAids Res 44(14):6794–6802. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw428
Mackenzie IR, Rademakers R, Neumann M (2010) TDP-43 and FUS in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Lancet Neurol 9(10):995–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70195-2
Masrori P, Van Damme P (2020) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical review. Eur J Neurol 27(10):1918–1929. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14393
Mehta P, Kaye W, Raymond J, Wu R, Larson T, Punjani R, Heller D, Cohen J, Peters T, Muravov O, Horton K (2018) Prevalence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—United States, 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2018 67:216–218. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6707a3
Mehta PR, Jones AR, Opie-Martin S, Shatunov A, Iacoangeli A, Al Khleifat A, Smith BN, Topp S, Morrison KE, Shaw PJ, Shaw CE, Morgan S, Pittman A, Al-Chalabi A (2019) Younger age of onset in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a result of pathogenic gene variants, rather than ascertainment bias. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(3):268–271. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-319089
Mejzini R, Flynn LL, Pitout IL, Fletcher S, Wilton SD, Akkari PA (2019) ALS genetics, mechanisms, and therapeutics: where are we now?.Front Neurosci 13:1310. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01310
Millecamps S, Julien JP (2013) Axonal transport deficits and neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(3):161–176. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3380
Moreira MC, Klur S, Watanabe M, Németh AH, Le Ber I, Moniz JC, Tranchant C, Aubourg P, Tazir M, Schöls L, Pandolfo M, Schulz JB, Pouget J, Calvas P, Shizuka-Ikeda M, Shoji M, Tanaka M, Izatt L, Shaw CE, M’Zahem A et al (2004) Senataxin, the ortholog of a yeast RNA helicase, is mutant in ataxia-ocular apraxia 2. Nat Genet 36(3):225–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1303
Obrador E, Salvador-Palmer R, López-Blanch R, Dellinger RW, Estrela JM (2021) NAD+ precursors and antioxidants for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biomedicines 9(8):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9081000
Ramachandran S, Ma TS, Griffin J, Ng N, Foskolou IP, Hwang MS, Victori P, Cheng WC, Buffa FM, Leszczynska KB, El-Khamisy SF, Gromak N, Hammond EM (2021) Hypoxia-induced SETX links replication stress with the unfolded protein response. Nat Commun 12(1):3686. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24066-z
Richard P, Manley FS, JL. (2013) A SUMO-dependent interaction between senataxin and the exosome, disrupted in the neurodegenerative disease AOA2, targets the exosome to sites of transcription-induced DNA damage. Genes Dev 27(20):2227–2232. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.224923.113
Richard P, Feng S, Tsai YL, Li W, Rinchetti P, Muhith U, Irizarry-Cole J, Stolz K, Sanz LA, Hartono S, Hoque M, Tadesse S, Seitz H, Lotti F, Hirano M, Chédin F, Tian B, Manley JL (2021) SETX (senataxin), the helicase mutated in AOA2 and ALS4, functions in autophagy regulation. Autophagy 17(8):1889–1906. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1796292
Richard P, Manley JL (2014) SETX sumoylation: a link between DNA damage and RNA surveillance disrupted in AOA2. Rare Dis 2:e27744. https://doi.org/10.4161/rdis.27744
Rivosecchi J, Larochelle M, Teste C, Grenier F, Malapert A, Ricci EP, Bernard P, Bachand F, Vanoosthuyse V (2019) Senataxin homologue Sen1 is required for efficient termination of RNA polymerase III transcription. EMBO J 38(16):e101955. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019101955
Skourti-Stathaki K, Proudfoot NJ, Gromak N (2011) Human senataxin resolves RNA/DNA hybrids formed at transcriptional pause sites to promote Xrn2-dependent termination. Mol Cell 42(6):794–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.026
Steinmetz EJ, Warren CL, Kuehner JN, Panbehi B, Ansari AZ, Brow DA (2006) Genome-wide distribution of yeast RNA polymerase II and its control by Sen1 helicase. Mol Cell 24(5):735–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.10.023
Suk TR, Rousseaux MWC (2020) The role of TDP-43 mislocalization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurodegener 15(1):45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-020-00397-1
Suraweera A, Becherel OJ, Chen P, Rundle N, Woods R, Nakamura J, Gatei M, Criscuolo C, Filla A, Chessa L, Fusser M, Epe B, Gueven N, Lavin MF (2007) Senataxin, defective in ataxia oculomotor apraxia type 2, is involved in the defense against oxidative DNA damage. J Cell Biol 177(6):969–979. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200701042
Suraweera A, Lim Y, Woods R, Birrell GW, Nasim T, Becherel OJ, Lavin MF (2009) Functional role for senataxin, defective in ataxia oculomotor apraxia type 2, in transcriptional regulation. Hum Mol Genet 18(18):3384–3396. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp278
Teasley DC, Parajuli S, Nguyen M, Moore HR, Alspach E, Lock YJ, Honaker Y, Saharia A, Piwnica-Worms H, Stewart SA (2015) Flap endonuclease 1 limits telomere fragility on the leading strand. J Biol Chem 290(24):15133–15145. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.647388
Theunissen F, West PK, Brennan S, Petrović B, Akkari HK, PA, Keon M, Guennewig B. (2021) New perspectives on cytoskeletal dysregulation and mitochondrial mislocalization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Trans Neurodegener 10(1):46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-021-00272-z
Tripolszki K, Török D, Goudenège D, Farkas K, Sulák A, Török N, Engelhardt JI, Klivényi P, Procaccio V, Nagy N, Széll M (2017) High-throughput sequencing revealed a novel SETX mutation in a Hungarian patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Behav 7(4):e00669. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.669
Turner MR, Barnwell J, Al-Chalabi A, Eisen A (2012) Young-onset amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: historical and other observations. Brain 135(Pt 9):2883–2891. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws144
Uruci S, Lo CSY, Wheeler D, Taneja N (2021) R-Loops and its chro-mates: the strange case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde. Int J Mol Sci 22(16):8850. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168850
Vantaggiato C, Bondioni S, Airoldi G, Bozzato A, Borsani G, Rugarli EI, Bresolin N, Clementi E, Bassi MT (2011) Senataxin modulates neurite growth through fibroblast growth factor 8 signalling. Brain 134(Pt 6):1808–1828. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr084
Winey M, Culbertson MR (1988) Mutations affecting the tRNA-splicing endonuclease activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 118(4):609–617. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/118.4.609
Yasuda K, Clatterbuck-Soper SF, Jackrel ME, Shorter J, Mili S (2017) FUS inclusions disrupt RNA localization by sequestering kinesin-1 and inhibiting microtubule detyrosination. J Cell Biol 216(4):1015–1034. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201608022
Yüce Ö, West SC (2013) Senataxin, defective in the neurodegenerative disorder ataxia with oculomotor apraxia 2, lies at the interface of transcription and the DNA damage response. Mol Cell Biol 33(2):406–417. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01195-12
Zou Z, Tao T, Li H, Zhu X (2020) mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: progress and challenges. Cell Biosci 10:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-020-00396-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the review conceptualization and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by A.T., I.F.T., V.L.K., M.F, and S.K. The first draft of the manuscript was written by A.T., and all authors participated in manuscript revisions and commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This article is a review of published materials and does not require any approval by Research Ethic Committee.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsui, A., Kouznetsova, V.L., Kesari, S. et al. Role of Senataxin in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 73, 996–1009 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02169-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02169-0