Abstract
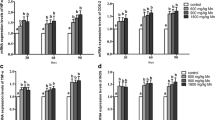
Manganese (Mn) poisoning can happen in the case of environmental pollution and occupational exposure. However, the underlying mechanisms of Mn-induced teste toxicity and whether mitochondrion and heat shock proteins (HSPs) are involved in toxic effect of Mn on chicken testes remain poorly understood. To investigate this, MnCl2·4H2O was administered in the diet (600, 900, and 1800 mg/kg Mn) of chickens for 30, 60, and 90 days. Electron microscopy and qPCR were performed. Results showed that Mn exposure suppressed dose- and time-dependently HSP40 and HSP60 mRNA levels, meanwhile increased does-dependently HSP27, HSP70, and HSP90 mRNA levels at all three time points under three Mn exposure concentrations. Furthermore, Mn treatment damaged myoid cells, spermatocytes, and Sertoli cells through electron microscopic observation, indicating that Mn treatment damaged chicken testes. In addition, abnormal shapes of mitochondria were found, and mitochondria displayed extensive vacuolation. The increase of HSP90 and HSP70 induced by Mn exposure inhibited HSP40 and stimulated HSP27, respectively, in chicken testes, which needs further to be explored. Taken together, our study suggested that there was toxic effect in excess Mn on chickens, and HSPs and mitochondria were involved in the mechanism of dose-dependent injury caused by Mn in chicken testes. This study provided new insights for Mn toxicity identification in animal husbandry production practice.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teng X, Liu Y, Li K, Liu X, Huang B, Li D, Tang Y (2021) Threat of environmental manganese pollution to biological health. J Northeast Agric Univ 52:90–96
Y Han, J Cheng, D An, Y He, Z Tang, 2021 Occurrence, potential release and health risks of heavy metals in popular take-out food containers from China, Environmental research, 112265.
A.f.T.S.a.D.R. (ATSDR), 2008 Toxicological profile for manganese, in, Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Services, Atlanta, GA, U.S
Liu Z, Kuang Y, Lan S, Cao W, Yan Z, Chen L, Chen Q, Feng Q, Zhou H (2021) Pollution distribution of potentially toxic elements in a karstic river affected by manganese mining in Changyang. Western Hubei, Central China, Int J Environ Res Publ Health 18:1870
Liu E, Yan T, Birch G, Zhu Y (2014) Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Sci Total Environ 476–477:522–531
Rodrigues EG, Kile M, Dobson C, Amarasiriwardena C, Quamruzzaman Q, Rahman M, Golam M, Christiani DC (2015) Maternal-infant biomarkers of prenatal exposure to arsenic and manganese. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 25:639–648
Miao Z, Zhang K, Bao R, Li J, Tang Y, Teng X (2021) The mechanism of manganese-caused inflammatory damage: Th1/Th2 imbalance and heat shock proteins mediated inflammation via activating NF-κB pathway in chicken nervous system in vivo and in vitro. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:44361–44437
Liu Y, Yu M, Cui J, Du Y, Teng X, Zhang Z (2021) Heat shock proteins took part in oxidative stress-mediated inflammatory injury via NF-κB pathway in excess manganese-treated chicken livers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 226:112833
Zhu Y, Li S, Teng XJC (2016) The involvement of the mitochondrial pathway in manganese-induced apoptosis of chicken splenic lymphocytes 153:462–470
Du Y, Zhu Y, Teng X, Zhang K, Teng X, Li S (2015) Toxicological effect of manganese on NF-κB/iNOS-COX-2 signaling pathway in chicken testes. Biol Trace Elem Res 168:1–8
Wu F, Yang H, Liu Y, Yang X, Deng Y (2020) Manganese exposure caused reproductive toxicity of male mice involving activation of GnRH secretion in the hypothalamus by prostaglandin E2 receptors EP1 and EP2. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110712
Mruk DD, Yan CC (2015) The mammalian blood-testis barrier: its biology and regulation. Endocr Rev 36:564–591
Hermo L, Oliveira RL, Smith CE, Bergeron J (2018) Differential expression of Golgi proteins during spermatogenesis. Encycl Reprod (Second Edition) 3:59–71
Khalife D, Khalil A, Ghazeeri G (2019) The developmental process of spermatogenesis. J Androl Gynaecol 7:3
Liu J, Li Z, Lu L, Wang Z, Wang L (2022) Glyphosate damages blood-testis barrier via NOX1-triggered oxidative stress in rats: long-term exposure as a potential risk for male reproductive health. Environ Int 159:107038
Wang H, Wang H, Xiong W, Chen Y, Ma Q, Ma J, Ge Y, Han D (2018) Evaluation on the phagocytosis of apoptotic spermatogenic cells by sertoli cells in vitro through detecting lipid droplet formation by Oil Red O staining. Reprod 132:485–492
Zhang J, Cui J, Wang Y, Lin X, Teng X, Tang Y (2022) Complex molecular mechanism of ammonia-induced apoptosis in chicken peripheral blood lymphocytes: miR-27b-3p, heat shock proteins, immunosuppression, death receptor pathway, and mitochondrial pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 236:113471
Shi X, Li X, Sun X, Cui W, Liu H, Xu S (2021) Pig lung fibrosis is active in the subacute CdCl2 exposure model and exerts cumulative toxicity through the M1/M2 imbalance. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 225:112757
Li Z, Shah SWA, Zhou Q, Yin X, Teng X (2021) The contributions of miR-25 3p, oxidative stress, and heat shock protein in a complex mechanism of autophagy caused by pollutant cadmium in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L) hepatopancreas. Environ Pollut 287:117554
Chander K, Vaibhav K, Ahmed ME, Javed H, Tabassum R, Khan A, Kumar M, Katyal A, Islam F, Siddiqui MS (2014) Quercetin mitigates lead acetate-induced behavioral and histological alterations via suppression of oxidative stress, Hsp-70, Bak and upregulation of Bcl-2. Food Chem Toxicol 68:297–306
Zhu Y, Lu X, Wu D, Cai S, Li S, Teng X (2013) The effect of manganese-induced cytotoxicity on mRNA expressions of HSP27, HSP40, HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90 in chicken spleen lymphocytes in vitro. Biol Trace Elem Res 156:144–152
He Z, Shen F, Qi P, Zhai Z, Wang Z (2021) miR-541-3p enhances the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells by inhibiting HSP27 expression and downregulating β-catenin. Cell Death Discov 7:18
Zininga T, Ramatsui L, Shonhai A (2018) Heat shock proteins as immunomodulants. Mol 23:2846
Kausar S, Abbas MN, Yang L, Cui H (2020) Biotic and abiotic stress induces the expression of Hsp70/90 organizing protein gene in silkworm, Bombyx mori - ScienceDirect. Int J Biol Macromol 143:610–618
Florian S, Maximilian B, Johannes B (2017) The HSP90 chaperone machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18:345–360
Chen J, Xu Y, Han Q, Yao Y, Xing H, Teng X (2019) Immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and glycometabolism disorder caused by cadmium in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): application of transcriptome analysis in risk assessment of environmental contaminant cadmium. J Hazard Mater 366:386–394
Fang Y, Zhu Y, Li L, Lai Z, Dong N, Shan A (2021) Biomaterial-interrelated bacterial sweeper: simplified self-assembled octapeptides with double-layered Trp zipper induces membrane destabilization and bacterial apoptosis-like death. Small Methods 5:2101304
Han Q, Tong J, Sun Q, Teng X, Zhang H, Teng X (2020) The involvement of miR-6615-5p/Smad7 axis and immune imbalance in ammonia-caused inflammatory injury via NF-κB pathway in broiler kidneys. Poult Sci 99:5378–5388
Han Q, Zhang J, Sun Q, Xu Y, Teng X (2020) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction involved in ammonia-induced nephrocyte necroptosis in chickens. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 203:110974
Shah SWA, Chen D, Zhang J, Liu Y, Ishfaq M, Tang Y, Teng X (2020) The effect of ammonia exposure on energy metabolism and mitochondrial dynamic proteins in chicken thymus: through oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 206:111413
Z Qi, Y Liu, H Yang, X Yang, H Wang, B Liu, Y Yuan, G. Wang, B Xu, W Liu, Z Xu, Y Deng, 2021 Protective role of mA binding protein YTHDC2 on CCNB2 in manganese-induced spermatogenesis dysfunction, Chemico-biological interactions, 109754
Trindade A, Simões A, Silva RJ, Macedo CS, Spadella CT (2013) Long term evaluation of morphometric and ultrastructural changes of testes of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Acta cirurgica brasileira / Sociedade Brasileira para Desenvolvimento Pesquisa em Cirurgia 28:256–265
Yuan L, Liang P, Qu Y, An T, Bai D (2020) Protective effect of astaxanthin against SnS2 nanoflowers induced testes toxicity by suppressing RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signaling in mice. Food Chem Toxicol: An Int J Publ British Industrial Biol Res Assoc 145:111736
Mohamed AR, Abdellatief SA, Khater SI, Ali H, Al-Gabri NA (2019) Fenpropathrin induces testicular damage, apoptosis, and genomic DNA damage in adult rats: protective role of camel milk. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:548–558
Miao Z, Miao Z, Shi X, Wu H, Yao Y, Xu S (2022) The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via P38/JNK/ERK pathway in chicken kidney. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 231:113176
Zhang DY, Shen XY, Qin R, Xu XL, Yang SP, Lu Y, Xu HY, Hao FL (2014) Effects of subchronic samarium exposure on the histopathological structure and apoptosis regulation in mouse testis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:505–512
Vergilio SC, Moreira VR, Ev C (2015) Carvalho, E. Jt, Melo, Evolution of cadmium effects in the testis and sperm of the tropical fish Gymnotus carapo, Tissue and Cell 47:132–139
Samali A, Cai J, Zhivotovsky B, Jones DP, Orrenius S (2014) Presence of a pre-apoptotic complex of pro-caspase-3, Hsp60 and Hsp10 in the mitochondrial fraction of Jurkat cells. Embo J 18:2040–2048
Kim BM, Rhee JS, Jeong CB, Seo JS, Park GS, Lee YM, Lee JS (2014) Heavy metals induce oxidative stress and trigger oxidative stress-mediated heat shock protein (hsp) modulation in the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol Cbp 166:65–74
Bruey J-M, Ducasse C, Bonniaud P, Ravagnan L, Susin S (2000) Hsp27 negatively regulates cell death by interacting with cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol 2:645–648
Mayer MP, Bukau B (2005) Hsp70 chaperones: cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:670–684
Queitsch C, Sangster TA, Lindquist S (2002) Hsp90 as a capacitor of phenotypic variation. Nature 417:618–624
Black AT, Hayden PJ, Casillas RP, Heck DE, Gerecke DR (2011) 2011 Regulation of Hsp27 and Hsp70 expression in human and mouse skin construct models by caveolae following exposure to the model sulfur mustard vesicant, 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide. Toxicol Appl Pharm 253(2):112–120
Ee HL, Kang C, Yoo YS, Hah DY, Kim CH, Kim E, Kim JS (2013) Cytotoxicity and the induction of the stress protein Hsp 70 in Chang liver cells in response to zearalenone-induced oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 36:732–740
Chen X, Bi M, Yang J, Cai J, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Liu Q, Shi G, Zhang Z (2021) Cadmium exposure triggers oxidative stress, necroptosis, Th1/Th2 imbalance and promotes inflammation through the TNF-α/NF-κB pathway in swine small intestine - ScienceDirect. J Hazard Mater 421:126704
Shao Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Liu J, Li J, Chai H, Xing M (2018) Arsenic and/or copper caused inflammatory response via activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway and triggered heat shock protein responses in testis tissues of chicken. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:7719–7729
Miao Z, Miao Z, Wang S, Wu H, Xu S (2021) Exposure to imidacloprid induce oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis and mitophagy via NF-kappaB/JNK pathway in grass carp hepatocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 120:674–685
Ng Y, Bindoff L, Gorman G, Klopstock T, Kornblum C, Mancuso M, McFarland R, Sue C, Suomalainen A, Taylor R, Thorburn D, Turnbull D (2021) Mitochondrial disease in adults: recent advances and future promise, The Lancet. Neurol 20:573–584
Cha J, Louis K, Gentil BJ, Tibshirani M, Durham HD (2014) A novel small molecule HSP90 inhibitor, NXD30001, differentially induces heat shock proteins in nervous tissue in culture and in vivo. Cell Stress Chaperones 19:437–437
Bruennert D, Langer C, Zimmermann L, Bargou RC, Stope MB (2019) The heat shock protein 70 inhibitor VER155008 suppresses the expression of HSP27, HOP and HSP90β and the androgen receptor, induces apoptosis, and attenuates prostate cancer cell growth. J Cell Biochem 2019:1–11
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31972612), and Harbin Hualong Feed Development Co., Ltd. Smart Agricultural Engineering Research Center of Jilin Province Foundation of China, and Digital Agriculture key discipline of Jilin Province Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Liang, J., Jiang, C. et al. Mitochondrion Participated in Effect Mechanism of Manganese Poisoning on Heat Shock Protein and Ultrastructure of Testes in Chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 1432–1441 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03259-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03259-7